false 2023-05-03 2023-05-03 2022-11-30 497 0000719423 VALIC Co I N-1A 41.19 38.81 9.14 11.04 0.85 36.21 1.97 29.84 34.37 16.38 0000719423 2023-05-01 2023-05-01 0000719423 valic:S000008005Member 2023-05-01 2023-05-01 0000719423 valic:S000008005Member valic:C000021774Member 2023-05-01 2023-05-01 0000719423 valic:S000008005Member valic:Russell1000GrowthIndexMember 2023-05-01 2023-05-01 0000719423 valic:S000008005Member valic:Sandp500IndexMember 2023-05-01 2023-05-01 xbrli:pure iso4217:USD
|
| VALIC Company I Prospectus, May 1, 2023 |
|
| SAVING : INVESTING : PLANNING |
VALIC Company I (“VC I”) is a mutual fund complex made up of 36 separate funds, one of which is described in this Prospectus. The investment objective of the Systematic Growth Fund (formerly, the Blue Chip Growth Fund) (the “Fund”) is to seek total return. The Fund is explained in more detail in its Fund Summary contained herein.
|
|
|
| |
|
Ticker Symbol: |
| Systematic Growth Fund (formerly, Blue Chip Growth Fund) |
|
VCBCX |
This Prospectus contains information you should know before investing, including information about risks. Please read it before you invest and keep it for future reference.
The Securities and Exchange Commission has not approved or disapproved these securities, nor has it determined that this Prospectus is accurate or complete. It is a criminal offense to state otherwise.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
1 |
|
| |
|
|
1 |
|
| |
|
|
1 |
|
| |
|
|
1 |
|
| |
|
|
2 |
|
| |
|
|
4 |
|
| |
|
|
4 |
|
| |
|
|
5 |
|
| |
|
|
5 |
|
| |
|
|
5 |
|
| |
|
|
6 |
|
| |
|
|
8 |
|
| |
|
|
8 |
|
| |
|
|
12 |
|
| |
|
|
14 |
|
| |
|
|
17 |
|
| |
|
|
17 |
|
| |
|
|
17 |
|
| |
|
|
19 |
|
| |
|
|
19 |
|
| |
|
|
20 |
|
| |
|
|
21 |
|
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
Investment Objective
The Fund seeks total return.
Fees and Expenses of the Fund
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold and sell shares of the Fund. The table and the example below do not reflect the separate account fees charged in the variable annuity or variable life insurance policy (“Variable Contracts”) in which the Fund is offered. If separate account fees were shown, the Fund’s annual operating expenses would be higher. Please see your Variable Contract prospectus for more details on the separate account fees.
Annual Fund Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment)
|
|
|
|
|
| Management Fees |
|
|
0.72 |
% |
| Other Expenses |
|
|
0.10 |
% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
| Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements1 |
|
|
0.17 |
% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements1 |
|
|
0.65 |
% |
| 1 |
The Fund’s investment adviser, The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company (“VALIC”), has contractually agreed to waive its advisory fee until September 30, 2024, so that the advisory fee payable by the Fund to VALIC equals 0.580% on the first $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.555% on the next $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.530% on the next 300 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.505% on the next $200 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets and 0.450% on the Fund’s average daily net assets over $1 billion. This agreement may be modified or discontinued prior to such time only with the approval of the Board of Directors of VALIC Company I (“VC I”), including a majority of the directors who are not “interested persons” of VC I as defined in the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended. |
Expense Example
This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem or hold all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the Fund’s operating expenses include fee waivers for year
one. The Example does not reflect charges imposed by the Variable Contract. If the Variable Contract fees were reflected, the expenses would be higher. See the Variable Contract prospectus for information on such charges. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions and the net expenses shown in the fee table, your costs would be:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 Year |
|
3 Years |
|
5 Years |
|
10 Years |
| $66 |
|
$245 |
|
$438 |
|
$998 |
Portfolio Turnover
The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the Example, affect the Fund’s performance.
During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 25% of the average value of its portfolio.
Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund
The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of issuers included in the Russell 1000® Growth Index (the “Index”) at the time of purchase. The Index is comprised of U.S. large- and mid‑cap companies that exhibit certain growth characteristics, as defined by the index provider. As of December 31, 2022, the market capitalization range of the companies in the Index was approximately $656.70 million to $2.10 trillion. The size of the companies in the Index changes with market conditions and the composition of the Index.
The equity securities in which the Fund invests include common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities, rights, and warrants. The Fund may at times have significant exposure to one or more industries or sectors and may be overweight with respect to certain securities (i.e., the Fund will hold a greater percentage of those securities than the Index) and underweight with respect to others (i.e., the Fund will hold a lesser percentage of those securities than the Index). Such weightings may change over time.
Each of the Fund’s subadvisers manages a portion of the Fund’s assets using different investment strategies and techniques.
One subadviser employs a proprietary, dynamic multifactor approach to managing the Fund’s assets that is based on quantitative and qualitative research and analysis. In selecting securities, the subadviser seeks to allocate its portion of the Fund’s assets to equity securities the subadviser believes share complementary
1
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
factor exposures. Factors are characteristics that are important in explaining the returns and risks of a group of securities. Among the factors that the subadviser uses to select equity securities for the Fund are: (1) mean reversion (e.g., stocks that are inexpensive relative to their historical fundamentals); (2) trend following (e.g., strong momentum and higher growth potential); and (3) risk aversion (e.g., financially healthy, stable, and lower volatility companies). In exceptional circumstances, the subadviser may exclude, remove or include an issuer or security in the Fund’s portfolio where it believes the data available does not accurately reflect current events, or to adjust the risk profile of the Fund appropriately. The subadviser may engage in frequent and active trading of portfolio securities with respect to its portion of the Fund’s assets.
The other subadviser uses a rules-based methodology that emphasizes quantitatively-based stock selection, portfolio construction, and efficient implementation to seek to capture common sources of active equity returns among factors. Among the factors that the subadviser’s methodology employs are: (1) value (i.e., how attractively a stock is priced relative to its “fundamentals,” such as book value and free cash flow); (2) momentum (i.e., whether a company’s share price is trending up or down); (3) quality (i.e., profitability) and (4) low volatility (i.e., a relatively low degree of fluctuation in a company’s share price over time). The subadviser seeks to capitalize on the low correlations in returns across these factors by diversifying exposure to securities selected based on such factors. The subadviser may, in its discretion, make changes to its quantitative techniques, or use other quantitative techniques that are based on the subadviser’s proprietary research.
The subadviser constructs its portion of the Fund’s portfolio by investing assets in the securities comprising the Index and adjusting the relative weight of each security based on the security’s attractiveness when evaluated based on the factors as described above, subject to the Fund being constrained to long-only positions. The subadviser will rebalance its portion of the Fund’s portfolio according to the process set forth above on a quarterly basis. The subadviser generally employs a strategy to continue to hold securities between quarterly rebalancings, even if there are adverse developments concerning a particular security, an industry, the economy, or the stock market generally. The subadviser may reduce the position size of a security or sell a security during quarterly rebalancings if the security no longer has favorable scores in one or more of the four factors.
In order to generate additional income, the Fund may lend portfolio securities to broker-dealers and other financial institutions provided that the value of the loaned
securities does not exceed 30% of the Fund’s total assets. These loans earn income for the Fund and are collateralized by cash and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities.
The Fund is a non‑diversified fund, which means that it may invest in a smaller number of issuers than a diversified fund.
Principal Risks of Investing in the Fund
As with any mutual fund, there can be no assurance that the Fund’s investment objective will be met or that the net return on an investment in the Fund will exceed what could have been obtained through other investment or savings vehicles. Shares of the Fund are not bank deposits and are not guaranteed or insured by any bank, government entity or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. If the value of the assets of the Fund goes down, you could lose money.
The following is a summary of the principal risks of investing in the Fund.
Management Risk. The investment style or strategy used by the subadviser may fail to produce the intended result. The subadviser’s assessment of a particular security or company may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or underperformance.
Equity Securities Risk. The Fund invests principally in equity securities and is therefore subject to the risk that stock prices will fall and may underperform other asset classes. Individual stock prices fluctuate from day‑to‑day and may decline significantly. The prices of individual stocks may be negatively affected by poor company results or other factors affecting individual prices, as well as industry and/or economic trends and developments affecting industries or the securities market as a whole.
Growth Style Risk. Generally, “growth” stocks are stocks of companies that a subadviser believes have anticipated earnings ranging from steady to accelerated growth. Many investors buy growth stocks because of anticipated superior earnings growth, but earnings disappointments often result in sharp price declines. Growth companies usually invest a high portion of earnings in their own businesses so their stocks may lack the dividends that can cushion share prices in a down market. In addition, the value of growth stocks may be more sensitive to changes in current or expected earnings than the value of other stocks, because growth stocks trade at higher prices relative to current earnings.
2
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
Factor-Based Investing Risk. There can be no assurance that the multi-factor selection process employed by a subadviser will enhance performance. Exposure to investment style factors may detract from performance in some market environments, which may continue for prolonged periods.
Large- and Mid‑Cap Company Risk. Investing in large- and mid‑cap companies carries the risk that due to current market conditions these companies may be out of favor with investors. Large‑cap companies may be unable to respond quickly to new competitive challenges or attain the high growth rate of successful smaller companies. Stocks of mid‑cap companies may be more volatile than those of larger companies due to, among other reasons, narrower product lines, more limited financial resources and fewer experienced managers.
Preferred Stock Risk. Unlike common stock, preferred stock generally pays a fixed dividend from a company’s earnings and may have a preference over common stock on the distribution of a company’s assets in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation. Preferred stockholders’ liquidation rights are subordinate to the company’s debt holders and creditors. If interest rates rise, the fixed dividend on preferred stocks may be less attractive and the price of preferred stocks may decline. Preferred stockholders typically do not have voting rights.
Convertible Securities Risk. Convertible security values may be affected by market interest rates, issuer defaults and underlying common stock values; security values may fall if market interest rates rise and rise if market interest rates fall. Additionally, an issuer may have the right to buy back the securities at a time unfavorable to the Fund.
Warrants and Rights Risk. Warrants and rights can provide a greater potential for profit or loss than an equivalent investment in the underlying security. Prices of warrants and rights do not necessarily move in tandem with the prices of the underlying securities and therefore are highly volatile and speculative investments. They have no voting rights, pay no dividends and have no rights with respect to the assets of the issuer other than a purchase option. If a warrant or right held by the Fund is not exercised by the date of its expiration, the Fund would lose the entire purchase price of the warrant or right.
Quantitative Investing Risk. The value of securities selected using quantitative analysis can react differently to issuer, political, market, and economic developments from the market as a whole or securities selected using only fundamental analysis. This may be the result of the
factors used in building the quantitative analytical framework, the weights placed on each factor, and the accuracy of historical data supplied by third parties. In addition, factors that affect a security’s value can change over time and these changes may not be reflected in the quantitative model.
Sector Risk. Companies with similar characteristics may be grouped together in broad categories called sectors. Sector risk is the risk that securities of companies within specific sectors of the economy can perform differently than the overall market. This may be due to changes in such things as the regulatory or competitive environment or to changes in investor perceptions regarding a sector. Because the Fund may allocate relatively more assets to certain sectors than others, the Fund’s performance may be more susceptible to any developments which affect those sectors emphasized by the Fund.
Market Risk. The Fund’s share price can fall because of weakness in the broad market, a particular industry, or specific holdings or due to adverse political or economic developments here or abroad, changes in investor psychology, or heavy institutional selling and other conditions or events (including, for example, military confrontations, war, terrorism, sanctions, disease/virus, outbreaks and epidemics). The prices of individual securities may fluctuate, sometimes dramatically, from day to day. The prices of stocks and other equity securities tend to be more volatile than those of fixed-income securities.
The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the related governmental and public responses have had and may continue to have an impact on the Fund’s investments and net asset value and have led and may continue to lead to increased market volatility and the potential for illiquidity in certain classes of securities and sectors of the market. Preventative or protective actions that governments may take in respect of pandemic or epidemic diseases may result in periods of business disruption, business closures, inability to obtain raw materials, supplies and component parts, and reduced or disrupted operations for the issuers in which the Fund invests. Government intervention in markets may impact interest rates, market volatility and security pricing. The occurrence, reoccurrence and pendency of such diseases could adversely affect the economies (including through changes in business activity and increased unemployment) and financial markets either in specific countries or worldwide.
Non‑Diversification Risk. Because the Fund may invest in a smaller number of issuers, its value may be affected to a greater extent by the performance of any one of those issuers or by any single economic, political,
3
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
market or regulatory event affecting any one of those issues than a fund that invests in a larger number of issuers.
Securities Lending Risk. Engaging in securities lending could increase the market and credit risk
for Fund investments. The Fund may lose money if it does not recover borrowed securities, the value of the collateral falls, or the value of investments made with cash collateral declines. The Fund’s loans will be collateralized by securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies and instrumentalities, which subjects the Fund to the credit risk of the U.S. Government or the issuing federal agency or instrumentality. If the value of either the cash collateral or the Fund’s investments of the cash collateral falls below the amount owed to a borrower, the Fund also may incur losses that exceed the amount it earned on lending the security. Securities lending also involves the risks of delay in receiving additional collateral or possible loss of rights in the collateral if the borrower fails. Another risk of securities lending is the risk that the loaned portfolio securities may not be available to the Fund on a timely basis and the Fund may therefore lose the opportunity to sell the securities at a desirable price.
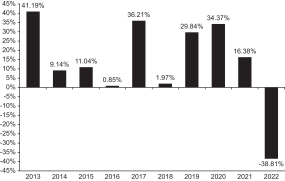
Performance Information
The following Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table illustrate the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund’s performance from calendar year to calendar year and comparing the Fund’s average annual returns to those of the Russell 1000® Growth Index and the S&P 500® Index. Effective May 1, 2023, the Fund changed its benchmark index against which the Fund measures its performance from the S&P 500® Index to the Russell 1000® Growth Index. Fund management believes that the Russell 1000® Growth Index is more representative of the securities in which the Fund invests. The Fund’s returns prior to May 1, 2023, as reflected in the bar chart and table, are the returns of the Fund when it followed different investment strategies under the name “Blue Chip Growth Fund.” Fees and expenses incurred at the contract level are not reflected in the bar chart or table. If these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. Of course, past performance of the Fund is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.
Effective May 1, 2023, Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”) and Wellington Management Company LLP (“Wellington Management”) assumed subadvisory responsibilities for the Fund. Prior to May 1, 2023, T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. served as subadviser to the Fund.
During the period shown in the bar chart:
Highest Quarterly Return: June 30, 2020 27.59%
Lowest Quarterly Return: June 30, 2022 ‑25.46%
Year to Date Most Recent Quarter: March 31, 2023 16.40%
Average Annual Total Returns (For the periods ended December 31, 2022)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
1
Year |
|
5
Years |
|
10
Years |
| Fund |
|
-38.81% |
|
4.84% |
|
11.53% |
| Russell 1000®
Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) |
|
-29.14% |
|
10.96% |
|
14.10% |
| S&P 500®
Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) |
|
-18.11% |
|
9.42% |
|
12.56% |
Investment Adviser
The Fund’s investment adviser is VALIC.
The Fund is subadvised by GSAM and Wellington Management.
4
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
Portfolio Managers
|
|
|
|
|
| Name and Title |
|
Portfolio
Manager of
the
Fund Since |
|
| GSAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Andrew Alford,
Managing Director and Portfolio Manager |
|
|
2023 |
|
| Karhan E. Akcoglu, PhD
Vice President and Portfolio Manager |
|
|
2023 |
|
| Wellington Management |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Thomas S. Simon, CFA,
FRM Senior Managing Director and Portfolio Manager |
|
|
2023 |
|
| Matthew J. Kyller,
CFA Managing Director and Portfolio Manager |
|
|
2023 |
|
Purchases and Sales of Fund Shares
Shares of the Fund may only be purchased or redeemed through Variable Contracts offered by the separate accounts of VALIC or other participating life insurance companies and through qualifying retirement plans (“Plans”) and individual retirement accounts (“IRAs”). Shares of the Fund may be purchased and redeemed each day the New York Stock Exchange is open, at the Fund’s net asset value determined after receipt of a request in good order.
The Fund does not have any initial or subsequent investment minimums. However, your insurance company may impose investment or account value minimums. The prospectus (or other offering document) for your Variable Contract contains additional information about purchases and redemptions of the Fund’s shares.
Tax Information
The Fund will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax so long as it qualifies as a regulated investment company and distributes its income and gains each year to its shareholders. However, contractholders may be subject to federal income tax (and a federal Medicare tax of 3.8% that applies to net income, including taxable annuity payments, if applicable) upon withdrawal from a Variable Contract. Contractholders should consult the prospectus (or other offering document) for the Variable Contract for additional information regarding taxation.
Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries
The Fund is not sold directly to the general public but instead is offered to registered and unregistered separate accounts of VALIC and its affiliates and to Plans and IRAs. The Fund and its related companies may make payments to the sponsoring insurance company or its affiliates for recordkeeping and distribution. These payments may create a conflict of interest as they may be a factor that the insurance company considers in including the Fund as an underlying investment option in a variable contract. Visit your sponsoring insurance company’s website for more information.
5
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE FUND’S INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE, STRATEGIES AND RISKS
The Fund’s investment objective, principal investment strategies and principal risks are summarized in the Fund Summary and a full description of the Fund’s principal investment strategies and principal risks is included below. In addition to the Fund’s principal investment strategies, the Fund may from time‑to‑time invest in other securities and use other investment techniques. The risks of these non‑principal securities and other investment techniques are included in the section “Investment Risks” below. In addition to the securities and investment techniques described in this Prospectus, there are other securities and investment techniques in which the Fund may invest in limited instances. These other securities and investment techniques are listed in the Statement of Additional Information (“SAI”), which you may obtain free of charge (see back cover).
From time to time, the Fund may take temporary defensive positions that are inconsistent with its principal investment strategies, in attempting to respond to adverse market, economic, political, or other conditions. There is no limit on the Fund’s investments in money market securities for temporary defensive purposes. If the Fund takes such a temporary defensive position, it may not achieve its investment objective.
The investment objective and principal strategies for the Fund in this Prospectus are non‑fundamental and may be changed by the Board of Directors of VALIC Company I (“VC I”) without investor approval. References to “net assets” in the Prospectus take into account any borrowings for investment purposes by the Fund. Unless stated otherwise, all percentages are calculated as of the time of purchase.
The Fund enters into contractual arrangements with various parties, including, among others, the Fund’s investment adviser, The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company (“VALIC” or the “Adviser”), which provide services to the Fund. Shareholders are not parties to, or intended (or “third-party”) beneficiaries, of those contractual arrangements and those contractual arrangements cannot be enforced by shareholders.
This Prospectus and SAI provide information concerning the Fund that you should consider in determining whether to purchase shares of the Fund. The Fund may make changes to this information from time to time. Neither this Prospectus nor the SAI is intended to give rise to any contract rights or other rights in any shareholder, other than any rights conferred by federal or state securities laws.
Systematic Growth Fund
The Fund seeks total return. The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of issuers included in the Russell 1000® Growth Index (the “Index”) at the time of purchase. The Index is comprised of U.S. large- and mid‑cap companies that exhibit certain growth characteristics, as defined by the index provider. As of December 31, 2022, the market capitalization range of the companies in the Index was approximately $656.70 million to $2.10 trillion. The size of the companies in the Index changes with market conditions and the composition of the Index.
The equity securities in which the Fund invests include common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities, rights, and warrants. The Fund may at times have significant exposure to one or more industries or sectors and may be overweight with respect to certain securities (i.e., the Fund will hold a greater percentage of those securities than the Index) and underweight with respect to others (i.e., the Fund will hold a lesser percentage of those securities than the Index). Such weightings may change over time.
Each of the Fund’s subadvisers manages a portion of the Fund’s assets using different investment strategies and techniques.
One subadviser employs a proprietary, dynamic multifactor approach to managing the Fund’s assets that is based on quantitative and qualitative research and analysis. In selecting securities, the subadviser seeks to allocate its portion of the Fund’s assets to equity securities the subadviser believes share complementary factor exposures. Factors are characteristics that are important in explaining the returns and risks of a group of securities. Among the factors that the subadviser uses to select equity securities for the Fund are: (1) mean reversion (e.g., stocks that are inexpensive relative to their historical fundamentals); (2) trend following (e.g., strong momentum and higher growth potential); and (3) risk aversion (e.g., financially healthy, stable, and lower volatility companies). In exceptional circumstances, the subadviser may exclude, remove or include an issuer or security in the Fund’s portfolio where it believes the data available does not accurately reflect current events, or to adjust the risk profile of the Fund appropriately. The subadviser may engage in frequent and active trading of portfolio securities with respect to its portion of the Fund’s assets.
6
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE FUND’S INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE, STRATEGIES AND RISKS
The other subadviser uses a rules-based methodology that emphasizes quantitatively-based stock selection, portfolio construction, and efficient implementation to seek to capture common sources of active equity returns among factors. The rules-based methodology involves two steps:
Step One
In the first step, individual factor portfolios are constructed at the same level of targeted tracking error to the Index. The subadviser assigns all securities in the Index a “factor score” that is derived from the measurements described below to create four factor portfolios.
| |
• |
|
Value: The value measurement is a composite of three valuation measures, which consist of book value‑to‑price, sales‑to‑price and free cash flow‑to‑price (earnings‑to‑price ratios are used for financial stocks or where free cash flow data are not available). |
| |
• |
|
Momentum: The momentum measurement is based on beta- and volatility-adjusted daily returns over an 11‑month period ending one month prior to the rebalance date. |
| |
• |
|
Quality: The quality measurement is gross profit divided by total assets or return on equity for financial stocks or when gross profit is not available. |
| |
• |
|
Low Volatility: The volatility measurement is defined as the inverse of the standard deviation of past 12‑month daily total stock returns. |
The securities are ranked and scored on each factor measurement independently. Based on these scores, securities with a favorable factor score will be generally overweight in the factor portfolio relative to the Index and securities with an unfavorable factor score will be generally underweight in the factor portfolio relative to the Index. Securities in each factor portfolio are also subject to minimum and maximum weights, depending on the securities’ relative weight in the Index. The portion of the Fund’s portfolio managed by the subadviser only includes long positions (i.e., short positions are impermissible).
Step Two
In the second step, the subadviser combines the factor portfolios in equal weights to create its portion of the Fund’s portfolio. As part of this combination, offsetting security positions are calculated and netted across the factor portfolios. As part of this netting process, trades are generally reduced across factor portfolios by offsetting trades in one factor portfolio against weights in another factor portfolio, subject to all security weights remaining within the upper and lower bounds around the target weight.
The subadviser will rebalance its portion of the Fund’s portfolio according to the process set forth above on a quarterly basis. The subadviser generally employs a strategy to continue to hold securities between quarterly rebalancings, even if there are adverse developments concerning a particular security, an industry, the economy, or the stock market generally. The subadviser may reduce the position size of a security or sell a security during quarterly rebalancings if the security no longer has favorable scores in one or more of the four factors. The subadviser may, in its discretion, make changes to its quantitative techniques or investment approach, including with respect to intra-quarter actions, from time‑to‑time.
In order to generate additional income, the Fund may lend portfolio securities to broker-dealers and other financial institutions provided that the value of the loaned securities does not exceed 30% of the Fund’s total assets. These loans earn income for the Fund and are collateralized by cash and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities.
The Fund is a non‑diversified fund, which means that it may invest in a smaller number of issuers than a diversified fund.
In addition to the Fund’s principal investment strategies described above, the Fund may also invest in equity securities of U.S. small cap companies. It may also invest in futures contracts and exchange-traded funds to manage the Fund’s cash position and real estate investment trusts. The Fund may hold a portion of its assets in cash or cash equivalents. The Fund is also subject to the following non-principal investment risks: Cybersecurity Risk, Derivatives Risk, Investment Company Risk, Privately Placed Securities Risk, REITs Risk and Small‑Cap Company Risk.
7
Investment Risks
Cybersecurity Risk. Intentional cybersecurity breaches include: unauthorized access to systems, networks, or devices (such as through “hacking” activity); infection from computer viruses or other malicious software code; and attacks that shut down, disable, slow, or otherwise disrupt operations, business processes, or website access or functionality. In addition, unintentional incidents can occur, such as the inadvertent release of confidential information (possibly resulting in the violation of applicable privacy laws).
A cybersecurity breach could result in the loss or theft of customer data or funds, the inability to access electronic systems (“denial of services”), loss or theft of proprietary information or corporate data, physical damage to a computer or network system, or costs associated with system repairs. Such incidents could cause the Fund, the Adviser, a subadviser, or other service providers to incur regulatory penalties, reputational damage, additional compliance costs, or financial loss. In addition, such incidents could affect issuers in which the Fund invests, and thereby cause the Fund’s investments to lose value
Derivatives Risk. Unlike stocks and bonds that represent actual ownership of a stock or bond, derivatives are instruments that “derive” their value from securities issued by a company, government, or government agency, such as futures and options. The use of derivatives involves risks different from, or possibly greater than, the risks associated with investing directly in the underlying assets. Derivatives can significantly increase the Fund’s exposure to market and credit risk. Derivatives can be highly volatile, illiquid and difficult to value, and there is the risk that changes in the value of a derivative held by the Fund will not correlate with the underlying instruments or the Fund’s other investments. A small investment in derivatives can have a potentially large impact on the Fund’s performance. Derivative instruments also involve the risk that a loss may be sustained as a result of the failure of the counterparty to the derivative instruments to make required payments or otherwise comply with the derivative instruments’ terms. Certain types of derivatives involve greater risks than the underlying obligations because, in addition to general market risks, they are subject to illiquidity risk, counterparty risk and credit risk.
Additionally, some derivatives involve economic leverage, which could increase the volatility of these investments as they may fluctuate in value more than the underlying instrument. Leveraging also may expose
the Fund to losses in excess of the amount invested. Due to their complexity, derivatives may not perform as intended. As a result, the Fund may not realize the anticipated benefits from a derivative it holds or it may realize losses. The Fund may not be able to terminate or sell a derivative under some market conditions, which could result in substantial losses.
Derivatives are often used to hedge against positions in a fund. A hedge is an investment made in order to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in a security, by taking an offsetting position in a related security (often a derivative, such as an option or a short sale). While hedging strategies can be very useful and inexpensive ways of reducing risk, they are sometimes ineffective due to unexpected changes in the market or exchange rates. Hedging also involves the risk that changes in the value of the related security will not match those of the instruments being hedged as expected, in which case any losses on the instruments being hedged may not be reduced. For gross currency hedges, there is an additional risk, to the extent that these transactions create exposure to currencies in which a fund’s securities are not denominated. Moreover, while hedging can reduce or eliminate losses, it can also reduce or eliminate gains. There are some investors who take higher risk (“speculate”) and buy derivatives to profit from a change in price of the underlying security. The Fund may purchase derivatives to hedge its investment portfolio and to earn additional income in order to help achieve its objective. Generally, the Fund does not buy derivatives to speculate.
Regulatory Risk. Over‑the‑counter derivatives are subject to regulation under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) in the United States and under comparable regimes in Europe, Asia and other non‑U.S. jurisdictions. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, with respect to uncleared swaps, swap dealers are required to collect variation margin from a fund and may be required by applicable regulations to collect initial margin from a fund. Both initial and variation margin may be comprised of cash and/or securities, subject to applicable regulatory haircuts. Shares of investment companies (other than money market funds) may not be posted as collateral under these regulations. In addition, regulations adopted by global prudential regulators require certain bank-regulated counterparties and certain of their affiliates to include in certain financial contracts, including many derivatives contracts, terms that delay or restrict the rights of counterparties, such as the Fund, to terminate such contracts, foreclose upon collateral, exercise other default rights or restrict transfers of credit support in the event that the counterparty and/or its affiliates are
8
subject to certain types of resolution or insolvency proceedings.
The implementation of these requirements with respect to derivatives, along with additional regulations under the Dodd-Frank Act regarding clearing and mandatory trading and trade reporting of derivatives, generally have increased the costs of trading in these instruments and, as a result, may affect returns to investors in the Fund.
Futures Risk. A futures contract is considered a derivative because it derives its value from the price of the underlying currency, security or financial index. The prices of futures contracts can be volatile and futures contracts may lack liquidity. In addition, there may be imperfect or even negative correlation between the price of a futures contract and the price of the underlying currency, security or financial index.
Equity Securities Risk. Equity securities represent an ownership position in a company. The prices of equity securities fluctuate based on changes in the financial condition of the issuing company and on market and economic conditions. If you own an equity security, you own a part of the company that issued it. Companies sell equity securities to get the money they need to grow.
Stocks are one type of equity security. Generally, there are three types of stocks:
| |
• |
|
Common stock — Each share of common stock represents a part of the ownership of the company. The holder of common stock participates in the growth of the company through increasing stock price and receipt of dividends. If the company runs into difficulty, the stock price can decline and dividends may not be paid. |
| |
• |
|
Preferred stock — Each share of preferred stock usually allows the holder to get a set dividend before the common stock shareholders receive any dividends on their shares. |
| |
• |
|
Convertible preferred stock — A stock with a set dividend which the holder may exchange for a certain amount of common stock. |
Stocks are not the only type of equity security. Other equity securities include but are not limited to convertible securities, depositary receipts, warrants, rights and partially paid shares, investment company securities, real estate securities, convertible bonds and American Depositary Receipts, European Depositary Receipts and Global Depositary Receipts. More information about
these equity securities is included elsewhere in this Prospectus or contained in the SAI.
Equity securities are subject to the risk that stock prices will fall over short or extended periods of time. Although the stock market has historically outperformed other asset classes over the long term, the stock market tends to move in cycles. Individual stock prices fluctuate from day‑to‑day and may underperform other asset classes over an extended period of time. Individual companies may report poor results or be negatively affected by industry and/or economic trends and developments. The prices of securities issued by such companies may suffer a decline in response. These price movements may result from factors affecting individual companies, industries or the securities market as a whole. In addition, the performance of different types of equity securities may rise or decline under varying market conditions — for example, “value” stocks may perform well under circumstances in which the prices of “growth” stocks in general have fallen, or vice versa.
Convertible Securities Risk. The values of the convertible securities in which the Fund may invest also will be affected by market interest rates, the risk that the issuer may default on interest or principal payments and the value of the underlying common stock into which these securities may be converted. Specifically, since these types of convertible securities pay fixed interest and dividends, their values may fall if market interest rates rise and rise if market interest rates fall. At times a convertible security may be more susceptible to fixed-income security related risks, while at other times such a security may be more susceptible to equity security related risks. Additionally, an issuer may have the right to buy back certain of the convertible securities at a time and a price that is unfavorable to the Fund.
Preferred Stock Risk. Unlike common stock, preferred stock generally pays a fixed dividend from a company’s earnings and may have a preference over common stock on the distribution of a company’s assets in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation. Preferred stockholders’ liquidation rights are subordinate to the company’s debt holders and creditors. If interest rates rise, the fixed dividend on preferred stocks may be less attractive and the price of preferred stocks may decline. Preferred stock usually does not require the issuer to pay dividends and may permit the issuer to defer dividend payments. Deferred dividend payments could have adverse tax consequences for the Fund and may cause the preferred stock to lose substantial value. Preferred stock usually does not require the issuer to pay dividends and may permit the issuer to defer dividend payments.
9
Factor-Based Investing Risk. There can be no assurance that the multi-factor selection process employed by a subadviser will enhance performance. Exposure to investment style factors may detract from performance in some market environments, which may continue for prolonged periods.
Investment Company Risk. An exchange-traded fund (“ETF”) or investment company may not achieve its investment objective or execute its investment strategy effectively, which may adversely affect the performance of a Fund investing in these instruments. Investments in ETFs and investment companies involve substantially the same risks as investing directly in the instruments held by these entities. However, the total return from such investments will be reduced by the operating expenses and fees of the ETF or investment company. In addition, the Fund that invests in shares of an ETF or another investment company bears a proportionate share of the ETF or other investment company’s expenses. In addition, an ETF may fail to accurately track the market segment or index that underlies its investment objective. The price of an ETF can fluctuate, and the Fund could lose money investing in an ETF.
Disruptions in the markets for the securities held by the other investment companies purchased or sold by the Fund could result in losses on the Fund’s investment in such securities. Other investment companies also have fees that increase their costs versus owning the underlying securities directly.
ETF Risk. ETFs are a type of investment company bought and sold on a securities exchange. An ETF trades like common stock. While some ETFs are passively-managed and seek to replicate the performance of a particular market index or segment, other ETFs are actively-managed and do not track a particular market index or segment, thereby subjecting investors to active management risk. The Fund could purchase an ETF to gain exposure to a portion of the U.S. or a foreign market while awaiting purchase of underlying securities. The risks of owning an ETF generally reflect the risks of owning the securities underlying the ETF, although an ETF has management fees which increase its cost. The Fund’s ability to invest in ETFs is limited by the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”).
Lending Portfolio Securities Risk. The Fund may make secured loans of its portfolio securities for purposes of realizing additional income. No lending may be made with any companies affiliated with VALIC. The Fund will only make loans to broker-dealers and other financial institutions deemed by State Street Bank and Trust Company (the “securities lending agent”) to be
creditworthy. The securities lending agent also holds the cash and the portfolio securities of VC I. Each loan of portfolio securities will be continuously secured by collateral in an amount at least equal to the market value of the securities loaned. Such collateral will be cash and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities, which subjects the Fund to the credit risk of the U.S. Government or the issuing federal agency or instrumentality. As with other extensions of credit, securities lending involves the risk that the borrower may fail to return the securities in a timely manner or at all. The Fund may lose money if the Fund does not recover the securities and/or the value of the collateral or the value of investments made with cash collateral falls. Such events may also trigger adverse tax consequences for the Fund. To the extent that either the value of the cash collateral or the Fund’s investments of the cash collateral declines below the amount owed to a borrower, the Fund also may incur losses that exceed the amount it earned on lending the security. Securities lending also involves the risks of delay in receiving additional collateral or possible loss of rights in the collateral should the borrower fail financially. Another risk of securities lending is the risk that the loaned portfolio securities may not be available to the Fund on a timely basis and the Fund may therefore lose the opportunity to sell the securities at a desirable price. Engaging in securities lending could also have a leveraging effect, which may intensify the market risk, credit risk and other risks associated with investments in the Fund.
Management Risk. Different investment styles and strategies tend to shift in and out of favor depending upon market and economic conditions, as well as investor sentiment. The investment style or strategy used by the Fund may fail to produce the intended result. Moreover, the Fund may outperform or underperform funds that employ a different investment style or strategy. A subadviser’s assessment of a particular security or company may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or underperformance.
Generally, stocks with growth characteristics can have relatively wide price swings as a result of their potentially high valuations. The share price of the Fund may be negatively affected by holding stocks with growth characteristics, as discussed in more detail below.
| |
• |
|
Growth Style Risk. Generally, “growth” stocks are stocks of companies that a subadviser believes have anticipated earnings ranging from steady to accelerated growth. They may be volatile for several reasons. Many investors buy growth stocks because of anticipated superior earnings growth, but earnings |
10
| |
|
disappointments often result in sharp price declines. Growth companies usually invest a high portion of earnings in their own businesses so their stocks may lack the dividends that can cushion share prices in a down market. In addition, the value of growth stocks may be more sensitive to changes in current or expected earnings than the value of other stocks, because growth stocks trade at higher prices relative to current earnings. Consequently, if earnings expectations are not met, the market price of growth stocks will often decline more than other stocks. |
Market Capitalization Risk. Companies are determined to be large‑cap companies, mid‑cap companies, or small‑cap companies based upon the total market value of the outstanding common stock (or similar securities) of the company at the time of purchase. The market capitalization of the companies in which the Fund invests and in the Index change over time. The Fund will not automatically sell or cease to purchase stock of a company that it already owns just because the company’s market capitalization grows or falls outside a range.
Large‑Cap Company Risk. Large‑cap companies tend to go in and out of favor based on market and economic conditions. Large‑cap companies tend to be less volatile than companies with smaller market capitalizations. In exchange for this potentially lower risk, the Fund’s value may not rise as much as the value of funds that emphasize smaller capitalization companies. Larger, more established companies may be unable to respond quickly to new competitive challenges, such as changes in technology and consumer tastes. Larger companies also may not be able to attain the high growth rate of successful smaller companies, particularly during extended periods of economic expansion.
Mid‑Cap Company Risk. The risk that mid‑cap companies, which usually do not have as much financial strength as very large companies, may not be able to do as well in difficult times. Investing in mid‑cap companies may be subject to special risks associated with narrower product lines, more limited financial resources, fewer experienced managers, dependence on a few key employees, and a more limited trading market for their stocks, as compared with larger companies.
Small‑Cap Company Risk. Investing in small companies involves greater risk than is customarily associated with larger companies. Stocks of small companies are subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements than larger company stocks. Small
companies often are in the early stages of development and have limited product lines, markets, or financial resources. Their managements may lack depth and experience. Such companies seldom pay significant dividends that could cushion returns in a falling market. In addition, these companies may be more affected by intense competition from larger companies, and the trading markets for their securities may be less liquid and more volatile than securities of larger companies. This means that the Fund could have greater difficulty selling a security of a small‑cap issuer at an acceptable price, especially in periods of market volatility. Also, it may take a substantial period of time before the Fund realizes a gain on an investment in a small‑cap company, if it realizes any gain at all.
Market Risk. The Fund’s share price can fall because of weakness in the broad market, a particular industry, or specific holdings. The market as a whole can decline for many reasons, including adverse political or economic developments here or abroad, changes in investor psychology, or heavy institutional selling and other conditions or events (including, for example, military confrontations, war, terrorism, sanctions, disease/virus, outbreaks and epidemics). The prospects for an industry or company may deteriorate because of a variety of factors, including disappointing earnings or changes in the competitive environment. In addition, a subadviser’s assessment of companies held in the Fund may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or poor performance even in a rising market. Markets tend to move in cycles with periods of rising prices and periods of falling prices. Like markets generally, the investment performance of the Fund will fluctuate, so an investor may lose money over short or even long periods.
The coronavirus (COVID‑19) pandemic and the related governmental and public responses have had and may continue to have an impact on the Fund’s investments and net asset value and have led and may continue to lead to increased market volatility and the potential for illiquidity in certain classes of securities and sectors of the market. Preventative or protective actions that governments may take in respect of pandemic or epidemic diseases may result in periods of business disruption, business closures, inability to obtain raw materials, supplies and component parts, and reduced or disrupted operations for the issuers in which the Fund invests. Government intervention in markets may impact interest rates, market volatility and security pricing. The occurrence, reoccurrence and pendency of such diseases could adversely affect the economies (including through changes in business activity and increased unemployment) and financial markets either in specific countries or worldwide.
11
Non‑Diversification Risk. The Fund is non‑diversified under the 1940 Act. A fund that is considered a non‑diversified investment company may invest a larger portion of its assets in the stock of a single company than a diversified investment company, and thus can invest in a smaller number of securities. As a result, the Fund’s value will be affected to a greater extent by the performance of any one company than would be a diversified investment company.
Privately Placed Securities Risk. The Fund’s investments may also include privately placed securities, which are subject to resale restrictions. These securities will have the effect of increasing the level of Fund illiquidity to the extent the Fund may be unable to sell or transfer these securities due to restrictions on transfers or on the ability to find buyers interested in purchasing the securities. The illiquidity of the market, as well as the lack of publicly available information regarding these securities, may also adversely affect the ability to arrive at a fair value for certain securities at certain times and could make it difficult for the Fund to sell certain securities.
Quantitative Investing Risk. The value of securities selected using quantitative analysis can react differently to issuer, political, market, and economic developments from the market as a whole or securities selected using only fundamental analysis. The factors used in quantitative analysis and the weight placed on those factors may not be predictive of a security’s value. In addition, factors that affect a security’s value can change over time and these changes may not be reflected in the quantitative model.
REITs Risk. Real Estate Investment Trusts (“REITs”) pool investors’ funds for investments primarily in commercial real estate properties. Like mutual funds, REITs have expenses, including advisory and administration fees that are paid by their shareholders. As a result, shareholders will absorb an additional layer of fees when the Fund invests in REITs. The performance of any Fund’s REITs holdings ultimately depends on the types of real property in which the REITs invest and how well the property is managed. A general downturn in real estate values also can hurt REITs performance. When a REIT focuses its investments in particular sub‑sectors of the real estate industry or particular geographic regions, the REIT’s performance would be especially sensitive to developments that significantly affected those particular sub‑sectors or geographic regions. Due to their dependence on the management skills of their managers, REITs may underperform if their managers are incorrect in their assessment of particular real estate investments. In
addition, REITs are subject to certain provisions under federal tax law. The failure of a company to qualify as a REIT could have adverse consequences for the Fund, including significantly reducing the return to the Fund on its investment in such company.
Sector Risk. Companies with similar characteristics may be grouped together in broad categories called sectors. Sector risk is the risk that securities of companies within specific sectors of the economy can perform differently than the overall market. This may be due to changes in such things as the regulatory or competitive environment or to changes in investor perceptions regarding a sector. Because the Fund may allocate relatively more assets to certain sectors than others, the Fund’s performance may be more susceptible to any developments which affect those sectors emphasized by the Fund.
At times, the Fund may have a significant portion of its assets invested in securities of companies conducting business in a broadly related group of industries within an economic sector. Companies in the same economic sector may be similarly affected by economic or market events, making the Fund more vulnerable to unfavorable developments in that economic sector than funds that invest more broadly.
Substantial investments in a particular market, industry, group of industries, country, region, group of countries, asset class or sector make the Fund’s performance more susceptible to any single economic, market, political or regulatory occurrence affecting that particular market, industry, group of industries, country, region, group of countries, asset class or sector than a fund that invests more broadly.
Warrants and Rights Risk. Warrants and rights can provide a greater potential for profit or loss than an equivalent investment in the underlying security. Prices of warrants and rights do not necessarily move in tandem with the prices of the underlying securities and therefore are highly volatile and speculative investments. They have no voting rights, pay no dividends and have no rights with respect to the assets of the issuer other than a purchase option. If a warrant or right held by the Fund is not exercised by the date of its expiration, the Fund would lose the entire purchase price of the warrant or right.
About the Indices
Unlike mutual funds, the indices do not incur expenses. If expenses were deducted, the actual returns of the indices would be lower.
12
The Russell 1000® Growth Index measures the performance of those Russell 1000® companies with higher price‑to‑book ratios and higher forecasted growth values.
The S&P 500® Index is an index of the stocks of 500 major large‑cap U.S. corporations, chosen for market
size, liquidity, and industry group representation. It is a market-value weighted index, with each stock’s percentage in the Index in proportion to its market value.
Additional Information About the S&P Index. “S&P 500®” is a trademark of S&P.
13
VC I Shares
VC I is an open‑end management investment company and may offer shares of the Fund for sale at any time. However, VC I offers shares of the Fund only to registered and unregistered separate accounts of VALIC and its affiliates and to qualifying retirement plans (previously defined as the “Plans”) and IRAs.
Buying and Selling Shares
As a participant in a Variable Contract, Plan, or IRA, you do not directly buy shares of the funds that make up VC I. Instead, you buy units in either a registered or unregistered separate account of VALIC or of its affiliates or through a trust or custodial account under a Plan or an IRA. When you buy these units, you specify the funds in which you want the separate account, trustee or custodian to invest your money. The separate account, trustee or custodian in turn, buys the shares of the funds according to your instructions. After you invest in a fund, you participate in fund earnings or losses in proportion to the amount of money you invest. When you provide instructions to buy, sell, or transfer shares of a fund, the separate account, trustee or custodian does not pay any sales or redemption charges related to these transactions. The value of such transactions is based on the next calculation of net asset value after the orders are placed with the fund.
For certain investors, there may be rules or procedures regarding the following:
| |
• |
|
any minimum initial investment amount and/or limitations on periodic investments; |
| |
• |
|
how to purchase, redeem or exchange your interest in the Fund; |
| |
• |
|
how to obtain information about your account, including account statements; and |
| |
• |
|
any fees applicable to your account. |
For more information on such rules or procedures, you should review your Variable Contract prospectus, Plan document or custodial agreement. The Fund does not currently foresee any disadvantages to participants arising out of the fact that it may offer its shares to separate accounts of various insurance companies to serve as the investment medium for their variable annuity and variable life insurance contracts. Nevertheless, the Board of Directors intends to monitor events in order to identify any material irreconcilable conflicts which may possibly arise and to determine what action, if any, should be taken in response to such conflicts. If such a conflict were to occur, one or more insurance companies’ separate accounts might be required to withdraw their investments in the Fund and
shares of another fund may be substituted. This might force the Fund to sell portfolio securities at disadvantageous prices. In addition, VC I reserves the right to refuse to sell shares of the Fund to any separate account, plan sponsor, trustee or custodian, or financial intermediary, or may suspend or terminate the offering of shares of the Fund if such action is required by law or regulatory authority or is in the best interests of the shareholders of the Fund.
Execution of requests. VC I is open on those days when the New York Stock Exchange is open for regular trading. Buy and sell requests are executed at the next net asset value (“NAV”) to be calculated after the request is accepted by VC I. If the order is received by VC I, or the insurance company as its authorized agent, before VC I’s close of business (generally 4:00 p.m., Eastern time), the order will receive that day’s closing price. If the order is received after that time, it will receive the next business day’s closing price.
Normally, VC I redeems Fund shares within seven days when the request is received in good order, but may postpone redemptions beyond seven days when: (i) the New York Stock Exchange is closed for other than weekends and customary holidays, or trading on the New York Stock Exchange becomes restricted; (ii) an emergency exists making disposal or valuation of the Fund’s assets not reasonably practicable; or (iii) the SEC has so permitted by order for the protection of VC I’s shareholders. For these purposes, the SEC determines the conditions under which trading shall be deemed to be restricted and an emergency shall be deemed to exist. The New York Stock Exchange is closed on the following holidays: New Year’s Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, Washington’s Birthday (observed), Good Friday, Memorial Day, Juneteenth, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving Day and Christmas.
Your redemption proceeds typically will be sent within three business days after your request is submitted, but in any event, within seven days. Under normal circumstances, VC I expects to meet redemption requests by using cash or cash equivalents in the Fund’s portfolio or by selling portfolio assets to generate cash. During periods of stressed market conditions, the Fund may be more likely to limit cash redemptions and may determine to pay redemption proceeds by borrowing under a line of credit.
Frequent or Short-term Trading
The Fund, which is offered only through Variable Contracts, Plans or IRAs, is intended for long-term investment and not as a frequent short-term trading (“market timing”) vehicle. Accordingly, organizations or
14
individuals that use market timing investment strategies and make frequent transfers or redemptions should not purchase shares of the Fund. The Board of Directors has adopted policies and procedures with respect to market timing activity as discussed below. VC I believes that market timing activity is not in the best interest of the participants of the Fund. Due to the disruptive nature of this activity, it can adversely impact the ability of the Subadvisers to invest assets in an orderly, long-term manner. In addition, market timing can disrupt the management of the Fund and raise its expenses through: increased trading and transaction costs; forced and unplanned portfolio turnover; and large asset swings that decrease the Fund’s ability to provide maximum investment return to all participants. This in turn can have an adverse effect on Fund performance.
The Fund may invest in foreign securities and/or high yield fixed income securities (often referred to as “junk bonds”), so it may be particularly vulnerable to market timing. Market timing may occur because of time zone differences between the foreign markets on which the Fund’s international portfolio securities trade and the time as of which the Fund’s net asset value is calculated. Market timing may also occur if market prices are not readily available for the Fund’s junk bond holdings. Market timers might try to purchase shares of the Fund based on events occurring after foreign market closing prices are established but before calculation of the Fund’s net asset value, or if they believe market prices for junk bonds are not accurately reflected by the Fund. One of the objectives of VC I’s fair value pricing procedures is to minimize the possibilities of this type of market timing (see “How Shares are Valued”).
Shares of the Fund are generally held through insurance company separate accounts, Plans or through a trust or custodial account (“Financial Intermediaries”). The ability of VC I to monitor transfers made by the participants in separate accounts or Plans maintained by Financial Intermediaries is limited by the institutional nature of Financial Intermediaries’ omnibus accounts. VC I’s policy is that the Fund will rely on the Financial Intermediaries to monitor market timing within the Fund to the extent that VC I believes that each Financial Intermediary’s practices are reasonably designed to detect and deter transactions that are not in the best interest of the Fund.
There is no guarantee that VC I will be able to detect market timing activity or the participants engaged in such activity, or, if it is detected, to prevent its recurrence. Whether or not VC I detects it, if market timing occurs, then you should anticipate that you will be subject to the disruptions and increased expenses discussed above. In situations in which VC I becomes aware of possible
market timing activity, it will notify the Financial Intermediary in order to help facilitate the enforcement of such entity’s market timing policies and procedures. VC I has entered into agreements with various Financial Intermediaries that require such intermediaries to provide certain information to help identify frequent trading activity and to prohibit further purchases or exchanges by a participant identified as having engaged in frequent trades. VC I reserves the right, in its sole discretion and without prior notice, to reject, restrict or refuse purchase orders received from a Financial Intermediary, whether directly or by transfer, including orders that have been accepted by a Financial Intermediary, that VC I determines not to be in the best interest of the Fund. Such rejections, restrictions or refusals will be applied uniformly without exception.
You should review your Variable Contract prospectus, Plan document or custodial agreement for more information regarding market timing, including any restrictions, limitations or fees that may be charged on trades made through a Variable Contract, Plan or IRA. Any restrictions or limitations imposed by the Variable Contract, Plan or IRA may differ from those imposed by VC I.
Payments in Connection with Distribution
VALIC and its affiliates may receive revenue sharing payments from the Subadvisers to the Fund in connection with certain administrative, marketing and other servicing activities, which payments help offset costs for education, marketing activities and training to support sales of the Fund, as well as occasional gifts, entertainment or other compensation as incentives. Payments may be derived from investment management fees received by the subadvisers.
Selective Disclosure of Portfolio Holdings
VC I’s policies and procedures with respect to the disclosure of the Fund’s portfolio securities are described in the SAI.
How Shares are Valued
The NAV for the Fund is determined each business day at the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (generally 4:00 p.m., Eastern Time) by dividing the net assets of the Fund by the number of outstanding shares. The NAV for the Fund also may be calculated on any other day in which there is sufficient liquidity in the securities held by the Fund. As a result, the value of the Fund’s shares may change on days when you will not be able to purchase or redeem your shares. The value of the investments held by the Fund are determined by VALIC, as the “valuation designee,”
15
pursuant to its valuation procedures. The Board of Directors oversees the valuation designee and at least annually reviews its valuation policies and procedures. Investments for which market quotations are readily available are valued at their market price as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange for the day, unless the market quotations are determined to be unreliable. Securities and other assets for which market quotations are unavailable or unreliable are valued by the valuation designee at fair value in accordance with valuation procedures. There is no single standard for making fair value determinations, which may result in prices that vary from those of other funds. In addition, there can be no assurance that fair value pricing will reflect actual market value and it is possible that the fair value determined for a security may differ materially from the value that could be realized upon the sale of the security.
Investments in registered investment companies that do not trade on an exchange are valued at the end of the day net asset value per share. Investments in registered investment companies that trade on an exchange are valued at the last sales price or official closing price as of the close of the customary trading session on the exchange where the security principally traded. The prospectus for any such open‑end funds should explain the circumstances under which these funds use fair value pricing and the effect of using fair value pricing.
As of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange, securities traded primarily on security exchanges outside the United States are valued at the last sale price on such exchanges on the day of valuation or if there is no sale on the day of valuation, at the last reported bid price. If a security’s price is available from more than one exchange, the Fund uses the exchange that is the primary market for the security. However, depending on the foreign market, closing prices may be up to 15 hours old when they are used to price the Fund’s shares, and the Fund may determine that certain closing prices do not reflect the fair value of a security. This determination will be based on review of a number of factors, including developments in foreign markets, the performance of U.S. securities markets, and the performance of instruments trading in U.S. markets that represent foreign securities and baskets of foreign securities. If the valuation designee determines that closing prices do not reflect the fair value of the securities, the valuation designee will adjust the previous closing prices in accordance with pricing procedures to reflect what it believes to be the fair value of the securities as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange. The Fund may also fair value securities in other situations, for example, when a
particular foreign market is closed but the Fund is open.
For foreign equity securities and foreign equity futures contracts, the Fund uses an outside pricing service to provide it with closing market prices and information used for adjusting those prices.
The Fund may invest in securities that are primarily listed on foreign exchanges that trade on weekends or other days when the Fund does not price its shares. As a result, the value of such foreign securities may change on days when the Fund is not open to purchases or redemptions.
During periods of extreme volatility or market crisis, the Fund may temporarily suspend the processing of sell requests or may postpone payment of proceeds for up to seven business days or longer, or as allowed by federal securities laws.
Dividends and Capital Gains
Dividends from Net Investment Income
Dividends from net investment income are declared and paid annually. Dividends from net investment income are automatically reinvested for you into additional shares of the Fund.
Distributions from Capital Gains
When the Fund sells a security for more than it paid for that security, a capital gain results. Distributions from capital gains, if any, are normally declared and paid annually. Distributions from capital gains are automatically reinvested for you into additional shares of the Fund.
Tax Consequences
As the owner of a Variable Contract, a participant under your employer’s Variable Contract or Plan or as an IRA account owner, you will not be directly affected by the federal income tax consequences of distributions, sales or redemptions of Fund shares. You should consult your Variable Contract prospectus, Plan document, custodial agreement or your tax professional for further information concerning the federal income tax consequences to you of investing in the Fund.
The Fund will annually designate certain amounts of its dividends paid as eligible for the dividend received deduction. If the Fund incurs foreign taxes, it will elect to pass-through allowable foreign tax credits. These designations and elections will benefit VALIC, in potentially material amounts, and will not beneficially or adversely affect you or the Fund. The benefits to VALIC will not be passed to you or the Fund.
16
Investment Adviser
VALIC is a stock life insurance company which has been in the investment advisory business since 1960 and is the investment adviser for the Fund. VALIC is an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Corebridge Financial, Inc. (“Corebridge”). VALIC is located at 2929 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019.
VALIC serves as investment adviser through an Investment Advisory Agreement with VC I. As investment adviser, VALIC oversees the day‑to‑day operations of the Fund and supervises the purchase and sale of Fund investments. VALIC employs investment subadvisers that make investment decisions for the Fund.
American International Group, Inc. (“AIG”), the parent of Corebridge, has announced its intention to sell all of its interest in Corebridge over time (such divestment, the “Separation Plan”). On September 19, 2022, AIG sold a portion of its interest in Corebridge in an initial public offering of Corebridge common stock, following which AIG’s interest in Corebridge is approximately 78%. While AIG and Corebridge believe that Corebridge’s initial public offering did not result in a transfer of a controlling block of outstanding voting securities of VALIC or Corebridge (“a Change of Control Event”), it is anticipated that one or more of the transactions contemplated by the Separation Plan will ultimately be deemed a Change of Control Event resulting in the assignment and automatic termination of the current Investment Advisory Agreement. To ensure that VALIC may continue to provide advisory services to the Fund without interruption, at meetings held on August 2‑3, 2022, the Board of Directors approved a new investment advisory agreement with VALIC, in connection with the Separation Plan. The Board of Directors also agreed to call and hold a joint meeting of shareholders on October 14, 2022, for shareholders of the Fund to (1) approve the new investment advisory agreement with VALIC that would be effective after the first Change of Control Event, and (2) approve any future investment advisory agreements approved by the Board of Directors and that have terms not materially different from the current agreement, in the event there are subsequent Change of Control Events arising from completion of the Separation Plan that terminate the investment advisory agreement after the first Change of Control Event. Approval of a future investment advisory agreement means that shareholders may not have another opportunity to vote on a new agreement with VALIC even upon a change of control, as long as no single person or group of persons acting together gains “control” (as defined in the 1940 Act) of VALIC. At the October 14, 2022 meeting, shareholders of the Fund
approved the new and future investment advisory agreements.
The investment advisory agreement between VALIC and VC I provides for VC I to pay all expenses not specifically assumed by VALIC. Examples of the expenses paid by VC I include transfer agency fees, custodial fees, the fees of outside legal and auditing firms, the costs of reports to shareholders and expenses of servicing shareholder accounts. These expenses are allocated to each Fund in a manner approved by the Board of Directors. For more information on these agreements, see the “Investment Adviser” section in the SAI.
Investment Subadvisers
VALIC works with the investment subadviser for the Fund. Subadvisers are financial services companies that specialize in certain types of investing. The subadviser’s role is to make investment decisions for the Fund according to the Fund’s investment objective and restrictions. VALIC compensates the subadviser out of the fees it receives from the Fund.
According to the agreements VALIC has with the subadvisers, VALIC will receive investment advice for the Fund. Under these agreements, VALIC gives the subadvisers the authority to buy and sell securities for the Fund. However, VALIC retains the responsibility for the overall management of the Fund. The subadvisers may buy and sell securities for the Fund with broker-dealers and other financial intermediaries that they select. The subadvisers may place orders to buy and sell securities of the Fund with a broker-dealer affiliated with the subadvisers, as allowed by law. This could include any affiliated futures commission merchants.
The 1940 Act permits the subadvisers, under certain conditions, to place an order to buy or sell securities with an affiliated broker. One of these conditions is that the commission received by the affiliated broker cannot be greater than the usual and customary brokers commission if the sale was completed on a securities exchange. VC I has adopted procedures, as required by the 1940 Act, which provide that any commissions received by a subadviser’s affiliated broker may be considered reasonable and fair if compared to the commission received by other brokers for the same type of securities transaction.
The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 prohibits members of national securities exchanges from effecting exchange transactions for accounts that they or their affiliates manage, except as allowed under rules adopted by the SEC. VC I and the subadvisers have entered into written
17
contracts, as required by the 1940 Act, to allow a subadviser’s affiliate to effect these types of transactions for commissions. The 1940 Act generally prohibits a subadviser or a subadviser’s affiliate, acting as principal, from engaging in securities transactions with the Fund, without an exemptive order from the SEC.
VALIC and the subadvisers may enter into simultaneous purchase and sale transactions for the Fund or affiliates of the Fund.
In selecting the subadvisers, the Board of Directors carefully evaluated: (i) the nature and quality of the services expected to be rendered to the Fund by the subadvisers; (ii) the distinct investment objective and policies of the Fund; (iii) the history, reputation, qualification and background of the subadvisers’ personnel and their financial condition; (iv) their performance track record; and (v) other factors deemed relevant. The Board of Directors also reviewed the fees to be paid by VALIC to the subadvisers. VALIC compensates each subadviser from the investment advisory fees paid to VALIC by VC I, on behalf of the Fund. A discussion of the basis for the Board of Directors’ approval of the investment subadvisory agreement with each of GSAM (defined below) and Wellington Management (defined below) is available in VC I’s most recent semi-annual report for the period ended November 30, 2022. For information on obtaining an annual or semi-annual report to shareholders, see the section “Interested in Learning More.”
VC I relies upon an exemptive order from the SEC that permits VALIC, subject to certain conditions, to enter into subadvisory agreements relating to the Fund with unaffiliated subadvisers approved by the Board without obtaining shareholder approval. The exemptive order permits VALIC, subject to the approval of the Board but without shareholder approval, to employ unaffiliated subadvisers for new or existing funds, change the terms of subadvisory agreements with unaffiliated subadvisers or continue the employment of existing unaffiliated subadvisers after events that would otherwise cause an automatic termination of a subadvisory agreement. Shareholders will be notified of any changes that are made pursuant to the exemptive order within 60 days of hiring a new subadviser or making a material change to an existing subadvisory agreement. The order also permits the Fund to disclose fees paid to subadvisers on an aggregate, rather than individual, basis. In addition, pursuant to no‑action relief, the SEC Staff has extended multi-manager relief to any affiliated subadviser, provided certain conditions are met. The Fund’s shareholders have approved the Fund’s reliance on the no‑action relief. VALIC will determine if and when the Fund should rely on the no‑action relief. The Prospectus
will be updated in advance of the no‑action relief being relied upon by the Fund.
The SAI provides information regarding the portfolio managers listed below, including other accounts they manage, their ownership interest in the Fund, and the structure and method used by the subadviser to determine their compensation.
Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”)
200 West Street, New York, NY 10282
GSAM has been registered as an investment adviser with the SEC since 1990 and is an affiliate of Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“Goldman”). As of December 31, 2022, GSAM, including its investment advisory affiliates, had assets under management of approximately $2,417,777.6 million in total assets under supervision. Assets under supervision include assets under management and other client assets for which Goldman does not have full discretion.
The team responsible for managing the Fund is Andrew Alford and Karhan E. Akcoglu.
Mr. Alford is a managing director in Quantitative Investment Strategies (QIS) within GSAM, serving as co‑head of equity research. He joined Goldman Sachs in 1998 on the QIS equity alpha research team and became head of equity alpha research in 2000. Prior to joining the firm, Andrew was an accounting professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management. He has also served as an academic fellow in the Office of Economic Analysis at the Securities and Exchange Commission in Washington, DC.
Mr. Akcoglu is head of portfolio management for the ActiveBeta Equity Strategies business within GSAM’s Rules-Based Factor Investing Strategies platform. He is responsible for portfolio management, including portfolio construction and risk management of global developed and emerging market equity portfolios and custom indexes. Mr. Akcoglu has held various roles within the Global Markets Division and, more recently, within GSAM, focused on developing mathematical and analytical tools across a variety of factor-based strategies.
Immediately before joining the ActiveBeta team in 2021, Mr. Akcoglu served as Head of Strats for the ActiveBeta, Alternative Investment Strategies, and Macro Alpha businesses within GSAM’s Quantitative Investment Strategies platform. In this role, he oversaw the
18
development of quantitative analytical tools driving portfolio construction and risk management of long-only and long-short factor-based portfolios investing in global equities, commodities, currencies, and fixed-income instruments.
Before joining GSAM in 2018, Mr. Akcoglu was head of Trading Strats for the macro Systematic Trading Strategies (STS) business within the Global Markets Division of Goldman Sachs. He held this position since 2011, initially based out of London and subsequently New York, and oversaw the development and risk management of rules-based index products for factor exposures across currencies, commodities, and fixed income. Before this, Mr. Akcoglu led the development of the analytics underpinning the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI) and developed customized, enhanced commodity index products for exposure to commodity market factor dynamics in long-only and beta-neutral long-short formats. In this capacity, Mr. Akcoglu has previously served on the S&P GSCI Index Advisory Panel. Mr. Akcoglu originally joined Goldman Sachs in 2002 upon earning a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Yale University and an Hon.B.Sc. in Computer Science and Mathematics from the University of Toronto.
Wellington Management Company LLP (“Wellington Management”)
280 Congress Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02210
Wellington Management is a Delaware limited liability partnership and is a professional investment counseling firm which provides investment services to investment companies, employee benefit plans, endowments, foundations, and other institutions. Wellington Management and its predecessor organizations have provided investment advisory services for over 80 years. Wellington Management is owned by the partners of Wellington Management Group LLP, a Massachusetts limited liability partnership. As of March 31, 2023, Wellington Management and its investment advisory affiliates had investment management authority with respect to approximately $1.176 trillion in assets.
The Fund is managed by Thomas S. Simon, CFA, FRM and Matthew J. Kyller, CFA. Mr. Simon is Senior Managing Director and portfolio manager of Wellington Management. Mr. Simon joined Wellington Management in 2009 and has been an investment professional since 2001. Mr. Kyller is Managing Director and portfolio manager of Wellington Management. Mr. Kyller joined
Wellington Management as an investment professional in 2015.
How VALIC is Paid for its Services
The Fund pays VALIC a monthly fee based on a percentage of average daily net assets.
A discussion of the basis for the Board of Directors’ approval of the investment advisory agreement is available in VC I’s most recent semi-annual report for the period ended November 30, 2022. For information on obtaining an annual or semi-annual report to shareholders, see the section “Interested in Learning More?”
For the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Fund paid VALIC 0.69% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. The Investment Advisory Agreement entered into with the Fund does not limit how much the Fund pays in expenses each year. However, VALIC has contractually agreed to cap certain Fund expenses by waiving a portion of its advisory fee, as shown in the Annual Fund Operating Expenses table in the Fund’s Summary. The Fund’s Advisory Fee Waiver Agreement may be modified or discontinued prior to September 30, 2024, only with the approval of the Board of Directors of VC I, including a majority of the directors who are not “interested persons” of VC I as defined in the 1940 Act.
Additional Information About Fund Expenses
Commission Recapture Program. A commission recapture arrangement includes those arrangements under which products or services (other than execution of securities transactions) or commissions are recaptured for a client from or through a broker-dealer, in exchange for directing the client’s brokerage transactions to that broker-dealer who commits to returning a portion of its commission to the Fund. The Board has determined that a commission recapture arrangement with Capital Institutional Services, Inc. is in the best interest of the Fund and its shareholders. Through the commission recapture program, a portion of the Fund’s expenses have been reduced. “Other Expenses,” as reflected in the Annual Fund Operating Expenses in the Fund Summary, do not take into account this expense reduction and are therefore higher than the actual expenses of the Fund. For more information about the commission recapture program, see the SAI.
19
The following Financial Highlights table is intended to help you understand the Fund’s financial performance for the past 5 years. Certain information reflects financial results for a single Fund share. The total returns in the table represent the rate that an investor would have earned on an investment in the Fund (assuming reinvestment of all dividends and distributions). Separate Account charges are not reflected in the total returns. If these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. This information has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, whose report, along with the Fund’s financial statements, is included in VC I’s Annual Report to shareholders, which is available upon request. The Fund’s unaudited financial statements for the semi-annual period ended November 30, 2022, are included in the VC I Semi-Annual Report to shareholders which is also available upon request.
Per share data assumes that you held each share from the beginning to the end of each fiscal year. Total return assumes that you bought additional shares with dividends paid by the Fund. Total returns for periods of less than one year are not annualized.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Systematic Growth Fund (formerly, Blue Chip Growth Fund) |
|
| |
|
Six Months
Ended
November 30,
2022# |
|
|
Year Ended May 31, |
|
| |
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
| PER SHARE DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Net asset value at beginning of period |
|
$ |
16.45 |
|
|
$ |
25.17 |
|
|
$ |
20.80 |
|
|
$ |
19.18 |
|
|
$ |
20.84 |
|
|
$ |
17.27 |
|
| Income (loss) from investment operations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Net investment income (loss)(d) |
|
|
(0.02 |
) |
|
|
(0.11 |
) |
|
|
(0.11 |
) |
|
|
(0.05 |
) |
|
|
(0.01 |
) |
|
|
(0.01 |
) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments and foreign currencies |
|
|
(1.12 |
) |
|
|
(4.98 |
) |
|
|
6.96 |
|
|
|
3.93 |
|
|
|
0.86 |
|
|
|
4.82 |
|
| Total income (loss) from investment operations |
|
|
(1.14 |
) |
|
|
(5.09 |
) |
|
|
6.85 |
|
|
|
3.88 |
|
|
|
0.85 |
|
|
|
4.81 |
|
| Distributions from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Net investment income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(0.01 |
) |
| Net realized gain on securities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3.63 |
) |
|
|
(2.48 |
) |
|
|
(2.26 |
) |
|
|
(2.51 |
) |
|
|
(1.23 |
) |
| Total distributions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3.63 |
) |
|
|
(2.48 |
) |
|
|
(2.26 |
) |
|
|
(2.51 |
) |
|
|
(1.24 |
) |
| Net asset value at end of period |
|
$ |
15.31 |
|
|
$ |
16.45 |
|
|
$ |
25.17 |
|
|
$ |
20.80 |
|
|
$ |
19.18 |
|
|
$ |
20.84 |
|
| TOTAL RETURN(a) |
|
|
(6.93 |
)% |
|
|
(21.75 |
)% |
|
|
33.74 |
% |
|
|
21.77 |
% |
|
|
4.22 |
% |
|
|
27.87 |
% |
| RATIOS/SUPPLEMENTAL DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ratio of expenses to average net assets(b) |
|
|
0.84 |
%@ |
|
|
0.79 |
% |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
|
|
0.83 |
% |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
|
|
0.83 |
% |
| Ratio of expenses to average net assets(c) |
|
|
0.84 |
%@ |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
|
|
0.83 |
% |
|
|
0.82 |
% |
|
|
0.83 |
% |
| Ratio of expense reductions to average net assets |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
0.00 |
% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets(b) |
|
|
(0.28 |
%)@ |
|
|
(0.44 |
)% |
|
|
(0.45 |
)% |
|
|
(0.24 |
)% |
|
|
(0.03 |
)% |
|
|
(0.07 |
)% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets(c) |
|
|
(0.29 |
%)@ |
|
|
(0.47 |
)% |
|
|
(0.45 |
)% |
|
|
(0.24 |
)% |
|
|
(0.03 |
)% |
|
|
(0.07 |
)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate |
|
|
21 |
% |
|
|
25 |
% |
|
|
28 |
% |
|
|
27 |
% |
|
|
30 |
% |
|
|
24 |
% |
| Number of shares outstanding at end of period (000’s) |
|
|
45,244 |
|
|
|
43,257 |
|
|
|
39,782 |
|
|
|
39,950 |
|
|
|
40,727 |
|
|
|
37,397 |
|
| Net assets at end of period (000’s) |
|
$ |
692,532 |
|
|
$ |
711,659 |
|
|
$ |
1,001,518 |
|
|
$ |
831,006 |
|
|
$ |
781,236 |
|
|
$ |
779,336 |
|
| (a) |
Total return includes, if any, expense reimbursements and expense reductions. The effect of fees and charges incurred at the separate account level are not reflected in these performance figures. If such expenses had been included, the total return would have been lower for each period presented. |
| (b) |
Includes, if any, expense reimbursement, but excludes, if any, expense reductions. |
| (c) |
Excludes, if any, expense reimbursements and expense reductions. |
| (d) |
The per share amounts are calculated using the average share method. |
20
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
The Statement of Additional Information (“SAI”) incorporated by reference into this prospectus contains additional information about VC I’s operations.
Further information about the Fund’s investments is available in VC I’s annual and semi-annual reports to shareholders. VC I’s annual report discusses market conditions and investment strategies that significantly affected the Fund’s performance results during its last fiscal year.
The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company (“VALIC”) can provide you with a free copy of these materials or other information about VC I. You may reach VALIC by calling 1‑800‑448‑2542 or by writing to P.O. Box 15648, Amarillo, Texas 79105-5648. VC I’s prospectus, SAI, and shareholder reports are available online at https://www.corebridgefinancial.com/rs/prospectus-and-reports/annuities#underlyingfunds.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) maintains copies of these documents, which are available on the EDGAR Database on the SEC’s web site at http://www.sec.gov. You may also request a paper copy from the SEC electronically at publicinfo@sec.gov. A duplicating fee will be assessed for all copies provided by the SEC.
Investment Company Act filing number 811‑03738
21
VALIC Company I
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ticker Symbol: |
| SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (formerly, Blue Chip Growth Fund) |
|
VCBCX |
STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
PART B
May 1, 2023
This Statement of Additional Information (“SAI”) is not a prospectus and contains information in addition to that in the Prospectus for VALIC Company I (“VC I”). It should be read in conjunction with the Prospectus. The SAI relates to the Prospectus dated May 1, 2023. The audited financial statements of the Systematic Growth Fund (the “Fund”) are incorporated in this SAI by reference to its Annual Report dated May 31, 2022, and its unaudited financial statements are incorporated in this SAI by reference to its Semi-Annual Report dated November 30, 2022. For an individual interested in a variable annuity contract issued by The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company (“VALIC”), a Prospectus may be obtained by visiting the Fund’s website at https://www.corebridgefinancial.com/rs/prospectus-and-reports/annuities#underlyingfunds, or upon request by calling 1-800-448-2542, or writing the Fund at Document Control, P.O. Box 15648, Amarillo, Texas 79105-5648.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION AND HISTORY
VC I was incorporated in Maryland on December 7, 1984, and is registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”), as an open-end, management investment company. Pursuant to an Investment Advisory Agreement with VC I and subject to the authority of VC I’s Board of Directors (the “Board”), VALIC (the “Adviser”) serves as the investment adviser to each portfolio of VC I and conducts the business and affairs of VC I. Additionally, VALIC has engaged one or more investment subadvisers (each hereinafter referred to as a “Subadviser” and collectively, as the “Subadvisers”) to provide investment subadvisory services for the Fund subject to VALIC’s oversight. VC I consists of separate investment portfolios, each of which is, in effect, a separate mutual fund, such as the Systematic Growth Fund (the “Fund”), issuing its own separate class of shares of common stock. The Fund is “non-diversified” as the term is used in the 1940 Act.
VC I issues shares of common stock of the Fund to certain employer-sponsored retirement plans (primarily, but not exclusively, governmental plans; collectively, the “Plans” and each, a “Plan”), individual retirement accounts (“IRAs”) and registered and unregistered separate accounts of VALIC and its affiliates to fund variable annuity contracts or variable life policies (the “Contracts”).
VC I was originally named VALIC Series Portfolio Company. The name changed to American General Series Portfolio Company on January 14, 1985, to North American Funds Variable Product Series I on October 1, 2000, and to VALIC Company I on December 31, 2001. On May 1, 2008, the name changed to AIG Retirement Company I; and it was renamed VALIC Company I on May 1, 2009.
Effective December 31, 2001, the North American-T. Rowe Price Blue Chip Growth Fund changed its name to the Blue Chip Growth Fund. Effective May 1, 2023, the Blue Chip Growth Fund changed its name to the Systematic Growth Fund.
INVESTMENT RESTRICTIONS
The Fund has adopted certain fundamental investment restrictions which, unlike the other investment objective, policies, and investment program of the Fund, may only be changed with the consent of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund. The 1940 Act defines such a majority as the lesser of (i) 67% or more of the voting securities present in person or by proxy at a shareholders’ meeting, if the holders of more than 50% of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund are present or represented by proxy, or (ii) more than 50% of the Fund’s outstanding voting securities.
The fundamental investment restrictions and operating policies of the Fund are listed below. The percentage limitations referenced in some of the restrictions are to be determined at the time of purchase. However, percentage limitations for illiquid investments and borrowings apply at all times. Calculation of the Fund’s total assets for compliance with any of the investment restrictions or any other restrictions will not include cash collateral held in connection with securities lending activities.
In applying the limitations on investments in any one industry (concentration), the Fund may use industry classifications based, where applicable, on industry classification guides such as Baseline, Bridge Information Systems, Reuters, or S&P Stock Guide, Global Industry Classification Standard information obtained from Bloomberg L.P. and Moody’s International, or Barra, and/or the industry classifications set forth in the prospectus of the issuing company of the investment. Further, regarding the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry: (i) there is no limitation with respect to obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, any state, territory or possession of the United States, the District of Columbia or any of their authorities, agencies, instrumentalities or political subdivisions and repurchase agreements secured by such instruments, (ii) wholly-owned finance companies will be considered to be in the industries of their parents if their activities are primarily related to financing the activities of the parents, (iii) utilities will be divided according to their services, for example, gas, gas transmission, electric and gas, electric and telephone will each be considered a separate industry, and (iv) personal credit and business credit businesses will be considered separate industries.
3
Fundamental Investment Restrictions
The Fund may not:
| |
1. |
Borrow money except as permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
2. |
Engage in the business of underwriting the securities of other issuers except as permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
3. |
Lend money or other assets except to the extent permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
4. |
Issue senior securities except as permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
5. |
Purchase or sell real estate except as permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
6. |
Purchase or sell commodities or contracts related to commodities except to the extent permitted by (i) the 1940 Act or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, or (ii) exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority. |
| |
7. |
Except as permitted by exemptive or other relief or permission from the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, make any investment if, as a result, the Fund’s investments will be concentrated in any one industry. |
The Fund’s fundamental investment restrictions will be interpreted broadly. For example, the restrictions will be interpreted to refer to the 1940 Act and the related rules as they are in effect from time to time, and to interpretations and modifications of or relating to the 1940 Act by the SEC and others as they are given from time to time. When a policy provides that an investment practice may be conducted as permitted by the 1940 Act, the policy will be interpreted to mean either that the 1940 Act expressly permits the practice or that the 1940 Act does not prohibit the practice.
The following descriptions of the 1940 Act may assist investors in understanding the above restrictions.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 1 above, the 1940 Act permits the Fund to borrow money in amounts of up to one-third of the Fund’s total assets from banks for any purpose, and to borrow up to an additional 5% of the Fund’s total assets from banks or other lenders for temporary purposes. (The Fund’s total assets include the amounts being borrowed.) To limit the risks attendant to borrowing, the 1940 Act requires the Fund to maintain an “asset coverage” of at least 300% of the amount of its borrowings (other than the 5% temporary borrowings); provided that in the event that the Fund’s asset coverage falls below 300%, the Fund is required to reduce the amount of its borrowings so that it meets the 300% asset coverage threshold within three days (not including Sundays and holidays). Asset coverage means the ratio that the value of the Fund’s total assets (including amounts borrowed), minus liabilities other than borrowings, bears to the aggregate amount of all borrowings. Certain trading practices and investments may be considered to be borrowings and thus subject to the 1940 Act restrictions. The investment restriction will be interpreted to permit the Fund to engage in trading practices and investments that may be considered to be borrowings to the extent consistent with the 1940 Act and applicable SEC and SEC staff interpretive positions and guidance. Short-term credits necessary for the settlement of securities transactions and arrangements with respect to securities lending are not considered to be borrowings under the restriction. Practices and investments that may involve leverage but are not considered to be borrowings are not subject to the restriction to the extent consistent with applicable SEC and SEC staff interpretive positions and guidance.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 2 above, the 1940 Act permits the Fund to engage in the underwriting business or underwrite the securities of other issuers within certain limits. The Fund engaging in transactions
4
involving the acquisition or disposition of portfolio securities may be considered to be an underwriter under the 1933 Act. Under the 1933 Act, an underwriter may be liable for material omissions or misstatements in an issuer’s registration statement or prospectus. Securities purchased from an issuer and not registered for sale under the 1933 Act are considered restricted securities. There may be a limited market for these securities. If these securities are registered under the 1933 Act, they may then be eligible for sale but participating in the sale may subject the seller to underwriter liability. These risks could apply to the Fund if it invests in restricted securities. Although it is not believed that the application of the 1933 Act provisions described above would cause the Fund to be engaged in the business of underwriting, investment restriction number 2 above will be interpreted not to prevent the Fund from engaging in transactions involving the acquisition or disposition of portfolio securities, regardless of whether the Fund may be considered to be an underwriter under the 1933 Act.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 3 above, the 1940 Act permits the Fund to make loans within certain limits. The fundamental investment restriction permits the Fund to engage in securities lending, enter into repurchase agreements, acquire debt and other securities (to the extent deemed lending) and allows the Fund to lend money and other assets, in each case to the fullest extent permitted by the 1940 Act. SEC staff interpretations currently prohibit funds from lending portfolio securities of more than one-third of their total assets. The fundamental investment restriction will be interpreted not to prevent the Fund from purchasing or investing in debt obligations and loans. In addition, collateral arrangements with respect to options, forward currency and futures transactions and other derivative instruments, as well as delays in the settlement of securities transactions, will not be considered loans under the restriction.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 4, the 1940 Act prohibits the Fund from issuing “senior securities,” which are defined as Fund obligations that have a priority over the Fund’s shares with respect to the payment of dividends or the distribution of Fund assets, except that the Fund may borrow money in amounts of up to one-third of the Fund’s total assets from banks for any purpose. The Fund also may borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets from banks or other lenders for temporary purposes, and these borrowings are not considered senior securities. The issuance of senior securities by the Fund can increase the speculative character of the Fund’s outstanding shares through leveraging. Leveraging of the Fund through the issuance of senior securities magnifies the potential for gain or loss on monies, because even though the Fund’s net assets remain the same, the total risk to investors is increased to the extent of the Fund’s gross assets. The fundamental investment restriction will be interpreted not to prevent collateral arrangements with respect to swaps, options, forward or futures contracts or other derivatives, or the posting of initial or variation margin.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 5, the 1940 Act does not prohibit the Fund from owning real estate; however, the Fund is limited in the amount of illiquid investments it may purchase (real estate is generally considered illiquid). Investing in real estate may involve risks, including that real estate is generally considered illiquid and may be difficult to value and sell. Owners of real estate may be subject to various liabilities, including environmental liabilities. To the extent that investments in real estate are considered illiquid, Rule 22e-4 under the 1940 Act (the “Liquidity Rule”) limits the Fund’s acquisition of any illiquid investment, if at any time, the Fund would have invested more than 15% of its net assets in illiquid investments that are assets. The restriction will be interpreted to permit the Fund to invest in real estate-related companies, companies whose businesses consist in whole or in part of investing in real estate, instruments (like mortgages) that are secured by real estate or interests therein, or real estate investment trust securities.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 6, the 1940 Act does not prohibit the Fund from owning commodities, whether physical commodities or contracts related to physical commodities (such as oil or grains and related futures contracts), or financial commodities and contracts related to financial commodities (such as currencies). However, the Fund is limited in the amount of illiquid investments it may purchase. To the extent that investments in commodities are considered illiquid, the Liquidity Rule limits the Fund’s acquisition of any illiquid investment, if at any time, the Fund would have invested more than 15% of its net assets in illiquid investments that are assets. If the Fund were to invest in a physical commodity or a physical commodity-related instrument, the Fund would be subject to the additional risks of the particular physical commodity and its related market. The value of commodities and commodity-related instruments may be extremely volatile and may be affected either directly or indirectly by a variety of factors. There also may be storage charges and risks of loss associated with physical commodities. The restriction will be interpreted to permit investments in exchange-traded funds that invest in physical and/or financial commodities.
With respect to fundamental investment restriction number 7, the 1940 Act does not define what constitutes “concentration” in an industry. The SEC staff has taken the position that investment of 25% or more of a fund’s total assets in one or more issuers
5
conducting their principal activities in the same industry or group of industries constitutes concentration. It is possible that interpretations of concentration could change in the future. A fund that invests a significant percentage of its total assets in a single industry may be particularly susceptible to adverse events affecting that industry and may be more risky than a fund that does not concentrate in an industry. The fundamental investment restriction will be interpreted to refer to concentration as it may be determined from time to time. The fundamental investment restriction also will be interpreted to permit investment without limit in the following: securities of the U.S. government and its agencies or instrumentalities; securities of state, territory, possession or municipal governments and their authorities, agencies, instrumentalities or political subdivisions (other than private activity municipal debt securities whose principal and interest payments are derived principally from the revenues and the assets of a non-governmental user); and repurchase agreements collateralized by any of such obligations. Accordingly, issuers of the foregoing securities will not be considered to be members of any industry. Finally, the restriction will be interpreted to give broad authority to the Fund as to how to classify issuers within or among industries.
Operating Policies
Asset-Backed Securities
The Fund will only invest in fixed-income asset-backed securities rated, at the time of purchase, in the same quality range as its other permissible investments.
Single Investment Companies
Unless otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act, the Fund may not invest more than 5% of its total assets in a single investment company.
Total Investment Company Investment
Unless otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act, the Fund may not invest more than 10% of its total assets in investment company securities.
Single Investment Company Voting Securities
Unless otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act, the Fund may not invest more than 3% of its total assets in the voting securities of a single investment company.
Certificates of Deposit and Bankers Acceptances
The Fund limits its investments in U.S. certificates of deposit and bankers acceptances to obligations of U.S. banks (including foreign branches) that have more than $1 billion in total assets at the time of investment and are members of the Federal Reserve System or are examined by the Comptroller of the Currency or where deposits are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”). The Fund may also invest in certificates of deposit of savings and loan associations (federally or state chartered and federally insured) having total assets in excess of $1 billion.
INVESTMENT PRACTICES
The Fund may assume a temporary defensive position in response to adverse market, economic, political or other conditions. The Fund may invest up to 100% of its total assets in high-quality, short-term debt securities and money market instruments for this purpose. These short-term debt securities and money market instruments include: shares of money market mutual funds, commercial paper, certificates of deposit, bankers’ acceptances, U.S. Government securities and repurchase agreements. When the Fund is in a defensive position, the opportunity to achieve its investment objective is limited. To the extent the Fund invests in money market mutual funds when in a defensive position, you will indirectly bear the cost of the money market funds’ advisory fees and operational fees.
For ease of reference, a table reflecting the investment practices in which the Fund may engage is located in Appendix B. Only information that is clearly identified as being applicable to the Fund is considered to form a part of the Fund’s SAI. Information that is not applicable to the Fund does not form a part of its SAI and therefore should not be relied on by investors in the Fund.
6
In the event of any discrepancy between Appendix B and the disclosure contained in the Prospectus and SAI, the latter shall control.
Adjustable Rate Instruments
The Fund may invest in adjustable rate money market instruments. Adjustable rate instruments (i.e., variable rate and floating rate instruments) are instruments that have interest rates that are adjusted periodically, according to a set formula. The maturity of some adjustable rate instruments may be shortened under certain special conditions described more fully below.
Variable rate instruments are obligations (usually certificates of deposit) that provide for the adjustment of their interest rates on predetermined dates or whenever a specific interest rate changes. A variable rate instrument whose principal amount is scheduled to be paid in 13 months or less is considered to have a maturity equal to the period remaining until the next readjustment of the interest rate. Many variable rate instruments are subject to demand features which entitle the purchaser to resell such securities to the issuer or another designated party, either (i) at any time upon notice of usually 30 days or less, or (ii) at specified intervals, not exceeding 13 months, and upon 30 days’ notice. A variable rate instrument subject to a demand feature is considered to have a maturity equal to the longer of the period remaining until the next readjustment of the interest rate or the period remaining until the principal amount can be recovered through demand.
Floating rate instruments (generally corporate notes, bank notes, or Eurodollar certificates of deposit) have interest rate reset provisions similar to those for variable rate instruments and may be subject to demand features like those for variable rate instruments. The maturity of a floating rate instrument is considered to be the period remaining until the principal amount can be recovered through demand.
In the case of adjustable rate instruments that are not subject to a demand feature, a Fund is reliant on the secondary market for liquidity. The lack of a liquid secondary market may have an adverse impact on the market price of an instrument and the Fund’s ability to dispose of particular issues when necessary to meet the Fund’s liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as deterioration in the creditworthiness of the issuer. As a result of possible extended settlement periods, the Fund may be required to sell other investments or temporarily borrow to meet its cash needs, including satisfying redemption requests.
In certain circumstances, some adjustable rate instruments may not be deemed to be securities, and in the event of fraud or misrepresentation by an issuer, purchasers of these types of instruments, such as the Fund, will not have the protection of the anti-fraud provisions of the federal securities laws, as would be the case for bonds or stocks. Instead, in such cases, purchasers generally must rely on the contractual provisions in the instrument itself and common-law fraud protections under applicable state law.
Asset-Backed Securities
The Fund may invest in asset-backed securities (unrelated to first mortgage loans) that represent fractional interests in pools of retail installment loans, both secured (such as certificates for automobile receivables) and unsecured, and leases, or revolving credit receivables both secured and unsecured (such as credit card receivable securities). These assets are generally held by a trust and payments of principal and interest, or interest only are passed through monthly or quarterly to certificate holders and may be guaranteed up to certain amounts by letters of credit issued by a financial institution affiliated or unaffiliated with the trustee or originator of the trust.
Underlying automobile sales contracts, leases or credit card receivables are subject to prepayment, which may reduce the overall return to certificate holders. Nevertheless, principal repayment rates tend not to vary much with interest rates and the short-term nature of the underlying loans, leases, or receivables tends to dampen the impact of any change in the prepayment level. Certificate holders may also experience delays in payment on the certificates if the full amounts due on underlying loans, leases or receivables are not realized by the trust because of unanticipated legal or administrative costs of enforcing the contracts or because of depreciation or damage to the collateral (usually automobiles) securing certain contracts, or other factors. If consistent with its investment objective(s) and policies, the Fund may invest in other asset-backed securities that may be developed in the future.
7
The Fund may invest in certain asset-backed securities known as structured investment vehicles (“SIVs”). SIVs are legal entities that are sponsored by banks, broker-dealers or other financial firms specifically created for the purpose of issuing particular securities or instruments. A SIV purchases mostly highly rated medium- and long-term, fixed income assets and issues shorter-term, highly rated commercial paper and medium-term notes at lower rates to investors. SIVs typically purchase finance company debt which is focused in large banks and may also include exposure to investment banks, insurance, and other finance companies. SIVs also invest in credit card, residential mortgage-backed securities, commercial mortgage-backed securities, collateralized loan obligations, and asset-backed securities. SIVs are often leveraged and securities issued by SIVs may have differing credit ratings. Investments in SIVs present issuer risks, although they may be subject to a guarantee or other financial support by the sponsoring entity. Investments in SIVs may be more volatile, less liquid and more difficult to price accurately than other types of investments. Because SIVs depend on short-term funding through the issuance of new debt, if there is a slowdown in issuing new debt or if a demand for the new debt declines significantly, the SIVs may have to liquidate assets at a loss. Also, to the extent that SIVs’ assets represent investments in finance companies, the Fund may have significant exposure to the financial services market and disruptions in that market could result in lower valuations of the Fund’s holdings of SIV securities.
Bank Obligations
The Fund may invest in bank obligations. Bank obligations in which the Fund may invest include certificates of deposit, bankers’ acceptances, and fixed time deposits. Certificates of deposit are negotiable certificates issued against funds deposited in a commercial bank for a definite period of time and earning a specified return. Bankers’ acceptances are negotiable drafts or bills of exchange, normally drawn by an importer or exporter to pay for specific merchandise, which are “accepted” by a bank, meaning, in effect, that the bank unconditionally agrees to pay the face value of the instrument on maturity. Fixed time deposits are bank obligations payable at a stated maturity date and bearing interest at a fixed rate. Fixed time deposits may be withdrawn on demand by the investor, but may be subject to early withdrawal penalties which vary depending upon market conditions and the remaining maturity of the obligation. There are no contractual restrictions on the right to transfer a beneficial interest in a fixed time deposit to a third party, although there is no market for such deposits. The Fund will not invest in fixed time deposits which (1) are not subject to prepayment or (2) provide for withdrawal penalties upon prepayment (other than overnight deposits) if, in the aggregate, more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in such deposits, repurchase agreements maturing in more than seven days and other illiquid investments.
The Fund limits investments in United States bank obligations to obligations of United States banks (including foreign branches) which have more than $1 billion in total assets at the time of investment and are members of the Federal Reserve System or are examined by the Comptroller of the Currency or whose deposits are insured by the FDIC. The Fund also may invest in certificates of deposit of savings and loan associations (federally or state chartered and federally insured) having total assets in excess of $1 billion.
The Fund limits investments in foreign bank obligations to United States dollar- or foreign currency-denominated obligations of foreign banks (including United States branches of foreign banks) which at the time of investment (i) have more than $10 billion, or the equivalent in other currencies, in total assets; (ii) in terms of assets are among the 75 largest foreign banks in the world; (iii) have branches or agencies (limited purpose offices which do not offer all banking services) in the United States; and (iv) in the opinion of a Subadviser, are of an investment quality comparable to obligations of United States banks in which the Fund may invest. Subject to the Fund’s limitation on concentration in the securities of issuers in a particular industry, there is no limitation on the amount of the Fund’s assets which may be invested in obligations of foreign banks which meet the conditions set forth herein.
Obligations of foreign banks involve somewhat different investment risks than those affecting obligations of United States banks, including the possibility that their liquidity could be impaired because of future political and economic developments, that their obligations may be less marketable than comparable obligations of United States banks, that a foreign jurisdiction might impose withholding taxes on interest income payable on those obligations, that foreign deposits may be seized or nationalized, that foreign governmental restrictions such as exchange controls may be adopted which might adversely affect the payment of principal and interest on those obligations and that the selection of those obligations may be more difficult because there may be less publicly available information concerning foreign banks or the accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards, practices and requirements applicable to foreign banks may differ from those applicable to United States banks. Foreign banks are not generally subject to examination by any U.S. Government agency or instrumentality.
8
Brady Bonds
The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s), policies and investment program, may invest in “Brady Bonds.” Brady Bonds are debt securities, generally denominated in U.S. dollars, issued under the framework of the “Brady Plan.” This was an initiative announced by former U.S. Treasury Secretary Nicholas F. Brady in 1989 as a mechanism for debtor nations to restructure their outstanding external commercial bank indebtedness. The Brady Plan framework, as it has developed, contemplates the exchange of external commercial bank debt for newly issued bonds (Brady Bonds). Brady Bonds may also be issued in respect of new money being advanced by existing lenders in connection with the debt restructuring. Brady Bonds generally have maturities of between 15 and 30 years from the date of issuance and have traded at a deep discount from their face value. In addition to Brady Bonds, the Fund may invest in emerging market governmental obligations issued as a result of debt restructuring agreements outside of the scope of the Brady Plan.
Agreements implemented under the Brady Plan have been designed to achieve debt and debt service reduction through specific options negotiated by a debtor nation with its creditors. As a result, the financial packages offered by each country differ. The types of options have included the exchange of outstanding commercial bank debt for bonds issued at 100% of face value of such debt which carry a below-market stated rate of interest (generally known as par bonds), bonds issued at a discount from the face value of such debt (generally known as discount bonds), bonds bearing an interest rate which increases over time and bonds issued in exchange for the advancement of new money by existing lenders. Brady Bonds have typically traded at a deep discount from their face value. Certain sovereign bonds are entitled to “value recovery payments” in certain circumstances, which in effect constitute supplemental interest payments but generally are not collateralized. Certain Brady Bonds have been collateralized as to principal due at maturity (typically 15 to 30 years from the date of issuance) by U.S. Treasury zero coupon bonds with a maturity equal to the final maturity of such Brady Bonds, although the collateral is not available to investors until the final maturity of the Brady Bonds. Collateral purchases are financed by the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank and the debtor nations’ reserves. In addition, interest payments on certain types of Brady Bonds may be collateralized by cash or high-grade securities in amounts that typically represent between 12 and 18 months of interest accruals on these instruments with the balance of the interest accruals being uncollateralized. The Fund may purchase Brady Bonds with no or limited collateralization, and would be relying for payment of interest and (except in the case of principal collateralized Brady Bonds) principal primarily on the willingness and ability of the foreign government to make payment in accordance with the terms of the Brady Bonds. Brady Bonds issued to date are purchased and sold in secondary markets through U.S. securities dealers and other financial institutions and are generally maintained through European transnational securities depositories.
Catastrophe Bonds
The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s), policies and investment program, may invest in “catastrophe bonds.” Catastrophe bonds are fixed-income securities, for which the return of principal and payment of interest is contingent on the non-occurrence of a specific “trigger” catastrophic event, such as a hurricane or an earthquake, or other occurrence that leads to physical or economic loss. They may be issued by government agencies, insurance companies, reinsurers, special purpose corporations or other on-shore or off-shore entities. If a trigger event causes losses exceeding a specific amount in the geographic region and time period specified in a bond, the Fund may lose a portion or its entire principal invested in the bond. If no trigger event occurs, the Fund will recover its principal plus interest. For some catastrophe bonds, the trigger event or losses may be based on company-wide losses, index-portfolio losses, industry indices, or readings of scientific instruments rather than specified actual losses. Often the catastrophe bonds provide for extensions of maturity that are mandatory or optional at the discretion of the issuer, in order to process and audit loss claims in those cases where a trigger event has, or possibly has, occurred. In addition to the specified trigger events, catastrophe bonds may also expose the Fund to certain unanticipated risks, including, but not limited, to issuer (credit) default, adverse regulatory or jurisdictional interpretations, and adverse tax consequences.
Catastrophe bonds may expose the Fund to liquidity risk. See “Illiquid Investments” below for more information with respect to the risks associated with illiquid investments. Lack of a liquid market may impose the risk of higher transaction costs and the possibility that the Fund may be forced to liquidate positions when it would not be advantageous to do so. Catastrophe bonds are typically rated, and the Fund will only invest in catastrophe bonds that meet the credit quality requirements for the Fund.
9
Collateralized Bond Obligations (“CBOs”)
CBOs are structured products ordinarily issued by a trust or other special purpose entity and are backed by a diversified pool of high-yield public or private fixed-income securities. The pool of high yield securities is typically separated into tranches representing different degrees of credit quality. The top tranche of CBOs, which represents the highest credit quality in the pool, has the greatest collateralization and pays the lowest interest rate. Lower CBO tranches represent lower degrees of credit quality and pay higher interest rates to compensate for the attendant risk. The bottom tranche specifically receives the residual interest payments (i.e., money that is left over after the higher tiers have been paid) rather than a fixed interest rate. The return on the bottom tranche of CBOs is especially sensitive to the rate of defaults in the collateral pool. CBOs may be deemed to be “illiquid” and subject to the Fund’s overall limitations on investments in illiquid investments.
Convertible Securities
The Fund may invest in convertible securities of foreign or domestic issuers. A convertible security is a security (a bond or preferred stock) which may be converted at a stated price within a specified period of time into a certain quantity of the common stock of the same or a different issuer. Convertible securities are senior to common stocks in a corporation’s capital structure but are usually subordinated to similar nonconvertible securities. Convertible securities provide, through their conversion feature, an opportunity to participate in capital appreciation resulting from a market price advance in a convertible security’s underlying common stock. The price of a convertible security is influenced by the market value of the underlying common stock and tends to increase as the market value of the underlying stock rises, whereas it tends to decrease as the market value of the underlying stock declines.
The Fund may be required to permit the issuer of a convertible security to redeem the security, convert it into the underlying common stock, or sell it to a third party. Thus, the Fund may not be able to control whether the issuer of a convertible security chooses to convert that security. If the issuer chooses to do so, this action could have an adverse effect on the Fund’s ability to achieve its investment objective(s).
Corporate Actions
From time to time, the issuer of a security held in the Fund’s portfolio may initiate a corporate action relating to that security. Corporate actions may be mandatory (e.g., calls, cash dividends, exchanges, mergers, spin-offs, stock dividends and stock splits) or voluntary (e.g., rights offerings, exchange offerings, and tender offers). Corporate actions may cause a decline in market value or credit quality of the issuer’s stocks or bonds due to factors including an unfavorable market response or a resulting increase in the issuer’s debt. Added debt may significantly reduce the credit quality and market value of an issuer’s bonds.
In the event of a mandatory corporate action, the Fund will not actively add to its position and generally will dispose of the securities as soon as reasonably practicable. These securities may be brand new and as a result might fail certain screens or even investment strategy restrictions (such as not being in the right index, etc.). In circumstances in which the Fund elects to participate in a voluntarily corporate action, such actions may enhance the value of the Fund’s investment portfolio. In cases where the Adviser or Subadviser receives sufficient advance notice of a voluntary corporate action, it will exercise its discretion, in good faith, to determine whether the Fund will participate in that corporate action. If it does not receive sufficient advance notice of a voluntary corporate action, the Fund may not be able to timely elect to participate in that corporate action. Participation or lack of participation in a voluntary corporate action may result in a negative impact on the value of the Fund’s investment portfolio.
Cyber Security Risk
With the increased use of technologies such as the Internet to conduct business, the Fund is susceptible to operational, information security and related risks. In general, cyber incidents can result from deliberate attacks or unintentional events. Cyber attacks include, but are not limited to, gaining unauthorized access to digital systems (e.g., through “hacking” or malicious software coding) for purposes of misappropriating assets or sensitive information, corrupting data, or causing operational disruption. Cyber attacks may also be carried out in a manner that does not require gaining unauthorized access, such as causing denial-of-service attacks on websites (i.e., efforts to make network services unavailable to intended users). Cyber incidents affecting VALIC or a Subadviser and other service providers (including, but not limited to, fund accountants,
10
custodians, transfer agents and financial intermediaries) have the ability to cause disruptions and impact business operations, potentially resulting in financial losses, interference with the Fund’s ability to calculate its net asset value, impediments to trading, the inability of Fund investors to transact business, violations of applicable privacy and other laws, regulatory fines, penalties, reputational damage, reimbursement or other compensation costs, or additional compliance costs. Similar adverse consequences could result from cyber incidents affecting issuers of securities in which the Fund invests, counterparties with which the Fund engages in transactions, governmental and other regulatory authorities, exchange and other financial market operators, banks, brokers, dealers, insurance companies and other financial institutions (including financial intermediaries and service providers for fund shareholders) and other parties. In addition, substantial costs may be incurred in order to prevent any cyber incidents in the future. Although service providers typically have business continuity plans in the event of, and risk management systems to prevent, such cyber incidents, there are inherent limitations in such plans and systems, including the possibility that certain risks have not been identified. Furthermore, the Fund cannot control the cyber security plans and systems put in place by its service providers or any other third parties whose operations may affect the Fund or its shareholders. The Fund and its investors could be negatively impacted as a result.
Depositary Receipts
The Fund may invest in depositary receipts. Depositary receipts include American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”), European Depositary Receipts (“EDRs”), Global Depositary Receipts (“GDRs”) or other similar securities convertible into securities of foreign issuers. ADRs are certificates issued by a United States bank or trust company and represent the right to receive securities of a foreign issuer deposited in a domestic bank or foreign branch of a United States bank and traded on a United States exchange or in an over-the-counter (“OTC”) market. GDRs, EDRs and other types of depositary receipts are typically issued by foreign depositaries, although they may also be issued by U.S. depositaries, and evidence ownership interests in a security or pool of securities issued by either a foreign or a U.S. corporation. Depositary receipts may not necessarily be denominated in the same currency as the securities into which they may be converted.
Investment in ADRs has certain advantages over direct investment in the underlying foreign securities since: (i) ADRs are U.S. dollar-denominated investments that are easily transferable and for which market quotations are readily available, and (ii) issuers whose securities are represented by ADRs are generally subject to auditing, accounting and financial reporting standards similar to those applied to domestic issuers. This limits the Fund’s exposure to foreign exchange risk.
Depositary receipts may be sponsored or unsponsored. A sponsored depositary receipt is issued by a depositary that has an exclusive relationship with the issuer of the underlying security. Generally, depositary receipts in registered form are designed for use in the U.S. securities market and depositary receipts in bearer form are designed for use in securities markets outside the United States. Holders of unsponsored depositary receipts generally bear all the costs associated with establishing the unsponsored depositary receipt. The depositary of unsponsored depositary receipts is under no obligation to distribute shareholder communications received from the underlying issuer or to pass through to the holders of the unsponsored depositary receipt voting rights with respect to the deposited securities or pool of securities. For purposes of the Fund’s investment policies, its investments in depositary receipts will be deemed to be investments in the underlying securities.
Derivatives
A derivative is any financial instrument whose value is derived from the value of other assets (such as stocks), reference rates or indices. Rule 18f-4 under the 1940 Act (“Rule 18f-4” or the “Derivatives Rule”) regulates the ability of the Fund to enter into derivative transactions and other leveraged transactions. Derivative transactions are defined by Rule 18f-4 to include (i) any swap, security-based swap, futures contract, forward contract, option, any combination of the foregoing, or any similar instrument, under which the Fund is or may be required to make any payment or delivery of cash or other assets during the life of the instrument or at maturity or early termination, whether as margin or settlement payment or otherwise; (ii) any short sale borrowing; (iii) any reverse repurchase agreement or similar financing transaction, if the Fund elects to treat them as derivatives transactions; and (iv) when-issued or forward-settling securities and non-standard settlement cycle securities, unless such transactions meet certain requirements.
11
Unless a fund qualifies as a Limited Derivatives User (defined below), Rule 18f-4 requires the fund to establish a derivatives risk management program, appoint a derivatives risk manager, and carry out enhanced reporting to the Board, the SEC and the public regarding the fund’s derivatives activities. In addition, the Derivatives Rule establishes limits on the derivatives transactions that a fund may enter into based on the value-at-risk (“VaR”) of the fund inclusive of derivatives. A fund will generally satisfy the limits under the Derivatives Rule if the VaR of its portfolio (inclusive of derivatives transactions) does not exceed 200% of the VaR of its “designated reference portfolio.” The “designated reference portfolio” is a representative unleveraged index or a fund’s own portfolio absent derivatives holdings, as determined by the fund’s derivatives risk manager. This limits test is referred to as the “Relative VaR Test.” If a fund determines that the Relative VaR Test is not appropriate for it in light of its strategy, subject to specified conditions, the fund may instead comply with the Absolute VaR Test. A fund will satisfy the Absolute VaR Test if the VaR of its portfolio does not exceed 20% of the value of the fund’s net assets.
A fund is not required to comply with the above requirements if it adopts and implements written policies and procedures reasonably designed to manage the fund’s derivatives risk and its derivatives exposure does not exceed 10 percent of its net assets (as calculated in accordance with Rule 18f-4) (a “Limited Derivatives User”). The Fund is classified as a Limited Derivatives User under Rule 18f-4.
Equity Securities
The Fund may invest in equity securities. Equity securities include common stock, preferred stock, securities convertible into common or preferred stock, warrants or rights to acquire common stock, including options, and depositary receipts. Equity securities are subject to financial and market risks and can be expected to fluctuate in value.
Preferred Securities. There are two basic types of preferred securities, traditional and hybrid-preferred securities. Traditional preferred securities consist of preferred stock issued by an entity taxable as a corporation. Preferred stocks, which may offer fixed or floating rate dividends, are perpetual instruments and considered equity securities. Preferred securities are subordinated to senior debt instruments in a company’s capital structure, in terms of priority to corporate income and claim to corporate assets, and therefore will be subject to greater credit risk than debt instruments. Alternatively, hybrid-preferred securities may be issued by corporations, generally in the form of interest-bearing notes with preferred securities characteristics, or by an affiliated trust or partnership of the corporation, generally in the form of preferred interests in subordinated debentures or similarly structured securities. The hybrid-preferred securities market consists of both fixed and adjustable coupon rate securities that are either perpetual in nature or have stated maturity dates. Hybrid-preferred securities are considered debt securities. Due to their similar attributes, the Adviser also considers senior debt perpetual issues, certain securities with convertible features as well as exchange-listed senior debt issues that trade with attributes of exchange-listed perpetual and hybrid-preferred securities to be part of the broader preferred securities market.
Eurodollar Obligations
The Fund may, in accordance with its investment objective, policies, and investment program, invest in Eurodollar obligations, including Eurodollar bonds and Eurodollar certificates of deposit. A Eurodollar obligation is a security denominated in U.S. dollars and originated principally in Europe, giving rise to the term Eurodollar.
Such securities are not registered with the SEC and generally may only be sold to U.S. investors after the initial offering and cooling-off periods. The market for Eurodollar securities is dominated by foreign-based investors and the primary trading market for these securities is London.
Eurodollar obligations, including Eurodollar bonds and Eurodollar certificates of deposit, are principally obligations of foreign branches of U.S. banks. These instruments represent the loan of funds actually on deposit in the U.S. VC I believes that the U.S. bank would be liable in the event that its foreign branch failed to pay on its U.S. dollar denominated obligations. Nevertheless, the assets supporting the liability could be expropriated or otherwise restricted if located outside the U.S. Exchange controls, taxes, or political and economic developments also could affect liquidity or repayment. Due to possibly conflicting laws or regulations, the foreign branch of the U.S. bank could maintain and prevail in the view that the liability is solely its own, thus exposing the Fund to a possible loss. Such U.S. dollar denominated obligations of foreign branches of FDIC member U.S. banks are not covered by the FDIC’s standard insurance limit if they are payable only at an office of such a bank located outside the U.S., Puerto Rico, Guam, American Samoa, and the Virgin Islands.
12
Moreover, there may be less publicly available information about foreign issuers whose securities are not registered with the SEC and such foreign issuers may not be subject to the accounting, auditing, and financial reporting standards applicable to issuers registered domestically. In addition, foreign issuers, stock exchanges, and brokers generally are subject to less government regulation. There are, however, no risks of currency fluctuation since the obligations are U.S. dollar denominated.
The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s), policies and investment program, may purchase and sell Eurodollar futures contracts, which enable purchasers to obtain a fixed rate for the lending of funds and sellers to obtain a fixed rate for borrowings. The Fund might use Eurodollar futures contracts and options thereon to hedge against changes in a foreign prime lending interest rate to which many interest swaps and fixed-income securities are linked.
Fixed-Income Securities
The Fund may invest in fixed income securities, also referred to as debt securities. Fixed-income securities may be considered high-quality if they are rated at least Aa by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. (“Moody’s”) or its equivalent by any other Nationally Recognized Statistical Ratings Organization or, if unrated, are determined to be of equivalent investment quality. High-quality fixed-income securities are considered to have a very strong capacity to pay principal and interest. Fixed-income securities are considered investment grade if they are rated, for example, at least Baa3 by Moody’s or BBB- by S&P Global Ratings (“S&P”) or Fitch Ratings, or, if not rated, are determined to be of equivalent investment quality. Investment grade fixed-income securities are regarded as having an adequate capacity to pay principal and interest. Lower-medium and lower-quality securities that do not meet the credit quality standards of an investment grade security (commonly known as “junk bonds”) are regarded on balance as high risk and predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer’s continuing ability to meet principal and interest payments. A Subadviser will not necessarily dispose of an investment grade security that has been downgraded to below investment grade. See Appendix A regarding “Description of Credit Rating Symbols and Definitions” for a description of each rating category and a more complete description of lower-medium and lower-quality fixed-income securities and their risks.
The maturity of fixed-income securities may be considered long- (ten plus years), intermediate- (one to ten years), or short-term (thirteen months or less). In general, the principal values of longer-term securities fluctuate more widely in response to changes in interest rates than those of shorter-term securities, providing greater opportunity for capital gain or risk of capital loss. A decline in interest rates usually produces an increase in the value of fixed-income securities, while an increase in interest rates generally reduces their value.
Inflation-Indexed Bonds
The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s), policies and investment programs, may invest in inflation-indexed bonds. Inflation-indexed bonds are fixed income securities whose principal values are periodically adjusted according to the rate of inflation. Interest payments are made to bondholders semi-annually and are made up of two components: a fixed “real coupon” or spread, and a variable coupon linked to an inflation index. Accordingly, payments will increase or decrease each period as a result of changes in the inflation index. In a period of deflation payments may decrease to zero, but in any event will not be less than zero.
Inflation-indexed bonds generally are issued at an interest rate lower than typical bonds, but are expected to retain their principal value over time. The interest rate on these bonds is fixed at issuance, but over the life of the bond this interest may be paid on an increasing principal value, which has been adjusted for inflation.
Inflation-indexed securities issued by the U.S. Treasury have maturities of five, ten or thirty years, although it is anticipated that securities with other maturities will be issued in the future. The securities pay interest on a semi-annual basis, equal to a fixed percentage of the inflation-adjusted principal amount. For example, if the Fund purchased an inflation-indexed bond with a par value of $1,000 and a 3% real rate of return coupon (payable 1.5% semi-annually), and inflation over the first six months was 1%, the mid-year par value of the bond would be $1,010 and the first semi-annual interest payment would be $15.15 ($1,010 times 1.5%). If inflation during the second half of the year reached 3%, the end-of-year par value of the bond would be $1,030 and the second semi-annual interest payment would be $15.45 ($1,030 times 1.5%).
13
If the periodic adjustment rate measuring inflation falls, the principal value of inflation-indexed bonds will be adjusted downward, and consequently the interest payable on these securities (calculated with respect to a smaller principal amount) will be reduced. Repayment of the original bond principal upon maturity (as adjusted for inflation) is guaranteed in the case of U.S. Treasury inflation-indexed bonds, even during a period of deflation. However, the current market value of the bonds is not guaranteed, and will fluctuate. The Fund may also invest in other inflation-related bonds which may or may not provide a similar guarantee. If a guarantee of principal is not provided, the adjusted principal value of the bond repaid at maturity may be less than the original principal.
The value of inflation-indexed bonds is expected to change in response to changes in real interest rates. Real interest rates in turn are tied to the relationship between nominal interest rates and the rate of inflation. Therefore, if inflation were to rise at a faster rate than nominal interest rates, real interest rates might decline, leading to an increase in value of inflation-indexed bonds. In contrast, if nominal interest rates increased at a faster rate than inflation, then real interest rates might rise, leading to a decrease in value of inflation-indexed bonds.
While these securities are expected to be protected from long-term inflationary trends, short-term increases in inflation may lead to a decline in value. If interest rates rise due to reasons other than inflation (for example, due to changes in currency exchange rates), then investors in these securities may not be protected to the extent that the increase is not reflected in the bond’s inflation measure.
The periodic adjustment of U.S. inflation-indexed bonds is tied to the Consumer Price Index for Urban Consumers (“CPI-U”), which is calculated monthly by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The CPI-U is a measurement of changes in the cost of living, made up of components such as housing, food, transportation and energy. Inflation-indexed bonds issued by a foreign government are generally adjusted to reflect a comparable inflation index, calculated by that government. There can be no assurance that the CPI-U or any foreign inflation index will accurately measure the real rate of inflation in the prices of goods and services. Moreover, there can be no assurance that the rate of inflation in a foreign country will be correlated to the rate of inflation in the United States.
Any increase in the principal amount of an inflation-indexed bond will be considered taxable ordinary income, even though investors do not receive their principal until maturity.
Lower Rated Fixed-Income Securities (“Junk Bonds”)
The Fund may invest in below investment grade fixed-income securities. Issuers of lower rated securities (or, if unrated, securities that are determined to be of equivalent investment quality) (“high yield” securities, commonly known as “junk bonds”) may be highly leveraged and may not have available to them more traditional methods of financing. Therefore, the risks associated with acquiring the securities of such issuers generally are greater than is the case with higher rated securities. For example, during an economic downturn or a sustained period of rising interest rates, issuers of high yield securities may be more likely to experience financial stress, especially if such issuers are highly leveraged. During such periods, such issuers may not have sufficient revenues to meet their interest payment obligations. The issuer’s ability to service its debt obligations also may be adversely affected by specific issuer developments, or the issuer’s inability to meet specific projected business forecasts, or the unavailability of additional financing. The risk of loss due to default by the issuer is significantly greater for the holders of lower-rated securities because such securities may be unsecured and may be subordinated to other creditors of the issuer.
Lower-rated, fixed income securities frequently have call or redemption features which would permit an issuer to repurchase the security from the Fund. If a call were exercised by the issuer during a period of declining interest rates, the Fund likely would have to replace such called security with a lower yielding security, thus decreasing the net investment income to the Fund and dividends to shareholders.
The Fund may have difficulty disposing of certain lower-rated, fixed income securities because there may be a thin trading market for such securities. The secondary trading market for high-yield securities is generally not as liquid as the secondary market for higher-rated securities. Reduced secondary market liquidity may have an adverse impact on market price and the Fund’s ability to dispose of particular issues when necessary to meet the Fund’s liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as deterioration in the creditworthiness of the issuer.
14
Adverse publicity and investor perceptions, which may not be based on fundamental analysis, also may decrease the value and liquidity of lower-rated, fixed income securities, particularly in a thinly traded market. Factors adversely affecting the market value of lower-rated, fixed income securities are likely to adversely affect the Fund’s net asset value. In addition, the Fund may incur additional expenses to the extent it is required to seek recovery upon the default of a portfolio holding or to participate in the restructuring of the obligation.
There are risks involved in applying credit ratings as a method for evaluating lower-rated, fixed income securities. For example, credit ratings evaluate the safety of principal and interest payments, not the market risks involved in lower-rated, fixed income securities. Since credit rating agencies may fail to change the credit ratings in a timely manner to reflect subsequent events, the Adviser or a Subadviser will monitor the issuers of lower-rated, fixed income securities in the Fund to determine if the issuers will have sufficient cash flow and profits to meet required principal and interest payments, and to assure the debt securities’ liquidity stays within the parameters of the Fund’s investment policies. A Subadviser will not necessarily dispose of a portfolio security when its ratings have been changed.
Investments in already defaulted securities pose an additional risk of loss, should nonpayment of principal and interest continue, in respect of such securities. Even if such securities are held to maturity, recovery of the Fund’s initial investment and any anticipated income or appreciation is uncertain. In addition, the Fund may incur additional expenses to the extent that it is required to seek recovery relating to the default in the payment of principal or interest on such securities or otherwise protect its interests. The Fund may be required to liquidate other portfolio securities to satisfy annual distribution obligations of the Fund in respect of accrued interest income on securities which are subsequently written off, even though the Fund has not received any cash payments of such interest.
Foreign Currency
The Fund may buy foreign currencies when it believes the value of the currency will increase. Changes in foreign exchange rates will affect the U.S. dollar value of securities that are denominated in non-U.S. currencies. In addition, the Fund’s income from foreign currency-denominated securities is typically denominated in foreign currency. When the Fund receives income denominated in foreign currencies, it computes the U.S. dollar value of that income earned by the Fund for purposes of determining Fund distributions at the foreign exchange rate in effect on that date. If the value of the foreign currency declines in relation to the U.S. dollar between the time that the Fund earns the income and the time that the income is converted into U.S. dollars, the Fund may be required to liquidate other assets in order to make up the shortfall. The Fund may also buy foreign currencies to pay for foreign securities bought for the Fund or for hedging purposes.
Foreign Currency Exchange Transactions and Forward Contracts
The Fund may enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts for various purposes, including to facilitate settlement of foreign currency denominated portfolio transactions, to attempt to protect securities and related receivables and payables against changes in future foreign exchange rates, to hedge exposure to benchmark currency allocations, to manage and/or gain exposure to certain foreign currencies or to enhance return. The Fund may conduct foreign currency transactions on a spot basis (i.e., cash) or forward basis (i.e., by entering into forward currency exchange contracts, currency options and futures transactions to purchase or sell foreign currencies). Although foreign exchange dealers generally do not charge a fee for such transactions, they do realize a profit based on the difference between the prices at which they are buying and selling various currencies.
Forward contracts are customized transactions that require a specific amount of a currency to be delivered at a specific exchange rate on a specific date or range of dates in the future. Forward contracts are generally traded in an interbank market directly between currency traders (usually larger commercial banks) and their customers. The parties to a forward contract may agree to offset or terminate the contract before its maturity, or may hold the contract to maturity and complete the contemplated currency exchange.
The following summarizes the principal currency management strategies involving forward contracts. The Fund may also use swap agreements, indexed securities, and options and futures contracts relating to foreign currencies for the same purposes.
15
| |
1. |
Settlement Hedges or Transaction Hedges. When a Subadviser wishes to lock in the U.S. dollar price of a foreign currency denominated security when the Fund is purchasing or selling the security, the Fund may enter into a forward contract. This type of currency transaction, often called a “settlement hedge” or “transaction hedge,” protects the Fund against an adverse change in foreign currency values between the date a security is purchased or sold and the date on which payment is made or received (i.e., “settled”). Forward contracts to purchase or sell a foreign currency may also be used by the Fund in anticipation of future purchases or sales of securities denominated in foreign currency, even if the specific investments have not yet been selected by a Subadviser. This strategy is often referred to as “anticipatory hedging.” |
| |
2. |
Position Hedges. When a Subadviser believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer substantial decline against the U.S. dollar, the Fund may enter into a forward contract to sell foreign currency for a fixed U.S. dollar amount approximating the value of some or all of its portfolio securities either denominated in, or whose value is tied to, such foreign currency. This use of a forward contract is sometimes referred to as a “position hedge.” For example, if the Fund owned securities denominated in Euros, it could enter into a forward contract to sell Euros in return for U.S. dollars to hedge against possible declines in the Euro’s value. This hedge would tend to offset both positive and negative currency fluctuations, but would not tend to offset changes in security values caused by other factors. |
The Fund could also hedge the position by entering into a forward contract to sell another currency expected to perform similarly to the currency in which the Fund’s existing investments are denominated. This type of hedge, often called a “proxy hedge,” could offer advantages in terms of cost, yield or efficiency, but may not hedge currency exposure as effectively as a simple position hedge against U.S. dollars. This type of hedge may result in losses if the currency used to hedge does not perform similarly to the currency in which the hedged securities are denominated.
Risks to the Fund of entering into forward contracts include counterparty risk and market risk. Counterparty risk arises upon entering into these contracts from the potential inability of counterparties to meet the terms of their contracts. If the counterparty defaults, the Fund’s loss will generally consist of the net amount of contractual payments that the Fund has not yet received though the Fund’s maximum risk due to counterparty credit risk could extend to the notional amount of the contract. Market risk is the risk that the value of the forward contract will depreciate due to unfavorable changes in the exchange rates. Currency transactions are also subject to risks different from those of other portfolio transactions. Because currency control is of great importance to the issuing governments and influences economic planning and policy, purchases and sales of currency and related instruments can be adversely affected by government exchange controls, limitations or restrictions on repatriation of currency, and manipulations or exchange restrictions imposed by governments.
The precise matching of forward contracts in the amounts and values of securities involved generally would not be possible because the future values of such foreign currencies will change as a consequence of market movements in the values of those securities between the date the forward contract is entered into and the date it matures. Predicting short-term currency market movements is extremely difficult, and the successful execution of a short-term hedging strategy is highly uncertain. Normally, consideration of the prospect for currency parities will be incorporated into the long-term investment decisions made with respect to overall diversification strategies. However, the Adviser or Subadviser each believe that it is important to have flexibility to enter into such forward contracts when they determine that the Fund’s best interests may be served.
At the maturity of the forward contract, the Fund may either sell the portfolio security and make delivery of the foreign currency, or it may retain the security and terminate the obligation to deliver the foreign currency by purchasing an “offsetting” forward contract with the same currency trader obligating the Fund to purchase, on the same maturity date, the same amount of the foreign currency.
It is impossible to forecast with absolute precision the market value of portfolio securities at the expiration of the forward contract. Accordingly, it may be necessary for the Fund to purchase additional foreign currency on the spot market (and bear the expense of such purchase) if the market value of the security is less than the amount of foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver and if a decision is made to sell the security and make delivery of the foreign currency the Fund is obligated to deliver.
16
Shifting Currency Exposure: The Fund may also enter into forward contracts to shift its investment exposure from one currency into another. This may include shifting exposure from U.S. dollars to foreign currency or from one foreign currency to another foreign currency. This strategy tends to limit exposure to the currency sold, and increase exposure to the currency that is purchased; much as if the Fund had sold a security denominated in one currency and purchased an equivalent security denominated in another currency. For example, if a Subadviser believed that the U.S. dollar may suffer a substantial decline against the Euro, the Subadviser could enter into a forward contract to purchase Euros for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars. This transaction would protect against losses resulting from a decline in the value of the U.S. dollar, but would cause the Fund to assume the risk of fluctuations in the value of the Euro.
Successful use of currency management strategies will depend on the Fund management team’s skill in analyzing currency values. Currency management strategies may substantially change the Fund’s investment exposure to changes in currency rates and could result in losses to the Fund if currencies do not perform as a Subadviser anticipates. For example, if a currency’s value rose at a time when a Subadviser hedged the Fund by selling the currency in exchange for U.S. dollars, the Fund would not participate in the currency’s appreciation. Similarly, if a Subadviser increases the Fund’s exposure to a currency and that currency’s value declines, the Fund will sustain a loss. There is no assurance that the use of foreign currency management strategies will be advantageous to the Fund or that a Subadviser will hedge at appropriate times.
Foreign Securities
The Fund may invest in foreign securities. A foreign security is a security issued by an entity domiciled or incorporated outside of the United States. A foreign security includes equity securities of foreign issuers, corporate debt securities of foreign issuers (including preferred or preference stock), certain foreign bank obligations (see “Bank Obligations”) and U.S. dollar or foreign currency-denominated obligations of foreign governments or their subdivisions, agencies and instrumentalities, international agencies and supranational entities. In addition, the Fund may invest in non-U.S. dollar-denominated foreign securities, in accordance with its specific investment objective(s), investment programs, policies, and restrictions. Investing in foreign securities may involve advantages and disadvantages not present in domestic investments. There may be less publicly available information about securities not registered domestically, or their issuers, than is available about domestic issuers or their domestically registered securities. Stock markets outside the U.S. may not be as developed as domestic markets, and there may also be less government supervision of foreign exchanges and brokers. Foreign securities may be less liquid or more volatile than U.S. securities. Trade settlements may be slower and could possibly be subject to failure. In addition, brokerage commissions and custodial costs with respect to foreign securities may be higher than those for domestic investments. Accounting, auditing, financial reporting and disclosure standards for foreign issuers may be different than those applicable to domestic issuers. Non-U.S. dollar-denominated foreign securities may be affected favorably or unfavorably by changes in currency exchange rates and exchange control regulations (including currency blockage) and the Fund may incur costs in connection with conversions between various currencies. Foreign securities may also involve risks due to changes in the political or economic conditions of such foreign countries, the possibility of expropriation of assets or nationalization, and possible difficulty in obtaining and enforcing judgments against foreign entities.
See “Recent Market Events” below for more information with respect to the risks associated with foreign securities.
Emerging Markets
The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s), policies and investment programs, may make investments in companies located in emerging market countries. Investments in companies domiciled in emerging market countries may be subject to additional risks. Specifically, volatile social, political and economic conditions may expose investments in emerging or developing markets to economic structures that are generally less diverse and mature. Emerging market countries may have less stable political systems than those of more developed countries. As a result, it is possible that recent favorable economic developments in certain emerging market countries may be suddenly slowed or reversed by unanticipated political or social events in such countries. Moreover, the economies of individual emerging market countries may differ favorably or unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects as the rate of growth in gross domestic product, the rate of inflation, capital reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency and balance of payments position.
17
Another risk is that the small current size of the markets for such securities and the currently low or nonexistent volume of trading can result in a lack of liquidity and in greater price volatility. In addition, there may be an absence of a capital market structure or market-oriented economy in certain emerging market countries. If the Fund’s securities will generally be denominated in foreign currencies, the value of such securities to the Fund will be affected by changes in currency exchange rates and in exchange control regulations. A change in the value of a foreign currency against the U.S. dollar will result in a corresponding change in the U.S. dollar value of the Fund’s securities. In addition, some emerging market countries may have fixed or managed currencies that are not free-floating against the U.S. dollar. Further, certain emerging market currencies may not be internationally traded. Certain of these currencies have experienced a steady devaluation relative to the U.S. dollar. Many emerging market countries have experienced substantial, and in some periods extremely high, rates of inflation for many years. Inflation and rapid fluctuations in inflation rates have had, and may continue to have, negative effects on the economies and securities markets of certain emerging market countries.
A further risk is that the existence of national policies may restrict the Fund’s investment opportunities and may include restrictions on investment in issuers or industries deemed sensitive to national interests. Also, some emerging market countries may not have developed structures governing private or foreign investment and may not allow for judicial redress for injury to private property.
Chinese Securities
The Fund may invest in securities of companies domiciled in the People’s Republic of China (“China” or the “PRC”). Investing in these securities involves special risks, including, but not limited to, an authoritarian government, less developed or less efficient trading markets, nationalization of assets, currency fluctuations or blockage, and restrictions on the repatriation of invested capital. In addition, there is no guarantee that the current rapid growth rate of the Chinese economy will continue, and the trend toward economic liberalization and disparities in wealth may result in social disorder. China is considered to be an emerging market and therefore carries high levels of risk associated with emerging markets. China has experienced security concerns, such as terrorism and strained international relations, as well as major health crises. These health crises include, but are not limited to, the rapid and pandemic spread of novel viruses commonly known as SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 (Coronavirus). Such health crises could exacerbate political, social, and economic risks previously mentioned. These and other factors could have a negative impact on the Fund’s performance and increase the volatility of an investment in the Fund.
Stock Connect. The Fund may invest in eligible exchange-traded funds and local equity Chinese securities (“China A-Shares”) of certain Chinese-domiciled companies (together, “Stock Connect Securities”) listed and traded on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (“SSE”) through the Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect program and on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (“SZSE”) through the Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect program (each, a “Stock Connect” and collectively, “Stock Connects”) or on such other stock exchanges in China which participate in Stock Connect from time to time. Each Stock Connect is a securities trading and clearing links program developed by Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (“HKEX”), the SSE or SZSE, as applicable, and the China Securities Depository and Clearing Corporation Limited that, among other things, permits foreign investment in the PRC via brokers in Hong Kong.
The Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect program launched in November 2014 and the Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect program launched in December 2016, and there is no certainty as to how the regulations governing them will be applied or interpreted. Significant risks exist with respect to investing in Stock Connect Securities through a Stock Connect. Stock Connect Securities may only be bought from, or sold to, the Fund when both the PRC and Hong Kong markets are open for trading and when banks in both markets are open on the corresponding settlement days. Accordingly, if one or both markets are closed on a U.S. trading day, the Fund may not be able to dispose of its shares in a timely manner and this could adversely affect the Fund’s performance. The China A-Shares market has a higher propensity for trading suspensions than many other global equity markets. Trading suspensions in certain stocks could lead to greater market execution risk and costs for the Fund. In addition, same day trading is not permitted on the China A-Shares market, which may inhibit the Fund’s ability to enter into or exit trades on a timely basis. PRC regulations require the pre-delivery of cash or securities to a broker before the market opens on the day of selling. If the cash or securities are not in the broker’s possession before the market opens on that day, the sell order will be rejected, which may limit the Fund’s ability to dispose of its China A-Shares purchased through a Stock Connect in a timely manner.
18
Although no individual investment quotas or licensing requirements apply to investors in Stock Connects, trading through a Stock Connect’s northbound trading link is subject to daily investment quota limitations, which may change. Once these quota limitations are reached, buy orders for Stock Connect Securities through a Stock Connect will be rejected, which could adversely affect the Fund’s ability to pursue its investment strategy. Stock Connect Securities purchased through a Stock Connect may only be sold through a Stock Connect and are not otherwise transferrable. Although Stock Connect Securities must be designated as eligible to be traded on a Stock Connect, such shares may lose their eligibility at any time, in which case they may be sold but cannot be purchased through a Stock Connect. Moreover, since all trades of eligible Stock Connect Securities through a Stock Connect must be settled in Renminbi (“RMB”), the Fund must have timely access to a reliable supply of offshore RMB, which cannot be guaranteed. Notably, different fees, costs and taxes are imposed on foreign investors acquiring Stock Connect Securities obtained through a Stock Connect, and these fees, costs and taxes may be higher than comparable fees, costs and taxes imposed on owners of other securities providing similar investment exposure. There is also no assurance that RMB will not be subject to devaluation. Any devaluation of RMB could adversely affect the Fund’s investments. If the Fund holds a class of shares denominated in a local currency other than RMB, the Fund will be exposed to currency exchange risk if the Fund converts the local currency into RMB for investments in China A-Shares. The Fund may also incur conversion costs.
The Fund’s Stock Connect Securities are held in an omnibus account and registered in nominee name, with Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company Limited (“HKSCC”) (a clearing house operated by HKEX) serving as nominee for the Fund. The exact nature and rights of the Fund as the beneficial owner of shares through HKSCC as nominee is not well defined under PRC law, and the exact nature and enforcement methods of those rights under PRC law are also unclear. As a result, the title to these shares, or the rights associated with them (i.e., participation in corporate actions, shareholder meetings, etc.) cannot be assured.
Russian Securities
In response to political and military actions, including state-sponsored cyberattacks against foreign companies and foreign governments undertaken by Russia, the United States, the European Union and the regulatory bodies of certain other countries have instituted numerous sanctions against certain Russian individuals and Russian entities. These sanctions, and other intergovernmental actions that may be undertaken against Russia in the future, may result in the devaluation of Russian currency, a downgrade in the country’s credit rating, and a decline in the value and liquidity of Russian stocks. These sanctions could result in the immediate freeze of Russian securities, including securities in the form of ADRs, impairing the ability of the Fund to buy, sell, receive or deliver those securities. Retaliatory action by the Russian government could involve the seizure of U.S. and/or European residents’ assets and any such actions are likely to impair the value and liquidity of such assets. Any or all of these potential results could push Russia’s economy into a recession. These sanctions, and the continued disruption of the Russian economy, could have a negative effect on the performance of funds that have significant exposure to Russia, including the Fund.
Money Market Securities of Foreign Issuers
The Fund may also, in accordance with its specific investment objective and investment program, policies and restrictions, purchase U.S. dollar-denominated money market securities of foreign issuers. Such money market securities may be registered domestically and traded on domestic exchanges or in the OTC market (e.g., Yankee securities) or may be (i) registered abroad and traded exclusively in foreign markets or (ii) registered domestically and issued in foreign markets (e.g., Eurodollar securities).
Foreign money market instruments utilized by the Fund will be limited to: (i) obligations of, or guaranteed by, a foreign government, its agencies or instrumentalities; (ii) certificates of deposit, bankers’ acceptances, short-term notes, negotiable time deposits and other obligations of the ten largest banks in each foreign country, measured in terms of net assets; and (iii) other short-term unsecured corporate obligations (usually 1 to 270 day commercial paper) of foreign companies. For temporary purposes or in light of adverse foreign political or economic conditions, the Fund may invest in short-term high quality foreign money market securities without limitation.
19
Hybrid Instruments
The Fund may invest in hybrid instruments (such as notes, bonds and debentures), up to 10% of its total assets. Hybrid instruments, which include indexed or structured securities, combine the elements of derivatives, including futures contracts or options with those of debt, preferred equity or a depository instrument. Generally, a hybrid instrument will be a debt security, preferred stock, depository share, trust certificate, certificate of deposit or other evidence of indebtedness on which a portion of or all interest payments, and/or the principal or stated amount payable at maturity, redemption or retirement, is determined by reference to prices, changes in prices, or differences between prices, of securities, currencies, intangibles, goods, articles or commodities (collectively “Underlying Assets”) or by another objective index, economic factor or other measure, such as interest rates, currency exchange rates, commodity indices, and securities indices (collectively “Benchmarks”). Thus, hybrid instruments may take a variety of forms, including, but not limited to, debt instruments with interest or principal payments or redemption terms determined by reference to the value of a currency or commodity or securities index at a future point in time, preferred stock with dividend rates determined by reference to the value of a currency, or convertible securities with the conversion terms related to a particular commodity.
Hybrid instruments may be an efficient means of creating exposure to a particular market, or segment of a market, with the objective of enhancing total return. For example, the Fund may wish to take advantage of expected declines in interest rates in several European countries, but avoid the transaction costs associated with buying and currency-hedging the foreign bond positions. One solution would be to purchase a U.S. dollar-denominated hybrid instrument whose redemption price is linked to the average three year interest rate in a designated group of countries. The redemption price formula would provide for payoffs of greater than par if the average interest rate was lower than a specified level and payoffs of less than par if rates were above the specified level. Furthermore, the Fund could limit the downside risk of the security by establishing a minimum redemption price so that the principal paid at maturity could not be below a predetermined minimum level if interest rates were to rise significantly. The purpose of this arrangement, known as a structured security with an embedded put option, would be to give the Fund the desired European bond exposure while avoiding currency risk, limiting downside market risk, and lowering transactions costs. Of course, there is no guarantee that the strategy will be successful and the Fund could lose money if, for example, interest rates do not move as anticipated or credit problems develop with the issuer of the hybrid instrument.
The risks of investing in hybrid instruments reflect a combination of the risks of investing in securities, options, futures and currencies. Thus, an investment in a hybrid instrument may entail significant risks that are not associated with a similar investment in a traditional debt instrument that has a fixed principal amount, is denominated in U.S. dollars or bears interest either at a fixed rate or a floating rate determined by reference to a common, nationally published Benchmark. The risks of a particular hybrid instrument will, of course, depend upon the terms of the instrument, but may include, without limitation, the possibility of significant changes in the Benchmarks or the prices of Underlying Assets to which the instrument is linked. Such risks generally depend upon factors unrelated to the operations or credit quality of the issuer of the hybrid instrument, which may not be readily foreseen by the purchaser, such as economic and political events, the supply and demand for the Underlying Assets and interest rate movements. In recent years, various Benchmarks and prices for Underlying Assets have been highly volatile, and such volatility may be expected in the future. Reference is also made to the discussion of futures, options, and forward contracts herein for a discussion of the risks associated with such investments.
Hybrid instruments are potentially more volatile and carry greater market risks than traditional debt instruments. Depending on the structure of the particular hybrid instrument, changes in a Benchmark may be magnified by the terms of the hybrid instrument and have an even more dramatic and substantial effect upon the value of the hybrid instrument. Also, the prices of the hybrid instrument and the Benchmark or Underlying Asset may not move in the same direction or at the same time.
Hybrid instruments may bear interest or pay preferred dividends at below market (or even relatively nominal) rates. Alternatively, hybrid instruments may bear interest at above market rates but bear an increased risk of principal loss (or gain). The latter scenario may result if “leverage” is used to structure the hybrid instrument. Leverage risk occurs when the hybrid instrument is structured so that a given change in a Benchmark or Underlying Asset is multiplied to produce a greater value change in the hybrid instrument, thereby magnifying the risk of loss as well as the potential for gain.
Hybrid instruments may also carry illiquidity risk since the instruments are often “customized” to meet the portfolio needs of a particular investor, and therefore, the number of investors that are willing and able to buy such instruments in the secondary market may be smaller than that for more traditional debt securities. Under certain conditions, the redemption (or sale) value of such an investment could be zero. In addition, because the purchase and sale of hybrid instruments could take place in an OTC market without the guarantee of a central clearing organization or in a transaction between the Fund and the issuer of the hybrid instrument, the creditworthiness of the counterparty or issuer of the hybrid instrument would be an additional risk factor
20
the Fund would have to consider and monitor. Hybrid instruments also may not be subject to regulation of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”), which generally regulates the trading of commodity futures by U.S. persons, the SEC, which regulates the offer and sale of securities by and to U.S. persons, or any other governmental regulatory authority.
The various risks discussed above, particularly the market risk of such instruments, may in turn cause significant fluctuations in the net asset value of the Fund. Accordingly, if the Fund so invests, it will limit its investments in hybrid instruments to 10% of its total assets.
Hybrid instruments include “market access products,” which are often referred to as equity-linked notes. A market access product is a derivative security with synthetic exposure to an underlying local foreign stock. They include, for example, warrants, zero strike options, and total return swaps. Market access products are subject to the same risks as direct investments in securities of foreign issuers. If the underlying stock decreases in value, the market access product will decrease commensurately. In addition, market access products are subject to counterparty risk due to the fact that the security is issued by a broker. If the broker suffers a significant credit event and cannot perform under the terms of the agreement, an access product may lose value regardless of the strength of the underlying stock.
Hybrid instruments also include Participation Notes and Participatory Notes (“P-notes”). P-notes are participation interest notes that are issued by banks or broker-dealers and are designed to offer a return linked to a particular underlying equity, debt, currency or market. If the P-note were held to maturity, the issuer would pay to, or receive from, the purchaser the difference between the nominal value of the underlying instrument at the time of purchase and that instrument’s value at maturity. The holder of a P-note that is linked to a particular underlying security or instrument may be entitled to receive any dividends paid in connection with that underlying security or instrument, but typically does not receive voting rights as it would if it directly owned the underlying security or instrument. P-notes involve transaction costs. Investments in P-notes involve the same risks associated with a direct investment in the underlying securities, instruments or markets that they seek to replicate. In addition, there can be no assurance that there will be a trading market for a P-note or that the trading price of a P-note will equal the underlying value of the security, instrument or market that it seeks to replicate. Due to liquidity and transfer restrictions, the secondary markets on which a P-note is traded may be less liquid than the market for other securities, or may be completely illiquid, which may also affect the ability of the Fund to accurately value a P-note. P-notes typically constitute general unsecured contractual obligations of the banks or broker-dealers that issue them, which subjects the Fund to counterparty risk (and this risk may be amplified if the Fund purchases P-notes from only a small number of issuers).
Structured securities include notes, bonds or debentures that provide for the payment of principal of, and/or interest in, amounts determined by reference to changes in the value of specific currencies, interest rates, commodities, indices or other financial indicators (the “Reference”) or the relative change in two or more References. The interest rate or the principal amount payable upon maturity or redemption may be increased or decreased depending upon changes in the applicable Reference. The terms of structured securities may provide that under certain circumstances no principal is due at maturity and, therefore, may result in the loss of the Fund’s entire investment in the structured security. Structured securities may be positively or negatively indexed, so that appreciation of the Reference may produce an increase or decrease in the interest rate or value of the security at maturity. In addition, the change in interest rate or the value of the security at maturity may be a multiple of the change in the value of the Reference (i.e., leveraged structured securities). Consequently, leveraged structured securities entail a greater degree of market risk than other types of debt obligations. Structured securities may also be more volatile, less liquid and more difficult to accurately price than less complex fixed income investments (e.g., investment grade corporate bonds). Structured securities generally will expose the Fund to credit risk, illiquidity risk and market risk.
Contingent convertible securities (sometimes referred to as “CoCos”) are a type of hybrid security that under certain circumstances either (i) converts into common shares of the issuer or (ii) undergoes a principal write-down. The mandatory conversion/write-down provision might relate, for instance, to maintenance of a capital minimum, whereby falling below the minimum would trigger the automatic conversion. Since the common stock of the issuer may not pay a dividend, investors in these instruments could experience a reduced income rate, potentially to zero; and conversion would deepen the subordination of the investor, hence worsening standing in a bankruptcy. Should an instrument undergo a write-down, investors may lose some or all of their original investment.
Structured Investments. Structured investments are organized and operated solely for the purpose of restructuring the investment characteristics of sovereign debt obligations. This type of restructuring involves the deposit with or purchase by an entity, such as a corporation or trust, of specified instruments (such as commercial bank loans) and the issuance by that entity
21
of one or more classes of securities (“Structured Securities”) backed by, or representing interests in, the underlying instruments. The cash flow on the underlying instruments may be apportioned among the newly issued Structured Securities to create securities with different investment characteristics, such as varying maturities, payment priorities and interest rate provisions, and the extent of the payments made with respect to Structured Securities is dependent on the extent of the cash flow on the underlying instruments. Because Structured Securities of this type typically involve no credit enhancement, their credit risk generally will be equivalent to that of the underlying instruments. Investments in Structured Securities are generally of a class of Structured Securities that is either subordinated or unsubordinated to the right of payment of another class. Subordinated Structured Securities typically have higher yields and present greater risks than unsubordinated Structured Securities. Structured Securities are typically sold in private placement transactions, and there currently is no active trading market for Structured Securities. Investments in government and government-related and restructured debt instruments are subject to special risks, including the inability or unwillingness to repay principal and interest, requests to reschedule or restructure outstanding debt and requests to extend additional loan amounts.
Illiquidity Investments
Under the Liquidity Rule, no more than 15% of the Fund’s net assets may be invested in illiquid investments. An illiquid investment is any investment that the Fund reasonably expects cannot be sold or disposed of in current market conditions in seven calendar days or less without the sale or disposition significantly changing the market value of the investment. If illiquid investments exceed 15% of the Fund’s net assets, the Liquidity Rule and the Liquidity Program (as defined below) require that certain remedial actions be taken. Investment of the Fund’s assets in illiquid investments may restrict the ability of the Fund to dispose of its investments in a timely fashion and for a fair price as well as its ability to take advantage of market opportunities. The risks associated with illiquidity will be particularly acute where the Fund’s operations require cash, such as when the Fund redeems shares or pays dividends, and could result in the Fund borrowing to meet short-term cash requirements or incurring capital losses on the sale of illiquid investments.
Initial Public Offering (“IPOs”)
The Fund may invest in IPOs. As such, a portion of the Fund’s returns may be attributable to the Fund’s investments in IPOs. There is no guarantee that as the Fund’s assets grow it will be able to experience significant improvement in performance by investing in IPOs.
The Fund’s purchase of shares issued as part of, or a short period after, companies’ IPOs, exposes it to the risks associated with companies that have little operating history as public companies, as well as to the risks inherent in those sectors of the market where these new issuers operate. The market for IPO issuers has been volatile, and share prices of newly-public companies have fluctuated in significant amounts over short periods of time.
Interfund Borrowing and Lending Program
VC I has received exemptive relief from the SEC which permits the Fund to participate in an interfund lending program among investment companies advised by VALIC or an affiliate. The interfund lending program allows the participating funds to borrow money from and loan money to each other for temporary or emergency purposes. The program is subject to a number of conditions designed to ensure fair and equitable treatment of participating funds, including the requirement that no fund may borrow from the program unless it receives a more favorable interest rate than would be available to any of the participating funds from a typical bank for a comparable transaction. In addition, the Fund may participate in the program only if and to the extent that such participation is consistent with the Fund’s investment objective and policies. Interfund loans and borrowings may extend overnight but could have a maximum duration of seven days. Loans may be called on one business days’ notice. The Fund may have to borrow from a bank at a higher interest rate if an interfund loan is called or not renewed. Any delay in repayment to a lending fund could result in a lost investment opportunity or additional costs. The program is subject to the oversight and periodic review of the Board of the participating funds. To the extent the Fund is actually engaged in borrowing through the interfund lending program, the Fund will comply with its investment policy or restriction on borrowing.
International Bonds
The Fund, in accordance with its investment practices and policies, may invest in international bonds, which include U.S. dollar-denominated bonds issued by foreign corporations for which the primary trading market is in the United States, or for which the primary trading market is abroad. International bonds may involve special risks and considerations not typically
22
associated with investing in U.S. companies, including differences in accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards; generally higher commission rates on foreign portfolio transactions; the possibility of nationalization, expropriation or confiscatory taxation; adverse changes in investment or exchange control regulations (which may include suspension of the ability to transfer currency from a country); and political instability which could affect U.S. investments in foreign countries. Additionally, dispositions of foreign securities and dividends and interest payable on those securities may be subject to foreign taxes, including withholding taxes. Foreign securities often trade with less frequency and volume than domestic securities and, therefore, may exhibit greater price volatility. The Fund’s investment in international bonds also may be affected either unfavorably or favorably by fluctuations in the relative rates of exchange between currencies of different nations, by exchange control regulations and by indigenous economic and political developments.
Lending Portfolio Securities
The Fund may make secured loans of its portfolio securities in amounts up to 30% of its total assets in accordance with its investment practices and policies. The lending of portfolio securities may increase the average annual return to shareholders. Lending of portfolio securities also involves certain risks to the Fund.
Collateral Requirements. Securities loans are made to broker-dealers and other financial institutions approved by the Custodian and pursuant to agreements requiring that the loans be continuously secured by collateral at least equal at all times to the loaned securities marked to market value on a daily basis. These loans of portfolio securities will be made only when the Custodian considers the borrowing broker-dealers or financial institutions to be creditworthy and of good standing and the interest and/or fees earned from such loans to justify the attendant risks. These loans of portfolio securities will be made only when the Custodian considers the borrowing broker-dealers or financial institutions to be creditworthy and of good standing and the interest earned from such loans to justify the attendant risks. The collateral received will consist of cash, U.S. Government securities, letters of credit or such other collateral as permitted by interpretations or rules of the SEC and agreed upon by the Fund and the Custodian. The initial collateral received shall have a value of 102% or 105% of the market value of the loaned securities for domestic securities and non-domestic securities, respectively. There will be a daily procedure to ensure that the pledged collateral is equal in value to at least 100% of the value of the securities loaned. Under such procedure, the value of the collateral pledged by the borrower as of any particular business day will be determined on the next succeeding business day. If such value is less than 100% of the value of the securities loaned, the borrower will be required to pledge additional collateral. The Fund may suffer losses if the value of the securities in which cash collateral is invested declines.
Rights with Respect to Loaned Securities. While the securities are on loan, the Fund will continue to receive the equivalent of the interest or dividends paid by the issuer on the securities, as well as interest on the investment of the cash collateral or a fee from the borrower.
Any loan of portfolio securities by the Fund will be callable at any time by the Fund upon notice of five business days and returned to the Fund within a period of time specified in the respective securities loan agreement and in no event later than the end of the customary settlement period for such loaned securities. When voting or consent rights which accompany loaned securities pass to the borrower, the Fund may call the loan, in whole or in part as appropriate, to permit the exercise of such rights if the matters involved would have a material effect on that the Fund’s investment in the securities being loaned. Although the Fund’s programs allow for the recall of securities for any reason, VALIC may determine not to vote securities on loan and it may not always be possible for securities on loan to be recalled in time to be voted.
Termination of Loans. If the borrower fails to maintain the requisite amount of collateral, the loan will automatically terminate and the Fund will be permitted to use the collateral to replace the securities while holding the borrower liable for any excess of replacement cost over collateral. As with any extensions of credit, there are risks of delay in receiving additional collateral or in the recovery of the securities or, in some cases, even loss of rights in the collateral should the borrower of the securities fail financially.
On termination of the loan, the borrower will be required to return the securities to the Fund. Any gain or loss in the market price during the loan would inure to the Fund. The Fund may pay reasonable finders, administrative and custodial fees in connection with a loan of its securities. There can be no assurance that the risks described above will not adversely affect the Fund.
23
Securities Lending Agreement. VC I, on behalf of the Fund, has entered into a Securities Lending Authorization Agreement (the “Securities Lending Agreement”) with State Street Bank and Trust Company (“State Street,” the “Custodian, ” or the “securities lending agent”) pursuant to which the securities lending agent implements and administers the Fund’s securities lending program. Under the Securities Lending Agreement, the securities lending agent provides the following services, among others: (i) selects borrowers from its list of approved borrowers and executes a securities loan agreement as agent on behalf of the Fund with each such borrower; (ii) negotiates the terms of securities loan agreements and certain individual securities loans, including fees; (iii) directs the delivery of loaned securities; (iv) monitors and credits to the Fund distributions on loaned securities (e.g., interest and dividends); (v) receives and holds, on behalf of the Fund, collateral from borrowers, monitors the daily value of loaned securities and directs the payment of additional collateral or the return of excess collateral, as required; (vi) invests cash collateral in connection with any loaned securities; (vii) establishes and maintains records with respect to securities lending activities; and (viii) terminates securities loans and arranges for the return of loaned securities to the Fund at loan termination.
The following table shows the dollar amounts of income and fees/compensation related to the securities lending activities of the Fund for the year ended May 31, 2022:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Fees and/or compensation for securities lending activities and related services |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Gross
income
from
securities
lending
activities |
|
Fees
paid to
securities
lending
agent
from
a revenue
split |
|
Fees paid for
any
cash
collateral
management
service
(including
fees deducted
from a pooled
cash
collateral
reinvestment
vehicle) that
are not
included
in the
revenue split |
|
Administrative
fees not
included in
revenue
split |
|
Indemnification
fees not
included in
revenue
split |
|
Rebate
(paid to
borrower) |
|
Other
fees not
included
in
revenue
split |
|
Aggregate
fees/
compensation
for securities
lending
activities |
|
Net
income
from
securities
lending
activities |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$24,749 |
|
$3,459 |
|
$249 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
$991 |
|
— |
|
$4,699 |
|
$20,050 |
Risks of Lending Portfolio Securities. Securities lending involves exposure to other risks, including operational risk (i.e., the risk of losses resulting from problems in the settlement and accounting process), “gap” risk (i.e., the risk of a mismatch between the return on cash collateral reinvestments and the fees the Fund has agreed to pay a borrower), and credit, legal, counterparty and market risk. In the event a borrower does not return the Fund’s securities as agreed, the Fund may experience losses if the proceeds received from liquidating the collateral do not at least equal the value of the loaned security at the time the collateral is liquidated plus the transaction costs incurred in purchasing replacement securities.
The Fund could also lose money if it does not recover the securities and/or the value of the collateral or the value of investments made with cash collateral falls. To the extent that the value of the Fund’s investments of the cash collateral declines below the amount owed to a borrower, the Fund may incur losses that exceed the amount it earned on lending the security.
There is also a risk that when lending portfolio securities, the securities may not be available to the Fund on a timely basis and the Fund may, therefore, lose the opportunity to sell the securities at a desirable price. In addition, engaging in securities lending could have a leveraging effect, which may intensify the market risk, credit risk and other risks associated with investments in the Fund.
LIBOR Risk
The Fund may invest in securities and other instruments whose interest payments are determined by references to the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”). In March 2021, the United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority (“FCA”), which regulates LIBOR, announced that the overnight, 1-month, 3-month, 6-month and 12-month U.S. dollar LIBOR settings will cease to be published under a panel bank methodology after June 30, 2023. In April 2023, the FCA announced that the 1-month, 3-month and 6-month U.S. dollar LIBOR settings will continue to be published under a synthetic methodology until September 30, 2024 for certain legacy contracts. All other LIBOR settings have ceased to be published.
24
On March 15, 2022, the Adjustable Interest Rate (LIBOR) Act (the “LIBOR Act”) was signed into law, providing a statutory fallback mechanism to replace LIBOR with a benchmark rate that is selected by the Federal Reserve Board and based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) for certain contracts that reference LIBOR without adequate fallback provisions. On December 16, 2022, the Federal Reserve Board adopted regulations implementing the LIBOR Act by identifying benchmark rates based on SOFR that will replace LIBOR in certain financial contracts after June 30, 2023. These regulations apply only to contracts governed by U.S. law, among other limitations. The LIBOR Act and any additional regulatory or market changes may have an adverse impact on the Fund or its investments. Neither the effect of the LIBOR transition process nor its ultimate success can yet be known.
Liquidity Risk Management
The Liquidity Rule requires open-end funds, such as the Fund, to establish a liquidity risk management program and enhance disclosures regarding fund liquidity. As required by the Liquidity Rule, the Fund has implemented its liquidity risk management program (the “Liquidity Program”), and the Board has appointed VALIC as the liquidity risk program administrator of the Liquidity Program. Under the Liquidity Program, VALIC assesses, manages, and periodically reviews the Fund’s liquidity risk and classifies each investment held by the Fund as a “highly liquid investment,” “moderately liquid investment,” “less liquid investment” or “illiquid investment.” The Liquidity Rule defines “liquidity risk” as the risk that the Fund could not meet requests to redeem shares issued by the Fund without significant dilution of the remaining investors’ interests in the Fund. The liquidity of the Fund’s portfolio investments is determined based on relevant market, trading and investment-specific considerations under the Liquidity Program. To the extent that an investment is deemed to be an illiquid investment or a less liquid investment, the Fund can expect to be exposed to greater liquidity risk.
Loan Participations and Assignments
Loan participations include investments in fixed and floating rate loans (“Loans”) arranged through private negotiations between an issuer of sovereign or corporate debt obligations and one or more financial institutions (“Lenders”). Investments in Loans are expected in most instances to be in the form of participations in Loans (“Participations”) and assignments of all or a portion of Loans (“Assignments”) from third parties. In the case of Participations, the Fund will have the right to receive payments of principal, interest and any fees to which it is entitled only from the Lender selling the Participation and only upon receipt by the Lender of the payments from the borrower. In the event of the insolvency of the Lender selling the Participation, the Fund may be treated as a general creditor of the Lender and may not benefit from any set-off between the Lender and the borrower. The Fund will acquire Participations only if the Lender interposed between the Fund and the borrower is determined by a Subadviser to be creditworthy. When the Fund purchases Assignments from Lenders it will acquire direct rights against the borrower on the Loan. Because Assignments are arranged through private negotiations between potential assignees and potential assignors, however, the rights and obligations acquired by the Fund as the purchaser of an Assignment may differ from, and be more limited than, those held by the assigning Lender. Because there is no liquid market for such securities, the Fund anticipates that such securities could be sold only to a limited number of institutional investors. The lack of a liquid secondary market may have an adverse impact on the value of such securities and the Fund’s ability to dispose of particular Assignments or Participations when necessary to meet the Fund’s liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as deterioration in the creditworthiness of the borrower. The lack of a liquid secondary market for Assignments and Participations also may make it more difficult for the Fund to assign a value to these securities for purposes of valuing the Fund and calculating its net asset value.
The highly leveraged nature of many such Loans may make such Loans especially vulnerable to adverse changes in economic or market conditions. Assignments, Participations and other direct investments may not be in the form of securities or may be subject to restrictions on transfer, and there may be no liquid market for such securities as described above. Participations and Assignments may be considered liquid, as determined by the Fund’s Subadviser.
In certain circumstances, Loans may not be deemed to be securities, and in the event of fraud or misrepresentation by a borrower or an arranger, Lenders and purchasers of interests in Loans, such as the Fund, will not have the protection of the anti-fraud provisions of the federal securities laws, as would be the case for bonds or stocks, and there may be less publicly available information about Loans than about securities. Instead, in such cases, Lenders generally rely on the contractual provisions in the Loan agreement itself and common-law fraud protections under applicable state law.
25
Master Limited Partnerships
The Fund may invest in master limited partnerships (“MLPs”) or limited partnerships. Certain companies are organized as master limited partnerships in which ownership interests are publicly traded. MLPs often own several properties or businesses (or directly own interests) that are related to real estate development and oil and gas industries, but they also may finance motion pictures, research and development and other projects. Generally, an MLP is operated under the supervision of one or more managing general partners. Limited partners (including the Fund if it invests in an MLP) are not involved in the day-to-day management of the partnership. They are allocated income and capital gains associated with the partnership project in accordance with the terms established in the partnership agreement.
Effective for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and on or before December 31, 2025, individuals and certain other non-corporate entities, such as partnerships, may claim a deduction for 20% of “qualified publicly traded partnership income,” such as income from MLPs. However, the new law does not include any provision for a regulated investment company to pass the character of its qualified publicly traded partnership income through to its shareholders. As a result, an investor who invests directly in MLPs will be able to receive the benefit of that deduction, while a shareholder in a Fund will not.
The risks of investing in an MLP are generally those inherent in investing in a partnership as opposed to a corporation. For example, state law governing partnerships is often less restrictive than state law governing corporations. Accordingly, there may be less protections afforded investors in an MLP than investors in a corporation. Additional risks involved with investing in an MLP are risks associated with the specific industry or industries in which the partnership invests, such as the risks of investing in real estate, or the oil and gas industries.
Mortgage-Related Securities
The Fund may invest in mortgage-related securities to the extent such investments are consistent with the Fund’s investment objective(s) and strategies. Mortgage-related securities are interests in pools of residential or commercial mortgage loans, including mortgage loans made by savings and loan institutions, mortgage bankers, commercial banks and others. Pools of mortgage loans are assembled as securities for sale to investors by various governmental, government-related and private organizations.
Mortgage-Backed Securities
Mortgage-backed securities include, but are not limited to, securities issued by the Government National Mortgage Association (“Ginnie Mae” or “GNMA”), Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae” or “FNMA”), and Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac” or “FHLMC”). These securities represent ownership in a pool of mortgage loans. They differ from conventional bonds in that principal is paid back to the investor as payments are made on the underlying mortgages in the pool. Accordingly, the Fund receives monthly scheduled payments of principal and interest along with any unscheduled principal prepayments on the underlying mortgages. Because these scheduled and unscheduled principal payments must be reinvested at prevailing interest rates, mortgage-backed securities do not provide an effective means of locking in long-term interest rates for the investor.
Like other fixed income securities, when interest rates rise, the value of mortgage-backed securities with prepayment features will generally decline. In addition, when interest rates are declining, the value of mortgage-backed securities with prepayment features may not increase as much as other fixed income securities. The weighted average life of such securities is likely to be substantially shorter than the stated final maturity as a result of scheduled principal payments and unscheduled principal prepayments.
Ginnie Mae is a government-owned corporation that is an agency of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. It guarantees, with the full faith and credit of the United States, full and timely payment of all monthly principal and interest on its mortgage-backed securities. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are each a government-sponsored enterprise. Both issue mortgage-related securities that contain guarantees as to timely payment of interest and principal but that are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
26
Mortgage Pass-Through Securities
Interests in pools of mortgage-related securities differ from other forms of fixed income securities, which normally provide for periodic payment of interest in fixed amounts with principal payments at maturity or specified call dates. Instead, these securities provide a monthly payment which consists of both interest and principal payments. In effect, these payments are a “pass-through” of the monthly payments made by the individual borrowers on their residential or commercial mortgage loans, net of any fees paid to the issuer or guarantor of such securities. Additional payments are caused by repayments of principal resulting from the sale of the underlying property, refinancing or foreclosure, net of fees or costs which may be incurred. Some mortgage-related securities (such as securities issued by GNMA) are described as “modified pass-through.” These securities entitle the holder to receive all interest and principal payments owed on the mortgage pool, net of certain fees, at the scheduled payment dates regardless of whether or not the mortgagor actually makes the payment.
The rate of prepayments on underlying mortgages will affect the price and volatility of a mortgage-related security, and may have the effect of shortening or extending the effective maturity of the security beyond what was anticipated at the time of purchase. To the extent that unanticipated rates of prepayment on underlying mortgages increase the effective maturity of a mortgage-related security, the volatility of such security can be expected to increase.
The principal governmental guarantors of mortgage-related securities are GNMA, FNMA and FHLMC. GNMA is a wholly owned United States Government corporation within the Department of Housing and Urban Development. GNMA is authorized to guarantee, with the full faith and credit of the United States Government, the timely payment of principal and interest on securities issued by institutions approved by GNMA (such as savings and loan institutions, commercial banks and mortgage bankers) and backed by pools of mortgages insured by the Federal Housing Administration (the “FHA”), or guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs (the “VA”).
Government-related guarantors (i.e., not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States Government) include FNMA and FHLMC. FNMA is subject to general regulation by the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development. FNMA purchases conventional (i.e., not insured or guaranteed by any government agency) residential mortgages from a list of approved seller/servicers which include state and federally chartered savings and loan associations, mutual savings banks, commercial banks and credit unions and mortgage bankers. Pass-through securities issued by FNMA are guaranteed as to timely payment of principal and interest by FNMA but are not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States Government. FHLMC was created by Congress in 1970 for the purpose of increasing the availability of mortgage credit for residential housing. It is a government-sponsored corporation formerly owned by the twelve Federal Home Loan Banks. FHLMC issues Participation Certificates (“PCs”) which represent interests in conventional mortgages from FHLMC’s national portfolio. FHLMC guarantees the timely payment of interest and ultimate collection of principal, but PCs are not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States Government.
Commercial banks, savings and loan institutions, private mortgage insurance companies, mortgage bankers and other secondary market issuers also create pass-through pools of conventional residential mortgage loans. Such issuers may, in addition, be the originators and/or servicers of the underlying mortgage loans as well as the guarantors of the mortgage-related securities. Pools created by such non-governmental issuers generally offer a higher rate of interest than government and government-related pools because there are no direct or indirect government or agency guarantees of payments in the former pools. However, timely payment of interest and principal of these pools may be supported by various forms of insurance or guarantees, including individual loan, title, pool and hazard insurance and letters of credit. The insurance and guarantees are issued by governmental entities, private insurers and the mortgage poolers. Such insurance and guarantees and the creditworthiness of the issuers thereof will be considered in determining whether a mortgage-related security meets VC I’s investment quality standards. There can be no assurance that the private insurers or guarantors can meet their obligations under the insurance policies or guarantee arrangements. The Fund may buy mortgage-related securities without insurance or guarantees if, through an examination of the loan experience and practices of the originator/servicers and poolers, a Subadviser determines that the securities meet VC I’s quality standards. Although the market for such securities is becoming increasingly liquid, securities issued by certain private organizations may not be readily marketable.
Mortgage-backed securities that are issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities are not subject to the Fund’s industry concentration restrictions, set forth above under “Investment Restrictions,” by virtue of the exclusion from that test available to all U.S. Government securities. In the case of privately issued mortgage-related securities, the Fund takes the position that mortgage-related securities do not represent interests in any particular “industry” or group of
27
industries. The assets underlying such securities may be represented by a portfolio of first lien residential mortgages (including both whole mortgage loans and mortgage participation interests) or portfolios of mortgage pass-through securities issued or guaranteed by GNMA, FNMA or FHLMC. Mortgage loans underlying a mortgage-related security may in turn be insured or guaranteed by the FHA or the VA. In the case of private issue mortgage-related securities whose underlying assets are neither U.S. Government securities nor U.S. Government-insured mortgages, to the extent that real properties securing such assets may be located in the same geographical region, the security may be subject to a greater risk of default than other comparable securities in the event of adverse economic, political or business developments that may affect such region and, ultimately, the ability of residential homeowners to make payments of principal and interest on the underlying mortgages.
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (“CMOs”)
The Fund may invest in CMOs. A CMO is a hybrid between a mortgage-backed bond and a mortgage pass-through security. Similar to a bond, interest and prepaid principal is paid, in most cases, monthly. CMOs may be collateralized by whole mortgage loans, but are more typically collateralized by portfolios of mortgage pass-through securities guaranteed by GNMA, FHLMC, or FNMA, and their income streams.
CMOs are structured in multiple classes, each bearing a different stated maturity. Actual maturity and average life will depend upon the prepayment experience of the collateral. CMOs provide for a modified form of call protection through a de facto breakdown of the underlying pool of mortgages according to how quickly the loans are repaid. Monthly payment of principal received from the pool of underlying mortgages, including prepayments, is first returned to investors holding the shortest maturity class. Investors holding the longer maturity classes receive principal only after the first class has been retired. An investor is partially guarded against a sooner than desired return of principal because of the sequential payments.
Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities
Commercial mortgage-backed securities include securities that reflect an interest in, and are secured by, mortgage loans on commercial real property. Many of the risks of investing in commercial mortgage-backed securities reflect the risks of investing in the real estate securing the underlying mortgage loans. These risks reflect the effects of local and other economic conditions on real estate markets, the ability of tenants to make loan payments, and the ability of a property to attract and retain tenants. Commercial mortgage-backed securities may be less liquid and exhibit greater price volatility than other types of mortgage- or asset-backed securities.
Additional Information about Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae
The volatility and disruption that impacted the capital and credit markets during late 2008 and into 2009 have led to increased market concerns about Freddie Mac’s and Fannie Mae’s ability to withstand future credit losses associated with securities held in their investment portfolios, and on which they provide guarantees, without the direct support of the federal government. On September 7, 2008, both Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae were placed under the conservatorship of the Federal Housing Finance Agency (“FHFA”). Under the plan of conservatorship, the FHFA has assumed control of, and generally has the power to direct, the operations of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, and is empowered to exercise all powers collectively held by their respective shareholders, directors and officers.
In connection with the conservatorship, the U.S. Treasury entered into a Senior Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement (“SPA”) with each of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac pursuant to which the U.S. Treasury agreed to purchase 1,000 shares of senior preferred stock with an initial liquidation preference of $1 billion and obtained warrants and options for the purchase of common stock of each of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Under the SPAs as currently amended, the U.S. Treasury has pledged to provide financial support to a government-sponsored enterprise (a “GSE”) in any quarter in which the GSE has a net worth deficit as defined in the respective SPA. The SPAs contain various covenants that severely limit each enterprise’s operations.
The conditions attached to entering into the SPAs place significant restrictions on the activities of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae must obtain the consent of the U.S. Treasury to, among other things, (i) make any payment to purchase or redeem its capital stock or pay any dividend other than in respect of the senior preferred stock, (ii) issue capital stock of any kind, (iii) terminate the conservatorship of the FHFA except in connection with a receivership, or (iv) increase its debt beyond certain specified levels. In addition, significant restrictions are placed on the maximum size of each of Freddie
28
Mac’s and Fannie Mae’s respective portfolios of mortgages and mortgage-backed securities, and the purchase agreements entered into by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae provide that the maximum size of their portfolios of these assets must decrease by a specified percentage each year. The future status and role of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae could be impacted by (among other things) the actions taken and restrictions placed on Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae by the FHFA in its role as conservator, the restrictions placed on Freddie Mac’s and Fannie Mae’s operations and activities as a result of the senior preferred stock investment made by the U.S. Treasury, market responses to developments at Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, and future legislative and regulatory action that alters the operations, ownership, structure and/or mission of these institutions, each of which may, in turn, impact the value of, and cash flows on, any mortgage-backed security guaranteed by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, including any such mortgage-backed security held by the Fund.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are continuing to operate as going concerns while in conservatorship and each remains liable for all of its obligations, including its guaranty obligations, associated with its mortgage-backed securities. The SPAs are intended to enhance each of Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s ability to meet its obligations. The FHFA has indicated that the conservatorship of each enterprise will end when the director of FHFA determines that FHFA’s plan to restore the enterprise to a safe and solvent condition has been completed. The FHFA recently announced plans to consider taking Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac out of conservatorship. Should Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac be taken out of conservatorship, it is unclear whether the U.S. Treasury would continue to enforce its rights or perform its obligations under the SPAs. It is also unclear how the capital structure of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac would be constructed post-conservatorship, and what effects, if any, the privatization of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac will have on their creditworthiness and guarantees of certain mortgage-backed securities. Accordingly, should the FHFA take Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac out of conservatorship, there could be an adverse impact on the value of their securities, which could cause the Fund’s investments to lose value.
Other Mortgage-Related Securities
Other mortgage-related securities include securities other than those described above that directly or indirectly represent a participation in, or are secured by and payable from, mortgage loans on real property, including CMO residuals, mortgage dollar rolls, or stripped mortgage-backed securities. Other mortgage-related securities may be equity or fixed income securities issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the U.S. Government or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan associations, homebuilders, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks, partnerships, trusts and special purpose entities of the foregoing.
CMO Residuals
CMO residuals are mortgage securities issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the U.S. Government or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan associations, homebuilders, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks and special purpose entities of the foregoing.
The cash flow generated by the mortgage assets underlying a series of CMOs is applied first to make required payments of principal and interest on the CMOs and second to pay the related administrative expenses of the issuer. The residual in a CMO structure generally represents the interest in any excess cash flow remaining after making the foregoing payments. Each payment of such excess cash flow to a holder of the related CMO residual represents income and/or a return of capital. The amount of residual cash flow resulting from a CMO will depend on, among other things, the characteristics of the mortgage assets, the coupon rate of each class of CMO, prevailing interest rates, the amount of administrative expenses and the prepayment experience on the mortgage assets. In particular, the yield to maturity on CMO residuals is extremely sensitive to prepayments on the related underlying mortgage assets, in the same manner as an interest-only (“IO”) class of stripped mortgage-backed securities. See “Mortgage-Related Securities – Other Mortgage-Related Securities – Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities.” In addition, if a series of a CMO includes a class that bears interest at an adjustable rate, the yield to maturity on the related CMO residual will also be extremely sensitive to changes in the level of the index upon which interest rate adjustments are based. As described below with respect to stripped mortgage-backed securities, in certain circumstances the Fund may fail to recoup fully its initial investment in a CMO residual.
CMO residuals are generally purchased and sold by institutional investors through several investment banking firms acting as brokers or dealers. Transactions in CMO residuals are generally completed only after careful review of the characteristics of the securities in question. In addition, CMO residuals may or, pursuant to an exemption there from, may not have been registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). CMO residuals, whether or not registered under the Securities Act, may be subject to certain restrictions on transferability, and may be deemed “illiquid” and subject to the Fund’s limitations on investments in illiquid investments.
29
Mortgage Dollar Rolls
The Fund may invest in mortgage dollar rolls. In a “dollar roll” transaction, the Fund sells a mortgage-related security, such as a security issued by GNMA, to a dealer and simultaneously agrees to repurchase a similar security (but not the same security) in the future at a pre-determined price. A “dollar roll” can be viewed as a collateralized borrowing in which the Fund pledges a mortgage-related security to a dealer to obtain cash. The dealer with which the Fund enters into a dollar roll transaction is not obligated to return the same securities as those originally sold by the Fund, but only securities which are “substantially identical.” To be considered “substantially identical,” the securities returned to the Fund generally must: (i) be collateralized by the same types of underlying mortgages; (ii) be issued by the same agency and be part of the same program; (iii) have a similar original stated maturity; (iv) have identical net coupon rates; (v) have similar market yields (and therefore price); and (vi) satisfy “good delivery” requirements, meaning that the aggregate principal amounts of the securities delivered and received must be within a specified percentage of the initial amount delivered.
Dollar rolls are generally subject to a number of risks such as leverage risk, liquidity risk, market risk, credit risk, default risk, counterparty risk, management risk, operational risk and legal risk. In addition, because dollar roll transactions may be for terms ranging between one and six months, they may be deemed “illiquid” and subject to the Fund’s overall limitations on investments in illiquid investments. Dollar roll transactions may increase the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate.
Rule 18f-4 under the 1940 Act permits the Fund to enter into when-issued or forward-settling securities, such as roll transactions, and non-standard settlement cycles securities notwithstanding the limitation on the issuance of senior securities in Section 18 of the 1940 Act, provided such transactions meet certain Rule 18f-4 requirements. If See “Investment Restrictions” above and “Derivatives” above.
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities (“SMBSs”)
The Fund may invest in SMBSs to the extent such investments are consistent with the Fund’s investment objective(s) and strategies.
SMBSs are derivative multi-class mortgage securities. SMBSs may be issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the U.S. Government, or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan associations, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks and special purpose entities of the foregoing.
SMBSs are usually structured with two classes that receive different proportions of the interest and principal distributions on a pool of mortgage assets. A common type of SMBSs will have one class receiving some of the interest and most of the principal from the mortgage assets, while the other class will receive most of the interest and the remainder of the principal. In the most extreme case, one class will receive all of the interest (the “IO” class), while the other class will receive the entire principal (the principal-only or “PO” class). The yield to maturity on an IO class is extremely sensitive to the rate of principal payments (including prepayments) on the related underlying mortgage assets, and a rapid rate of principal payments may have a material adverse effect on the Fund’s yield to maturity from these securities. If the underlying mortgage assets experience greater than anticipated prepayments of principal, the Fund may fail to recoup some or all of its initial investment in these securities even if the security is in one of the highest rating categories.
While IOs and POs are generally regarded as being illiquid, such securities may be deemed to be liquid if they can be disposed of promptly in the ordinary course of business at a value reasonably close to that used in the calculation of the Fund’s net asset value per share. Only government IOs and POs backed by fixed-rate mortgages and determined to be liquid under established guidelines and standards may be considered liquid securities not subject to the Fund’s limitation on investments in illiquid investments.
Options and Futures Contracts
The Fund may invest in options and futures contracts as described in more detail herein. The Fund may enter into option contracts for various purposes, including to facilitate trading, increase or decrease the Fund’s market exposure, to seek higher investment returns, to seek protection against a decline in the value of the Fund’s securities or an increase in prices of securities that may be purchased, or to generate income.
30
Options on Securities and Securities Indices
The Fund may write covered call and put options on securities and securities indices.
Writing Options on Securities/Securities Indices. The Fund may write options on securities and securities indices. Such investment strategies will not be used for speculation. If the Fund writes an option which expires unexercised or is closed out by the Fund at a profit, it will retain the premium received for the option, which will increase its gross income. If the price of the underlying security or currency moves adversely to the Fund’s position, the option may be exercised and the Fund, as the writer of the option, will be required to sell or purchase the underlying security or currency at a disadvantageous price, which may only be partially offset by the amount of premium received.
Options on stock indices are similar to options on stock, except that all settlements are made in cash rather than by delivery of stock, and gains or losses depend on price movements in the stock market generally (or in a particular industry or segment of the market represented by the index) rather than price movements of individual stocks. When the Fund writes an option on a securities index, and the underlying index moves adversely to the Fund’s position, the option may be exercised. Upon such exercise, the Fund, as the writer of the option, will be required to pay in cash an amount equal to the difference between the exercise settlement value of the underlying index and the exercise price of the option, multiplied by a specified index “multiplier.”
Call or put options on a stock index may be written at an exercise or “strike” price which is either below or above the current value of the index. If the exercise price at the time of writing the option is below the current value of the index for a call option or above the current value of the index for a put option the option is considered to be “in the money.”
Stock indices for which options are currently traded include the S&P 500® Index, Value Line Index, National OTC Index, Major Market Index, Computer Technology Index, Oil Index, NYSE Options Index, Technology Index, Gold/Silver Index, Institutional Index and NYSE Beta Index. The Fund may also use options on such other indices as might now or in the future be available.
Purchasing Options on Securities/Securities Indices. The Fund may also purchase put or call options on securities and securities indices in order to (i) hedge against anticipated changes in interest rates or stock prices that may adversely affect the prices of securities that the Fund intends to purchase at a later date, (ii) hedge its investments against an anticipated decline in value, or (iii) attempt to reduce the risk of missing a market or industry segment advance.
The premium paid for a put or call option plus any transaction costs will reduce the benefit, if any, realized by the Fund upon exercise or liquidation of the option, and, unless the price of the underlying security, securities index, or currency changes sufficiently, the option may expire without value to the Fund. To close option positions purchased by the Fund, the Fund may sell put or call options identical to options previously purchased, which could result in a net gain or loss depending on whether the amount received on the sale is more or less than the premium and other transaction costs paid on the put or call option purchased.
Over-the-Counter Options. Options used by the Fund may be traded on the national securities exchanges or in the OTC market. The Fund may use OTC options. The Fund may invest in OTC options as a means of generating additional income. Options traded in the OTC market may not be as actively traded as those on an exchange. Accordingly, it may be more difficult to value such options. In addition, it may be more difficult to enter into closing transactions with respect to options traded OTC. In this regard, the Fund may enter into contracts with the primary dealers with whom they write OTC options. The contracts will provide that the Fund has the absolute right to repurchase an option it writes at any time at a repurchase price which represents the fair market value of such option, as determined in good faith through negotiations between the parties, but which in no event will exceed a price determined pursuant to a formula contained in the contract. Although the specific details of the formula to determine the maximum price at which the Fund can repurchase the option at any time may vary between contracts with different primary dealers, the formula will generally be based on a multiple of the premium received by the Fund for writing the option, plus the amount, if any, of the option’s intrinsic value (i.e., the amount the option is “in-the-money”). The formula will also include a factor to account for the difference between the price of the security and the strike price of the option if the option is written “out-of-the-money.” The Fund has established standards of creditworthiness for these primary dealers.
31
Writing Covered Call and Put Options and Purchasing Call and Put Options
The Fund may write exchange-traded covered call and put options on or relating to specific securities for the reasons described earlier. To “cover” an option means, for example, to identify and make available for sale the specific portfolio security or foreign currency to which the option relates. Through the writing of a covered call option, the Fund receives premium income but obligates itself to sell to the purchaser of such an option the particular security or foreign currency underlying the option at a specified price at any time prior to the expiration of the option period, regardless of the market value of the security or the exchange rate for the foreign currency during this period. Through the writing of a covered put option, the Fund receives premium income but obligates itself to purchase a particular security or foreign currency underlying the option at a specified price at any time prior to the expiration of the option period, regardless of market value or exchange rate during the option period.
Writing Uncovered Options. From time to time, the Fund will write a call option that is not covered but where the Fund will establish and maintain with its Custodian for the term of the option, an account consisting of cash, U.S. Government securities, other liquid high-grade debt obligations, or other suitable cover as permitted by the SEC having a value equal to the fluctuating market value of the optioned securities or currencies. While such an option would be “covered” with sufficient collateral to satisfy SEC prohibitions on issuing senior securities, this type of strategy would expose the Fund to the risks of writing uncovered options. If the Fund writes an uncovered option as described above, it will bear the risk of having to purchase the security subject to the option at a price higher than the exercise price of the option. As the price of a security could appreciate substantially, the Fund’s loss could be significant.
Writing Exchange-Traded Covered Options on Securities Indices. The Fund, in accordance with its investment objective(s) and investment program(s), may also write exchange-traded covered call and put options on stock indices and may purchase call and put options on stock indices that correlate with the Fund’s portfolio securities. The Fund may engage in such transactions for the same purposes as they may engage in such transactions with respect to individual portfolio securities or foreign currencies. In economic effect, a stock index call or put option is similar to an option on a particular security, except that the value of the option depends on the weighted value of the group of securities comprising the index, rather than a particular security, and settlements are made in cash rather than by delivery of a particular security.
Purchasing Exchange-Traded Covered Options. The Fund may also purchase exchange-traded call and put options with respect to securities and stock indices that correlate with that Fund’s particular portfolio securities.
The Fund may purchase put options for defensive purposes in order to protect against an anticipated decline in the value of its portfolio securities or currencies. As the holder of a put option with respect to individual securities or currencies, the Fund has the right to sell the securities or currencies underlying the options and to receive a cash payment at the exercise price at any time during the option period. As the holder of a put option on an index, the Fund has the right to receive, upon exercise of the option, a cash payment equal to a multiple of any excess of the strike price specified by the option over the value of the index.
The Fund may purchase call options on individual securities, currencies or stock indices in order to take advantage of anticipated increases in the price of those securities or currencies by purchasing the right to acquire the securities or currencies underlying the option or, with respect to options on indices, to receive income equal to the value of such index over the strike price. As the holder of a call option with respect to individual securities or currencies, the Fund obtains the right to purchase the underlying securities or currencies at the exercise price at any time during the option period. As the holder of a call option on a stock index, the Fund obtains the right to receive, upon exercise of the option, a cash payment equal to the multiple of any excess of the value of the index on the exercise date over the strike price specified in the option.
Financial Futures Contracts
The Fund in accordance with its investment objective, investment program, policies, and restrictions, may enter into futures contracts for various purposes, including to increase or decrease exposure to equity or bond markets, to hedge against changes in interest rates, prices of stocks, bonds or other instruments, or currency rates, to manage duration and yield curve positioning or to enhance income or total return. The Fund may also write covered call options and purchase put and call options on futures contracts for the same purposes or to earn additional income. The Fund may also write covered put options on stock index futures contracts.
32
Futures contracts consist of interest rate futures contracts, single stock futures contracts, stock index futures contracts, and currency futures contracts. A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell a security (or deliver a final cash settlement price, in the case of a contract relating to an index or otherwise not calling for physical delivery of a specified security) for a set price in the future. Exchange-traded futures contracts are designated by boards of trade which have been designated “contracts markets” by the CFTC. An interest rate futures contract is a contract to buy or sell specified debt securities at a future time for a fixed price. A single stock futures contract is based on a single stock. A stock index futures contract is similar in economic effect, except that rather than being based on specific securities it is based on a specified index of stocks and not the stocks themselves. A currency futures contract is a contract to buy or sell a specific foreign currency at a future time for a fixed price.
An interest rate futures contract binds the seller to deliver to the purchaser on a specified future date a specified quantity of one of several listed financial instruments, against payment of a settlement price specified in the contract. A public market currently exists for futures contracts covering a number of indices as well as financial instruments and foreign currencies, including: U.S. Treasury bonds; U.S. Treasury notes; GNMA Certificates; three-month U.S. Treasury bills; 90-day commercial paper; bank certificates of deposit; Eurodollar certificates of deposit; the Australian dollar; the Canadian dollar; the British pound; the Japanese yen; the Swiss franc; the Mexican peso; and certain multinational currencies, such as the Euro. It is expected that other futures contracts for other currencies will be developed and traded in the future.
Single stock futures contracts or stock index futures contracts bind purchaser and seller to deliver, at a future date specified in the contract, a cash amount equal to a multiple of the difference between the value of a single stock or a specified stock index on that date and the settlement price specified by the contract. That is, the seller of the futures contract must pay and the purchaser would receive a multiple of any excess of the value of the stock or index over the settlement price, and conversely, the purchaser must pay and the seller would receive a multiple of any excess of the settlement price over the value of the stock or index. Single stock futures started trading in the U.S. in December 2001. A public market exists for stock index futures contracts based on a number of indices, including, but not limited to, the S&P 500® Index, the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index, the Value Line Stock Index, and the Major Market Index. It is expected that financial instruments related to broad-based indices, in addition to those for which futures contracts are currently traded, will in the future be the subject of publicly-traded futures contracts, and the Fund may use any of these, which are appropriate, in its hedging strategies.
Positions taken in the futures markets are not normally held until delivery or until cash settlement is required, but are instead liquidated through offsetting transactions which may result in a gain or a loss. While futures positions taken by the Fund will usually be liquidated in this manner, the Fund may instead make or take delivery of underlying securities whenever it appears economically advantageous to the Fund to do so. A clearing organization associated with the relevant exchange assumes responsibility for closing out transactions and guarantees that, as between the clearing members of an exchange, the sale and purchase obligations will be performed with regard to all positions that remain open at the termination of the contract.
Unlisted futures contracts, which may be purchased or sold only by the Fund, like unlisted options, are not traded on an exchange and, generally, are not as actively traded as listed futures contracts or listed securities. Such futures contracts generally do not have the following elements: standardized contract terms, margin requirements relating to price movements, clearing organizations that guarantee counterparty performance, open and competitive trading in centralized markets, and public price dissemination. These elements in listed instruments serve to facilitate their trading and accurate valuation. As a result, the accurate valuation of unlisted futures contracts may be difficult. In addition, it may be difficult or even impossible, in some cases, to close out an unlisted futures contract, which may, in turn, result in significant losses to the Fund. Such unlisted futures contracts will be considered by the Fund to be illiquid investments and together with other illiquid investments will be limited to no more than 15% of the value of the Fund’s total assets. In making such determination, the value of unlisted futures contracts will be based upon the “face amount” of such contracts.
When futures contracts are entered into by the Fund, either as the purchaser or the seller of such contracts, the Fund is required to deposit with the futures commission merchant (“FCM”) an initial margin of cash or U.S. Treasury bills equaling as much as 5% to 10% or more of the contract settlement price. The nature of initial margin requirements in futures transactions differs from traditional margin payments made in securities transactions in that initial margins for futures contracts do not involve the
33
borrowing of funds by the customer to finance the transaction. Instead, a customer’s initial margin on a futures contract represents a good faith deposit securing the customer’s contractual obligations under the futures contract. The initial margin deposit is returned, assuming these obligations have been met, when the futures contract is terminated. In addition, subsequent payments to and from the FCM, called “variation margin,” are made on a daily basis as the price of the underlying security, stock index, or currency fluctuates, reflecting the change in value in the long (purchase) or short (sale) positions in the futures contract, a process known as “marking to market.”
The Fund, as an internal operating policy, may not hold futures contracts in an amount greater than 33 1/3% of the Fund’s net assets. The Fund may not adhere to this internal operating policy in circumstances where the Fund is required to invest a large cash infusion.
Futures contracts generally are not entered into to acquire the underlying asset and generally are not held to term. Prior to the contract settlement date, the Fund will normally close all futures positions by entering into an offsetting transaction which operates to cancel the position held, and which usually results in a profit or loss.
Options on Futures Contracts
The Fund may also purchase call and put options on futures contracts and write call options on futures contracts of the type which the Fund is authorized to enter into. Options on futures contracts used by the Fund are traded on exchanges that are licensed and regulated by the CFTC. A call option on a futures contract gives the purchaser the right, in return for the premium paid, to purchase a futures contract (assume a “long” position) at a specified exercise price at any time before the option expires. A put option gives the purchaser the right, in return for the premium paid, to sell a futures contract (assume a “short” position), for a specified exercise price, at any time before the option expires.
Unlike entering into futures contracts, purchasing options on futures contracts allows the Fund to decline to exercise the option, thereby avoiding any loss beyond foregoing the purchase price (or “premium”) paid for the options. Therefore, the purchase of options on futures contracts may be a preferable hedging strategy when the Fund desires maximum flexibility. Whether, in order to achieve a particular objective, the Fund enters into a futures contract, on the one hand, or an option contract, on the other, will depend on all the circumstances, including the relative costs, liquidity, availability and capital requirements of such futures and options contracts. Also, the Fund will consider the relative risks involved, which may be quite different. These factors, among others, will be considered in light of market conditions and the particular objective to be achieved.
Certain Additional Risks of Options and Futures Contracts
The use of options and futures contracts may entail certain risks. First, although such instruments when used by the Fund are intended to correlate with the Fund’s portfolio securities or currencies, in many cases the options or futures contracts used may be based on securities, currencies, or stock indices the components of which are not identical to the portfolio securities owned or intended to be acquired by the Fund. Second, due to supply and demand imbalances and other market factors, the price movements of futures contracts, options thereon, currency options, and stock index options may not necessarily correspond exactly to the price movements of the securities, currencies, or stock indices on which such instruments are based. Accordingly, there is a risk that the Fund’s transactions in those instruments will not in fact offset the impact on the Fund of adverse market developments in the manner or to the extent contemplated or that such transactions will result in losses to the Fund which are not offset by gains with respect to corresponding portfolio securities owned or to be purchased by the Fund. To some extent, these risks can be minimized by careful management of hedging activities. For example, where price movements in a futures or option contract are expected to be less volatile than price movements in the related portfolio securities owned or intended to be acquired by the Fund, it may, in order to compensate for this difference, use an amount of futures or option contracts which is greater than the amount of such portfolio securities. Similarly, where the price movement of a futures or option contract is anticipated to be more volatile, the Fund may use an amount of such contracts which is smaller than the amount of portfolio securities to which such contracts relate.
The risk that the hedging technique used will not actually or entirely offset an adverse change in the Fund’s portfolio securities is particularly relevant to futures contracts and options written on stock indices and currencies. The Fund, in entering into a futures purchase contract, potentially could lose, any or all, of the contract’s settlement price. In entering into a futures sale contract, the Fund could potentially lose a sum equal to the excess of the contract’s value (marked to market daily) over the contract’s settlement price. In writing options on stock indices or currencies, the Fund could potentially lose a sum equal to the
34
excess of the value of the index or currency (marked to market daily) over the exercise price. In addition, because futures contracts require delivery at a future date of either a specified security or currency, or an amount of cash equal to a multiple of the difference between the value of a specified stock index on that date and the settlement price, an algebraic relationship exists between any price movement in the underlying security or currency or index and the potential cost of settlement to the Fund. A small increase or decrease in the value of the underlying security or currency or stock index can, therefore, result in a much greater increase or decrease in the cost to the Fund.
Stock index call options written also pose another risk as hedging tools. Because exercises of stock index options are settled in cash, there is an inherent timing risk that the value of the Fund’s portfolio securities “covering” a stock index call option written by it may decline during the time between exercise of the option by the option holder and notice to the Fund of such exercise (usually one day or more) thereby requiring the Fund to use additional assets to settle the transaction. This risk is not present in the case of covered call options on individual securities, which are settled by delivery of the actual securities.
There are also special risks in using currency options, including the following: (i) settlement of such options must occur in the country issuing the currency in conformity with foreign regulations for such delivery, including the possible imposition of additional costs and taxes, (ii) no systematic reporting of “last sale” information for foreign currencies, and (iii) the need to use “odd lot” transactions for underlying currencies at prices less favorable than those for “round lot” transactions.
Although the Fund intends to establish positions in these instruments only when there appears to be an active market, there is no assurance that a liquid market for such instruments will exist when the Fund seeks to “close out” (i.e., terminate) a particular futures contract or option position. This is particularly relevant for OTC options and futures contracts, as previously noted. Trading in such instruments could be interrupted, for example, because of a lack of either buyers or sellers. In addition, the futures and options exchanges may suspend trading after the price of such instruments has risen or fallen more than the maximum amount specified by the exchange. Exercise of options could also be restricted or delayed because of regulatory restrictions or other factors. The Fund may be able, by adjusting investment strategy in the cash or other contract markets, to offset to some extent any adverse effects of being unable to liquidate a hedge position. Nevertheless, in some cases, the Fund may experience losses as a result of such inability. Therefore, it may have to liquidate other more advantageous investments to meet its cash needs.
In addition, FCMs or brokers in certain circumstances will have access to the Fund’s assets posted as margin in connection with these transactions as permitted under the 1940 Act. The Fund will use only FCMs or brokers in whose reliability and financial soundness they have full confidence and have adopted certain other procedures and limitations to reduce the risk of loss with respect to any assets which brokers hold or to which they may have access. Nevertheless, in the event of a broker’s insolvency or bankruptcy, it is possible that the Fund could experience a delay or incur costs in recovering such assets or might recover less than the full amount due. Also the value of such assets could decline by the time the Fund could affect such recovery.
The success of the Fund in using hedging techniques depends, among other things, on a Subadviser’s ability to predict the direction and volatility of price movements in both the futures and options markets as well as the securities markets and on a Subadviser’s ability to select the proper type, time, and duration of hedges. There can be no assurance that these techniques will produce their intended results. A Subadviser will not speculate; however, purchasing futures to efficiently invest cash may be considered more risky than to invest the cash in equities over time. Hedging transactions also, of course, may be more, rather than less, favorable to the Fund than originally anticipated.
Limitations
The Fund will not enter into any futures contract or purchase any option thereon if immediately thereafter the total amount of its assets required to be on deposit as initial margin to secure its obligations under such futures contracts, plus the amount of premiums paid by it for outstanding options to purchase futures contracts, exceeds 5% of the market value of its net assets; provided, however that in the case of an option that is in-the-money at the time of purchase, the in-the-money amount may be excluded in calculating the 5% limitation. In addition, the Fund has an operating policy which provides that it will not enter into custodial arrangements with respect to initial or variation margin deposits or marked-to-market amounts unless the custody of such initial and variation margin deposits and marked-to-market amounts are in compliance with current SEC or CFTC staff interpretive positions or no-action letters or rules adopted by the SEC.
35
The Fund is operated by persons who have claimed an exclusion from registration as a “commodity pool operator” with respect to the Fund under the Commodity Exchange Act. As a result, the Fund is limited in its ability to use futures contracts (which include futures as broad-based securities indexes and interest rate futures) or options on futures, engage in certain swaps transactions or make certain other investments (whether directly or indirectly through investments in other investment vehicles) for purposes other than “bona fide hedging” as defined in the rules of the CFTC, with respect to transactions other than for bona fide hedging purposes, either: (1) the aggregate initial margin and premiums required to establish the company’s positions in such investments may not exceed five percent (5%) of the liquidation value of the company’s portfolio (after accounting for unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such investments and calculated in accordance with CFTC Rule 4.5); or (2) the aggregate net notional value of such instruments, determined at the time the most recent position was established, may not exceed one hundred percent (100%) of the liquidation value of the company’s portfolio (after accounting for unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such positions). In addition to meeting one of the foregoing trading limitations, the Fund is also subject to certain marketing limitations imposed by CFTC Rule 4.5. In the event that VALIC is required to register as a “commodity pool operator,” the disclosure and operations of the Fund would need to comply with all applicable CFTC regulations. Compliance with these additional registration and regulatory requirements would increase the Fund’s expenses. Other potentially adverse regulatory initiatives could also develop. In August 2013, the CFTC issued a rule (“Harmonization Rule”) that harmonizes certain of the CFTC’s compliance obligations with those of the SEC in order to facilitate compliance with both regulatory regimes. Under the Harmonization Rule, a registered investment company may elect to comply with certain CFTC obligations by agreeing to comply with certain SEC disclosure, reporting and recordkeeping requirements. The Fund has claimed exclusion from the definition of a commodity pool under CFTC Rule 4.5.
Other Investment Companies
The Fund may invest in securities of other investment companies, including exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”), up to the maximum extent permissible under the 1940 Act. Investments in other investment companies are subject to statutory limitations prescribed by the 1940Act. Except for investments in money market funds permitted by Rule 12d1-1, Section 12(d) of the 1940 Act prohibits the Fund from acquiring more than 3% of the voting shares of any other investment company, and prohibits more than 5% of the Fund’s total assets being invested in securities of any one investment company or more than 10% of its total assets being invested in securities of all investment companies, unless the Fund is able to rely on and meet the requirements of one or more rules under the 1940 Act that permit investments in other investment companies in excess of these limits. In addition, to the extent the Fund has knowledge that its shares are purchased by another investment company in reliance on the provisions of paragraph (G) of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act, the Fund will not acquire shares of other affiliated or unaffiliated registered open-end investment companies or registered unit investment trusts in reliance on paragraph (F) or (G) of Section 12(d)(1) of the 1940 Act. The Fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of any management fees and other expenses paid by such other investment companies. Investments in other investment companies are subject to market and selection risk.
An ETF trades like common stock. ETFs are typically designed to represent a fixed portfolio of securities designed to track a particular market index. ETFs may be passively- or actively-managed. Funds purchase an ETF to temporarily gain exposure to a portion of the U.S. or a foreign market while awaiting purchase of underlying securities. The risks of owning an ETF generally reflect the risks of owning the underlying securities.
iShares are shares of an investment company that invests substantially all of its assets in securities included in specified indices, including the Morgan Stanley Capital International (“MSCI”) indices or various countries and regions. iShares are managed by BlackRock Fund Advisors and are listed on the New York Stock Exchange Arca, Inc. (“NYSE Arca”). The market prices of iShares are expected to fluctuate in accordance with both changes in the net asset values of their underlying indices and supply and demand of iShares on the NYSE Arca. iShares have traded at relatively modest discounts and premiums to their net asset values. In the event substantial market or other disruptions affecting iShares should occur in the future, the liquidity and value of the Fund’s shares could also be substantially and adversely affected. If such disruptions were to occur, the Fund could be required to reconsider the use of iShares as part of its investment strategy.
36
Standard & Poor’s Depositary Receipts (“SPDRs”) are NYSE Arca-traded securities that represent ownership in the SPDR Trust, a trust established to accumulate and hold a portfolio of common stocks intended to track the price performance and dividend yield of the S&P 500® Index. SPDRs may be used for several reasons, including but not limited to facilitating the handling of cash flows or trading, or reducing transaction costs. The use of SPDRs would introduce additional risk, as the price movement of the instrument does not perfectly correlate with the price action of the underlying index. SPDRs are investment companies and investments in SPDRs are subject to the Fund’s limitations on investment company holdings.
Partnership Securities
The Fund may invest in securities issued by publicly traded partnerships or MLPs (together referred to as “PTPs/MLPs”) publicly traded on stock exchanges or markets in the United States such as the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ.
These entities are various forms of partnerships or limited liability companies that elect to be taxed as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Generally PTPs/MLPs are operated under the supervision of one or more managing partners or members. Limited partners, unit holders, or members (such as the Fund if it invests in a partnership) are not involved in the day-to-day management of the company. Limited partners, unit holders, or members are allocated income and capital gains associated with the partnership project in accordance with the terms of the partnership or limited liability company agreement.
Risks involved with investing in PTPs/MLPs include, among other things, risks associated with the (i) partnership structure itself and (ii) specific industry or industries in which the partnership invests, such as the risks of investing in real estate, or oil and gas industries.
At times PTPs/MLPs may potentially offer relatively high yields compared to common stocks. Because PTPs/MLPs are generally treated as “pass-through” entities for tax purposes, they do not ordinarily pay income tax, but pass their earnings on to unit holders (except in the case of some publicly traded firms that may be taxed as corporations). See also “Master Limited Partnerships.”
Passive Foreign Investment Companies
The Fund may invest in passive foreign investment companies (“PFICs”). PFICs are any foreign corporations which generate certain amounts of passive income or hold certain amounts of assets for the production of passive income. Passive income includes dividends, interest, royalties, rents and annuities. To avoid taxes and interest that the Fund must pay if these investments are profitable, the Fund may make various elections permitted by the tax laws. These elections could require that the Fund recognizes taxable income, which in turn must be distributed, before the securities are sold and before cash is received to pay the distributions.
Private Investments in Public Equity
Private Investments in Public Equity (“PIPEs”) are equity securities issued in a private placement by companies that have outstanding, publicly traded equity securities of the same class. Shares in PIPEs generally are not registered with the SEC until after a certain time period from the date the private sale is completed. PIPE transactions will generally result in the Fund acquiring either restricted stock or an instrument convertible into restricted stock. As with investments in other types of restricted securities, such an investment may be illiquid. The Fund’s ability to dispose of securities acquired in PIPE transactions may depend upon the registration of such securities for resale. Any number of factors may prevent or delay a proposed registration. Alternatively, it may be possible for securities acquired in a PIPE transaction to be resold in transactions exempt from registration in accordance with Rule 144 under the Securities Act, or otherwise under the federal securities laws. There is no guarantee, however, that an active trading market for the securities will exist at the time of disposition of the securities, and the lack of such a market could hurt the market value of the Fund’s investments. As a result, even if the Fund is able to have securities acquired in a PIPE transaction registered or sell such securities through an exempt transaction, the Fund may not be able to sell all the securities on short notice, and the sale of the securities could lower the market price of the securities. PIPEs may contain provisions that the issuer will pay specified financial penalties to the holder if the issuer does not publicly register the restricted equity securities within a specified period of time, but there is no assurance that the restricted equity securities will be publicly registered, or that the registration will remain in effect.
37
Privately Placed Securities
The Fund may invest in privately placed securities, to the extent consistent with its investment objectives, which are subject to resale restrictions and may additionally be limited by restrictions on investments in illiquid investments or Rule 144A securities.
Real Estate Securities and Real Estate Investment Trusts (“REITs”)
The Fund may invest in real estate securities. Real estate securities are equity securities consisting of (i) common stocks, (ii) rights or warrants to purchase common stocks, (iii) securities convertible into common stocks and (iv) preferred stocks issued by real estate companies. A real estate company is one that derives at least 50% of its revenues from the ownership, construction, financing, management or sale of commercial, industrial, or residential real estate or that has at least 50% of its assets invested in real estate. The Fund may also invest in REITs. REITs are pooled investment vehicles that invest primarily in income producing real estate or real estate related loans or interest. REITs are generally classified as equity REITs, mortgage REITs or hybrid REITs which combine the characteristics of equity and mortgage REITs (hybrid REITs). Equity REITs invest the majority of their assets directly in real property and derive income primarily from the collection of rents. Equity REITs can also realize capital gains by selling properties that have appreciated in value. Mortgage REITs invest the majority of their assets in real estate mortgages and derive income from the collection of interest payments. REITs can be listed and traded on national securities exchanges or can be traded privately between individual owners. The Fund may invest in both publicly and privately traded REITs. Like regulated investment companies such as the Fund, REITs are not taxed on income distributed to shareholders provided they comply with certain requirements under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”). The Fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of any expenses paid by REITs in which it invests in addition to the expenses paid by the Fund.
Investing in REITs involves certain unique risks. Equity REITs may be affected by changes in the value of the underlying property owned by such REITs, while mortgage REITs may be affected by the quality of any credit extended. REITs are dependent upon management skills, are not diversified (except to the extent the Code requires), and are subject to the risks of financing projects. REITs are subject to heavy cash flow dependency, default by borrowers, self-liquidation, and the possibilities of failing to qualify for the exemption from tax for distributed income under the Code and failing to maintain their exemptions from the 1940 Act. REITs (especially mortgage REITs) are also subject to interest rate risks.
Effective for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026, a direct REIT shareholder may claim a 20% “qualified business income” deduction for ordinary REIT dividends, and a regulated investment company paying dividends attributable to such income (reduced by allocable expenses) may pass through this special treatment to its shareholders, provided that holding period and other requirements are met by the Fund and the shareholders.
Recent Market Events
In the past decade, the U.S. and global financial markets have experienced depressed valuations, decreased liquidity, unprecedented volatility and heighted uncertainty. These conditions may continue, recur, worsen or spread. Those events that have contributed to these market conditions include, but are not limited to, geopolitical events (including terrorism, sanctions and war); infectious disease epidemics and pandemics; natural disasters; measures to address budget deficits; changes in oil and commodity prices; and public sentiment. The U.S. government and the Federal Reserve, as well as certain foreign governments and central banks, have taken numerous steps to support financial markets, including, but not limited to, providing liquidity in fixed income, commercial paper and other markets, implementing stimulus packages and providing tax breaks. The withdrawal or reduction of this support or failure of efforts to respond to a crisis could negatively affect financial markets, as well as the value and liquidity of certain securities. In addition, this support and other government intervention may not work as intended, particularly if the efforts are perceived by investors as being unlikely to achieve the desired results. The current market environment could make identifying and assessing investment risks and opportunities in connection with the management of the Fund’s portfolios more challenging.
A number of countries have experienced severe economic and financial difficulties. Many non-governmental issuers, and even certain governments, have defaulted on, or been forced to restructure, their debts; many other issuers have faced difficulties obtaining credit or refinancing existing obligations; financial institutions have in many cases required government or central bank support, have needed to raise capital, and/or have been impaired in their ability to extend credit; and many financial
38
markets have experienced extreme volatility and declines in asset values and liquidity. These difficulties may continue, worsen or spread. Responses to the financial problems by governments, central banks and others, including austerity measures and reforms, may not work, may result in social unrest and may limit future growth and economic recovery or have other unintended consequences. Further defaults or restructurings by governments and others of their debt could have additional adverse effects on economies, financial markets and asset valuations around the world.
Brexit/European Union
On January 31, 2020, the United Kingdom (the “UK”) formally withdrew from the European Union (commonly referred to as “Brexit”). This historic event is widely expected to have consequences that are both profound and uncertain for the economic and political future of the UK and the European Union, and those consequences include significant legal and business uncertainties pertaining to an investment in the Fund. The full scope and nature of the consequences of Brexit are not at this time known and are unlikely to be known for a significant period of time. At the same time, it is reasonable to assume that the significant uncertainty in the business, legal and political environment engendered by this event has resulted in immediate and longer term risks that would not have been applicable had the UK not sought to withdraw from the European Union.
Other countries may seek to withdraw from the European Union and/or abandon the euro, the common currency of the European Union. A number of countries in Europe have suffered terror attacks, and additional attacks may occur in the future. The Ukraine has experienced ongoing military conflict; this conflict may expand, and military attacks could occur elsewhere in Europe. Europe has also been struggling with mass migration from the Middle East and Africa. The ultimate effects of these events and other socio-political or geographical issues are not known but could profoundly affect global economies and markets.
COVID-19
An outbreak of respiratory disease caused by a novel coronavirus, known as “COVID-19,” was first detected in China in December 2019. It has since been detected internationally and the World Health Organization has declared it a pandemic. Although vaccines have been developed and approved for use by many governments, there is no guarantee that the vaccines will be effective against emerging variants of the disease. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in closed borders and travel restrictions, shelter in place orders, enhanced health screenings, healthcare service preparation and delivery, quarantines, cancellations, disruptions to supply chains and customer activity, and reduced or suspended production, as well as general concern and uncertainty. The COVID-19 pandemic has also caused volatility in the global financial markets. The impact of COVID-19, and other epidemics and pandemics that may arise in the future, could affect the economies of many nations, individual companies and the financial markets in general in ways that cannot necessarily be foreseen at the present time.
In addition, the impact of infectious diseases in developing or emerging market countries may be greater due to less established health care systems. Health crises caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may exacerbate other pre-existing political, social and economic risks in certain countries. The impact of the outbreak may last for a prolonged period of time.
Notwithstanding business continuity planning and other controls that are designed to mitigate operational risks related to significant business disruptions, there is no guarantee that the COVID-19 pandemic and/or other epidemics or pandemics will not disrupt the operations of the Fund and its service providers. These disruptions could adversely affect the Fund and its shareholders.
Whether or not the Fund invests in securities of issuers located in or with significant exposure to countries experiencing economic, political, financial and/or social difficulties, these events could negatively affect the value and liquidity of the Fund’s investments.
39
Repurchase Agreements
Repurchase agreements typically obligate a seller, at the time it sells securities to the Fund, to repurchase the securities at a specific future time and price. The price for which the Fund resells the securities is calculated to exceed the price the Fund initially paid for the same securities, thereby determining the yield during the Fund’s holding period. This results in a fixed market rate of interest, agreed upon by the Fund and the seller, which is accrued as ordinary income. Most repurchase agreements mature within seven days although some may have a longer duration. The underlying securities constitute collateral for these repurchase agreements, which are considered loans under the 1940 Act.
The Fund may hold commercial paper, certificates of deposit, and government obligations (including government guaranteed obligations) subject to repurchase agreements with certain well-established domestic banks and certain broker-dealers, including primary government securities dealers, approved as creditworthy by a Subadviser pursuant to guidelines and procedures established by VC I’s Board. Unless the Fund participates in a joint repurchase transaction, the underlying security must be a high-quality domestic money market security (unless the Fund’s investment objective(s), policies and investment program permit the use of foreign money market securities) and the seller must be a well-established securities dealer or bank that is a member of the Federal Reserve System. To the extent the Fund participates in a joint repurchase transaction, the collateral will consist solely of U.S. Government obligations. Repurchase agreements are generally for short periods, usually less than a week.
The Fund may not sell the underlying securities subject to a repurchase agreement (except to the seller upon maturity of the agreement). During the term of the repurchase agreement, the Fund (i) retains the securities subject to the repurchase agreement as collateral securing the seller’s obligation to repurchase the securities, (ii) monitors on a daily basis the market value of the securities subject to the repurchase agreement, and (iii) requires the seller to deposit with VC I’s Custodian collateral equal to any amount by which the market value of the securities subject to the repurchase agreement falls below the resale amount provided under the repurchase agreement. In the event that a seller defaults on its obligation to repurchase the securities, the Fund must hold the securities until they mature or may sell them on the open market, either of which may result in a loss to the Fund if, and to the extent that, the values of the securities decline. Additionally, the Fund may incur disposition expenses when selling the securities. Bankruptcy proceedings by the seller may also limit or delay realization and liquidation of the collateral by the Fund and may result in a loss to the Fund. A Subadviser will evaluate the creditworthiness of all banks and broker-dealers with which VC I proposes to enter into repurchase agreements. The Fund will not invest in repurchase agreements that do not mature within seven days if any such investment, together with any illiquid investments held by the Fund, exceeds 15% of the value of the Fund’s total assets.
Restricted Securities
Securities that have not been registered under the Securities Act, are referred to as “private placements” or “restricted securities” and are purchased directly from the issuer or in the secondary market. Mutual funds do not typically hold a significant amount of these restricted securities because of the potential for delays on resale and uncertainty in valuation. Limitations on resale may have an adverse effect on the marketability of portfolio securities and a mutual fund might be unable to dispose of restricted securities promptly or at reasonable prices and might thereby experience difficulty satisfying redemptions within seven days. A mutual fund might also have to register such restricted securities in order to dispose of them, resulting in additional expense and delay. There will generally be a lapse of time between a mutual fund’s decision to sell an unregistered security and the registration of such security promoting the sale. Adverse market conditions could impede a public offering of such securities. When purchasing unregistered securities, the Fund will generally seek to obtain the right of registration at the expense of the issuer (except in the case of Rule 144A securities, discussed below).
A large institutional market has developed for certain securities that are not registered under the Securities Act, including repurchase agreements, commercial paper, foreign securities, municipal securities and corporate bonds and notes. Institutional investors depend on an efficient institutional market in which the unregistered security can be readily resold or on an issuer’s ability to honor a demand for repayment. The fact that there are contractual or legal restrictions on resale to the general public or to certain institutions may not be indicative of the liquidity of such investments.
Commercial paper issues in which the Fund’s net assets may be invested include securities issued by major corporations without registration under the Securities Act in reliance on the exemption from such registration afforded by Section 3(a)(3) thereof, and commercial paper issued in reliance on the so-called private placement exemption from registration afforded by Section
40
4(a)(2) of the Securities Act (“Section 4(a)(2) paper”). Section 4(a)(2) paper is restricted as to disposition under the federal securities laws in that any resale must similarly be made in an exempt transaction. Section 4(a)(2) paper is normally resold to other institutional investors through or with the assistance of investment dealers who make a market in Section 4(a)(2) paper, thus providing liquidity. Section 4(a)(2) paper issued by a company that files reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is generally eligible to be sold in reliance on the safe harbor of Rule 144A described above.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements
The Fund, in accordance with its investment practices and policies, may enter into reverse repurchase agreements. A reverse repurchase agreement involves the sale of a portfolio-eligible security by the Fund, coupled with its agreement to repurchase the instrument at a specified time and price. Under a reverse repurchase agreement, the Fund continues to receive any principal and interest payments on the underlying security during the term of the agreement. Reverse repurchase agreements involve the risk that the market value of securities retained by the Fund may decline below the repurchase price of the securities sold by the Fund which it is obligated to repurchase. In the event that the buyer of securities under a reverse repurchase agreement files for bankruptcy or becomes insolvent, the buyer or its trustee or receiver may receive an extension of time to determine whether to enforce the Fund’s repurchase obligation, and the Fund’s use of proceeds of the agreement may effectively be restricted pending such decision.
Rule 18f-4 under the 1940 Act permits the Fund to enter into reverse repurchase agreements and similar financing transactions notwithstanding the limitation on the issuance of senior securities in Section 18 of the 1940 Act, provided the Fund either complies with the 300% asset coverage ratio with respect to such transactions and any other borrowings in the aggregate or treats such transactions as derivatives transactions under Rule 18f-4. See “Investment Restrictions” above and “Derivatives” above.
Short Sales
Short sales are affected by selling a security that the Fund does not own. The Fund may engage in “short sales against the box.” This technique involves selling either a security that the Fund owns or a security equivalent in kind and amount to the security sold short that the Fund has the right to obtain, for delivery at a specified date in the future. The Fund may enter into a short sale against the box to hedge against anticipated declines in the market price of portfolio securities. If the value of the securities sold short increases prior to the scheduled delivery date, the Fund loses the opportunity to participate in the gain.
Rule 18f-4 treats short sales of securities as derivatives and subjects such transactions to the VaR limits, unless the fund entering into such transactions is a Limited Derivatives User. In addition, Rule 18f-4 treats certain securities lending transactions entered into by the Fund to facilitate short sales, fails or similar transactions by third parties as transactions that are similar to reverse repurchase transactions and as senior securities, as described in Section 18 of the 1940 Act. Rule 18f-4 limits the ability of the Fund to enter into short selling transactions and may limit its ability to lend portfolio securities, unless the collateral for such transactions was limited to cash and cash equivalents.
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies
The Fund may invest in stock, warrants, and other securities of special purpose acquisition companies (“SPACs”) or similar special purpose entities that pool funds to seek potential acquisition opportunities. A SPAC is typically a publicly traded company that raises funds through an IPO for the purpose of acquiring or merging with another company to be identified subsequent to the SPAC’s IPO. The securities of a SPAC are often issued in “units” that include one share of common stock and one right or warrant (or partial right or warrant) conveying the right to purchase additional shares or partial shares. Unless and until a transaction is completed, a SPAC generally invests its assets (less a portion retained to cover expenses) in U.S. government securities, money market funds and similar investments. If an acquisition or merger that meets the requirements for the SPAC is not completed within a pre-established period of time, the invested funds are returned to the SPAC’s shareholders, less certain permitted expenses, and any rights or warrants issued by the SPAC will expire worthless.
Because SPACs and similar entities are in essence blank check companies without operating history or ongoing business other than seeking acquisitions, the value of their securities is particularly dependent on the ability of the entity’s management to identify and complete a profitable acquisition. An investment in a SPAC is subject to a variety of risks, including that (i) a
41
portion of the monies raised by the SPAC for the purpose of effecting an acquisition or merger may be expended prior to the transaction for payment of taxes and other expenses; (ii) prior to any acquisition or merger, a SPAC’s assets are typically invested in U.S. government securities, money market funds and similar investments whose returns or yields may be significantly lower than those of the Fund’s other investments; (iii) the Fund generally will not receive significant income from its investments in SPACs (both prior to and after any acquisition or merger) and, therefore, the Fund’s investments in SPACs will not significantly contribute to the Fund’s distributions to shareholders; (iv) attractive acquisition or merger targets may become scarce if the number of SPACs seeking to acquire operating businesses increases; (v) an attractive acquisition or merger target may not be identified at all, in which case the SPAC will be required to return any remaining monies to shareholders; (vi) if an acquisition or merger target is identified, the Fund may elect not to participate in, or vote to approve, the proposed transaction or the Fund may be required to divest its interests in the SPAC, due to regulatory or other considerations, in which case the Fund may not reap any resulting benefits; (vii) the warrants or other rights with respect to the SPAC held by the Fund may expire worthless or may be redeemed by the SPAC at an unfavorable price; (viii) any proposed merger or acquisition may be unable to obtain the requisite approval, if any, of SPAC shareholders and/or antitrust and securities regulators; (ix) under any circumstances in which the Fund receives a refund of all or a portion of its original investment (which typically represents a pro rata share of the proceeds of the SPAC’s assets, less any applicable taxes), the returns on that investment may be negligible, and the Fund may be subject to opportunity costs to the extent that alternative investments would have produced higher returns; (x) to the extent an acquisition or merger is announced or completed, shareholders who redeem their shares prior to that time may not reap any resulting benefits; (xi) the Fund may be delayed in receiving any redemption or liquidation proceeds from a SPAC to which it is entitled; (xii) an acquisition or merger once effected may prove unsuccessful and an investment in the SPAC may lose value; (xiii) an investment in a SPAC may be diluted by additional later offerings of interests in the SPAC or by other investors exercising existing rights to purchase shares of the SPAC; (xiv) only a thinly traded market for shares of or interests in a SPAC may develop, or there may be no market at all, leaving the Fund unable to sell its interest in a SPAC or to sell its interest only at a price below what the Fund believes is the SPAC interest’s intrinsic value; and (xv) the values of investments in SPACs may be highly volatile and may depreciate significantly over time.
In addition, from time to time, the Fund may serve as an “anchor” investor by purchasing a significant portion of the units offered in a SPAC’s IPO. The Fund may also purchase private warrants from a SPAC and/or enter into a forward purchase agreement or similar arrangement through which the Fund makes a non-binding commitment to purchase additional units of the SPAC in the future. In exchange, the Fund receives certain private rights and other interests issued by a SPAC (commonly referred to as “founder shares”). Founder shares are generally subject to all of the risks described above (including the risk that the founder shares will expire worthless to the extent an acquisition or merger is not completed). Founder shares are also subject to restrictions on transferability, which significantly reduces their liquidity. In addition, the Fund may be required to forfeit all or a portion of any founder shares it holds, including, for example, (i) if the Fund does not purchase additional units of the SPAC pursuant to the terms of any forward purchase agreement it enters into, (ii) if the Fund sells shares that it purchased in the IPO prior to the SPAC effecting a merger or acquisition or (iii) if the SPAC’s sponsor forfeits its founders shares to effect a merger or acquisition.
Structured Notes
Subject to its individual investment practices and policies, the Fund may purchase structured notes. Structured notes are derivative fixed-income securities, the interest rate or principal of which is determined by an unrelated indicator. Indexed securities include structured notes as well as securities other than debt securities, the interest rate or principal of which is determined by an unrelated indicator. Indexed securities may include a multiplier that multiplies the indexed element by a specified factor and, therefore, the value of such securities may be very volatile. To the extent the Fund invests in these securities, however, a Subadviser will analyze these securities in its overall assessment of the effective duration of the Fund’s portfolio in an effort to monitor the Fund’s interest rate risk.
Swap Agreements
Swap agreements are two party contracts entered into primarily by institutional investors for periods ranging from a few weeks to more than one year. In a standard “swap” transaction, two parties agree to exchange the returns (or differentials in rates of return) earned or realized on particular predetermined investments or instruments, which may be adjusted for an interest factor.
42
The gross returns to be exchanged or “swapped” between the parties are generally calculated with respect to a “notional amount,” i.e., the return on or increase in value of a particular dollar amount invested at a particular interest rate, or in a particular foreign currency, or in a “basket” of securities representing a particular index. Forms of swap agreements include interest rate caps, under which, in return for a premium, one party agrees to make payments to the other to the extent that interest rates exceed a specified rate, or “cap;” interest rate floors, under which, in return for a premium, one party agrees to make payments to the other to the extent that interest rates fall below a specified rate, or “floor”; and interest rate collars, under which a party sells a cap and purchases a floor or vice versa in an attempt to protect itself against interest rate movements exceeding minimum or maximum levels.
The Fund may enter into interest rate, index and currency exchange rate swap agreements in accordance with its individual investment strategies. The Fund will not enter into a swap agreement with any single counterparty if the net amount owed or to be received under existing contracts with that party would exceed 5% of the Fund’s assets. The Fund may invest in equity swaps for various purposes, including to hedge exposure to market risk or to gain exposure to a security or market index. An equity swap is a special type of total return swap, where the underlying asset is a stock, a basket of stocks, or a stock index. One party to an equity swap agrees to make periodic payments based on the change in market value of a specified equity security, basket of equity securities or equity index in return for periodic payments from the other party based on a fixed or variable interest rate or the change in market value of a different equity security, basket of equity securities or equity index. The parties to an equity swap do not make an initial payment and do not have any voting or other rights of a stockholder.
Most swap agreements entered into by the Fund would calculate the obligations of the parties to the agreement on a “net basis.” Consequently, the Fund’s current obligations (or rights) under a swap agreement will generally be equal only to the net amount to be paid or received under the agreement based on the relative values of the positions held by each party to the agreement (the “net amount”). The risk of loss with respect to swaps is limited to the net amount of payments that the Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to a swap defaults, the Fund’s risk of loss consists of the net amount of payments that the Fund contractually is entitled to receive.
Credit Default Swaps (“CDS”). CDS involve the receipt of floating or fixed rate payments in exchange for assuming potential credit losses of an underlying security. CDS give one party to a transaction the right to dispose of or acquire an asset (or group of assets), or the right to receive or make a payment from the other party, upon the occurrence of specified credit events. The Fund may invest in CDS. The Fund may enter into CDS for various purposes, including managing credit risk (i.e., hedging), enhancing returns, a substitute for physical securities or speculation. Credit swaps give one party to a transaction the right to dispose of or acquire an asset (or group of assets), or the right to receive or make a payment from the other party, upon the occurrence of specified credit events, which is typically a default. CDS may be direct (“unfunded swaps”) or indirect in the form of a structured note (“funded swaps”). CDS transactions are typically individually negotiated and structured. CDS transactions may be entered into for investment or hedging purposes. CDS involve greater risks than if the Fund had invested in the reference obligation directly, since, in addition to general market risks, they are subject to illiquidity risk, counterparty risk and credit risks.
The Fund may be either the buyer or seller in the CDS transaction. If the Fund is a buyer and no credit event occurs, the Fund recovers nothing if the swap is held through its termination date. However, if a credit event occurs, the buyer may elect to receive the full notional value of the swap in exchange for an equal face amount of deliverable obligations of the reference entity that may have little or no value. As a seller, the Fund generally receives an up-front payment or a fixed rate of income throughout the term of the swap provided that there is no credit event. If a credit event occurs, generally the seller must pay the buyer the full notional value of the swap in exchange for an equal face amount of deliverable obligations of the reference entity that may have little or no value.
Whether the Fund’s use of swap agreements will be successful in furthering its investment objective of total return will depend on a Subadviser’s ability to predict correctly whether certain types of investments are likely to produce greater returns than other investments. Because they are two party contracts and because they may have terms of greater than seven days, swap agreements may be considered to be illiquid. Moreover, the Fund bears the risk of loss of the amount expected to be received under a swap agreement in the event of the default or bankruptcy of a swap agreement counterparty. The Fund will enter into swap agreements only with counterparties that meet certain standards of creditworthiness (generally, such counterparties would have to be eligible counterparties under the terms of the Fund’s repurchase agreement guidelines). Certain restrictions imposed
43
on the Fund by the Code may limit the Fund’s ability to use swap agreements. The swaps market is a relatively new market and is largely unregulated. It is possible that developments in the swaps market, including potential government regulation, could adversely affect the Fund’s ability to terminate existing swap agreements or to realize amounts to be received under such agreements.
Potential Government Regulation of Derivatives
It is possible that government regulation of various types of derivative instruments, including futures and swap agreements, may limit or prevent the Fund from using such instruments as a part of its investment strategy, and could ultimately prevent the Fund from being able to achieve its investment objective. It is impossible to predict fully the effects of legislation and regulation in this area, but the effects could be substantial and adverse.
The futures markets are subject to comprehensive statutes, regulations, and margin requirements. The SEC, the CFTC and the exchanges are authorized to take extraordinary actions in the event of a market emergency, including, for example, the implementation or reduction of speculative position limits, the implementation of higher margin requirements, the establishment of daily price limits and the suspension of trading.
The regulation of swaps and futures transactions in the U.S. is a rapidly changing area of law and is subject to modification by government and judicial action. There is a possibility of future regulatory changes altering, perhaps to a material extent, the nature of an investment in the Fund or the ability of the Fund to continue to implement its investment strategies. In particular, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (“Dodd-Frank Act”), enacted in July 2010, includes provisions that comprehensively regulate the OTC derivatives markets for the first time. While the CFTC and other U.S. regulators have adopted many of the required Dodd-Frank Act regulations, certain regulations have only recently become effective and other regulations remain to be adopted. The full impact of the Dodd-Frank Act on the Fund remains uncertain.
Transactions in some types of swaps (including interest rate swaps and credit default swaps on certain North American and European indices) are required to be centrally cleared. In a transaction involving those swaps (“cleared derivatives”), the Fund’s counterparty is a clearing house, rather than a bank or broker. Since the Fund is not a member of clearing houses and only clearing members can participate directly in the clearing house, the Fund will hold cleared derivatives through accounts at clearing members. In cleared derivatives transactions, the Fund will make payments (including margin payments) to and receive payments from a clearing house through its accounts at clearing members. Clearing members guarantee performance of their clients’ obligations to the clearing house.
Under the Dodd-Frank Act, certain derivatives are subject to margin requirements and swap dealers are required to collect margin from the Fund with respect to such derivatives. Specifically, swap dealers are required to collect variation margin in connection with trading of OTC swaps with the Fund and may be required by applicable regulations to collect initial margin from the Fund. Both initial and variation margin may be comprised of cash and/or securities, subject to applicable regulatory haircuts. Shares of investment companies (other than certain money market funds) may not be posted as collateral under these regulations. In addition, regulations adopted by prudential regulators require certain bank-regulated counterparties and certain of their affiliates to include in certain financial contracts, including many derivatives contracts, terms that delay or restrict the rights of counterparties, such as the Fund, to terminate such contracts, foreclose upon collateral, exercise other default rights or restrict transfers of affiliate credit enhancements (such as guarantees) in the event that the bank-regulated counterparty and/or its affiliates are subject to certain types of resolution or insolvency proceedings. Similar regulations and laws have been adopted in non-U.S. jurisdictions that may apply to the Fund’s counterparties located in those jurisdictions. It is possible that these requirements, as well as potential additional government regulation and other developments in the market, could adversely affect the Fund’s ability to terminate existing derivatives agreements or to realize amounts to be received under such agreements.
In many ways, cleared derivative arrangements are less favorable to mutual funds than bilateral arrangements. For example, the Fund may be required to provide more margin for cleared derivatives transactions than for bilateral derivatives transactions. Also, in contrast to a bilateral derivatives transaction, following a period of notice to the Fund, a clearing member generally can require termination of an existing cleared derivatives transaction at any time or an increase in margin requirements above the margin that the clearing member required at the beginning of a transaction. Clearing houses also have broad rights to increase margin requirements for existing transactions or to terminate those transactions at any time. Any increase in margin
44
requirements or termination of existing cleared derivatives transactions by the clearing member or the clearing house could interfere with the ability of the Fund to pursue its investment strategy. Further, any increase in margin requirements by a clearing member could expose the Fund to greater credit risk to its clearing member, because margin for cleared derivatives transactions in excess of a clearing house’s margin requirements typically is held by the clearing member. Also, the Fund is subject to risk if it enters into a derivatives transaction that is required to be cleared (or that VALIC or a Subadviser expects to be cleared), and no clearing member is willing or able to clear the transaction on the Fund’s behalf. In those cases, the transaction might have to be terminated, and the Fund could lose some or all of the benefit of the transaction, including loss of an increase in the value of the transaction and/or loss of hedging protection. In addition, the documentation governing the relationship between the Fund and clearing members is drafted by the clearing members and generally is less favorable to the Fund than typical bilateral derivatives documentation. For example, documentation relating to cleared derivatives generally includes a one-way indemnity by the Fund in favor of the clearing member for losses the clearing member incurs as the Fund’s clearing member and typically does not provide the Fund any remedies if the clearing member defaults or becomes insolvent.
Some types of cleared derivatives are required to be executed on an exchange or on a swap execution facility. A swap execution facility is a trading platform where multiple market participants can execute derivatives by accepting bids and offers made by multiple other participants in the platform. While this execution requirement is designed to increase transparency and liquidity in the cleared derivatives market, trading on a swap execution facility can create additional costs and risks for the Fund. For example, swap execution facilities typically charge fees, and if the Fund executes derivatives on a swap execution facility through a broker intermediary, the intermediary may impose fees as well. Also, the Fund may indemnify a swap execution facility, or a broker intermediary who executes cleared derivatives on a swap execution facility on the Fund’s behalf, against any losses or costs that may be incurred as a result of the Fund’s transactions on the swap execution facility.
These and other new rules and regulations could, among other things, further restrict the Fund’s ability to engage in, or increase the cost to the Fund of, derivatives transactions, for example, by making some types of derivatives no longer available to the Fund, increasing margin or capital requirements, or otherwise limiting liquidity or increasing transaction costs. These regulations are new and evolving, so their potential impact on the Fund and the financial system are not yet known. While the new regulations and central clearing of some derivatives transactions are designed to reduce systemic risk (i.e., the risk that the interdependence of large derivatives dealers could cause them to suffer liquidity, solvency or other challenges simultaneously), there is no assurance that the new clearing mechanisms will achieve that result, and in the meantime, as noted above, central clearing and related requirements expose the Fund to new kinds of risks and costs.
Unseasoned Issuers
Unseasoned issuers are companies that have (together with their predecessors) generally operated for less than three years. The securities of such companies may have limited liquidity, which can result in their being priced higher or lower than might otherwise be the case. In addition, investments in unseasoned issuers are more speculative and entail greater risk than do investments in companies with an established operating record.
U.S. Government Obligations
The Fund may invest in a variety of debt securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. These securities include a variety of Treasury securities that differ primarily in their interest rates, the length of their maturities and dates of issuance. Treasury bills are obligations issued with maturities of one year or less. Treasury notes are generally issued with maturities from one to ten years. Treasury bonds are generally issued with maturities of more than ten years. Obligations issued by agencies and instrumentalities of the U.S. Government, which may be purchased by the Fund, also vary in terms of their maturities at the time of issuance.
U.S. Treasury obligations are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. Government and are generally considered to have minimal credit risk. Securities issued or guaranteed by federal agencies or authorities and U.S. Government-sponsored instrumentalities or enterprises may or may not be backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. For example, securities issued by the FHLMC, the FNMA and the Federal Home Loan Banks are neither insured nor guaranteed by the U.S. Government. These securities may be supported by the ability to borrow from the U.S. Treasury or by the credit of the issuing agency, authority, instrumentality or enterprise and, as a result, are subject to greater credit risk than securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Treasury.
45
Variable Rate Demand Notes (“VRDNs”)
The Fund may invest in VRDNs. VRDNs are either taxable or tax-exempt obligations containing a floating or variable interest rate adjustment formula, together with an unconditional right to demand payment of the unpaid principal balance plus accrued interest upon a short notice period, generally not to exceed seven days. Any purchase of VRDNs will meet applicable diversification and concentration requirements.
Warrants and Rights
The Fund may invest in or acquire warrants or rights to purchase equity or fixed income securities. Bonds with warrants attached to purchase equity securities have many characteristics of convertible bonds and their prices may, to some degree, reflect the performance of the underlying stock. Bonds also may be issued with warrants attached to purchase additional fixed-income securities at the same coupon rate. A decline in interest rates would permit the Fund to buy additional bonds at the favorable rate or to sell the warrants at a profit. If interest rates rise, the warrants would generally expire with no value. Warrants do not entitle a holder to dividends or voting rights with respect to the underlying securities and do not represent any rights in the assets of the issuing company. In addition, the value of warrants does not, necessarily, in all cases change to the same extent as the value of the underlying securities to which they relate. These factors can make warrants more speculative than other types of investments. Rights represent a preemptive right of stockholders to purchase additional shares of a stock at the time of a new issuance before the stock is offered to the general public. The purchase of rights or warrants involves the risk that the Fund could lose the purchase value of a right or warrant if the right to subscribe to additional shares is not exercised prior to the rights’ and warrants’ expiration.
When-Issued, Delayed Delivery and Forward Commitment Securities
The Fund may purchase securities on a when-issued basis or purchase or sell securities on a delayed delivery or forward commitment basis beyond the customary settlement time. These transactions involve a commitment by the Fund to purchase or sell securities at a future date. The price of the underlying securities (usually expressed in terms of yield) and the date when the securities will be delivered and paid for (the settlement date) are fixed at the time the transaction is negotiated. These transactions are negotiated directly with the other party, and such commitments are not traded on exchanges. The Fund will generally purchase securities on a when-issued basis or purchase or sell securities on a delayed delivery or forward commitment basis only with the intention of completing the transaction and actually purchasing or selling the securities. If deemed advisable as a matter of investment strategy, however, the Fund may dispose of or negotiate a commitment after entering into it. The Fund may realize capital gains or losses in connection with these transactions. Securities purchased or sold on a when-issued, delayed delivery or forward commitment basis involve a risk of loss if the value of the security to be purchased declines prior to the settlement date or if the value of the security to be sold increases prior to the settlement date.
Rule 18f-4 under the 1940 Act permits the Fund to enter into when-issued or forward-settling securities and non-standard settlement cycles securities notwithstanding the limitation on the issuance of senior securities in Section 18 of the 1940 Act, provided such transactions meet certain Rule 18f-4 requirements. See “Investment Restrictions” above and “Derivatives” above.
Zero Coupon Securities
In accordance with its investment practices and policies, the Fund may invest in zero coupon securities, which are debt obligations that do not entitle the holder to any periodic payment of interest prior to maturity or that specify a future date when the securities begin to pay current interest.
Zero coupon securities are issued and traded at a discount from their face amount or par value. This discount varies depending on prevailing interest rates, the time remaining until cash payments begin, the liquidity of the security, and the perceived credit quality of the issuer.
The discount on zero coupon securities (“original issue discount”) must be taken into income ratably by the Fund prior to the receipt of any actual payments. Because the Fund must distribute substantially all of its net income to its shareholders each year for income and excise tax purposes, the Fund may have to dispose of portfolio securities under disadvantageous circumstances to generate cash, or may be required to borrow, to satisfy its distribution requirements.
46
The market prices of zero coupon securities generally are more volatile than the prices of securities that pay interest periodically. Zero coupon securities are likely to respond to changes in interest rates to a greater degree than other types of debt securities having a similar maturity and credit quality.
INVESTMENT ADVISER
VALIC serves as the investment adviser to the Fund pursuant to an investment advisory agreement (“Advisory Agreement”) dated January 1, 2002 that was last approved by the Board on August 2-3, 2021. Under the Advisory Agreement, the Fund pays VALIC an annual fee, payable monthly, based on its average daily net assets.
VALIC is a stock life insurance company organized on August 20, 1968, under the Texas Insurance Code as a successor to The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company of America, a District of Columbia insurance company organized in 1955. VALIC’s sole business consists of offering fixed and variable (and combinations thereof) retirement annuity contracts, IRAs and Plans. VALIC is an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Corebridge Financial, Inc. (“Corebridge”), which is a majority-owned subsidiary of American International Group, Inc. (“AIG”). AIG is a holding company which through its subsidiaries is engaged in a broad range of insurance and insurance related activities and financial services in the United States and abroad.
AIG, the parent of Corebridge, has announced its intention to sell all of its interest in Corebridge over time (such divestment, the “Separation Plan”). On September 19, 2022, AIG sold a portion of its interest in Corebridge in an initial public offering of Corebridge common stock, following which AIG’s interest in Corebridge is approximately 78%. While AIG and Corebridge believe that Corebridge’s initial public offering did not result in a transfer of a controlling block of outstanding voting securities of VALIC, SunAmerica Asset Management, LLC (“SunAmerica”) or Corebridge (“a Change of Control Event”), it is anticipated that one or more of the transactions contemplated by the Separation Plan will ultimately be deemed a Change of Control Event resulting in the assignment and automatic termination of the current Advisory Agreement. To ensure that VALIC may continue to provide advisory services to the Fund without interruption, at meetings held on August 2-3, 2022, the Board approved a new investment advisory agreement with VALIC, in connection with the Separation Plan. The Board also agreed to call and hold a joint meeting of shareholders on October 14, 2022, for shareholders of the Fund to (1) approve the new investment advisory agreement with VALIC that would be effective after the first Change of Control Event, and (2) approve any future investment advisory agreements approved by the Board and that have terms not materially different from the current agreement, in the event there are subsequent Change of Control Events arising from completion of the Separation Plan that terminate the investment advisory agreement after the first Change of Control Event. Approval of a future investment advisory agreement means that shareholders may not have another opportunity to vote on a new agreement with VALIC even upon a change of control, as long as no single person or group of persons acting together gains “control” (as defined in the 1940 Act) of VALIC. At the October 14, 2022 meeting, shareholders of the Fund approved the new and future investment advisory agreements.
Pursuant to the Advisory Agreement, VC I retains VALIC to manage the Fund’s day-to-day operations, to prepare the various reports and statements required by law, and to conduct any other recurring or nonrecurring activity which the Fund may need to continue operations. As permitted by the Advisory Agreement, VALIC has entered into a subadvisory agreement with each Subadviser (the “Subadvisory Agreement”), which agreement provides that the Subadviser will be responsible for the investment and reinvestment of the assets of the Fund, maintaining a trading desk, and placing orders for the purchase and sale of portfolio securities. The Advisory Agreement provides that VC I pay all expenses not specifically assumed by VALIC under the Advisory Agreement. Examples of the expenses paid by VC I include, but are not limited to, transfer agency fees, custodial fees, the fees of outside legal and auditing firms, the costs of reports to shareholders, and expenses of servicing shareholder accounts (e.g., daily calculation of the net asset value).
VC I pays VALIC a monthly fee calculated daily at the following annual percentages of the Fund’s assets:
|
|
|
| Fund Name |
|
Advisory Fee Rate |
| Systematic Growth Fund1 |
|
0.75% on the first $250 million 0.725% on the next $250 million and 0.70% on assets over $500 million |
47
| 1 |
Pursuant to an Amended and Restated Advisory Fee Waiver Agreement, effective May 1, 2023, VALIC has contractually agreed to waive the Fund’s advisory fees in order that such fees equal: 0.580% on the first $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.555% on the next $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.530% on the next $300 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.505% on the next $200 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, and 0.450% of the Fund’s average daily net assets over $1 billion. From September 28, 2021 through April 30, 2023, VALIC had contractually agreed to waive the Fund’s advisory fees in order that such fees equaled: 0.75% on the first $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.725% on the next $250 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.70% on the next $300 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, 0.36% on the next $200 million of the Fund’s average daily net assets, and 0.65% of the Fund’s average daily net assets over $1 billion. |
The below table sets forth the total advisory fees received by VALIC from the Fund pursuant to the Advisory Agreement for the last three fiscal years. The percentages and amounts shown in the table do not reflect any fee waivers and/or expense reimbursements.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2020 |
|
| Fund Name |
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
|
0.72 |
% |
|
$ |
6,939,191 |
|
|
|
0.72 |
% |
|
$ |
6,878,182 |
|
|
|
0.72 |
% |
|
$ |
5,908,671 |
|
The below table sets forth the advisory fees retained by VALIC with respect to the Fund after paying all subadvisory fees to the Subadviser(s) of the Fund for the past three fiscal years. The percentages and amounts shown in the table do not reflect any fee waivers and/or expense reimbursements.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2020 |
|
| Fund Name |
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
|
0.38 |
% |
|
$ |
3,642,141 |
|
|
|
0.35 |
% |
|
$ |
3,345,341 |
|
|
|
0.35 |
% |
|
$ |
2,860,585 |
|
For the last three fiscal years ended May 31, with respect to the Fund, VALIC waived advisory fees or reimbursed (or recouped) pursuant to contractual expense caps in the following amounts:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Amounts Waived or Reimbursed (Recouped) by VALIC For the Fiscal Year Ended May 31, |
|
| Fund Name |
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2020 |
|
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$ |
259,002 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
The Advisory Agreement requires that VALIC’s advisory fee be reduced by any commissions, tender and exchange offer solicitation fees and other fees, or similar payments (less any direct expenses incurred) received by VALIC or its affiliates in connection with the purchase and sale of portfolio investments of the Fund. In this regard, the Advisory Agreement requires VALIC to use its best efforts to recapture tender and exchange solicitation offer fees for the Fund’s benefit, and to advise VC I’s Board of any other fees, or similar payments that it (or any of its affiliates) may receive in connection with the Fund’s portfolio transactions or of other arrangements that may benefit the Fund or VC I.
Code of Ethics
VC I and VALIC have adopted an Investment Company and Investment Adviser Code of Ethics (the “VALIC Code”), which prescribes general rules of conduct and sets forth guidelines with respect to personal securities trading by “Access Persons” thereof. An Access Person as defined in the VALIC Code generally is (1) any trustee, director, officer, general partner or advisory person of VC I or VALIC, (2) any trustee, director, officer or general partner of the underwriter, AIG Capital Services, Inc. (“ACS”), who in the ordinary course of business makes, participates in, or obtains information regarding the purchase or sale of securities for VC I or whose functions or duties as part of the ordinary course of business relate to the making of any recommendation to VC I regarding the purchase or sale of securities, (3) any Supervised Person, as defined below, who has access to non-public information to VALIC’s purchase or sale of securities, or non-public information regarding the portfolio holdings of the Fund, (4) any Supervised Person who is involved in making securities recommendations to the Fund, or has access to such recommendations that are non-public, and (5) any other persons designated by the Review Officer (as defined in the VALIC Code) as having access to current trading information. A “Supervised Person” means VALIC’s partners, officers, directors and employees, and any other person who provide advice on behalf of VALIC and is subject to VALIC’s supervision and control. The guidelines on personal securities trading relate to: (i) securities being considered for purchase or sale, or purchased or sold, by any investment company advised by VALIC; (ii) initial public offerings; (iii) private placements; (iv) blackout periods; (v) short-term trading profits; and (vi) involvement in outside activities, including but not limited to board memberships of publicly traded companies. Subject to certain restrictions, Access Persons may invest in securities, including securities that may be purchased or held by the Fund. These guidelines are substantially similar to those contained in the Report of the Advisory Group on Personal Investing issued by the Investment Company Institute’s Advisory Panel. VALIC reports to the Board on a quarterly basis, as to whether there were any violations of the VALIC Code by Access Persons of VC I or any material violations by a Subadviser’s access persons involved with the Fund.
48
Each of the Subadvisers has adopted a code of ethics. Provisions of a Subadviser’s code of ethics are applicable to persons who, in connection with their regular functions or duties as employees of the Subadviser, make, participate in, or obtain information regarding the purchase or sale of a security, or whose functions relate to the making of any recommendation with respect to such purchase or sale by the Fund managed by such Subadviser. Such provisions may be more restrictive than the provision set forth in the VALIC Code. Material violations of the Subadviser’s code of ethics by a Subadviser’s access persons who are involved with the Fund will be reported to VC I’s Board.
The VALIC Code is available on the EDGAR Database on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. You may also request paper copies from the SEC electronically at publicinfo@sec.gov. A duplicating fee will be assessed for all copies provided by the SEC.
INVESTMENT SUBADVISERS
Subject to the control, supervision and direction of VALIC, subadvisory services are provided as follows:
|
|
|
| Fund Name |
|
Subadviser Name |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”) |
|
|
Wellington Management Company LLP (“Wellington Management”) 1 |
| 1 |
Effective May 1, 2023, GSAM and Wellington Management assumed subadvisory responsibility for the Fund. Prior to May 1, 2023, T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. (“T. Rowe Price”) served as subadviser to the Fund. |
GSAM is an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. Wellington Management is a Delaware limited liability partnership.
Pursuant to the subadvisory agreements VALIC has with each Subadviser and subject to VALIC’s oversight, the Subadvisers will manage the investment and reinvestment of the assets of the Fund, including the evaluation of pertinent economic, statistical, financial and other data, and the determination of industries and companies to be represented in the Fund. Further, each Subadviser will maintain a trading desk and place orders for the purchase and sale of portfolio investments for the Fund, establish accounts with brokers and dealers selected by the Subadviser, or arrange for any other entity to provide a trading desk and to place orders with brokers and dealers selected by the Subadviser and VALIC.
VALIC may terminate any subadvisory agreement with a Subadviser without shareholder approval. Moreover, VC I relies upon an exemptive order from the SEC that permits VALIC, subject to certain conditions, to enter into subadvisory agreements relating to the Fund with unaffiliated subadvisers approved by the Board without obtaining shareholder approval. The exemptive order permits VALIC, subject to the approval of the Board but without shareholder approval, to employ unaffiliated subadvisers for new or existing funds, change the terms of subadvisory agreements with unaffiliated subadvisers or continue the employment of existing unaffiliated subadvisers after events that would otherwise cause an automatic termination of a subadvisory agreement. Shareholders will be notified of any changes that are made pursuant to the exemptive order within 60 days of hiring a new subadviser or making a material change to an existing subadvisory agreement. The order also permits the Fund to disclose fees paid to subadvisers on an aggregate, rather than individual, basis. In addition, pursuant to no-action relief, the SEC Staff has extended multi-manager relief to any affiliated subadviser, provided certain conditions are met. The Fund’s shareholders have approved the Fund’s reliance on the no-action relief. VALIC will determine if and when the Fund should rely on the no-action relief.
VALIC pays each Subadviser a monthly fee with respect to the Fund for which such Subadviser performs services, computed on average daily net assets. As noted above, VALIC relies on an exemptive order that, among other things, permits VC I to disclose to shareholders the Subadvisers’ fees only in the aggregate for the Fund. The aggregate annual rates, as a percentage of daily net assets, of the fees payable by VALIC to a Subadviser for the Fund may vary according to the level of assets of the Fund.
49
The following table sets forth the aggregate subadvisory fees paid to T. Rowe Price by VALIC for the past three fiscal years:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2020 |
|
| Fund Name |
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
|
% of Net
Assets |
|
|
Dollar
Amount |
|
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
|
0.34 |
% |
|
$ |
3,297,050 |
|
|
|
0.37 |
% |
|
$ |
3,532,841 |
|
|
|
0.37 |
% |
|
$ |
3,048,086 |
|
SERVICE AGREEMENTS
Amended and Restated Administrative Services Agreement
VC I has entered into an Amended and Restated Administrative Services Agreement (“Administrative Services Agreement”) with SunAmerica (the “Administrator”) on behalf of the Fund to provide certain accounting and administrative services to the Fund. Pursuant to the Administrative Services Agreement, the Administrator provides administrative services to the Board, regulatory reporting, internal legal and compliance services, fund accounting and related portfolio accounting services, all necessary office space, equipment, personnel, compensation and facilities for handling the affairs of the Fund and other services. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, the Administrator (or its appointed service provider): assists with the preparation of prospectuses, statements of additional information, registration statements, and proxy materials; develops and prepares communications to shareholders, including the annual and semi-annual reports to shareholders; coordinates and supervises the preparation and filing of Fund tax returns; assists with the design, development, and operation of the Fund; prepares the Fund’s financial statements; determines the net asset value of the Fund’s shares; supervises the Fund’s transfer agent with respect to the payment of dividends and other distributions to shareholders; and calculates performance data of the Fund.
Pursuant to the Administrative Services Agreement, VC I pays the Administrator an annual fee of 0.06% based on average daily net assets plus an accounting basis point fee.1 These fees are paid directly by the Fund. For the last three fiscal years ended May 31, the Fund paid the Administrator the following administrative services fees under the Administrative Services Agreement:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund Name |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$643,774 |
|
$637,538 |
|
$545,440 |
| 1 |
Annual fee of 6 basis points based upon the Fund’s average daily net assets, plus the following Accounting Basis Point Fee: |
|
|
|
Accounting Basis Point Fee (Fund complex)†
Net Assets Per Fund |
|
Basis Points |
| First $25 Billion |
|
0.61 |
| Next $75 Billion |
|
0.70 |
| Excess |
|
0.50 |
† Accounting Basis Point Fee is calculated based upon all assets in all registered management investment companies managed and/or administered by the Administrator and VALIC, other than “Funds-of-Funds” and “Feeder Funds.”
Master Transfer Agency and Service Agreement
VC I has entered into a Transfer Agency Agreement (the “TA Agreement”) with VALIC Retirement Services Company (“VRSCO”), an affiliate of VALIC located at 2929 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019, pursuant to which VRSCO provides transfer agency services to the Fund, including shareholder servicing and dividend disbursement services.
For the last three fiscal years ended May 31, the Fund paid VRSCO the following transfer agency fees under the TA Agreement.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund Name |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$3,404 |
|
$1,095 |
|
$2,491 |
50
PORTFOLIO MANAGERS
Other Accounts
The portfolio managers primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the Fund, as provided in the Prospectus (“Portfolio Managers”), are often engaged in the management of various other accounts. The total number of other accounts managed by each Portfolio Manager (whether managed as part of a team or individually) and the total assets in those accounts, as of March 31, 2023, is provided in the table below. If applicable, the total number of accounts and total assets in accounts that have an advisory fee which is all or partly based on the account’s performance is provided in parentheses.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Adviser/ Subadviser |
|
Portfolio Manager |
|
Other Accounts (As of March 31, 2023) |
| |
Registered Investment
Companies |
|
Pooled Investment Vehicles |
|
Other Accounts |
| |
No. of
Accounts |
|
Assets
($ millions) |
|
No. of Accounts |
|
Assets ($ millions) |
|
No. of Accounts |
|
Assets ($ millions) |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
GSAM |
|
Andrew Alford Karhan E. Akcoglu |
|
8
7 |
|
$8,264
$2,591 |
|
0 0 |
|
$0 $0 |
|
9 9 |
|
$7,571 $7,571 |
| |
Wellington
Management |
|
Thomas Simon Matthew Kyller |
|
10
7 |
|
$10,839
$779 |
|
8 8 |
|
$135 $97 |
|
3 1 |
|
$1,417 $71 |
Potential Conflicts of Interest
As shown in the table above, the Portfolio Managers are responsible for managing other accounts for multiple clients, including affiliated clients (“Other Client Accounts”), in addition to the Fund. In certain instances, conflicts may arise in their management of the Fund and such Other Client Accounts. The Portfolio Managers aim to conduct their activities in such a manner that permits them to deal fairly with each of their clients on an overall basis in accordance with applicable securities laws and fiduciary obligations.
| |
• |
|
Trade Allocations. One situation where a conflict may arise between the Fund and Other Client Accounts is in the allocation of trades among the Fund and the Other Client Accounts. For example, VALIC or a Subadviser may determine that there is a security that is suitable for the Fund as well as for Other Client Accounts which have a similar investment objective. Likewise, a particular security may be bought for one or more clients when one or more other clients are selling that same security, which may adversely affect the value of securities held by the Fund. The Fund, VALIC and the Subadvisers have adopted policies and procedures regarding the allocation of trades and brokerage, which the Fund, VALIC and the Subadvisers believe address the conflicts associated with managing multiple accounts for multiple clients (including affiliated clients). The policies and procedures generally require that securities be allocated among the Fund and Other Client Accounts in a manner that is fair, equitable and consistent with their fiduciary obligations to each. |
| |
• |
|
Allocation of Portfolio Managers’ Time. The Portfolio Managers’ management of the Fund and Other Client Accounts may result in a Portfolio Manager devoting a disproportionate amount of time and attention to the management of the Fund and Other Client Accounts if the Fund and Other Client Accounts have different objectives, benchmarks, time horizons, and fees. Generally, VALIC and/or a Subadviser, as the case may be, seek to manage such competing interests for the time and attention of the Portfolio Managers. Although VALIC and a Subadviser do not track the time a Portfolio Manager spends on the Fund or a single Other Client Account, they do periodically assess whether a Portfolio Manager has adequate time and resources to effectively manage all of such Portfolio Manager’s accounts. In certain instances, Portfolio Managers may be employed by two or more employers. |
| |
• |
|
Personal Trading by Portfolio Managers. The management of personal accounts by a Portfolio Manager may give rise to potential conflicts of interest. While generally, VALIC’s and a Subadviser’s Codes of Ethics will impose limits on the ability of a Portfolio Manager to trade for his or her personal account, especially where such trading might give rise to a potential conflict of interest, there is no assurance that VALIC’s and the Subadviser’s Codes of Ethics will eliminate such conflicts. |
Other than the conflicts described above and in the sections below, VC I is not aware of any material conflicts that may arise in connection with each Portfolio Manager’s management of the Fund’s investments and such Other Client Accounts. We believe each Subadviser has adopted procedures reasonably designed to ensure that the Portfolio Managers meet their fiduciary obligations to the Fund and treat the Fund fairly and equitably over time.
51
Compensation of Portfolio Managers
Pursuant to the Subadvisory Agreements, each Subadviser is responsible for paying its own expenses in connection with the management of the Fund, including the compensation of its Portfolio Managers. The structure and method of compensation of the Portfolio Managers is described below.
GSAM. Compensation for GSAM Portfolio Managers is comprised of a base salary and year-end discretionary variable compensation. The base salary is fixed from year to year. Year-end discretionary variable compensation is primarily a function of each Portfolio Manager’s individual performance and his or her contribution to overall team performance; the performance of GSAM and Goldman Sachs; the team’s net revenues for the past year which in part is derived from advisory fees, and for certain accounts, performance-based fees; and anticipated compensation levels among competitor firms. Portfolio Managers are rewarded, in part, for their delivery of investment performance, which is reasonably expected to meet or exceed the expectations of clients and fund shareholders in terms of: excess return over an applicable benchmark, peer group ranking, risk management and factors specific to certain funds such as yield or regional focus. Performance is judged over one-, three- and five-year time horizons.
The benchmark for the Fund is the Russell 1000® Growth Index.
The discretionary variable compensation for Portfolio Managers is also significantly influenced by various factors, including: (1) effective participation in team research discussions and process; and (2) management of risk in alignment with the targeted risk parameters and investment objectives of the Portfolio. Other factors may also be considered including: (1) general client/shareholder orientation, and (2) teamwork and leadership.
As part of their year-end discretionary variable compensation and subject to certain eligibility requirements, GSAM Portfolio Managers may receive deferred equity-based and similar awards, in the form of: (1) shares of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (restricted stock units); and, (2) for certain Portfolio Managers, performance-tracking (or “phantom”) shares of the GSAM mutual funds that they oversee or service. Performance-tracking shares are designed to provide a rate of return (net of fees) equal to that of the fund(s) that a Portfolio Manager manages, or one or more other eligible funds, as determined by senior management, thereby aligning portfolio manager compensation with fund shareholder interests. The awards are subject to vesting requirements, deferred payment and clawback and forfeiture provisions. GSAM, Goldman Sachs or their affiliates expect, but are not required to, hedge the exposure of the performance-tracking shares of a fund by, among other things, purchasing shares of the relevant fund(s).
Other Compensation. In addition to base salary and year-end discretionary variable compensation, the firm has a number of additional benefits in place including (1) a 401k program that enables employees to direct a percentage of their base salary and bonus income into a tax-qualified retirement plan; and (2) investment opportunity programs in which certain professionals may participate subject to certain eligibility requirements.
Conflicts of Interest
GSAM is part of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (together with its affiliates, directors, partners, trustees, managers, members, officers and employees, “Goldman Sachs”) a financial holding company. The involvement of GSAM, Goldman Sachs and their affiliates in the management of, or their interest in, other accounts and other activities of Goldman Sachs will present conflicts of interest with respect to your Fund and will, under certain circumstances, limit your Fund’s investment activities. Goldman Sachs is a worldwide, full service investment banking, broker dealer, asset management and financial services organization and a major participant in global financial markets that provides a wide range of financial services to a substantial and diversified client base that includes corporations, financial institutions, governments, and individuals. Goldman Sachs acts as a broker-dealer, investment adviser, investment banker, underwriter, research provider, administrator, financier, adviser, market maker, trader, prime broker, derivatives dealer, clearing agent, lender, counterparty, agent, principal, distributor, investor or in other commercial capacities for accounts or companies or affiliated or unaffiliated investment funds (including pooled investment vehicles and private funds). In those and other capacities, Goldman Sachs advises and deals with clients and third parties in all markets and transactions and purchases, sells, holds and recommends a broad array of investments, including securities, derivatives, loans, commodities, currencies, credit default swaps, indices, baskets and other financial instruments and products for its own account and for the accounts of clients and of its personnel. In addition, Goldman Sachs has other direct and indirect interests in the global fixed income, currency, commodity, equities, bank loan and other markets and the securities and issuers in which your
52
Fund may directly and indirectly invest. Thus, it is expected that your Fund will have multiple business relationships with and will invest in, engage in transactions with, make voting decisions with respect to, or obtain services from entities for which Goldman Sachs and affiliates perform or seek to perform investment banking or other services.
As manager of your Fund, GSAM receives management fees from the Fund. In addition, GSAM’s affiliates may earn fees from relationships with your Fund.
Although these fees are generally based on asset levels, the fees are not directly contingent on Fund performance, Goldman Sachs will still receive significant compensation from your Fund even if shareholders lose money. Goldman Sachs and its affiliates engage in proprietary trading and advise accounts and funds which have investment objectives similar to those of your Fund and/or which engage in and compete for transactions in the same types of securities, currencies and instruments as your Fund. Goldman Sachs and its affiliates will not have any obligation to make available any information regarding their activities or strategies, or the activities or strategies used for other accounts managed by them, for the benefit of the management of your Fund. The results of your Fund’s investment activities, therefore, will likely differ from those of Goldman Sachs, its affiliates, and other accounts managed by Goldman Sachs, and it is possible that your Fund could sustain losses during periods in which Goldman Sachs and its affiliates and other accounts achieve significant profits on their trading for proprietary or other accounts. In addition, your Fund may enter into transactions in which Goldman Sachs and its affiliates or their other clients have an adverse interest. For example, your Fund may take a long position in a security at the same time that Goldman Sachs and its affiliates or other accounts managed by GSAM take a short position in the same security (or vice versa). These and other transactions undertaken by Goldman Sachs, its affiliates or Goldman Sachs-advised clients may, individually or in the aggregate, adversely impact your Fund. In some cases, such adverse impacts may result from differences in timing of transactions by accounts relative to when a Fund executes transactions in the same securities. Transactions by one or more Goldman Sachs advised clients or GSAM may have the effect of diluting or otherwise disadvantaging the values, prices or investment strategies of your Fund.
Your Fund’s activities will, under certain circumstances, be limited because of regulatory restrictions applicable to Goldman Sachs and its affiliates, and/or their internal policies designed to comply with such restrictions.
As a global financial services firm, Goldman Sachs and its affiliates provide a wide range of investment banking and financial services to issuers of securities and investors in securities. Goldman Sachs, its affiliates and others associated with it are expected to create markets or specialize in, have positions in and/or effect transactions in, securities of issuers held by your Fund, and will likely also perform or seek to perform investment banking and financial services for one or more of those issuers. Goldman Sachs and its affiliates are expected to have business relationships with and purchase or distribute or sell services or products from or to distributors, consultants or others who recommend your Fund or who engage in transactions with or for your Fund.
For a more detailed description of potential conflicts of interest, please refer to the language from GSAM’s ADV Part 2.
Wellington Management
Conflicts of Interest
Individual investment professionals at Wellington Management manage multiple accounts for multiple clients. These accounts may include mutual funds, separate accounts (assets managed on behalf of institutions such as pension funds, insurance companies, foundations, or separately managed account programs sponsored by financial intermediaries), bank common trust accounts, and hedge funds. Each Fund’s managers listed in the prospectus who are primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the Funds (“Investment Professionals”) generally manage accounts in several different investment styles. These accounts may have investment objectives, strategies, time horizons, tax considerations and risk profiles that differ from those of the Funds. The Investment Professionals make investment decisions for each account, including the relevant Fund, based on the investment objectives, policies, practices, benchmarks, cash flows, tax and other relevant investment considerations applicable to that account. Consequently, the Investment Professionals may purchase or sell securities, including IPOs, for one account and not another account, and the performance of securities purchased for one account may vary from the performance of securities purchased for other accounts. Alternatively, these accounts may be managed in a similar fashion to the relevant Fund and thus the accounts may have similar, and in some cases nearly identical, objectives, strategies and/or holdings to that of the relevant Fund.
An Investment Professional or other investment professionals at Wellington Management may place transactions on behalf of other accounts that are directly or indirectly contrary to investment decisions made on behalf of the relevant Fund, or make investment decisions that are similar to those made for the relevant Fund, both of which have the potential to adversely impact the relevant Fund depending on market conditions. For example an Investment Professional may
53
purchase a security in one account while appropriately selling that same security in another account. Similarly, an Investment Professional may purchase the same security for the relevant Fund and one or more other accounts at or about the same time. In those instances the other accounts will have access to their respective holdings prior to the public disclosure of the relevant Fund’s holdings. In addition, some of these accounts have fee structures, including performance fees, which are or have the potential to be higher, in some cases significantly higher, than the fees Wellington Management receives for managing the Funds. Because incentive payments paid by Wellington Management to the Investment Professionals are tied to revenues earned by Wellington Management and, where noted, to the performance achieved by the manager in each account, the incentives associated with any given account may be significantly higher or lower than those associated with other accounts managed by a given Investment Professional. Finally, the Investment Professionals may hold shares or investments in the other pooled investment vehicles and/or other accounts identified above.
Wellington Management’s goal is to meet its fiduciary obligation to treat all clients fairly and provide high quality investment services to all of its clients. Wellington Management has adopted and implemented policies and procedures, including brokerage and trade allocation policies and procedures, which it believes address the conflicts associated with managing multiple accounts for multiple clients. In addition, Wellington Management monitors a variety of areas, including compliance with primary account guidelines, the allocation of IPOs, and compliance with the firm’s Code of Ethics, and places additional investment restrictions on investment professionals who manage hedge funds and certain other accounts. Furthermore, senior investment and business personnel at Wellington Management periodically review the performance of Wellington Management’s investment professionals. Although Wellington Management does not track the time an investment professional spends on a single account, Wellington Management does periodically assess whether an investment professional has adequate time and resources to effectively manage the investment professional’s various client mandates.
Compensation
Wellington Management receives a fee based on the assets under management of each Fund as set forth in the Investment Subadvisory Agreement between Wellington Management and VALIC on behalf of each Fund. Wellington Management pays its Investment Professionals out of its total revenues, including the advisory fees earned with respect to each Fund. The following information relates to the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022.
Wellington Management’s compensation structure is designed to attract and retain high-caliber investment professionals necessary to deliver high quality investment management services to its clients. Wellington Management’s compensation of each Fund’s managers listed in the prospectus who are primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the Funds (“Investment Professionals”) includes a base salary and incentive components. The base salary for each Investment Professional who is a partner (a “Partner”) of Wellington Management Group LLP, the ultimate holding company of Wellington Management, is generally a fixed amount that is determined by the managing partners of Wellington Management Group LLP. The base salary for each other Investment Professional is determined by the Investment Professional’s experience and performance in their role as an Investment Professional. Base salaries for Wellington Management’s employees are reviewed annually and may be adjusted based on the recommendation of an Investment Professional’s manager, using guidelines established by Wellington Management’s Compensation Committee, which has final oversight responsibility for base salaries of employees of the firm. Each Investment Professional is eligible to receive an incentive payment based on the revenues earned by Wellington Management from the Fund managed by the Investment Professional and generally each other account managed by such Investment Professional. Each Investment Professional’s incentive payment relating to the relevant Fund is linked to the gross pre-tax performance of the portion of the Fund managed by the Investment Professional compared to the benchmark index and/or peer group identified below over one, three, and five year periods, with an emphasis on five year results. Wellington Management applies similar incentive compensation structures (although the benchmarks or peer groups, time periods and rates may differ) to other accounts managed by these Investment Professionals, including accounts with performance fees. The incentive paid to the Investment Professionals for the Inflation Protected Fund, which has no performance-related component, is based on the revenues earned by Wellington Management.
Portfolio-based incentives across all accounts managed by an Investment Professional can, and typically do, represent a significant portion of an Investment Professional’s overall compensation; incentive compensation varies significantly by individual and can vary significantly from year to year. The Investment Professionals may also be eligible for bonus payments based on their overall contribution to Wellington Management’s business operations. Senior management at Wellington Management may reward individuals as it deems appropriate based on other factors. Each Partner is eligible to participate in a Partner-funded tax qualified retirement plan, the contributions to which are made pursuant to an actuarial formula. Mr. Simon is a Partner.
54
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Benchmark Index and/or Peer Group for Incentive Period |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
Russell 1000® Growth Index |
Ownership of Portfolio Managers
As of the date of this SAI, the Portfolio Managers of the Fund did not have any ownership interest in the Fund.
PORTFOLIO TRANSACTIONS AND BROKERAGE
VALIC utilizes the assistance of the Subadvisers in selecting brokers or dealers to handle transactions for the Fund. A Subadviser may employ affiliated brokers for portfolio transactions under circumstances described in the Prospectus.
VC I normally enters into principal transactions directly with the issuer or the market-maker.
When the Fund purchases or sells securities or futures contracts on an exchange, it pays a commission to any FCM or broker executing the transaction. When the Fund purchases securities from the issuer, an underwriter usually receives a commission or “concession” paid by the issuer. When the Fund purchases securities from a market-maker, it pays no commission, but the price includes a “spread” or “mark-up” (between the bid and asked price) earned by the market-making dealer on the transaction.
In the OTC market, securities are generally traded on a “net” basis with dealers acting as principals for their own accounts without a stated commission, although the price of a security usually includes a profit to the dealer. The Fund may, however, effect certain “riskless principal transactions” in the OTC market with a stated commission. In underwritten offerings, securities are purchased at a fixed price, which includes an amount of compensation to the underwriter, generally referred to as the underwriter’s concession or discount. On occasion, certain money market instruments may be purchased directly from an issuer, in which case no commissions or discounts are paid.
In purchasing and selling the Fund’s portfolio securities, it is the policy of each Subadviser to seek the best execution at the most favorable price through responsible broker-dealers and, in the case of agency transactions, at competitive commission rates. When selecting brokers or dealers, and in negotiating prices and commissions, each Subadviser considers such factors as: the broker or dealer’s reliability; the quality of the broker or dealer’s execution services on a continuing basis; the rate of the commission; the size and difficulty of the order and the timeliness of execution; and the reliability, integrity, financial condition, general execution, and operational capabilities of that firm and competing broker-dealers. In OTC transactions, each Subadviser places orders directly with the principal market-maker unless it believes the Fund can obtain a better price (or receive better execution of orders) from a broker on an agency basis. In transactions executed on securities or commodities exchanges, each Subadviser seeks the best overall price and execution at the most favorable commission rate (except when higher brokerage commissions are paid to obtain brokerage and research services, as explained below). When a Subadviser believes that more than one firm meets these criteria, the Subadviser may prefer brokers who provide the Subadviser or the Fund with brokerage and research services, described below.
Commission Recapture Program: A commission recapture arrangement includes those arrangements under which products or services (other than execution of securities transactions) or commissions are recaptured for a client from or through a broker-dealer, in exchange for directing the client’s brokerage transactions to that broker-dealer. VC I’s Board has determined that a commission recapture arrangement with Capital Institutional Services, Inc. is in the best interest of the Fund and its shareholders and, therefore, has conveyed the information to each Subadviser. The Fund may participate in a commission recapture arrangement, provided the Portfolio Manager can still obtain the best price and execution for trades. Thus, the Fund may benefit from the products or services or recaptured commissions obtained through the commission recapture arrangement, although there may be other transaction costs, greater spreads, or less favorable net prices on transactions. As long as the trader executing the transaction for the Fund indicates that it is a directed brokerage transaction, the Fund will get a percentage of commissions paid on either domestic trades or international trades credited back to the Fund. The brokerage of the Fund will not be used to help pay the expenses of any other fund. VALIC will continue to waive its fees or reimburse expenses for the Fund for which it has agreed to do so. All expenses paid through the commission recapture arrangement will be over and above such waivers and/or reimbursements, so that VALIC will not receive any direct or indirect economic benefit from the commission recapture arrangement.
55
The following chart reflects the commission recapture activity for the last three fiscal years ended May 31.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Fiscal Year Ending 05/31/2022 |
|
% of Average Net Assets 05/31/2022 |
|
Fiscal Year Ending 05/31/2021 |
|
% of Average Net Assets 05/31/2021 |
|
Fiscal Year Ending 05/31/2020 |
|
% of Average Net Assets 05/31/2020 |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Research Services: The Subadvisers may cause the Fund to pay a broker-dealer a commission (for executing a securities transaction) that is greater than the commission another broker-dealer would have received for executing the same transaction, if the Subadvisers determine in good faith that the greater commission paid to the first broker-dealer is reasonable in relation to the value of brokerage and research services provided to the Subadvisers viewed in terms of either that particular transaction or the overall responsibilities of the Subadvisers. The Subadvisers receive a wide range of research services from broker-dealers, including: information on securities markets, the economy and individual companies; statistical information; accounting and tax law interpretations; technical market action; pricing and appraisal services; and credit analyses.
The Subadvisers evaluate whether such research services provide lawful and appropriate assistance to it in the performance of its investment decision-making responsibilities for the Fund. The Subadvisers will not cause the Fund to pay higher commissions without first determining, in good faith, that the cost is reasonable considering the brokerage and research services provided, with respect to either the particular transaction or the Subadvisers’ overall responsibilities with respect to accounts for which it exercises investment discretion. The Subadvisers receive research services at no cost and cannot assign any specific monetary value to them; nevertheless, the Subadvisers believe these supplemental investment research services are essential to the Subadvisers’ ability to provide high quality portfolio management to the Fund. Research services furnished by broker-dealers through whom the Fund affects securities transactions may be used by the Subadvisers in servicing other clients as well as the Fund, and the Subadvisers may not use all such services in managing the Fund. The Fund may benefit from research services obtained through securities transactions effected by the Subadvisers on behalf of its other clients.
A Subadviser may obtain research from brokers or non-broker-dealers by entering into commission sharing arrangements (“CSAs”). Under a CSA, the executing broker agrees that part of the commissions it earns on certain equity trades will be allocated to one or more research providers as payment for research. CSAs allow a Subadviser to direct brokers to pool commissions that are generated from orders executed at that broker (for equity transactions on behalf of the Fund and other client accounts), and then periodically direct the broker to pay third-party research providers for research. The use of CSAs by a Subadviser is subject to the Subadviser’s best execution obligations to the Fund.
The amount of brokerage commissions paid, the quality of execution, the nature and quality of research services provided, and the amount of commissions paid to firms providing research services are reviewed quarterly by VC I’s Board.
The following tables list the brokerage commissions paid by the Fund on portfolio transactions for the last three fiscal years ended May 31. Unless otherwise noted, the Fund paid no brokerage commissions to brokers for research services provided to the Subadvisers or to VALIC.
2022 Brokerage Commissions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Aggregate Brokerage Commission |
|
Amount paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Commissions paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Amount of Transactions Involving Payments of Commissions to Affiliated Broker-Dealers |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$59,179 |
|
$— |
|
0.00% |
|
0.00% |
56
2021 Brokerage Commissions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Aggregate Brokerage Commission |
|
Amount paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Commissions paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Amount of Transactions Involving Payments of Commissions to Affiliated Broker-Dealers |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$83,545 |
|
$— |
|
0.00% |
|
0.00% |
2020 Brokerage Commissions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Aggregate Brokerage Commission |
|
Amount paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Commissions paid to Affiliated Broker-Dealers* |
|
Percentage of Amount of Transactions Involving Payments of Commissions to Affiliated Broker-Dealers |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$79,142 |
|
$— |
|
0.00% |
|
0.00% |
| * |
There were no affiliated broker-dealer transactions. |
In addition, for the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Fund directed the following amounts of portfolio securities transactions, and commissions paid thereon, to broker-dealers which provided research services to the Fund’s Subadvisers:
|
|
|
|
|
| Portfolio |
|
Gross Dollar
Value of
Purchase/ Sales Directed to
Research
Providers
($) |
|
Dollar Amount of Commissions
Directed to Research
Providers ($) |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
$0 |
|
$0 |
The following table sets forth the value of the Fund’s holdings of securities of VC I’s regular brokers and dealers (as defined under Rule 10b-1 under the 1940 Act) and their parents as of May 31, 2022.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Fund |
|
Broker Dealer |
|
Value (000’s) |
|
Debt/Equity |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. |
|
$8,496 |
|
Equity |
|
|
State Street Corp. |
|
2,244 |
|
Equity |
|
|
T. Rowe Price Investment Services, Inc. |
|
201 |
|
Equity |
Occasions may arise when the Fund, or other accounts that may be considered affiliated persons of the Fund under the 1940 Act, desire to purchase or sell the same portfolio security at approximately the same time. In such event, generally, the assets actually purchased or sold may be allocated among accounts on a good faith equitable basis at the discretion of the account’s adviser pursuant to written procedures. In some cases, this system may adversely affect the price or size of the position obtainable for the Fund. However, the Fund may, alternatively, benefit from lower broker’s commissions and/or correspondingly lower costs for brokerage and research services by engaging in such combined transactions. A Subadviser will not engage in a transaction as described above unless, in the Subadviser’s opinion, the results of the transaction will, on the whole, be in the best interest of the Fund.
OFFERING, PURCHASE, AND REDEMPTION OF FUND SHARES
Shares of the Fund are sold in a continuous offering. Pursuant to a Distribution Agreement, ACS acts without remuneration as VC I’s agent in the distribution of Fund shares to the VALIC separate accounts, separate accounts of other life insurance companies that may or may not be affiliated with VALIC, and, subject to applicable law, to qualified pension and retirement plans and individual retirement accounts outside of the separate account context (the “Distribution Agreement”). Under the
57
terms of the Distribution Agreement, the Fund pays for, among other expenses, all expenses of the offering of its shares incurred in connection with (1) the registration of the Fund or the registration or qualification of the Fund’s shares for offer or sale under the federal securities laws and the securities laws of any state or other jurisdiction in which the Fund’s shares are offered; (2) printing and distributing the Fund’s prospectuses to existing participants as required under the federal securities laws and applicable securities laws of any state or other jurisdiction; and (3) preparation, printing and distribution of proxy statements, notices and reports; and (4) issuance of the Fund’s shares, including share issue and transfer taxes.
ACS, or one of its affiliates, pays all expenses incurred by it attributable to any activity primarily intended to result in the sale of shares of the Fund and in connection with the performance of distribution duties or will promptly reimburse the Fund for all expenses in connection with (1) printing and distributing prospectuses utilized in marketing the Fund to eligible purchasers; (2) preparation, printing and distribution of advertising and sales literature for the use in the offering of the Fund’s shares and printing and distribution of reports to purchasers and/or participants used as sales literature; (3) qualification of ACS as a distributor or broker or dealer under applicable federal and state securities laws; (4) any investment program of the Fund, including the reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions, to the extent such expenses exceed the Fund’s normal cost of issuing its shares; and all other expenses in connection with offering for sale and sale of the Fund’s shares, which have not been specifically allocated to the Fund. The Fund does not compensate ACS for services provided under the Distribution Agreement. The distribution agreement between ACS and VC I provides that it shall continue in force from year to year, provided that such continuance is approved at least annually (a) (i) by the Board of VC I, or (ii) by vote of a majority of VC I’s outstanding voting securities (as defined in the 1940 Act) and (b) by the affirmative vote of a majority of VC I’s Directors who are not “interested persons” (as defined in the 1940 Act) of VC I by votes cast in person at a meeting called for such purpose. The distribution agreement may be terminated at any time, without penalty, by a vote of the Board of VC I or by a vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of VC I, or by ACS, on sixty days’ written notice to the other party. The Distribution Agreement also provides that it shall automatically terminate in the event of its assignment.
Payments of surrender values, as well as lump sum payments available under the annuity options of the Contracts, may be suspended or postponed at any time when redemption of shares is suspended. Normally, VC I redeems Fund shares within seven days when the request is received in good order, but may postpone redemptions beyond seven days when: (i) the New York Stock Exchange is closed for other than weekends and customary holidays, or trading on the New York Stock Exchange becomes restricted; (ii) an emergency exists making disposal or valuation of the Fund’s assets not reasonably practicable; or (iii) the SEC has so permitted by order for the protection of VC I’s shareholders.
VC I redeems Fund shares for cash. VC I, pursuant to Rule 18f-1 under the 1940 Act, has filed a notification of election on Form 18f-1. Pursuant to this election, VC I has committed to pay the separate accounts, in cash, all redemptions made during any 90 day period, up to the lesser of $250,000 or 1% of VC I’s net asset value. This election is irrevocable while Rule 18f-1 is in effect, unless the SEC by order permits the withdrawal of the election.
All shares are offered for sale and redeemed at net asset value. Net asset value per share is determined by dividing the net assets of the Fund by the number of the Fund’s outstanding shares at such time.
DETERMINATION OF NET ASSET VALUE
Shares of the Fund are valued at least daily as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (generally, 4:00 p.m. Eastern time). The Fund calculates the net asset value of its shares by dividing the total value of its net assets by the number of shares outstanding. The days and times of such computation may, in the future, be changed by the Directors in the event that the portfolio securities are traded in significant amounts in markets other than the New York Stock Exchange, or on days or at times other than those during which the New York Stock Exchange is open for trading. The Board designated VALIC as its “valuation designee,” subject to its oversight. VALIC utilizes the Fund’s policies and procedures (the “PRC Procedures”) for valuing the securities and other assets held by the Fund, including procedures for the fair valuation of securities and other assets for which market quotations are not readily available or are unreliable. The PRC Procedures provide for the establishment of a pricing review committee which is responsible for, among other things, making certain determinations in connection with the Fund’s fair valuation procedures. There is no single standard for making fair value determinations, which may result in prices that vary from those of the Fund. A description of the pricing procedures that are generally used to value the securities held by the Fund are described below.
58
Stocks are generally valued based upon closing sales prices reported on recognized securities exchanges on which the securities are principally traded. Stocks listed on the NASDAQ are valued using the NASDAQ Official Closing Price (“NOCP”). Generally, the NOCP will be the last sale price unless the reported trade for the stock is outside the range of the bid/ask price. In such cases, the NOCP will be normalized to the nearer of the bid or ask price. For listed securities having no sales reported and for unlisted securities, such securities will be valued based upon the last reported bid price.
As of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange, securities traded primarily on security exchanges outside the United States are valued at the last sale price on such exchanges on the day of valuation, or if there is no sale on the day of valuation, at the last-reported bid price. If a security’s price is available from more than one exchange, a portfolio uses the exchange that is the primary market for the security. However, depending on the foreign market, closing prices may be up to 15 hours old when they are used to price the Fund’s shares, and the Fund may determine that certain closing prices do not reflect the fair value of the security. This determination will be based on review of a number of factors, including developments in foreign markets, the performance of U.S. securities markets, and the performance of instruments trading in U.S. markets that represent foreign securities and baskets of foreign securities. If the Fund determines that closing prices do not reflect the fair value of the securities, the valuation designee will adjust the previous closing prices in accordance with the Fund’s pricing procedures to reflect what it believes to be the fair value of the securities as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange. The Fund may also fair value securities in other situations, for example, when a particular foreign market is closed but the Fund is open. For foreign equity securities and foreign equity futures contracts, the Fund uses an outside pricing service to provide it with closing market prices and information used for adjusting those prices.
Bonds, debentures and other debt securities are valued at evaluated bid prices obtained for the day of valuation from a pricing service approved by the valuation designee. The pricing service may use valuation models or matrix pricing which considers information with respect to comparable bond and note transactions, quotations from bond dealers, or by reference to other securities that are considered comparable in such characteristics as rating, interest rate, and maturity date, option adjusted spread models, prepayments projections, interest rate spreads, and yield curves to determine current value. If a price is unavailable from a pricing service approved by the valuation designee, the securities may be priced at the mean of two independent quotes obtained from brokers.
Senior floating rate loans are valued at the average of available bids in the market for such senior floating rate loans, as provided by a loan pricing service approved by the valuation designee.
Investments in registered investment companies that do not trade on an exchange are valued at the end of day net asset value per share. Investments in registered investment companies that trade on an exchange are valued at the last sales price or official closing price as of the close of the customary trading session on the exchange where the security is principally traded.
Futures contracts traded on national securities exchanges are valued at the quoted daily settlement price established by the exchange on which they trade reported by a pricing service approved by the valuation designee. Option contracts traded on national securities exchanges are valued at the mean of the last bid and ask price reported by a pricing service approved by the valuation designee as of the close of the exchange on which they are traded. Option contracts traded over the counter will be valued based upon the average of quotations received from at least two brokers in such securities or currencies. Option contracts on swaps and other option derivatives (i.e., straddle options) are valued at a mid-valuation provided by a pricing service approved by the valuation designee. Swap contracts traded on national securities exchanges are valued at the closing price of the exchange on which they are traded or if a closing price of the exchange is not available, the swap will be valued using a mid-valuation provided by a pricing service approved by the valuation designee. Swap contracts traded over the counter will be valued at a mid-valuation provided by a pricing service approved by the valuation designee. Forward foreign currency contracts (“forward contracts”) are valued at the 4:00 p.m. eastern time forward rate.
59
Securities for which market quotations are not readily available or if a development/significant event occurs that may significantly impact the value of the security, then these securities are valued as determined pursuant to procedures adopted in good faith by VC I’s Board. There is no single standard for making fair value determinations, which may result in prices that vary from those of other funds.
The Fund’s liabilities, including proper accruals of expense times, are deducted from total assets. The net asset value of the Fund is divided by the total number of shares outstanding to arrive at the net asset value per share.
ACCOUNTING AND TAX TREATMENT
Under the Code, the Fund is treated as a separate entity, and as a regulated investment company if qualification requirements are met. To qualify as a regulated investment company, the Fund must, among other things, (a) derive at least 90% of its gross income in each taxable year from dividends, interest, payments with respect to securities loans and gains from the sale or other disposition of stock or securities or foreign currencies, other income (including, but not limited to, gains from options, futures or forward contracts) derived with respect to its business of investing in such stock, securities or currencies and net income derived from interests in “qualified publicly traded partnerships” (i.e., partnerships that are traded on an established securities market or tradable on a secondary market, other than partnerships that derive 90% of their income from interest, dividends, capital gains, and other traditionally permitted mutual fund income); and (b) diversify its holdings so that, at the end of each quarter of the Fund’s taxable year, (i) at least 50% of the market value of the Fund’s assets is represented by cash, securities of other regulated investment companies, U.S. Government securities and other securities, with such other securities limited, in respect of any one issuer, to an amount not greater than 5% of the Fund’s assets and not greater than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer and (ii) not more than 25% of the value of its assets is invested in the securities (other than U.S. Government securities or securities of other regulated investment companies) of any one issuer, any two or more issuers of which 20% or more of the voting stock is held by the Fund and that are determined to be engaged in the same or similar trades or businesses or related trades or businesses, or in the securities of one or more qualified publicly traded partnerships.
Although in general the passive loss rules of the Code do not apply to regulated investment companies, such rules do apply to a regulated investment company with respect to items attributable to an interest in a qualified publicly traded partnership. Fund investments in partnerships, including in qualified publicly traded partnerships, may result in the Fund’s being subject to state, local or foreign income, and franchise or withholding tax liabilities.
So long as the Fund qualifies as a regulated investment company, the Fund will not be subject to federal income tax on the net investment company taxable income or net capital gains (calculated before deductions for dividends paid) distributed to shareholders as ordinary income dividends or capital gain dividends, provided that it distributes to its shareholders at least 90% of its net investment income and 90% of its net exempt interest income for the taxable year. Dividends from net investment income and capital gain distributions, if any, are paid annually. All distributions are reinvested in shares (of the same class) of the Fund at net asset value unless the transfer agent is instructed otherwise by the owner of the shares.
If, in any taxable year, the Fund fails to qualify as a regulated investment company under the Code or fails to meet the distribution requirement, it will be taxed in the same manner as an ordinary corporation and distributions to its shareholders will not be deductible by the Fund in computing its taxable income. In addition, in the event of a failure to qualify, the Fund’s distributions, to the extent derived from the Fund’s current or accumulated earnings and profits, including any distributions of net long-term capital gains, will be taxable to shareholders as dividend income. Moreover, if the Fund fails to qualify as a regulated investment company in any year, it must pay out its earnings and profits accumulated in that year in order to qualify again as a regulated investment company. If the Fund fails to qualify as a regulated investment company for a period greater than two taxable years, the Fund may be required to recognize any net built-in gains with respect to certain of its assets (i.e., the excess of the aggregate gains, including items of income, over aggregate losses that would have been realized with respect to such assets if the Fund had been liquidated) if it qualifies as a regulated investment company in a subsequent year; various remedial opportunities may be available. Further, if the Fund should fail to qualify as a regulated investment company, the Fund would be considered as a single investment, which may result in Contracts invested in the Fund not being treated as annuity, endowment or life insurance contracts under the Code. All income and gain inside the Contract would be taxed currently to the holder, and the holder would remain subject to taxation thereafter even if the contract later becomes adequately diversified.
60
Generally, a regulated investment company must timely distribute substantially all of its ordinary income and capital gains in accordance with a calendar year distribution requirement in order to avoid imposition of a nondeductible 4% excise tax. However, the excise tax generally does not apply to regulated investment companies whose only shareholders are certain tax-exempt trusts or segregated asset accounts of life insurance companies held in connection with variable contracts. In order to avoid imposition of the excise tax, the Fund intends to qualify for this exemption or to comply with the calendar year distribution requirement.
The Fund may sell its shares directly to separate accounts established and maintained by insurance companies for the purpose of funding variable annuity and variable life insurance contracts and to certain tax qualified pension and retirement plans. A variable contract must meet certain diversification requirements in order to maintain its favorable tax status. In particular, a separate account backing a variable contract may not invest more than 55% of its assets in the securities of any one issuer, or 70% in two issuers, 80% in three, or 90% in four. Generally, all securities of the same issuer are treated as a single investment. For the purposes of Section 817(h), obligations of the U.S. Treasury and of each U.S. Government agency or instrumentality are treated as securities of separate issuers. If shares of the Fund are not sold outside of the very limited group consisting of separate accounts backing variable contracts, tax qualified retirement plans, and a few other specialized categories, then in making the diversification test the separate account backing the contract is treated as owning its proportional share of the assets of the Fund; this makes the diversification test relatively easy to meet. If the shares are owned outside the permitted group, then the Fund itself is the issuer of securities owned by the separate account and the diversification test may be much harder to meet. Failure to meet the diversification requirements has the unfavorable tax consequences described in the last sentence of the fourth paragraph of this section. In addition, if the owner of a variable contract has too much investment power over the investments in the separate account which backs the contract, the owner will be taxed currently on the income earned under his or her contract.
The capital losses of the Fund, if any, do not flow through to shareholders. Rather, the Fund may use its capital losses, subject to applicable limitations, to offset its capital gains without being required to pay taxes on or distribute to shareholders such gains that are offset by the losses. If the Fund has a “net capital loss” (that is, capital losses in excess of capital gains) for a taxable year, the excess (if any) of the Fund’s net short-term capital losses over its net long-term capital gains is treated as a short-term capital loss arising on the first day of the Fund’s next taxable year, and the excess (if any) of the Fund’s net long-term capital losses over its net short-term capital gains is treated as a long-term capital loss arising on the first day of the Fund’s next taxable year.
Since the shares of the Fund are offered only in connection with the Contracts, no discussion is set forth herein as to the U.S. federal income tax consequences at the Contract holder level. For information concerning the U.S. federal income tax consequences to purchasers of the Contracts, see the Prospectus for such Contracts. Purchasers of the Contracts should consult their tax advisors regarding specific questions as to federal, state and local taxes.
The Fund may invest in debt securities issued at a discount or providing for deferred interest, which may result in income to the Fund equal, generally, to a portion of the excess of the face value of the securities over the issue price thereof (“original issue discount”) each year that the securities are held, even though the Fund receives no actual interest payments thereon. Original issue discount is treated as income earned by the Fund and, therefore, is subject to distribution requirements of the Code applicable to regulated investment companies. Since the original issue discount income earned by the Fund in a taxable year may not be represented by cash income, the Fund may have to dispose of securities, which it might otherwise have continued to hold, or borrow to generate cash in order to satisfy its distribution requirements. In addition, the Fund’s investment in foreign currencies or foreign currency denominated or referenced debt securities and contingent payment or inflation-indexed debt instruments also may accelerate the Fund’s recognition of taxable income in excess of cash generated by such investments.
61
Options, forward contracts, futures contracts and foreign currency transactions entered into by the Fund will be subject to special tax rules. These rules may accelerate income to the Fund; defer Fund losses; cause adjustments in the holding periods of Fund securities; convert capital gain into ordinary income; and/or convert short-term capital losses into long-term capital losses. As a result, these rules could affect the amount, timing and character of distributions by the Fund.
In certain situations, the Fund may, for a taxable year, defer all or a portion of its capital losses and currency losses realized after October until the next taxable year in computing its investment company taxable income and net capital gain, which will defer the recognition of such realized losses. Such deferrals and other rules regarding gains and losses realized after October may affect the tax character of shareholder distributions.
Under the Code, gains or losses attributable to fluctuations in exchange rates which occur between the time the Fund accrues interest or other receivables or accrues expenses or other liabilities denominated in a foreign currency and the time the Fund actually collects such receivables or pays such liabilities are treated as ordinary income or ordinary loss. Similarly, gains or losses from sales of currencies or dispositions of debt securities or certain forward contracts, futures contracts, options or similar financial instruments denominated in a foreign currency or determined by reference to the value of one or several foreign currencies also are treated as ordinary income or loss.
REITs in which the Fund invests may hold residual interests in real estate mortgage investment conduits (“REMICs”). Certain types of income received by the Fund from REITs, REMICs, taxable mortgage pools or other investments may cause the Fund to designate some or all of its distributions as “excess inclusion income.” To shareholders of the Fund, such excess inclusion income may (1) constitute taxable income, as unrelated business taxable income; (2) not be offset by otherwise allowable deductions for tax purposes; (3) not be eligible for reduced U.S. withholding for non-U.S. shareholders even from tax treaty countries; and (4) cause the Fund to be subject to tax if certain “disqualified organizations” as defined by the Code are shareholders of the Fund.
The Code includes special rules applicable to the listed non-equity options, regulated futures contracts, and options on futures contracts that the Fund may write, purchase or sell. Such options and contracts are classified as Section 1256 contracts under the Code. The character of gain or loss resulting from the sale, disposition, closing out, expiration or other termination of Section 1256 contracts, except forward foreign currency exchange contracts, is generally treated as long-term capital gain or loss to the extent of 60% thereof and short-term capital gain or loss to the extent of 40% thereof (“60/40 gain or loss”). Such contracts, when held by the Fund at the end of a fiscal year, generally are required to be treated as sold at market value on the last day of such fiscal year for federal income tax purposes (“marked-to-market”). OTC options are not classified as Section 1256 contracts and are not subject to the marked-to-market rule or to 60/40 gain or loss treatment. Any gains or losses recognized by the Fund from transactions in OTC options written by the Fund generally constitute short-term capital gains or losses. Any gain or loss recognized by the Fund from transactions in OTC options purchased by the Fund generally has the same character as the property to which the option relates has in the hands of the Fund (or would have if acquired by the Fund). When call options written, or put options purchased, by the Fund are exercised, the gain or loss realized on the sale of the underlying securities may be either short-term or long-term, depending on the holding period of the securities. In determining the amount of such gain or loss, the sales proceeds are reduced by the premium paid for the OTC puts or increased by the premium received for OTC calls.
A substantial portion of the Fund’s transactions in options, futures contracts and options on futures contracts, particularly its hedging transactions, may constitute “straddles” which are defined in the Code as offsetting positions with respect to personal property. A straddle in which at least one (but not all) of the positions is a Section 1256 contract would constitute a “mixed straddle” under the Code. The Code generally provides with respect to straddles (i) “loss deferral” rules which may postpone recognition for tax purposes of losses from certain closing purchase transactions or other dispositions of a position in the straddle to the extent of unrealized gains in the offsetting position, (ii) “wash sale” rules which may postpone recognition for tax purposes of losses where a position is sold and a new offsetting position is acquired within a prescribed period, (iii) “short sale” rules which may terminate the holding period of securities owned by the Fund when offsetting positions are established and which may convert certain losses from short-term to long-term, and (iv) “conversion transaction” rules which may treat all or a portion of the gain on a transaction as ordinary income rather than as capital gains. The Code provides that certain elections may be made for mixed straddles that can alter the character of the capital gain or loss recognized upon disposition of positions which form part of a straddle. Certain other elections also are provided in the Code; no determination has been reached to make any of these elections.
62
Code Section 1259 requires the recognition of gain if the Fund makes a “constructive sale” of an appreciated financial position (e.g., stock). The Fund generally will be considered to make a constructive sale of an appreciated financial position if it sells the same or substantially identical property short, enters into a futures or forward contract to deliver the same or substantially identical property, or enters into certain other similar transactions.
Under the “wash sale” rule, losses incurred by the Fund on the sale of (or on a contract or option to sell) stock or securities are not deductible if, within a 61-day period beginning 30 days before and ending 30 days after the date of the sale, the Fund acquires or has entered into a contract or option to acquire stock or securities that are substantially identical. In such a case, the basis of the stock or securities acquired by the Fund will be adjusted to reflect the disallowed loss.
In general, gain or loss on a short sale, to the extent permitted, is recognized when the Fund closes the sale by delivering the borrowed property to the lender, not when the borrowed property is sold. Gain or loss from a short sale is generally considered as capital gain or loss to the extent that the property used to close the short sale constitutes a capital asset in the Fund’s hands. Except with respect to certain situations where the property used by the Fund to close a short sale has a long-term holding period on the date of the short sale, special rules would generally treat the gains on short sales as short-term capital gains. These rules may also terminate the running of the holding period of “substantially identical property” held by the Fund. Moreover, a loss on a short sale will be treated as a long-term capital loss if, on the date of the short sale, “substantially identical property” has been held by the Fund for more than one year. In general, the Fund will not be permitted to deduct payments made to reimburse the lender of securities for dividends paid on borrowed stock if the short sale is closed on or before the 45th day after the short sale is entered into.
As a result of entering into swap contracts, the Fund may make or receive periodic net payments. The Fund may also make or receive a payment when a swap is terminated prior to maturity through an assignment of the swap or other closing transaction. Periodic net payments will generally constitute ordinary income or deductions, while termination of a swap will generally result in capital gain or loss (which will be a long-term capital gain or loss if the Fund has been a party to the swap for more than one year). With respect to certain types of swaps, the Fund may be required to currently recognize income or loss with respect to future payments on such swaps or may elect under certain circumstances to mark such swaps to market annually for tax purposes as ordinary income or loss. The tax treatment of many types of credit default swaps is uncertain.
A PFIC is a foreign corporation that, in general, meets either of the following tests: (a) at least 75% of its gross income is passive or (b) an average of at least 50% of its assets produce, or are held for the production of, passive income. If the Fund acquires and holds stock in a PFIC beyond the end of the year of its acquisition, the Fund will be subject to federal income tax on a portion of any “excess distribution” received on the stock or on any gain from disposition of the stock (collectively, the “PFIC income”), plus a certain interest charge, even if the Fund distributes the PFIC income as a taxable dividend to its shareholders. The balance of the PFIC income will be included in the Fund’s investment company taxable income and, accordingly, will not be taxable to it to the extent that income is distributed to its shareholders. The Fund may make a mark-to-market election with respect to any stock it holds of a PFIC, if such stock is marketable (as defined by the Code for purposes of such election). For these purposes, all stock in a PFIC that is owned directly or indirectly by a regulated investment company is treated as marketable stock. If the election is in effect, at the end of the Fund’s taxable year, the Fund will recognize annually the amount of mark-to-market gains, if any, with respect to PFIC stock as ordinary income. No ordinary loss will be recognized on the marking to market of PFIC stock, except to the extent of gains recognized in prior years. Alternatively, the Fund may elect to treat any PFIC in which it invests as a “qualified electing fund,” in which case, in lieu of the foregoing tax and interest obligation, the Fund will be required to include in its income each year its pro rata share of the qualified electing fund’s annual ordinary earnings and net capital gain, even if they are not distributed to the Fund; those amounts would be subject to the distribution requirements applicable to the Fund described above. In order to make this election, the Fund would be required to obtain certain information from the PFIC, which, in many cases, may be difficult to do.
Income received by the Fund from sources within foreign countries may be subject to withholding and other taxes imposed by such countries. Income tax treaties between certain countries and the United States may reduce or eliminate such taxes. It is impossible to determine in advance the effective rate of foreign tax to which the Fund will be subject, since the amount of the Fund assets to be invested in various countries is not known. Shareholders are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding specific questions as to federal, state and local taxes.
63
OTHER INFORMATION
Shareholder Reports
Annual Reports containing audited financial statements of the Fund and Semi-Annual Reports containing unaudited financial statements, as well as proxy materials, are sent to Contract owners, annuitants, or beneficiaries as appropriate. The Fund’s Annual Report dated May 31, 2022 and Semi-Annual Report dated November 30, 2022 are incorporated by reference into this SAI.
Voting and Other Rights
VC I has an authorized capitalization of 37,250,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.01 par value per share. Each class of stock is comprised of 750 million to 1 billion shares each. Each of the classes of stock corresponds to one of the series and represents an ownership interest in that series.
Each outstanding share has one vote on all matters that shareholders vote on. Participants vote on these matters indirectly, by voting their units. The way participants vote their units depends on their Contract or Plan. See your Contract prospectus or Plan document for specific details When a matter comes up for vote, the separate account will vote its shares in the same proportion as the unit votes it actually receives. If VALIC determines that it may, under the current interpretation of the 1940 Act, vote shares directly instead of voting through its units, it may decide to vote that way.
Maryland law does not require VC I to hold regular, annual shareholder meetings. However, VC I must hold shareholder meetings on the following matters: (a) to approve certain agreements as required by the 1940 Act; (b) to change fundamental investment restrictions; and (c) to fill vacancies on VC I’s Board if the shareholders have elected less than a majority of the Directors.
Shareholders may call a meeting to remove a Director from the Board if at least 10% of the outstanding shares of all of the series vote to have this meeting. Then, to remove a Director at the meeting, at least 67% of all the outstanding shares of all the series must vote in favor of removing the Director.
VC I will assist in shareholder communications.
Control Persons and Principal Holders of Securities
VALIC Separate Account A (a registered separate account of VALIC) ownership of more than 25% of the outstanding shares may result in VALIC being deemed a controlling entity of the Fund as that term is defined in the 1940 Act. Such control will dilute the effect of the votes of other shareholders, Contract owners and beneficiaries.
As of April 14, 2023, VALIC, a stock life insurance company organized under the laws of the state of Texas with an address of 2929 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019, American General Life Insurance Company, a stock life insurance company organized under the laws of the state of Texas with an address of 2727-A Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019 (“AGL”), and The United States Life Insurance Company in the City of New York, a stock life insurance company organized under laws of the state of New York with an address of 28 Liberty Street, Floor 45, New York, NY 10005-1400 (“USL”) through their insurance company separate accounts, and the Conservative Growth Lifestyle Fund (“VCG”), Moderate Growth Lifestyle Fund (“VMG”), Aggressive Growth Lifestyle Fund (“VAG”) and Dynamic Allocation Fund (“VDA”) each an independent fund, with an address of 2929 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019, each of which is managed as a “fund of funds” for which VALIC serves as investment adviser, owned over five percent of the outstanding shares of the Fund:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
VALIC |
|
AGL |
|
USL |
|
VAG |
|
VCG |
|
VDA |
|
VMG |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
87.70% |
|
* |
|
— |
|
* |
|
* |
|
* |
|
5.72% |
| * |
Less than 5% ownership. |
As of April 14, 2023, the other shareholders of the Fund included separate accounts sponsored by VALIC and its affiliates, IRAs and Plans. None of these other shareholders owned of record more than 5% of any Fund’s outstanding shares.
64
Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures
Proxy Voting Responsibility
VC I has adopted policies and procedures for the voting of proxies relating to Fund securities (the “Policies”). The Policies were drafted according to recommendations by SunAmerica, VC I’s administrator, and an independent proxy voting agent. The Policies enable the Fund to vote proxies in a manner consistent with the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders. A committee has been established (the “Proxy Voting Committee”) to administer the voting of Fund proxies in accordance with the Policies. The Proxy Voting Committee will consist of a member of SunAmerica’s Investment Management Department, at least one member of the Legal and Compliance Departments, and at least one person who oversees sub-advisers or their designees.
The Proxy Voting Committee has engaged the services of an independent voting agent to assist in issue analyses, vote recommendations for proxy proposals, and to assist the Fund with certain responsibilities including recordkeeping of proxy votes.
The Fund is generally a passive investor in holding portfolio securities, seeking to maximize shareholder value, but not necessarily to exercise control over the issuers of portfolio securities, or otherwise advance a particular agenda. Except for funds with “social” or “ESG” investment strategies, a fund generally will abstain on “environmental,” “social” and or “social and environmental” (collectively “ESG Proposals”) issues proposals unless otherwise indicated in the Guidelines (as defined below) or as determined by the Proxy Voting Committee pursuant to the Policies. The terms “environmental, “social” and “social and environmental” with respect to issue proposals have the meanings assigned to those terms by the independent proxy voting agent.
In addition, in accordance with local law or business practices, many foreign companies prevent the sales of shares that have been voted for a certain period beginning prior to the shareholder meeting and ending on the day following the meeting. The Board has determined that the costs of voting proxies with respect to such shares of foreign companies generally outweigh any benefits that may be achieved by voting such proxies. The costs of voting such proxies include the potentially serious portfolio management consequences of reduced flexibility to sell the shares at the most advantageous time for the Fund. As a result, such proxies generally will not be voted in the absence of an unusual, significant vote of compelling economic importance.
Case-By-Case Voting Matters
The Proxy Voting Committee has established proxy voting guidelines (the “Guidelines”), which identify certain vote items to be determined on a case-by-case basis. In these circumstances, and in proposals not specifically addressed by the Policies, the Proxy Voting Committee generally will rely on guidance or a recommendation from the independent proxy voting agent or other sources. In these instances, the Proxy Voting Committee will recommend the vote that will maximize value for, and is in the best interests of, the Fund’s shareholders.
The Proxy Voting Committee has established Guidelines specifically for funds with social or ESG investment strategies. The Proxy Coting Committee will generally approach ESG Proposals on behalf of funds with social or ESG investment strategies on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration whether implementation of the proposal is likely to enhance or protect shareholder value. The Guidelines for ESG Proposals on behalf of funds with social or ESG investment strategies include specific approaches with respect to consumer issues and public safety, environment and energy, general corporate issues, labor standards and human rights, military business, and workplace diversity.
Examples of the Fund’s Positions on Voting Matters
Consistent with the approaches described above, the following are examples of the Fund’s voting positions on specific matters:
| |
• |
Vote on a case-by-case basis on proposals to increase authorized common stock; |
| |
• |
Vote on a case-by-case basis on most mutual fund matter shareholder proposals to terminate the investment adviser; |
| |
• |
Vote against authorization of preferred stock with unspecified voting, conversion, dividend distribution and other rights (“blank check” preferred stock); |
| |
• |
Vote on a case-by-case basis regarding merger and acquisition matters; and |
| |
• |
Vote on a case-by-case basis on equity compensation plans. |
65
Conflicts of Interest
Members of the Proxy Voting Committee will resolve conflicts of interest presented by a proxy vote. In practice, application of the Guidelines will in most instances adequately address any possible conflicts of interest, as votes generally are effected according to the policies or recommendations of the independent proxy voting agent.
However, if a situation arises where a vote presents a conflict between the interests of the Fund’s shareholders and the interest of VALIC, SunAmerica, the Fund’s principal underwriter, or the underwriter’s affiliates, and the conflict is known to the Proxy Voting Committee, the Committee will consult with one Director who is not an “interested person,” as that term is defined in the 1940 Act, time permitting, before casting the vote to ensure that the Fund votes in the best interest of its shareholders. Any individual with a known conflict may be required by the Proxy Voting Committee to recuse himself or herself from being involved in the proxy voting decision.
Proxy Voting Records
The Proxy Voting Committee will be responsible for documenting its basis for any determination to vote in a non-uniform or contrary manner, as well as, for ensuring the maintenance of records for each proxy vote cast on behalf of the Fund. The independent proxy voting agent will maintain records of voting decisions for each vote cast on behalf of the Fund. The proxy voting record for the most recent twelve-month period ended June 30 is available on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov, or can be obtained, without charge, upon request, by calling (800) 858-8850.
Board Reporting
The Fund’s Chief Compliance Officer will provide a summary report at each quarterly meeting of the Board which describes any Proxy Voting Committee meeting(s) held during the prior quarter.
Proxy Voting Records
ISS maintains records of voting decisions for each vote cast on behalf of the Fund. Information regarding how the Fund voted proxies relating to portfolio securities during the most recent 12-month period ended June 30 has been filed with the SEC on Form N-PX and is available (1) without charge, upon request, by calling VALIC, toll-free at 1-800-448-2542, and (2) on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Disclosure of Portfolio Holdings Policies and Procedures
The Board of VC I has adopted policies and procedures relating to disclosure of the Fund’s portfolio securities. These policies and procedures generally prohibit the release of information concerning portfolio holdings which have not previously been made public to individual investors, institutional investors, intermediaries that distribute the Fund’s shares and other parties which are not employed by VALIC or its affiliates except under certain circumstances. Except when there are legitimate business purposes for selective disclosure and other conditions (designed to protect the Fund and its participants) are met, VC I does not provide or permit others to provide information about the Fund’s portfolio holdings on a selective basis.
VC I makes the Fund’s portfolio holdings available semi-annually in shareholder reports filed on Form N-CSR and quarterly in regulatory filings on Form N-PORT. These shareholder reports and regulatory filings are filed with the SEC, as required by federal securities laws, and are generally available within sixty (60) days after the end of the Fund’s fiscal quarter. In addition, the Fund’s complete holdings information will be made available on VC I’s website on a monthly basis. The Fund’s holdings at the end of each month will be posted approximately 30 days after the month end.
In addition, VC I generally makes publicly available on a periodic basis, information regarding the Fund’s top ten holdings (including name and percentage of the Fund’s assets invested in each holding) and the percentage breakdown of the Fund’s investments by country, sector and industry, as applicable. This information may be made available through VALIC’s website, marketing communications (including printed advertising and sales literature), and/or VC I’s telephone customer service centers. This information is generally not released until the information is at least 15 days after the applicable quarter-end, unless otherwise approved by VC I’s legal department. VC I and its affiliates are not authorized to receive compensation or other consideration for the non-public disclosure of portfolio holdings information.
66
Before any non-public disclosure of information about the Fund’s portfolio holdings is permitted, the employee seeking to disclose such information must submit a written form to his or her department head requesting the release of non-public portfolio holdings information. The request must be submitted to the legal and compliance departments. VC I’s Chief Compliance Officer and/or VALIC’s legal counsel are/is responsible for authorizing the selective release of portfolio holding information. If the request is approved, VC I and the third party must execute a confidentiality agreement governing the third party’s duties with respect to the portfolio holdings information, which includes the duty to keep such information confidential and not to trade on such information.
Non-public holdings information may be provided to VC I’s service providers on an as-needed basis in connection with the services provided to the Fund by such service providers. Information may be provided to these parties without a time lag. Service providers that may be provided with information concerning the Fund’s holdings include the Fund’s adviser, VALIC, and its affiliates, legal counsel, independent registered public accounting firms, custodian, fund accounting agent, financial printers, proxy voting service providers and broker-dealers who are involved in executing portfolio transactions on behalf of the Fund. Portfolio holdings information may also be provided to the Board. The entities to which VC I provides portfolio holdings information either by explicit arrangement or by virtue of their respective duties to the Fund are required to maintain the confidentiality of the information provided.
VC I’s Chief Compliance Officer and VALIC’s legal counsel are responsible for determining whether there is a legitimate business purpose for the disclosure of such information and whether there are conflicts between the Fund’s participants and the Fund’s affiliates.
To find that there is a legitimate business purpose, it must be determined that the selective disclosure of portfolio holdings information is necessary to the Fund’s operation or useful to the Fund’s participants without compromising the integrity or performance of the Fund.
At each quarterly meeting of the Board of VC I, the Board reviews a report detailing third parties to whom the Fund’s portfolio holdings information has been disclosed and the purpose for such disclosure, and considers whether or not the release of information to such third parties is in the best interest of the Fund and its participants.
In the event a subadviser is engaged to assume subadvisory duties of the Fund, VC I routinely discloses portfolio holdings information to the subadviser prior to its assumption of duties. VC I does not receive any compensation, or other consideration from these arrangements for the release of the Fund’s portfolio holdings information.
Each of the below listed third parties has been approved to receive information concerning the Fund’s holdings: (1) PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (“PwC”), the Independent Registered Public Accountants; (2) Institutional Shareholder Services (“ISS”), a proxy voting service provider; (3) State Street, Custodian; (4) Zeno Consulting Group and ITG, brokerage transaction analysis; (5) Morningstar, Lipper and Bloomberg LLP, database services; (6) RR Donnelley, financial printer, (7) Investment Company Institute, survey information; (8) Manhattan Creative Partners (d/b/a “Diligent”), VC I’s Board materials; (9) Fluent Technologies, marketing materials; (10) Finadium, LLC (“Finadium”), a securities lending consultant; and (11) Ernst & Young LLP, tax accountants. PwC is provided with entire portfolio holdings information during periods in which it reviews shareholder reports and regulatory filings, and does not publicly disclose this information. ISS receives entire portfolio holdings information on a weekly basis for the purpose of voting proxies on behalf of the Fund and does not publicly disclose this information. State Street has daily access to the Fund’s portfolio holdings information as the Fund’s custodian and does not publicly disclose this information. Zeno Consulting Group and ITG receive portfolio holdings information for the purpose of analyzing brokerage execution statistics approximately 15 days after the quarter end and do not publicly disclose this information. Lipper receives portfolio holdings information within 20 days of each month end and makes certain information available approximately 30 days after its receipt. Morningstar receives portfolio holdings information approximately 35 days after each month end and makes information available through Morningstar Direct to subscribers approximately one week after its receipt. Bloomberg receives portfolio holdings information for the Fund on a monthly basis, approximately 45 days after the month end and makes information available to subscribers of Bloomberg’s databases within 1 to 14 days of its receipt. RR Donnelley has access to portfolio holdings information approximately 30 days after the Fund’s fiscal quarter in preparation of shareholder reports and regulatory filings and does not make publicly disclose this information. The Investment Company
67
Institute receives certain portfolio holdings information approximately 15 days after each calendar quarter and does not publicly disclose the information before the Fund’s release of such information. Manhattan Creative Partners has access to certain portfolio holdings information provided to the Board approximately thirty days after each quarter end, and does not publicly disclose this information. Fluent Technologies receives certain portfolio holdings information on a quarterly basis within 10 business days of each calendar quarter for the preparation of marketing materials, and does not publicly disclose this information. Finadium receives portfolio holdings information as necessary to render securities lending consulting services and does not publicly disclose this information.
In addition, Wellington Management discloses the portfolio holdings of the Fund to the following third parties in connection with the services it provides to the Fund (subject to confidentiality agreements between Wellington Management and such third parties):
| |
• |
Accenture performs certain operational functions on behalf of Wellington Management and has access to portfolio holdings on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. performs certain operational functions for Wellington Management and receives portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
FactSet Research Systems Inc. provides analytical services for Wellington Management and receives portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
Glass, Lewis & Co. provides proxy voting services for Wellington Management and receives portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
Markit WSO Corporation performs certain operational functions on behalf of Wellington Management and receives syndicated bank loan portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
MSCI, Inc provides analytical services for Wellington Management and receives portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
State Street performs certain operational functions on behalf of Wellington Management and receives portfolio holdings information on a daily basis. |
| |
• |
Dynamo Software Inc. provides a technology platform to Wellington Management to support private placement transactions, integrating the components of a private investment lifecycle into one system. |
| |
• |
Wellington Management also makes disclosures of 1940 Act client portfolio holdings to third parties without attribution to specific clients. |
Custodian
Pursuant to a Custodian Contract with VC I, State Street, 225 Franklin Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02110, holds the cash and portfolio securities of the Fund as Custodian.
State Street is responsible for holding all securities and cash of the Fund, receiving and paying for securities purchased, delivering against payment securities sold, receiving and collecting income from investments, making all payments covering expenses of VC I, and performing other administrative duties, all as directed by persons authorized by VC I. The Custodian does not exercise any supervisory function in such matters as the purchase and sale of portfolio securities, payment of dividends, or payment of expenses of the Fund or VC I. Portfolio securities of the Fund purchased domestically are maintained in the custody of the Custodian and may be entered into the book entry systems of securities depositories approved by VC I’s Board. Pursuant to the Custodian Contract, portfolio securities purchased outside the United States will be maintained in the custody of various foreign branches of the Custodian and such other custodians, including foreign banks and foreign securities depositories.
68
State Street also acts as VC I’s securities lending agent and receives a share of the income generated by such activities.
Principal Underwriter
The Fund’s principal underwriter is ACS, Harborside 5, 185 Hudson Street, Suite 3300, Jersey City, New Jersey 07311-4992. ACS is an affiliate of VALIC.
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board has selected PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, at 1000 Louisiana Street, Suite 5800, Houston, Texas 77002, to serve as the Independent Registered Public Accounting firm of the Fund.
MANAGEMENT OF VC I
The following tables list the Directors and officers of VC I, their ages, current position(s) held with VC I, length of time served, principal occupations during the past five years, number of funds overseen within the Fund Complex (as defined below) and other directorships/trusteeships held outside of the Fund Complex. Unless otherwise noted, the address of each executive officer and Director is 2929 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019. Directors who are not deemed to be “interested persons” of VC I as defined in the 1940 Act are referred to as “Independent Directors.” A Director who is deemed to be an “interested person” of VC I is referred to as “Interested Director.” Directors and officers of VC I are also directors or trustees and officers of some or all of the other investment companies managed or advised by VALIC, administered by SunAmerica and distributed by ACS, and/or other affiliates of VALIC
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name and Age |
|
Position(s) Held With Fund1 |
|
Term of Office and Length of Time Served |
|
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
|
Number of Portfolios In Fund Complex Overseen by Director2 |
|
Other
Directorships
Held by Director3 |
| Independent Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Thomas J. Brown Age: 76 |
|
Director |
|
2005 – Present |
|
Retired. |
|
36 |
|
Trustee, Virtus Funds (2011-2020). |
| Dr. Judith L. Craven Age: 75 |
|
Director |
|
1998 – Present |
|
Retired. |
|
36 |
|
Director, A.G. Belo Corporation, a media company (1992-2014); Director, SYSCO Corporation, a food marketing and distribution company (1996-2017); Director, Luby’s Inc. (1998-2019). |
| Cheryl Creuzot4 Age: 63 |
|
Director |
|
2022 – Present |
|
President and Chief Executive Officer of Wealth Development Strategies, LLC (2012-2019); President Emeritus, Wealth Development Strategies LLC (2019-Present). |
|
36 |
|
Director, The Bancorp, Inc. – Audit and Risk Committees (2021-Present); Director, Amegy Bank (2021); Director, The Frenchy’s Companies (2013-Present); Commissioner, Port of Houston – Audit, Governance, Dredge Task Force and Community Relations Committees (2020-Present); Executive Committee Member, MD Anderson University Cancer Foundation Board of Visitors (2010-Present); Director, Unity National Bank – Chair of Compliance, Audit, and Investment Committees (2008-2015). |
69
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Yvonne M. Curl Age: 67 |
|
Director |
|
2020 – Present |
|
Retired. |
|
36 |
|
Director, Encompass Health, provider of post-acute healthcare services (2004-2022); Director, Community Foundation of the Lowcountry (2018-Present); Director, Nationwide Insurance, insurance company (1998-2019); Director, Hilton Head Humane Association, animal shelter (2006-2019); Director, Enhabit, Inc., provider of home health and hospice services (2022-Present). |
| Darlene T. DeRemer4 Age: 66 |
|
Director |
|
2022 – Present |
|
Managing Partner, Grail Partners LLC (2005-2019). |
|
36 |
|
Trustee, ARK ETF Trust (2014-Present); Trustee, Member of Investment and Endowment Committee of Syracuse University (2010-Present); Director, Alpha Healthcare Acquisition Corp. III (2021-Present); Interested Trustee, Esoterica Thematic Trust (2020-2021); Interested Trustee, American Independence Funds (2015-2019); Trustee, Risk X Investment Funds (2016-2020); Director, United Capital Financial Planners (2008-2019); Director, Hillcrest Asset Management (since 2007); Board Member, Confluence Technologies LLC (2018-2021). |
| Dr. Timothy J. Ebner Age: 73 |
|
Director |
|
1998 – Present |
|
Professor and Head- Department of Neuroscience Medical School (1980-Present) and Pickworth Chair (2000-Present), University of Minnesota; Scientific Director, Society for Research on the Cerebellum (2008-Present); President, Association of Medical School Neuroscience Department Chairpersons (2011-2014). |
|
36 |
|
Trustee, Minnesota Medical Foundation (2003-2013). |
70
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Peter A. Harbeck5 Age: 68 |
|
Director |
|
2001 – Present |
|
Retired June 2019, formerly President (1995-2019), CEO (1997-2019) and Director (1992-2019), SunAmerica; Director, AIG Capital Services, Inc. (“ACS”) (1993-2019); Chairman, President and CEO, Advisor Group, Inc. (2004-2016). |
|
36 |
|
None. |
| Eileen A. Kamerick4 Age: 64 |
|
Director |
|
2022 – Present |
|
Chief Executive Officer, The Governance Partners, LLC (consulting firm) (2015-Present); National Association of Corporate Directors Board Leadership Fellow (2016-Present, with Directorship Certification since 2019 and NACD 2022 Directorship 100 honoree); Adjunct Professor, Georgetown University Law Center (2021-Present); Adjunct Professor, The University of Chicago Law School (2018-Present); Adjunct Professor University of Iowa College of Law (2007 – present); formerly, Chief Financial Officer, Press Ganey Associates (health care informatics company) (2012 to 2014); Managing Director and Chief Financial Officer, Houlihan Lokey (international investment bank) and President, Houlihan Lokey Foundation (2010 to 2012). |
|
36 |
|
Director of the Legg Mason Closed-End Funds (2013-Present); Director of ACV Auctions Inc. (2021-Present); Director of Hochschild Mining plc (precious metals company) (2016-Present); Director of Associated Banc-Corp (financial services company) (2007-Present); formerly, Director of Anchor Series Trust, SunAmerica Equity Funds, SunAmerica Income Funds, SunAmerica Money Market Funds, Inc., SunAmerica Senior Floating Rate Fund, Inc., SunAmerica Series, Inc. and SunAmerica Specialty Series (2018-2022). |
| Dr. John E. Maupin, Jr. Age: 75 |
|
Director and Chair |
|
1998 – Present |
|
Retired. President/CEO, Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia (2006-2014). |
|
36 |
|
Director, Regions Financials Inc., bank holding company (2007-2019); Director, LifePoint Hospitals, Inc., hospital management (1999-2018); Director, Enhabit, Inc., provider of home health and hospice services (2022-Present); Director, Encompass Health, provider of post-acute healthcare services (2004-2022). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Interested Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Eric S. Levy6 2919 Allen Parkway Houston, TX 77019 Age: 57 |
|
Director |
|
2017 – Present |
|
Executive Vice President, VALIC (2015-Present); Executive Vice President, Group Retirement, AIG (2015-Present); and Senior Vice President, Lincoln Financial Group (2010-2015). |
|
36 |
|
None. |
| 1 |
Directors serve until their successors are duly elected and qualified. |
| 2 |
The term “Fund Complex” means two or more registered investment companies that (i) hold themselves out to investors as related companies for purposes of investment and investor services or (ii) have a common investment adviser or an investment adviser that is an affiliated person of the investment adviser of any of the other registered investment companies, VALIC. The Fund Complex includes VC I (36 funds), SunAmerica Series Trust (61 portfolios), and SST (19 portfolios). |
| 3 |
Directorships of companies required to report to the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (i.e., “public companies”) or other investment companies regulated under the 1940 Act, other than those listed under the preceding column. |
| 4 |
Mses. Creuzot, DeRemer and Kamerick were elected as new Independent Directors to VC I’s Board as of the close of business on October 14, 2022. |
| 5 |
Prior to December 31, 2022, Mr. Harbeck was considered to be an Interested Director because he owned shares of AIG, the ultimate parent of VALIC. |
| 6 |
Mr. Levy is considered to be an Interested Director because he serves as an officer of the Adviser and AIG, the Adviser’s ultimate parent company. |
71
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name and Age |
|
Position(s) Held With Fund |
|
Length of Time Served |
|
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
| Officers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kevin J. Adamson Age: 56 |
|
Vice President |
|
2018 – Present |
|
Senior Vice President, VALIC (2018-Present); Vice President Lincoln Financial Group (2004-2017). |
| Gregory N. Bressler Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 55 |
|
Vice President and Assistant Secretary |
|
2005 – Present |
|
Senior Vice President and General Counsel (2005-Present) and Assistant Secretary (2013-Present), SunAmerica. |
| Kathleen D. Fuentes Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 53 |
|
Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary |
|
2015 – Present |
|
Vice President and Deputy General Counsel, SunAmerica (2006-Present). |
| John T. Genoy Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 53 |
|
President and Principal Executive Officer |
|
2014 – Present |
|
President (2021-Present), Chief Financial Officer (2002-Present), Senior Vice President (2004-2021), Chief Operating Officer (2006-Present) and Director, SunAmerica (2014-Present). |
| Matthew J. Hackethal Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 50 |
|
Anti-Money Laundering (“AML”) Compliance Officer |
|
2006 – Present |
|
Acting Chief Compliance Officer (2016-2017), Vice President (2011-Present), and Chief Compliance Officer, SunAmerica (2006-Present); AML Compliance Officer, SunAmerica Fund Complex (2006-Present). |
72
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Christopher C. Joe Age: 53 |
|
Chief Compliance Officer and Vice President |
|
2017 – Present |
|
Chief Compliance Officer, AIG Funds, Anchor Series Trust, Seasons Series Trust, SunAmerica Series Trust, VALIC Company I and VALIC Company II (2017-Present); Chief Compliance Officer, VALIC Retirement Services Company (2017-Present); Chief Compliance Officer, Invesco PowerShares (2012-2017); Chief Compliance Officer, Invesco Investment Advisers, LLC (2010-2013); U.S. Compliance Director, Invesco Ltd. (2006-2014); Deputy Chief Compliance Officer, Invesco Advisers, LLC (2014-2015). |
| Gregory R. Kingston Age: 56 |
|
Treasurer and Principal Financial and Accounting Officer |
|
2000 – Present |
|
Vice President (2001-Present) and Head of Mutual Fund Administration, SunAmerica (2014-Present). |
| Donna McManus Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 61 |
|
Vice President and Assistant Treasurer |
|
2014 - Present |
|
Vice President, SunAmerica (2014-Present); Managing Director, BNY Mellon (2009-2014). |
| Shawn Parry Age: 50 |
|
Vice President and Assistant Treasurer |
|
2014 - Present |
|
Vice President (2014-Present) and Assistant Vice President (2010-2014), SunAmerica. |
| Mark R. Szycher Age: 57 |
|
Vice President and Senior Investment Officer |
|
2021 – Present |
|
Vice President, Fund Due Diligence, VALIC (2019-2021); Managing Director, GM Asset Management (2015-2019). |
| Christopher J. Tafone Harborside 5 185 Hudson Street Suite 3300 Jersey City, NJ 07311-4992 Age: 47 |
|
Vice President and Assistant Secretary |
|
2021 – Present (Vice President); (2016 – Present) (Assistant Secretary) |
|
Vice President, SunAmerica (2016-Present); Associate General Counsel, Corebridge Life & Retirement (2016 - Present). |
| Thomas M. Ward Age: 55 |
|
Vice President |
|
2008 – Present |
|
Vice President (2009-Present), VALIC; Vice President, VALIC Financial Advisors, Inc. (2009-Present). |
Leadership Structure of the Board
Overall responsibility for oversight of the VC I funds (“VALIC Funds”) rests with the Board. The VALIC Funds have engaged VALIC as the investment adviser which oversees the day-to-day operations of the VALIC Funds and have engaged subadvisers who manage the VALIC Funds’ assets on a day-to-day basis. The VALIC Funds have also engaged SunAmerica as the VALIC Funds’ administrator. The Board is responsible for overseeing VALIC, SunAmerica and the subadvisers and any other service providers in the operations of the VALIC Funds in accordance with the provisions of the 1940 Act, applicable provisions of state and other laws, VC I’s Articles of Incorporation and By-laws and the VALIC Funds’ investment objectives and strategies. The Board is presently composed of ten members, nine of whom are Independent Directors. The Board currently conducts regular in-person meetings at least quarterly and holds special in-person or telephonic meetings, or informal conference calls, to discuss specific matters that may arise or require action between regular Board meetings. The Independent Directors also meet at least quarterly in executive session, at which no Interested Directors is present. The Independent Directors have engaged independent legal counsel to assist them in performing their oversight responsibilities.
The Board has appointed Dr. Maupin, an Independent Director, to serve as Chair of the Board. The Chair’s role is to preside at all meetings of the Board and to act as a liaison with service providers, including VALIC, SunAmerica, officers, attorneys, and other Directors generally, between meetings. The Chair may also perform such other functions as may be delegated by the Board from time to time. The Board has established four committees, i.e., Audit Committee, Governance Committee, Brokerage Committee and Compliance and Ethics Committee (each, a “Committee”) to assist the Board in the oversight and direction of the business and affairs of the VALIC Funds, and from to time may establish informal working groups to review and address the policies and practices of the VALIC Funds with respect to certain specified matters. The Committee system facilitates the timely and efficient consideration of matters by the Directors, and facilitates effective oversight of compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and of the VALIC Funds’ activities and associated risks. The standing Committees currently conduct an annual review of their charters, which includes a review of their responsibilities and operations. The Governance Committee and the Board as a whole also conduct an annual evaluation of the performance of the Board, including
73
consideration of the effectiveness of the Board’s committee structure. The Board has determined that the Board’s leadership structure is appropriate because it allows the Board to exercise informed and independent judgment over the matters under its purview and it allocates areas of responsibility among the Committees and the full Board in a manner that enhances efficient and effective oversight.
The VALIC Funds are subject to a number of risks, including, among others, investment, compliance, operational and valuation risks. Risk oversight forms part of the Board’s general oversight of the VALIC Funds and is addressed as part of various Board and Committee activities. Day-to-day risk management functions are subsumed within the responsibilities of VALIC and SunAmerica, who carry out the VALIC Funds’ investment management and business affairs, and also by the VALIC Funds’ subadvisers and other service providers in connection with the services they provide to the VALIC Funds. Each of VALIC, SunAmerica, the subadvisers and other service providers have their own, independent interest in risk management, and their policies and methods of risk management will depend on their functions and business models. As part of its regular oversight of the VALIC Funds, the Board, directly and/or through a Committee, interacts with and reviews reports from, among others, VALIC, SunAmerica, the subadvisers of VALIC Funds and the VALIC Funds’ other service providers (including the VALIC Funds’ distributor and transfer agent), the VALIC Funds’ Chief Compliance Officer, the independent registered public accounting firm for the VALIC Funds, legal counsel to the VALIC Funds, and internal auditors, as appropriate, relating to the operations of the VALIC Funds. The Board recognizes that it may not be possible to identify all of the risks that may affect each VALIC Fund or to develop processes and controls to eliminate or mitigate their occurrence or effects. The Board may, at any time and in its discretion, change the manner in which it conducts risk oversight.
Board and Committees
The Board believes that each Director’s experience, qualifications, attributes or skills on an individual basis and in combination with those of the other Directors lead to the conclusion that the Directors possess the requisite experience, qualifications, attributes and skills to serve on the Board. Among the attributes common to all Directors are their ability to review critically, evaluate, question and discuss information provided to them, to interact effectively with the other Directors, VALIC, the subadvisers, other service providers, legal counsel and the independent registered public accounting firm, and to exercise effective business judgment in the performance of their duties as Directors. The Board has also considered the contributions that each Director can make to the Board and the VALIC Funds. A Director’s ability to perform his or her duties effectively may have been attained, as set forth below, through the Director’s executive, business, consulting, public service and/or academic positions; experience from service as a Director of the VALIC Funds and the other funds/portfolios in the Fund Complex (and/or in other capacities), other investment funds, public companies, or non-profit entities or other organizations; educational background or professional training; and/or other life experiences. References to the qualifications, attributes and skills of Directors are pursuant to requirements of the SEC, do not constitute holding out the Board or any Director as having any special expertise or experience, and shall not impose any greater responsibility on any such person or on the Board by reason thereof.
Thomas J. Brown. Mr. Brown has served as Director since 2005. Mr. Brown is also the chair of the Audit Committee and serves as the Audit Committee Financial Expert and as a member of each of the Brokerage, the Compliance and Ethics, and the Governance Committees. An “Audit Committee Financial Expert” is defined as a person who has the following attributes: (i) an understanding of generally accepted accounting principles and financial statements; (ii) the ability to assess the general application of such principles in connection with the accounting for estimates, accruals and reserves; (iii) experience preparing, auditing, analyzing or evaluating financial statements that present a breadth and level of complexity of accounting issues that are generally comparable to the breadth and complexity of issues that can reasonably be expected to be raised by the registrant’s financial statements, or experience actively supervising one or more persons engaged in such activities; (iv) an understanding of internal controls and procedures for financial reporting; and (v) an understanding of audit committee functions. Mr. Brown is a retired Chief Operating Officer and Chief Financial Officer of American General Asset Management, and previously was the Treasurer and CFO of the North American Funds. Mr. Brown also has substantial experience serving on boards of other mutual fund complexes.
Dr. Judith L. Craven. Dr. Craven has served as Director since 1998. Dr. Craven is also the chair of the Compliance and Ethics Committee and serves as a member of each of the Audit, the Brokerage, and the Governance Committees. Dr. Craven is a retired administrator, and has held numerous executive and directorship positions within the healthcare industry. Dr. Craven has substantial experience serving on local, state, and national boards, and is currently a director of Luby’s Restaurant and SYSCO Corporation, among other organizations.
74
Cheryl Creuzot. Ms. Creuzot has served as Director since 2022. Ms. Creuzot was formerly the President and Chief Executive Officer and Principal of Wealth Development Strategies, LLC and Wealth Development Investment Advisory, LLC, both Financial Industry Regulatory Authority and SEC regulated, financial advisory firms. Ms. Creuzot also has substantial experience serving on non-profit boards, and has significant securities and financial planning experience.
Yvonne M. Curl. Ms. Curl has served as a Director since 2020. Ms. Curl is also the chair of the Brokerage Committee and serves as a member of each of the Audit, the Compliance and Ethics, and the Governance Committees. In addition, she has nearly 30 years of executive and business experience in various industries. Ms. Curl also has corporate governance experience serving on multiple public company and non-profit boards for nearly 30 years.
Darlene T. DeRemer. Ms. DeRemer has served as Director since 2022. Ms. DeRemer was formerly Managing Partner of Grail Partners, an advisory merchant bank serving the investment management industry. Prior to becoming an investment banker at Putnam Lovell NBF in 2003, Ms. DeRemer spent twenty-five years as a leading adviser to the financial services industry. Ms. DeRemer also has substantial experience serving on investment company boards and currently serves as Chair of ARK ETF Trust.
Dr. Timothy J. Ebner. Dr. Ebner has served as Director since 1998. Dr. Ebner is also the chair of the Governance Committee and serves as a member of each of the Audit, the Compliance and Ethics, and the Brokerage Committees. Dr. Ebner is Head of the Department of Neuroscience of the Medical School at the University of Minnesota. Dr. Ebner has experience serving on the boards of other mutual funds, as well as on the boards of several scientific foundations and non-profit organizations. Dr. Ebner is also an editor for the Journal of Neuroscience and is on the editorial board of three other neuroscience journals.
Peter A. Harbeck. Mr. Harbeck previously served as President, Chief Executive Officer and Director of SunAmerica and Director of ACS. As President and Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Harbeck was responsible for all of SunAmerica’s mutual fund businesses. During his over twenty-year tenure at SunAmerica, Mr. Harbeck held various positions, including Chief Operating Officer and Chief Administrative Officer. In addition, Mr. Harbeck has extensive experience on various fund and annuity boards.
Eileen A. Kamerick. Ms. Kamerick has served as Director since 2022. Ms. Kamerick has substantial experience in business and finance, including financial reporting, and experience as a board member of a highly regulated financial services company. Ms. Kamerick also has substantial experience serving on investment company boards and is currently a board member of the Legg Mason Closed End Funds, for which she serves as audit committee financial expert.
Dr. John E. Maupin, Jr. Dr. Maupin has served as Director since 1998. Dr. Maupin is the Chair of the Board and also serves as a member of each of the Audit, the Brokerage, the Compliance and Ethics, and the Governance Committees. Dr. Maupin is the retired President and Chief Executive Officer of Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, and has extensive executive and administrative experience at other organizations and companies within the healthcare industry. Dr. Maupin also currently serves on the boards of LifePoint Hospitals, Inc., HealthSouth Corporation, and Regions Financials, Inc.
Interested Director
Eric S. Levy. Mr. Levy has served as a Director since May 1, 2017. Mr. Levy is Executive Vice President of VALIC and Executive Vice President, Group Retirement of AIG. Mr. Levy is also a Registered Principal for VALIC Financial Advisors, Inc., an affiliate of VALIC. Mr. Levy’s experience spans thirty-five years in financial services, including mutual funds, sub-advisory services, retirement services and insurance products at Fidelity, Allmerica Financial, Putnam Investments, Mercer and Lincoln Financial Group.
Effective January 1, 2022, Independent Directors receive an annual retainer of $263,000 (Chair receives an additional $57,750 retainer). The Independent Directors receive a fee of $4,000 for additional special meetings ($13,125 if it is determined a full meeting fee is appropriate). The Audit Committee chair, also the Audit Committee Financial Expert, receives a retainer of $38,500. The Governance Committee chair receives a retainer of $26,000, the Compliance and Ethics Committee chair receives a retainer of $15,000, and the Brokerage Committee chair receives a retainer of $15,000.
75
The Audit Committee is comprised of all Independent Directors, with Mr. Brown as chair and Mr. Brown serving as the “Audit Committee Financial Expert.” The Audit Committee recommends to the Board the selection of independent registered public accounting firm for the Fund and reviews with such independent accounting firm the scope and results of the annual audit, reviews the performance of the accounts, and considers any comments of the independent accounting firm regarding the Fund’s financial statements or books of account. The Audit Committee has a Sub-Committee to approve audit and non-audit services and it is comprised of Mr. Brown, Dr. Ebner and Dr. Maupin. During the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Audit Committee held four (4) meetings.
The Governance Committee is comprised of all Independent Directors, with Dr. Ebner as chair. The Governance Committee recommends to the Board nominees for Independent Director membership, reviews governance procedures and Board composition, and periodically reviews Director compensation. The Fund does not have a standing compensation committee. The Governance Committee will consider any candidate for Director recommended by a current shareholder if required by law to do so. Any such recommendation must contain sufficient background information concerning the candidate to enable the Governance Committee to make a proper judgment as to the candidate’s qualification. Recommendations from shareholders must be submitted in writing and addressed to the Governance Committee and the Secretary of VALIC Company I at 2919 Allen Parkway, Houston, Texas 77019. During the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Governance Committee held six (6) meetings.
The Brokerage Committee is comprised of all Independent Directors, with Ms. Curl as chair. The Brokerage Committee reviews brokerage issues but does not meet on a formal basis. During the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Brokerage Committee held three (3) meetings.
The Compliance and Ethics Committee is comprised of all Independent Directors, with Dr. Craven as chair. The Compliance and Ethics Committee addresses issues that arise under the Code of Ethics for the Principal Executive and Principal Accounting Officers as well as any material compliance matters arising under Rule 38a-1 policies and procedures as approved by the Board. During the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022, the Compliance and Ethics Committee held one (1) meeting.
The Independent Directors are reimbursed for certain out-of-pocket expenses by VC I.
The Directors and officers of VC I and members of their families as a group beneficially owned less than 1% of the common stock of the Fund outstanding as of April 27, 2023.
Director Ownership of Shares
The following table shows the dollar range of shares beneficially owned by each Director as of December 31, 2022. Other than VC I, the Directors do not oversee any other registered investment companies in the Fund Complex.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name of Director |
|
Dollar
Range of
Equity
Securities
in the
Fund |
|
|
Aggregate
Dollar
Range
of Equity
Securities
in All
Funds
Overseen
by
Director in
Family1 |
|
| Independent Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Thomas J. Brown |
|
$ |
0 |
|
|
$ |
0 |
|
| Dr. Judith L. Craven |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Cheryl Creuzot |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Yvonne M. Curl |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Darlene T. DeRemer |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
76
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Dr. Timothy J. Ebner |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Peter A. Harbeck |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Eileen A. Kamerick |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Dr. John E. Maupin, Jr. |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| Interested Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Eric S. Levy |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
| 1 |
Includes the value of shares beneficially owned by each Director in VC I (36 series). |
As of December 31, 2022, no Independent Directors or any of their immediate family members owned beneficially or of record any securities in VALIC, the Subadvisers, ACS or any person other than a registered investment company, directly or indirectly, controlling, controlled by or under common control with such entities.
Compensation of Directors
The following table sets forth information regarding compensation and benefits earned by the Independent Directors for the fiscal year ended May 31, 2022. Interested Directors are not eligible for compensation or retirement benefits and thus, are not shown below.
Compensation Table
Fiscal Year Ended May 31, 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name of Director1 |
|
Aggregate
Compensation
from Series
Company |
|
|
Total
Compensation
From Fund
Complex
Paid to
Directors2 |
|
| Mr. Thomas J. Brown |
|
$ |
305,375 |
|
|
$ |
305,375 |
|
| Dr. Judith L. Craven |
|
$ |
281,875 |
|
|
$ |
343,999 |
|
| Cheryl Creuzot3 |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
| Yvonne M. Curl |
|
$ |
266,875 |
|
|
$ |
266,875 |
|
| Darlene T. DeRemer3 |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
| Dr. Timothy Ebner4 |
|
$ |
260,700 |
|
|
$ |
260,700 |
|
| Peter A. Harbeck5 |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
| Eileen A. Kamerick3 |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
N/A |
|
| Mr. Kenneth J. Lavery6 |
|
$ |
281,875 |
|
|
$ |
281,875 |
|
| Dr. John E. Maupin, Jr. |
|
$ |
324,625 |
|
|
$ |
324,625 |
|
| 1 |
Directors receive no pension or retirement benefits from the Fund or any other funds in the Fund Complex. |
| 2 |
Includes VC I, SunAmerica Senior Floating Rate Fund, Inc., SunAmerica Income Funds, SunAmerica Equity Funds, SunAmerica Series, Inc., SunAmerica Specialty Series, SunAmerica Money Market Funds, Inc. and Anchor Series Trust. |
| 3 |
Mses. Creuzot, DeRemer and Kamerick were elected as new Independent Directors to VC I’s Board as of the close of business on October 14, 2022. |
| 4 |
Dr. Ebner has chosen to defer a portion of compensation under the Deferred Compensation Plan discussed below. As of May 31, 2022, the current value of the deferred compensation is $862,903. |
| 5 |
Prior to December 31, 2022, Mr. Harbeck was considered to be an Interested Director because he owned shares of AIG, the ultimate parent of VALIC. |
| 6 |
Mr. Lavery retired from the Board effective as of the close of business on June 30, 2022. |
The Board has approved a Deferred Compensation Plan (the “Deferred Plan”) for its Independent Directors who are not officers, directors, or employees of VALIC or an affiliate of VALIC. The purpose of the Deferred Plan is to permit such Independent Directors to elect to defer receipt of all or some portion of the fees payable to them for their services to VC I, therefore allowing postponement of taxation of income and tax-deferred growth on the earnings. Under the Deferred Plan, an Independent Director may make an annual election to defer all or a portion of his/her future compensation from VC I.
77
The Fund’s retirement policy provides that each Independent Director shall retire from service as an Independent Director at the end of the calendar year in which he or she turns 75 years of age, except that for an Independent director whose term of service began prior to January 1, 2016, such Independent Director may request an additional year of eligibility as an Independent Director, subject to approval by the other Independent Directors up to a maximum of five additional years (to age 80).
78
APPENDIX A
Description of Credit Rating Symbols and Definitions
Moody’s Global Long-Term Rating Scale:
Ratings assigned on Moody’s global long-term rating scales are forward-looking opinions of the relative credit risks of financial obligations issued by non-financial corporates, financial institutions, structured finance vehicles, project finance vehicles, and public sector entities. Long-term ratings are assigned to issuers or obligations with an original maturity of eleven months or more and reflect both on the likelihood of a default or impairment on contractual financial obligations and the expected financial loss suffered in the event of default or impairment.
|
|
|
| Aaa |
|
Obligations rated Aaa are judged to be of the highest quality, subject to the lowest level of credit risk. |
| Aa |
|
Obligations rated Aa are judged to be of high quality and are subject to very low credit risk. |
| A |
|
Obligations rated A are judged to be upper-medium grade and are subject to low credit risk |
| Baa |
|
Obligations rated Baa are judged to be medium-grade and subject to moderate credit risk and as such may possess certain speculative characteristics. |
| Ba |
|
Obligations rated Ba are judged to be speculative and are subject to substantial credit risk. |
| B |
|
Obligations rated B are considered speculative and are subject to high credit risk. |
| Caa |
|
Obligations rated Caa are judged to be speculative of poor standing and are subject to very high credit risk. |
| Ca |
|
Obligations rated Ca are highly speculative and are likely in, or very near, default, with some prospect of recovery of principal and interest. |
| C |
|
Obligations rated C are the lowest rated and are typically in default, with little prospect for recovery of principal or interest. |
Note: Moody’s appends numerical modifiers 1, 2, and 3 to each generic rating classification from Aa through Caa. The modifier 1 indicates that the obligation ranks in the higher end of its generic rating category; the modifier 2 indicates a mid-range ranking; and the modifier 3 indicates a ranking in the lower end of that generic rating category. Additionally, a “(hyb)” indicator is appended to all ratings of hybrid securities issued by banks, insurers, finance companies, and securities firms. By their terms, hybrid securities allow for the omission of scheduled dividends, interest, or principal payments, which can potentially result in impairment if such an omission occurs. Hybrid securities may also be subject to contractually allowable write-downs of principal that could result in impairment. Together with the hybrid indicator, the long-term obligation rating assigned to a hybrid security is an expression of the relative credit risk associated with that security.
Moody’s Global Short-Term Ratings Scale:
Ratings assigned on Moody’s global short-term rating scales are forward-looking opinions of the relative credit risks of financial obligations issued by non-financial corporates, financial institutions, structured finance vehicles, project finance vehicles, and public sector entities. Short-term ratings are assigned to obligations with an original maturity of thirteen months or less and reflect both on the likelihood of a default or impairment on contractual financial obligations and the expected financial loss suffered in the event of default or impairment
Moody’s employs the following designations to indicate the relative repayment ability of rated issuers:
|
|
|
| P-1 |
|
Ratings of Prime-1 reflect a superior ability to repay short-term debt obligations. |
| P-2 |
|
Ratings of Prime-2 reflect a strong ability to repay short-term debt obligations. |
| P-3 |
|
Ratings of Prime-3 reflect an acceptable ability to repay short-term obligations. |
| NP |
|
Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Not Prime do not fall within any of the Prime rating categories. |
US Municipal Short-Term Debt Ratings
The Municipal Investment Grade (MIG) scale is used to rate US municipal bond anticipation notes of up to three years maturity. Municipal notes rated on the MIG scale may be secured by either pledged revenues or proceeds of a take-out financing received prior to note maturity. MIG ratings expire at the maturity of the obligation, and the issuer’s long-term rating is only one consideration in assigning the MIG rating. MIG ratings are divided into three levels-MIG 1 through MIG 3-while speculative grade short-term obligations are designated SG.
A-1
MIG 1: This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by established cash flows, highly reliable liquidity support, or demonstrated broad-based access to the market for refinancing.
MIG 2: This designation denotes strong credit quality. Margins of protection are ample, although not as large as in the preceding group.
MIG 3: This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Liquidity and cash-flow protection may be narrow, and market access for refinancing is likely to be less well-established.
SG: This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Debt instruments in this category may lack sufficient margins of protection.
S&P Long-Term Issue Credit Ratings
Issue credit ratings are based, in varying degrees, on S&P Global Ratings analysis of the following considerations:
| |
• |
|
The likelihood of payment-the capacity and willingness of the obligor to meet its financial commitments on an obligation in accordance with the terms of the obligation; |
| |
• |
|
The nature and provisions of the financial obligation, and the promise we impute; and |
| |
• |
|
The protection afforded by, and relative position of, the financial obligation in the event of a bankruptcy, reorganization, or other arrangement under the laws of bankruptcy and other laws affecting creditors’ rights. |
An issue rating is an assessment of default risk, but may incorporate an assessment of relative seniority or ultimate recovery in the event of default. Junior obligations are typically rated lower than senior obligations, to reflect lower priority in bankruptcy, as noted above. (Such differentiation may apply when an entity has both senior and subordinated obligations, secured and unsecured obligations, or operating company and holding company obligations.)
|
|
|
| AAA |
|
An obligation rated ‘AAA’ has the highest rating assigned by S&P Global Ratings. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is extremely strong. |
| AA |
|
An obligation rated ‘AA’ differs from the highest-rated obligations only to a small degree. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is very strong. |
| A |
|
An obligation rated ‘A’ is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher-rated categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is still strong. |
| BBB |
|
An obligation rated ‘BBB’ exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to weaken the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. |
BB; B; CCC; CC; and C
Obligations rated ‘BB’, ‘B’, ‘CCC’, ‘CC’, and ‘C’ are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. ‘BB’ indicates the least degree of speculation and ‘C’ the highest. While such obligations will likely have some quality and protective characteristics, these may be outweighed by large uncertainties or major exposure to adverse conditions.
|
|
|
| BB |
|
An obligation rated ‘BB’ is less vulnerable to nonpayment than other speculative issues. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions that could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. |
| B |
|
An obligation rated ‘B’ is more vulnerable to nonpayment than obligations rated ‘BB’, but the obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. Adverse business, financial, or economic conditions will likely impair the obligor’s capacity or willingness to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. |
| CCC |
|
An obligation rated ‘CCC’ is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. In the event of adverse business, financial, or economic conditions, the obligor is not likely to have the capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. |
| CC |
|
An obligation rated ‘CC’ is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment. The ‘CC’ rating is used when a default has not yet occurred, but S&P Global Ratings expects default to be a virtual certainty, regardless of the anticipated time to default. |
| C |
|
An obligation rated ‘C’ is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment, and the obligation is expected to have lower relative seniority or lower ultimate recovery compared with obligations that are rated higher. |
A-2
|
|
|
| D |
|
An obligation rated ‘D’ is in default or in breach of an imputed promise. For non-hybrid capital instruments, the ‘D’ rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due, unless S&P Global Ratings believes that such payments will be made within the next five business days in the absence of a stated grace period or within the earlier of the stated grace period or the next 30 calendar days. The ‘D’ rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of similar action and where default on an obligation is a virtual certainty, for example due to automatic stay provisions. A rating on an obligation is lowered to ‘D’ if it is subject to a distressed debt restructuring. |
*Plus (+) or minus (-)
S&P Short-Term Issue Credit Ratings
Short-term issue credit ratings are generally assigned to those obligations considered short-term in the relevant market, typically with an original maturity of no more than 365 days. Short-term issue credit ratings are also used to indicate the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to put features on long-term obligations. These categories are as follows:
|
|
|
| A-1 |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘A-1’ is rated in the highest category by S&P Global Ratings. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is strong. Within this category, certain obligations are designated with a plus sign (+). This indicates that the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on these obligations is extremely strong. |
| A-2 |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘A-2’ is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher rating categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is satisfactory. |
| A-3 |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘A-3’ exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to weaken an obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. |
| B |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘B’ is regarded as vulnerable and has significant speculative characteristics. The obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments; however, it faces major ongoing uncertainties that could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments. |
| C |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘C’ is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitments on the obligation |
| D |
|
A short-term obligation rated ‘D’ is in default or in breach of an imputed promise. For non-hybrid capital instruments, the ‘D’ rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due, unless S&P Global Ratings believes that such payments will be made within any stated grace period. However, any stated grace period longer than five business days will be treated as five business days. The ‘D’ rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of a similar action and where default on an obligation is a virtual certainty, for example due to automatic stay provisions. A rating on an obligation is lowered to ‘D’ if it is subject to a distressed debt restructuring. |
Dual Ratings: Dual ratings may be assigned to debt issues that have a put option or demand feature. The first component of the rating addresses the likelihood of repayment of principal and interest as due, and the second component of the rating addresses only the demand feature. The first component of the rating can relate to either a short-term or long-term transaction and accordingly use either short-term or long-term rating symbols. The second component of the rating relates to the put option and is assigned a short-term rating symbol (for example, “AAA/A-1+” or “A-1+/A-1”). With U.S. municipal short-term demand debt, the U.S. municipal short-term note rating symbols are used for the first component of the rating (for example, “SP-1+/A-1+”).
S&P Active Qualifiers (Currently applied and/or outstanding)
|
| L Ratings qualified with ‘L’ apply only to amounts invested up to federal deposit insurance limits. |
| p This suffix is used for issues in which the credit factors, the terms, or both, that determine the likelihood of receipt of payment of principal are different from the credit factors, terms or both that determine the likelihood of receipt of interest on the obligation. The ‘p’ suffix indicates that the rating addresses the principal portion of the obligation only and that the interest is not rated. |
prelim
Preliminary ratings, with the ‘prelim’ suffix, may be assigned to obligors or obligations, including financial programs, in the circumstances described below. Assignment of a final rating is conditional on the receipt by S&P Global Ratings of appropriate documentation. S&P Global Ratings reserves the right not to issue a final rating. Moreover, if a final rating is issued, it may differ from the preliminary rating.
A-3
| |
• |
Preliminary ratings may be assigned to obligations, most commonly structured and project finance issues, pending receipt of final documentation and legal opinions. |
| |
• |
Preliminary ratings may be assigned to obligations that will likely be issued upon the obligor’s emergence from bankruptcy or similar reorganization, based on late-stage reorganization plans, documentation, and discussions with the obligor. Preliminary ratings may also be assigned to the obligors. These ratings consider the anticipated general credit quality of the reorganized or post-bankruptcy issuer as well as attributes of the anticipated obligation(s). |
| |
• |
Preliminary ratings may be assigned to entities that are being formed or that are in the process of being independently established when, in S&P Global Ratings’ opinion, documentation is close to final. Preliminary ratings may also be assigned to the obligations of these entities. |
| |
• |
Preliminary ratings may be assigned when a previously unrated entity is undergoing a well-formulated restructuring, recapitalization, significant financing, or other transformative event, generally at the point that investor or lender commitments are invited. The preliminary rating may be assigned to the entity and to its proposed obligation(s). These preliminary ratings consider the anticipated general credit quality of the obligor, as well as attributes of the anticipated obligation(s), assuming successful completion of the transformative event. Should the transformative event not occur, S&P Global Ratings would likely withdraw these preliminary ratings. |
| |
• |
A preliminary recovery rating may be assigned to an obligation that has a preliminary issue credit rating. |
|
|
|
| t |
|
This symbol indicates termination structures that are designed to honor their contracts to full maturity or, should certain events occur, to terminate and cash settle all their contracts before their final maturity date. |
| cir |
|
This symbol indicates a counterparty instrument rating (CIR), which is a forward-looking opinion about the creditworthiness of an issuer in a securitization structure with respect to a specific financial obligation to a counterparty (including interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and liquidity facilities). The CIR is determined on an ultimate payment basis; these opinions do not take into account timeliness of payment. |
S&P Inactive Qualifiers (No longer applied or outstanding)
*: This symbol indicated that the rating was contingent upon Standard & Poor’s receipt of an executed copy of the escrow agreement or closing documentation confirming investments and cash flows. Discontinued use in August 1998.
c: This qualifier was used to provide additional information to investors that the bank may terminate its obligation to purchase tendered bonds if the long-term credit rating of the issuer was lowered to below an investment-grade level and/or the issuer’s bonds are deemed taxable. Discontinued use in January 2001.
G: The letter ‘G’ followed the rating symbol when a fund’s portfolio consists primarily of direct U.S. government securities.
pi: This qualifier was used to indicate ratings that were based on an analysis of an issuer’s published financial information, as well as additional information in the public domain. Such ratings did not, however, reflect in-depth meetings with an issuer’s management and therefore could have been based on less comprehensive information than ratings without a ‘pi’ suffix. Discontinued use as of December 2014 and as of August 2015 for Lloyd’s Syndicate Assessments.
pr: The letters “pr” indicate that the rating was provisional. A provisional rating assumed the successful completion of a project financed by the debt being rated and indicates that payment of debt service requirements was largely or entirely dependent upon the successful, timely completion of the project. This rating, however, while addressing credit quality subsequent to completion of the project, made no comment on the likelihood of or the risk of default upon failure of such completion.
q: A “q” subscript indicates that the rating is based solely on quantitative analysis of publicly available information. Discontinued use in April 2001.
r: The “r” modifier was assigned to securities containing extraordinary risks, particularly market risks, which are not covered in the credit rating. The absence of an “r” modifier should not be taken as an indication that an obligation would not exhibit extraordinary non-credit related risks. Standard & Poor’s discontinued the use of the “r” modifier for most obligations in June 2000 and for the balance of obligations (mainly structured finance transactions) in November 2002.
Municipal Short-Term Note Ratings
An S&P Global Ratings U.S. municipal note rating reflects S&P Global Ratings’ opinion about the liquidity factors and market access risks unique to the notes. Notes due in three years or less will likely receive a note rating. Notes with an original maturity of more than three years will most likely receive a long-term debt rating. In determining which type of rating, if any, to assign, S&P Global Ratings’ analysis will review the following considerations:
A-4
| |
• |
Amortization schedule-the larger the final maturity relative to other maturities, the more likely it will be treated as a note; and |
| |
• |
Source of payment-the more dependent the issue is on the market for its refinancing, the more likely it will be treated as a note. |
SP-1: Strong capacity to pay principal and interest. An issue determined to possess a very strong capacity to pay debt service is given a plus (+) designation.
SP-2: Satisfactory capacity to pay principal and interest, with some vulnerability to adverse financial and economic changes over the term of the notes.
SP-3: Speculative capacity to pay principal and interest.
D: “D” is assigned upon failure to pay the note when due, completion of a distressed debt restructuring, or the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of similar action and where default on an obligation is a virtual certainty, for example due to automatic stay provisions.
Fitch Ratings, Inc.
Long-Term Credit Ratings
Ratings of individual securities or financial obligations of a corporate issuer address relative vulnerability to default on an ordinal scale. In addition, for financial obligations in corporate finance, a measure of recovery given default on that liability is also included in the rating assessment. This notably applies to covered bonds ratings, which incorporate both an indication of the probability of default and of the recovery given a default of this debt instrument.
The relationship between issuer and obligation scale assumes an historical average recovery of between 30%-50% on the senior, unsecured obligations of an issuer. As a result, individual obligations of entities, such as corporations, are assigned ratings higher, lower, or the same as that entity’s issuer rating or Issuer Default Rating (“IDR”). At the lower end of the ratings scale, Fitch Ratings now additionally publishes explicit Recovery Ratings in many cases to complement issuer and obligation ratings.
Investment Grade
AAA: Highest credit quality. AAA’ ratings denote the lowest expectation of default risk. They are assigned only in cases of exceptionally strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
AA: Very high credit quality. AA’ ratings denote expectations of very low default risk. They indicate very strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is not significantly vulnerable to foreseeable events.
A: High credit quality. A’ ratings denote expectations of low default risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered strong. This capacity may, nevertheless, be more vulnerable to adverse business or economic conditions than is the case for higher ratings
BBB: Good credit quality. BBB’ ratings indicate that expectations of default risk are currently low. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
Speculative Grade
BB: Speculative. BB’ ratings indicate an elevated vulnerability to default risk, particularly in the event of adverse changes in business or economic conditions over time; however, business or financial flexibility exists that supports the servicing of financial commitments.
B: Highly speculative. B’ ratings indicate that material default risk is present, but a limited margin of safety remains. Financial commitments are currently being met; however, capacity for continued payment is vulnerable to deterioration in the business and economic environment. †
CCC: Substantial credit risk. Default is a real possibility. †
CC: Very high levels of credit risk. Default of some kind appears probable. †
A-5
C: Near default. A default or default-like process has begun, or the issuer is in standstill, or for a closed funding vehicle, payment capacity is irrevocably impaired. †
| † |
Table of the Relationship between Performing and Non-performing Corporate Obligations in Low Speculative Grade (Recovery Ratings are discussed in their own section) |
Defaulted obligations typically are not assigned “RD” or “D” ratings, but are instead rated in the “B” to “C” rating categories, depending upon their recovery prospects and other relevant characteristics. This approach better aligns obligations that have comparable overall expected loss but varying vulnerability to default and loss.
Note: The modifiers “+” or “-” may be appended to a rating to denote relative status within major rating categories. Such suffixes are not added to the “AAA” obligation rating category, or to corporate finance obligation ratings in the categories below “CCC”.
The subscript “emr” is appended to a rating to denote embedded market risk which is beyond the scope of the rating. The designation is intended to make clear that the rating solely addresses the counterparty risk of the issuing bank. It is not meant to indicate any limitation in the analysis of the counterparty risk, which in all other respects follows published Fitch criteria for analyzing the issuing financial institution. Fitch does not rate these instruments where the principal is to any degree subject to market risk.
|
|
|
|
|
| B Category |
|
• Default risk is commensurate with an IDR in the ranges “BB” to “C”. For issuers with an IDR below “B”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is moderated by the expected level of recoveries should a default occur. • For issuers with an IDR above “B”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is exacerbated by the expected low level of recoveries should a default occur. • Default risk is commensurate with an IDR in the ranges “B” to “C”. |
|
The obligation or issuer is in default, or has deferred payment, but the rated obligation is expected to have extremely high recovery rates consistent with a Recovery Rating of “RR1”. |
| CCC Category |
|
• Default risk is commensurate with an IDR in the ranges “B” to “C”. • For issuers with an IDR below “CCC”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is moderated by the expected level of recoveries should a default occur. • For issuers with an IDR above “CCC”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is exacerbated by the expected low level of recoveries should a default occur. • Default risk is commensurate with an IDR in the ranges “B” to “C”. |
|
The obligation or issuer is in default, or has deferred payment, but the rated obligation is expected to have a superior recovery rate consistent with a Recovery Rating of “RR2”. |
| CC Category |
|
• For issuers with an IDR below “CC”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is moderated by the expected level of recoveries should a default occur. • For issuers with an IDR above “CC”, the overall credit risk of this obligation is exacerbated by the expected low level of recoveries should a default occur. • Default risk is commensurate with an IDR in the ranges “B” to “C”. |
|
The obligation or issuer is in default, or has deferred payment, but the rated obligation is expected to have a good recovery rate consistent with a Recovery Rating of “RR3”. |
| C Category |
|
• The overall credit risk of this obligation is exacerbated by the expected low level of recoveries should a default occur. |
|
The obligation or issuer is in default, or has deferred payment, and the rated obligation is expected to have an average, below-average or poor recovery rate consistent with a Recovery Rating of “RR4”, “RR5” or “RR6”. |
A-6
Short-Term Credit Ratings
Short-Term Ratings Assigned to Obligations in Corporate, Public and Structured Finance
A short-term issuer or obligation rating is based in all cases on the short-term vulnerability to default of the rated entity or security stream, and relates to the capacity to meet financial obligations in accordance with the documentation governing the relevant obligation. Short-Term Ratings are assigned to obligations whose initial maturity is viewed as “short term” based on market convention. Typically, this means up to 13 months for corporate, sovereign, and structured obligations, and up to 36 months for obligations in US public finance markets.
F1: Indicates the strongest capacity for timely payment of financial commitments relative to other issuers or obligations in the same country. Under the agency’s National Rating scale, this rating is assigned to the lowest default risk relative to others in the same country or monetary union. Where the liquidity profile is particularly strong, a “+” is added to the assigned rating.
F2: Indicates a good capacity for timely payment of financial commitments relative to other issuers or obligations in the same country or monetary union. However, the margin of safety is not as great as in the case of the higher ratings.
F3: Indicates an adequate capacity for timely payment of financial commitments relative to other issuers or obligations in the same country or monetary union.
B: Indicates an uncertain capacity for timely payment of financial commitments relative to other issuers or obligations in the same country or monetary union.
C: Indicates a highly uncertain capacity for timely payment of financial commitments relative to other issuers or obligations in the same country or monetary union.
RD: Indicates an entity that has defaulted on one or more of its financial commitments, although it continues to meet other financial obligations. Applicable to entity ratings only.
D: Indicates a broad-based default event for an entity, or the default of a short-term obligation.
A-7
APPENDIX B
INVESTMENT PRACTICES
For ease of reference, this table reflects the investment practices in which the Fund may engage.
|
|
|
| |
|
Systematic Growth Fund |
| Adjustable Rate Securities |
|
Y |
| Asset-Backed Securities |
|
Y |
| Bank Obligations |
|
Y |
| Convertible Securities |
|
Y |
| Depositary Receipts |
|
Y |
| Derivatives |
|
Y |
| Equity Securities |
|
Y |
| Common Stocks - Large Cap Issuers |
|
Y |
| Common Stocks - Mid-Cap Issuers |
|
Y |
| Common Stocks - Small Cap Issuers |
|
Y |
| Preferred Stocks |
|
Y |
| Warrants/Rights |
|
Y |
| Eurodollar Obligations |
|
Y |
| Fixed Income Securities (Investment Grade) |
|
Y |
| Brady Bonds |
|
Y |
| Catastrophe Bonds |
|
Y |
| CBOs |
|
Y |
| Inflation-Indexed Bonds |
|
Y |
| International Bonds |
|
Y |
| Junk Bonds |
|
Y |
| Variable Rate Demand Notes |
|
Y |
| Zero Coupon Bonds |
|
Y |
| Foreign Currency |
|
Y |
| Foreign Currency Exchange Trans./Forward Contracts |
|
Y |
| Foreign Securities (Including Non-U.S. Denominated) |
|
Y |
| Equity Securities |
|
Y |
| Fixed Income Securities (Including Money Market Securities) |
|
Y |
| Emerging Markets |
|
Y |
| Hybrid Instruments |
|
Y(10)% |
| Illiquid Securities |
|
Y (15%) |
| IPOs |
|
Y |
| Lending Portfolio Securities |
|
Y |
| Loan Participations and Assignments |
|
Y |
| Master Limited Partnerships |
|
Y |
| Money Market Securities |
|
Y |
| Mortgage-Related Securities |
|
Y |
| Mortgage Pass Through Securities (Including GNMA, FNMA or GHLMC) |
|
Y |
| CMOs |
|
Y |
| Commercial Mort-Based Secs. |
|
Y |
| Stripped Mortgage Backed Securities |
|
Y |
| CMO Residuals |
|
Y |
| Mortgage Dollar Rolls |
|
Y |
| Options and Futures Contracts |
|
Y |
| Options on Securities/Indexes |
|
Y |
| Writing/Purchasing Covered Call/Put Options |
|
Y |
| Futures Contracts |
|
Y |
| Options on Futures Contracts |
|
Y |
| OTC Options |
|
Y |
| Unlisted Options |
|
Y |
B-1
|
|
|
| Other Investment Companies (and ETFs) |
|
Y |
| Privately Placed Securities |
|
Y |
| Real Estate Securities & REITs |
|
Y |
| Repurchase Agreements and Purchase and Sale Contracts |
|
Y |
| Restricted Securities |
|
Y |
| Reverse Repurchase Agreements |
|
Y |
| Short Sales (Against the Box) |
|
Y |
| Short Sales (Other than Against the Box) |
|
N |
| Structured Notes |
|
Y |
| Swap Agreements |
|
Y |
| Credit Default Swaps |
|
Y |
| Currency Exchange Rate Swaps |
|
N |
| Interest Rate Swaps |
|
N |
| Total Return Swaps (Equity) |
|
Y |
| Unseasoned Issuers |
|
N |
| When-Issued (Delayed-Delivery) Securities |
|
Y |
B-2
v3.23.1
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe date the document was made available and submitted, in YYYY-MM-DD format. The date of submission, date of acceptance by the recipient, and the document effective date are all potentially different.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentCreationDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe date when a document, upon receipt and acceptance, becomes officially effective, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Usually it is a system-assigned date time value, but it may be declared by the submitter in some cases.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentEffectiveDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation 12B
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionOne of: N-1A (Mutual Fund), N-1 (Open-End Separate Account with No Variable Annuities), N-2 (Closed-End Investment Company), N-3 (Separate Account Registered as Open-End Management Investment Company), N-4 (Variable Annuity UIT Separate Account), N-5 (Small Business Investment Company), N-6 (Variable Life UIT Separate Account), S-1 or S-3 (Face Amount Certificate Company), S-6 (UIT, Non-Insurance Product). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 313
| Name: |
dei_EntityInvCompanyType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:invCompanyType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation 12B
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe date of the prospectus. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 1
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 3
| Name: |
rr_ProspectusDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.23.1
| Label |
Element |
Value |
| Systematic Growth Fund |
|
|
|
| Risk/Return: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
|
|
| Risk/Return [Heading] |
rr_RiskReturnHeading |
FUND SUMMARY: SYSTEMATIC GROWTH FUND (FORMERLY, BLUE CHIP GROWTH FUND)
|
|
| Objective [Heading] |
rr_ObjectiveHeading |
Investment Objective
|
|
| Objective, Primary [Text Block] |
rr_ObjectivePrimaryTextBlock |
The Fund seeks total return.
|
|
| Expense [Heading] |
rr_ExpenseHeading |
Fees and Expenses of the Fund
|
|
| Expense Narrative [Text Block] |
rr_ExpenseNarrativeTextBlock |
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold and sell shares of the Fund. The table and the example below do not reflect the separate account fees charged in the variable annuity or variable life insurance policy (“Variable Contracts”) in which the Fund is offered. If separate account fees were shown, the Fund’s annual operating expenses would be higher. Please see your Variable Contract prospectus for more details on the separate account fees.
|
|
| Operating Expenses Caption [Text] |
rr_OperatingExpensesCaption |
Annual Fund Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment)
|
|
| Fee Waiver or Reimbursement over Assets, Date of Termination |
rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssetsDateOfTermination |
September 30, 2024
|
|
| Portfolio Turnover [Heading] |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverHeading |
Portfolio Turnover
|
|
| Portfolio Turnover [Text Block] |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverTextBlock |
The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the Example, affect the Fund’s performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 25% of the average value of its portfolio.
|
|
| Portfolio Turnover, Rate |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverRate |
25.00%
|
|
| Expense Example [Heading] |
rr_ExpenseExampleHeading |
Expense Example
|
|
| Expense Example Narrative [Text Block] |
rr_ExpenseExampleNarrativeTextBlock |
This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem or hold all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the Fund’s operating expenses include fee waivers for year one. The Example does not reflect charges imposed by the Variable Contract. If the Variable Contract fees were reflected, the expenses would be higher. See the Variable Contract prospectus for information on such charges. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions and the net expenses shown in the fee table, your costs would be:
|
|
| Strategy [Heading] |
rr_StrategyHeading |
Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund
|
|
| Strategy Narrative [Text Block] |
rr_StrategyNarrativeTextBlock |
The Fund invests primarily in equity securities of issuers included in the Russell 1000® Growth Index (the “Index”) at the time of purchase. The Index is comprised of U.S. large- and mid‑cap companies that exhibit certain growth characteristics, as defined by the index provider. As of December 31, 2022, the market capitalization range of the companies in the Index was approximately $656.70 million to $2.10 trillion. The size of the companies in the Index changes with market conditions and the composition of the Index. The equity securities in which the Fund invests include common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities, rights, and warrants. The Fund may at times have significant exposure to one or more industries or sectors and may be overweight with respect to certain securities (i.e., the Fund will hold a greater percentage of those securities than the Index) and underweight with respect to others (i.e., the Fund will hold a lesser percentage of those securities than the Index). Such weightings may change over time. Each of the Fund’s subadvisers manages a portion of the Fund’s assets using different investment strategies and techniques. One subadviser employs a proprietary, dynamic multifactor approach to managing the Fund’s assets that is based on quantitative and qualitative research and analysis. In selecting securities, the subadviser seeks to allocate its portion of the Fund’s assets to equity securities the subadviser believes share complementary factor exposures. Factors are characteristics that are important in explaining the returns and risks of a group of securities. Among the factors that the subadviser uses to select equity securities for the Fund are: (1) mean reversion (e.g., stocks that are inexpensive relative to their historical fundamentals); (2) trend following (e.g., strong momentum and higher growth potential); and (3) risk aversion (e.g., financially healthy, stable, and lower volatility companies). In exceptional circumstances, the subadviser may exclude, remove or include an issuer or security in the Fund’s portfolio where it believes the data available does not accurately reflect current events, or to adjust the risk profile of the Fund appropriately. The subadviser may engage in frequent and active trading of portfolio securities with respect to its portion of the Fund’s assets. The other subadviser uses a rules-based methodology that emphasizes quantitatively-based stock selection, portfolio construction, and efficient implementation to seek to capture common sources of active equity returns among factors. Among the factors that the subadviser’s methodology employs are: (1) value (i.e., how attractively a stock is priced relative to its “fundamentals,” such as book value and free cash flow); (2) momentum (i.e., whether a company’s share price is trending up or down); (3) quality (i.e., profitability) and (4) low volatility (i.e., a relatively low degree of fluctuation in a company’s share price over time). The subadviser seeks to capitalize on the low correlations in returns across these factors by diversifying exposure to securities selected based on such factors. The subadviser may, in its discretion, make changes to its quantitative techniques, or use other quantitative techniques that are based on the subadviser’s proprietary research. The subadviser constructs its portion of the Fund’s portfolio by investing assets in the securities comprising the Index and adjusting the relative weight of each security based on the security’s attractiveness when evaluated based on the factors as described above, subject to the Fund being constrained to long-only positions. The subadviser will rebalance its portion of the Fund’s portfolio according to the process set forth above on a quarterly basis. The subadviser generally employs a strategy to continue to hold securities between quarterly rebalancings, even if there are adverse developments concerning a particular security, an industry, the economy, or the stock market generally. The subadviser may reduce the position size of a security or sell a security during quarterly rebalancings if the security no longer has favorable scores in one or more of the four factors. In order to generate additional income, the Fund may lend portfolio securities to broker-dealers and other financial institutions provided that the value of the loaned securities does not exceed 30% of the Fund’s total assets. These loans earn income for the Fund and are collateralized by cash and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities. The Fund is a non‑diversified fund, which means that it may invest in a smaller number of issuers than a diversified fund.
|
|
| Risk [Heading] |
rr_RiskHeading |
Principal Risks of Investing in the Fund
|
|
| Risk Narrative [Text Block] |
rr_RiskNarrativeTextBlock |
As with any mutual fund, there can be no assurance that the Fund’s investment objective will be met or that the net return on an investment in the Fund will exceed what could have been obtained through other investment or savings vehicles. Shares of the Fund are not bank deposits and are not guaranteed or insured by any bank, government entity or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. If the value of the assets of the Fund goes down, you could lose money. The following is a summary of the principal risks of investing in the Fund. Management Risk. The investment style or strategy used by the subadviser may fail to produce the intended result. The subadviser’s assessment of a particular security or company may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or underperformance. Equity Securities Risk. The Fund invests principally in equity securities and is therefore subject to the risk that stock prices will fall and may underperform other asset classes. Individual stock prices fluctuate from day‑to‑day and may decline significantly. The prices of individual stocks may be negatively affected by poor company results or other factors affecting individual prices, as well as industry and/or economic trends and developments affecting industries or the securities market as a whole. Growth Style Risk. Generally, “growth” stocks are stocks of companies that a subadviser believes have anticipated earnings ranging from steady to accelerated growth. Many investors buy growth stocks because of anticipated superior earnings growth, but earnings disappointments often result in sharp price declines. Growth companies usually invest a high portion of earnings in their own businesses so their stocks may lack the dividends that can cushion share prices in a down market. In addition, the value of growth stocks may be more sensitive to changes in current or expected earnings than the value of other stocks, because growth stocks trade at higher prices relative to current earnings. Factor-Based Investing Risk. There can be no assurance that the multi-factor selection process employed by a subadviser will enhance performance. Exposure to investment style factors may detract from performance in some market environments, which may continue for prolonged periods. Large- and Mid‑Cap Company Risk. Investing in large- and mid‑cap companies carries the risk that due to current market conditions these companies may be out of favor with investors. Large‑cap companies may be unable to respond quickly to new competitive challenges or attain the high growth rate of successful smaller companies. Stocks of mid‑cap companies may be more volatile than those of larger companies due to, among other reasons, narrower product lines, more limited financial resources and fewer experienced managers. Preferred Stock Risk. Unlike common stock, preferred stock generally pays a fixed dividend from a company’s earnings and may have a preference over common stock on the distribution of a company’s assets in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation. Preferred stockholders’ liquidation rights are subordinate to the company’s debt holders and creditors. If interest rates rise, the fixed dividend on preferred stocks may be less attractive and the price of preferred stocks may decline. Preferred stockholders typically do not have voting rights. Convertible Securities Risk. Convertible security values may be affected by market interest rates, issuer defaults and underlying common stock values; security values may fall if market interest rates rise and rise if market interest rates fall. Additionally, an issuer may have the right to buy back the securities at a time unfavorable to the Fund. Warrants and Rights Risk. Warrants and rights can provide a greater potential for profit or loss than an equivalent investment in the underlying security. Prices of warrants and rights do not necessarily move in tandem with the prices of the underlying securities and therefore are highly volatile and speculative investments. They have no voting rights, pay no dividends and have no rights with respect to the assets of the issuer other than a purchase option. If a warrant or right held by the Fund is not exercised by the date of its expiration, the Fund would lose the entire purchase price of the warrant or right. Quantitative Investing Risk. The value of securities selected using quantitative analysis can react differently to issuer, political, market, and economic developments from the market as a whole or securities selected using only fundamental analysis. This may be the result of the factors used in building the quantitative analytical framework, the weights placed on each factor, and the accuracy of historical data supplied by third parties. In addition, factors that affect a security’s value can change over time and these changes may not be reflected in the quantitative model. Sector Risk. Companies with similar characteristics may be grouped together in broad categories called sectors. Sector risk is the risk that securities of companies within specific sectors of the economy can perform differently than the overall market. This may be due to changes in such things as the regulatory or competitive environment or to changes in investor perceptions regarding a sector. Because the Fund may allocate relatively more assets to certain sectors than others, the Fund’s performance may be more susceptible to any developments which affect those sectors emphasized by the Fund. Market Risk. The Fund’s share price can fall because of weakness in the broad market, a particular industry, or specific holdings or due to adverse political or economic developments here or abroad, changes in investor psychology, or heavy institutional selling and other conditions or events (including, for example, military confrontations, war, terrorism, sanctions, disease/virus, outbreaks and epidemics). The prices of individual securities may fluctuate, sometimes dramatically, from day to day. The prices of stocks and other equity securities tend to be more volatile than those of fixed-income securities. The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the related governmental and public responses have had and may continue to have an impact on the Fund’s investments and net asset value and have led and may continue to lead to increased market volatility and the potential for illiquidity in certain classes of securities and sectors of the market. Preventative or protective actions that governments may take in respect of pandemic or epidemic diseases may result in periods of business disruption, business closures, inability to obtain raw materials, supplies and component parts, and reduced or disrupted operations for the issuers in which the Fund invests. Government intervention in markets may impact interest rates, market volatility and security pricing. The occurrence, reoccurrence and pendency of such diseases could adversely affect the economies (including through changes in business activity and increased unemployment) and financial markets either in specific countries or worldwide. Non‑Diversification Risk. Because the Fund may invest in a smaller number of issuers, its value may be affected to a greater extent by the performance of any one of those issuers or by any single economic, political, market or regulatory event affecting any one of those issues than a fund that invests in a larger number of issuers. Securities Lending Risk. Engaging in securities lending could increase the market and credit risk for Fund investments. The Fund may lose money if it does not recover borrowed securities, the value of the collateral falls, or the value of investments made with cash collateral declines. The Fund’s loans will be collateralized by securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies and instrumentalities, which subjects the Fund to the credit risk of the U.S. Government or the issuing federal agency or instrumentality. If the value of either the cash collateral or the Fund’s investments of the cash collateral falls below the amount owed to a borrower, the Fund also may incur losses that exceed the amount it earned on lending the security. Securities lending also involves the risks of delay in receiving additional collateral or possible loss of rights in the collateral if the borrower fails. Another risk of securities lending is the risk that the loaned portfolio securities may not be available to the Fund on a timely basis and the Fund may therefore lose the opportunity to sell the securities at a desirable price.
|
|
| Risk Lose Money [Text] |
rr_RiskLoseMoney |
If the value of the assets of the Fund goes down, you could lose money.
|
|
| Risk Not Insured Depository Institution [Text] |
rr_RiskNotInsuredDepositoryInstitution |
Shares of the Fund are not bank deposits and are not guaranteed or insured by any bank, government entity or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
|
|
| Risk Nondiversified Status [Text] |
rr_RiskNondiversifiedStatus |
Non‑Diversification Risk. Because the Fund may invest in a smaller number of issuers, its value may be affected to a greater extent by the performance of any one of those issuers or by any single economic, political, market or regulatory event affecting any one of those issues than a fund that invests in a larger number of issuers.
|
|
| Bar Chart and Performance Table [Heading] |
rr_BarChartAndPerformanceTableHeading |
Performance Information
|
|
| Performance Narrative [Text Block] |
rr_PerformanceNarrativeTextBlock |
The following Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table illustrate the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund’s performance from calendar year to calendar year and comparing the Fund’s average annual returns to those of the Russell 1000® Growth Index and the S&P 500® Index. Effective May 1, 2023, the Fund changed its benchmark index against which the Fund measures its performance from the S&P 500® Index to the Russell 1000® Growth Index. Fund management believes that the Russell 1000® Growth Index is more representative of the securities in which the Fund invests. The Fund’s returns prior to May 1, 2023, as reflected in the bar chart and table, are the returns of the Fund when it followed different investment strategies under the name “Blue Chip Growth Fund.” Fees and expenses incurred at the contract level are not reflected in the bar chart or table. If these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. Of course, past performance of the Fund is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future. Effective May 1, 2023, Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”) and Wellington Management Company LLP (“Wellington Management”) assumed subadvisory responsibilities for the Fund. Prior to May 1, 2023, T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. served as subadviser to the Fund.
|
|
| Performance Information Illustrates Variability of Returns [Text] |
rr_PerformanceInformationIllustratesVariabilityOfReturns |
The following Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table illustrate the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund’s performance from calendar year to calendar year and comparing the Fund’s average annual returns to those of the Russell 1000® Growth Index and the S&P 500® Index.
|
|
| Performance Past Does Not Indicate Future [Text] |
rr_PerformancePastDoesNotIndicateFuture |
Of course, past performance of the Fund is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.
|
|
| Bar Chart Does Not Reflect Sales Loads [Text] |
rr_BarChartDoesNotReflectSalesLoads |
Fees and expenses incurred at the contract level are not reflected in the bar chart or table. If these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown.
|
|
| Bar Chart Closing [Text Block] |
rr_BarChartClosingTextBlock |
During the period shown in the bar chart: Highest Quarterly Return: June 30, 2020 27.59% Lowest Quarterly Return: June 30, 2022 ‑25.46% Year to Date Most Recent Quarter: March 31, 2023 16.40%
|
|
| Performance Table Heading |
rr_PerformanceTableHeading |
Average Annual Total Returns (For the periods ended December 31, 2022)
|
|
| Performance Table Market Index Changed |
rr_PerformanceTableMarketIndexChanged |
Effective May 1, 2023, the Fund changed its benchmark index against which the Fund measures its performance from the S&P 500® Index to the Russell 1000® Growth Index.
|
|
| Systematic Growth Fund | Systematic Growth Fund |
|
|
|
| Risk/Return: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
|
|
| Management Fees |
rr_ManagementFeesOverAssets |
0.72%
|
|
| Other Expenses |
rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets |
0.10%
|
|
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
rr_ExpensesOverAssets |
0.82%
|
|
| Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements |
rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssets |
0.17%
|
[1] |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements |
rr_NetExpensesOverAssets |
0.65%
|
[1] |
| 1 Year |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear01 |
$ 66
|
|
| 3 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear03 |
245
|
|
| 5 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear05 |
438
|
|
| 10 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear10 |
998
|
|
| 1 Year |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear01 |
66
|
|
| 3 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear03 |
245
|
|
| 5 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear05 |
438
|
|
| 10 Years |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear10 |
$ 998
|
|
| 2013 |
rr_AnnualReturn2013 |
41.19%
|
|
| 2014 |
rr_AnnualReturn2014 |
9.14%
|
|
| 2015 |
rr_AnnualReturn2015 |
11.04%
|
|
| 2016 |
rr_AnnualReturn2016 |
0.85%
|
|
| 2017 |
rr_AnnualReturn2017 |
36.21%
|
|
| 2018 |
rr_AnnualReturn2018 |
1.97%
|
|
| 2019 |
rr_AnnualReturn2019 |
29.84%
|
|
| 2020 |
rr_AnnualReturn2020 |
34.37%
|
|
| 2021 |
rr_AnnualReturn2021 |
16.38%
|
|
| 2022 |
rr_AnnualReturn2022 |
(38.81%)
|
|
| Year to Date Return, Label |
rr_YearToDateReturnLabel |
Year to Date Most Recent Quarter:
|
|
| Bar Chart, Year to Date Return, Date |
rr_BarChartYearToDateReturnDate |
Mar. 31, 2023
|
|
| Bar Chart, Year to Date Return |
rr_BarChartYearToDateReturn |
16.40%
|
|
| Highest Quarterly Return, Label |
rr_HighestQuarterlyReturnLabel |
Highest Quarterly Return:
|
|
| Highest Quarterly Return, Date |
rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturnDate |
Jun. 30, 2020
|
|
| Highest Quarterly Return |
rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturn |
27.59%
|
|
| Lowest Quarterly Return, Label |
rr_LowestQuarterlyReturnLabel |
Lowest Quarterly Return:
|
|
| Lowest Quarterly Return, Date |
rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturnDate |
Jun. 30, 2022
|
|
| Lowest Quarterly Return |
rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturn |
(25.46%)
|
|
| 1 Year |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear01 |
(38.81%)
|
|
| 5 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear05 |
4.84%
|
|
| 10 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear10 |
11.53%
|
|
| Systematic Growth Fund | Russell 1000® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) |
|
|
|
| Risk/Return: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
|
|
| 1 Year |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear01 |
(29.14%)
|
|
| 5 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear05 |
10.96%
|
|
| 10 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear10 |
14.10%
|
|
| Systematic Growth Fund | S&P 500® Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) |
|
|
|
| Risk/Return: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
|
|
| 1 Year |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear01 |
(18.11%)
|
|
| 5 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear05 |
9.42%
|
|
| 10 Years |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear10 |
12.56%
|
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2013 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2014 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2015 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2016 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2017 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2018 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2019 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2020 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2021 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_AnnualReturn2022 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph iii
-Clause 1
-Exhibit 2
| Name: |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph iii
-Clause 1
-Exhibit 2
| Name: |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear05 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph iii
-Clause 1
-Exhibit 2
| Name: |
rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear10 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartClosingTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionInclude the bar chart and table required by Item 4 (b)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section. Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future. Provide annual total returns beginning with the earliest calendar year. Calculate annual returns using the Instructions to Item 8(a), except that the calculations should be based on calendar years. If a Fund's shares are sold subject to a sales load or account fees, state that sales loads or account fees are not reflected in the bar chart and that, if these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph i
| Name: |
rr_BarChartDoesNotReflectSalesLoads |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturn |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturnDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturn |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturnDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartYearToDateReturn |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_BarChartYearToDateReturnDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionHeading for Expense Example. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 4
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 1
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleNarrativeTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionYou would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph 1
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionYou would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph 1
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear03 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionYou would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph f
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear05 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionYou would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph f
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear10 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 4
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear01 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 2
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear03 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 2
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear05 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 2
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseExampleYear10 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativeMonetaryType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRisk/Return Summary Fee Table Includes the following information, in plain English under rule 421(d) under the Securities Act, after Item 2 Fees and expenses of the Fund This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shared of the Fund. You may qualify for sales charge discounts if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $[_____] in [name of fund family] funds. Shareholder Fees (fees paid directly from your investment) Example This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares The Example does not reflect sales charges (loads) on reinvested dividends [and other distributions]. If these sales charges (loads) were included, your costs would be higher. Portfolio Turnover The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or "turns over" its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover may indicate higher transaction costs. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the example, affect the Fund's performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund's portfolio turnover rate was __% of the average value of its whole portfolio. Instructions. A.3.instructions.6 New Funds. For purposes of this Item, a "New Fund" is a Fund that does not include in Form N-1A financial statements reporting operating results or that includes financial statements for the Fund's initial fiscal year reporting operating results for a period of 6 months or less. The following Instructions apply to New Funds. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph d
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold, and sell shares of the Fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to financial intermediaries, which are not reflected in the tables and examples below. You may qualify for sales charge discounts if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $[ ] in [name of fund family] funds. More information about these and other discounts is available from your financial intermediary and in [identify section heading and page number] of the Fund's prospectus and [identify section heading and page number] of the Fund's statement of additional information Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph b
| Name: |
rr_ExpenseNarrativeTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal Annual Fund Operating Expenses. If the Fund is a Feeder Fund, reflect the aggregate expenses of the Feeder Fund and the Master Fund in a single fee table using the captions provided. In a footnote to the fee table, state that the table and Example reflect the expenses of both the Feeder and Master Funds. If the prospectus offers more than one Class of a Multiple Class Fund or more than one Feeder Fund that invests in the same Master Fund, provide a separate response for each Class or Feeder Fund. Base the percentages of "Annual Fund Operating Expenses" on amounts incurred during the Fund's most recent fiscal year, but include in expenses amounts that would have been incurred absent expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements. If the Fund has changed its fiscal year and, as a result, the most recent fiscal year is less than three months, use the fiscal year prior to the most recent fiscal year as the basis for determining "Annual Fund Operating Expenses." Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph d
| Name: |
rr_ExpensesOverAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativePure4Type |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal Annual Fund Operating Expenses. If there were expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements that reduced any Fund operating expenses and will continue to reduce them for no less than one year from the effective date of the Fund's registration statement, a Fund may add two captions to the table one caption showing the amount of the expense reimbursement or fee waiver, and a second caption showing the Fund's net expenses after subtracting the fee reimbursement or expense waiver from the total fund operating expenses. The Fund should place these additional captions directly below the "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses" caption of the table and should use appropriate descriptive captions, such as "Fee Waiver [and/or Expense Reimbursement]" and "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waiver [and/or Expense Reimbursement]," respectively. If the Fund provides this disclosure, also disclose the period for which the expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangement is expected to continue, and briefly describe who can terminate the arrangement and under what circumstances. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection table
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 11
| Name: |
rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonPositivePure4Type |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis element represents the date of expected termination of any expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements that reduce any Fund operating expenses (SEC Form N-1A 2006-09-14 A.3.table.1.11 Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses A.3.instructions.3.e). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph e
| Name: |
rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssetsDateOfTermination |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_HighestQuarterlyReturnLabel |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_LowestQuarterlyReturnLabel |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionManagement Fees include investment advisory fees (including any fees based on the Fund's performance), any other management fees payable to the investment adviser or its affiliates, and administrative fees payable to the investment adviser or its affiliates that are not included as "Other Expenses." Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph a
| Name: |
rr_ManagementFeesOverAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativePure4Type |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal Annual Fund Operating Expenses. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection table
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 11
| Name: |
rr_NetExpensesOverAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativePure4Type |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionInvestment Objectives/Goals. Disclose the Fund's investment objectives or goals. A Fund also may identify its type or category (e.g., that it is a Money Market Fund or a balanced fund). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 2
-Subsection a
| Name: |
rr_ObjectiveHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionInvestment Objectives/Goals. Disclose the Fund's investment objectives or goals. A Fund also may identify its type or category (e.g., that it is a Money Market Fund or a balanced fund). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 2
-Subsection a
| Name: |
rr_ObjectivePrimaryTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAnnual Fund Operating Expenses (ongoing expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment) Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection table
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph 7
| Name: |
rr_OperatingExpensesCaption |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition"Other Expenses" include all expenses not otherwise disclosed in the table that are deducted from the Fund's assets or charged to all shareholder accounts. The amount of expenses deducted from the Fund's assets are the amounts shown as expenses in the Fund's statement of operations (including increases resulting from complying with paragraph 2(g) of rule 6-07 of Regulation S-X [17 CFR 210.6-07]). "Other Expenses" do not include extraordinary expenses as determined under generally accepted accounting principles (see Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 30). If extraordinary expenses were incurred that materially affected the Fund's "Other Expenses," disclose in a footnote to the table what "Other Expenses" would have been had the extraordinary expenses been included. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph c
-Clause i
| Name: |
rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
rr:NonNegativePure4Type |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRisk/Return Bar Chart and Table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
| Name: |
rr_PerformanceNarrativeTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclose the portfolio turnover rate provided in response to Item 14(a) for the most recent fiscal year (or for such shorter period as the Fund has been in operation). Disclose the period for which the information is provided if less than a full fiscal year. A Fund that is a Money Market Fund may omit the portfolio turnover information required by this Item. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection instructions
-Paragraph 5
| Name: |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis element represents the rate of portfolio turnover presented as a percentage (SEC Form N-1A 2006-09-14 A.3.example.3 Portfolio Turnover A.3.instructions.5 Portfolio Turnover). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 3
| Name: |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverRate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclose the portfolio turnover rate provided in response to Item 14(a) for the most recent fiscal year (or for such shorter period as the Fund has been in operation). Disclose the period for which the information is provided if less than a full fiscal year. A Fund that is a Money Market Fund may omit the portfolio turnover information required by this Item. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 3
-Subsection example
-Paragraph 3
| Name: |
rr_PortfolioTurnoverTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNarrative Risk Disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
rr_RiskHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSummarize the principal risks of investing in the Fund, including the risks to which the Fund's portfolio as a whole is subject and the circumstances reasonably likely to affect adversely the Fund's net asset value, yield, and total return. Unless the Fund is a Money Market Fund, disclose that loss of money is a risk of investing in the Fund. If the Fund is a Money Market Fund, include the following statement: "You could lose money by investing in the Fund." Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph ii
-Clause A
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph ii
-Clause B
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph ii
-Clause C
| Name: |
rr_RiskLoseMoney |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNarrative Risk Disclosure. A Fund may, in responding to this Item, describe the types of investors for whom the Fund is intended or the types of investment goals that may be consistent with an investment in the Fund. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph i
-Clause instruction
| Name: |
rr_RiskNarrativeTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf applicable, state that the Fund is non-diversified, describe the effect of non-diversification (e.g., disclose that, compared with other funds, the Fund may invest a greater percentage of its assets in a particular issuer), and summarize the risks of investing in a non-diversified fund. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph iv
| Name: |
rr_RiskNondiversifiedStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund is advised by or sold through an insured depository institution, state that "An investment in the Fund is not a deposit of the bank and is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency." Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph iii
| Name: |
rr_RiskNotInsuredDepositoryInstitution |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
rr_RiskReturnAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRisk/Return Summary Investment Objectives/Goals Include the following information, in plain English under rule 421(d) under the Securities Act, in the order and subject matter indicated Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 2
| Name: |
rr_RiskReturnHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPrincipal investment strategies of the Fund. Summarize how the Fund intends to achieve its investment objectives by identifying the Fund's principal investment strategies (including the type or types of securities in which the Fund invests or will invest principally) and any policy to concentrate in securities of issuers in a particular industry or group of industries. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection a
| Name: |
rr_StrategyHeading |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPrincipal investment strategies of the Fund. Summarize how the Fund intends to achieve its investment objectives by identifying the Fund's principal investment strategies (including the type or types of securities in which the Fund invests or will invest principally) and any policy to concentrate in securities of issuers in a particular industry or group of industries. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection a
| Name: |
rr_StrategyNarrativeTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIf the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form
-Number N-1A
-Chapter A
-Section 4
-Subsection b
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ii
| Name: |
rr_YearToDateReturnLabel |
| Namespace Prefix: |
rr_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
dei_LegalEntityAxis=valic_S000008005Member |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
rr_ProspectusShareClassAxis=valic_C000021774Member |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
{
"instance": {
"d150800d497.htm": {
"axisCustom": 0,
"axisStandard": 3,
"baseTaxonomies": {
"http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021": 8,
"http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021": 69
},
"contextCount": 5,
"dts": {
"calculationLink": {
"local": [
"valic-20230503_cal.xml"
]
},
"definitionLink": {
"local": [
"valic-20230503_def.xml"
]
},
"inline": {
"local": [
"d150800d497.htm"
]
},
"labelLink": {
"local": [
"valic-20230503_lab.xml"
]
},
"presentationLink": {
"local": [
"valic-20230503_pre.xml"
]
},
"schema": {
"local": [
"valic-20230503.xsd"
],
"remote": [
"http://www.xbrl.org/2003/xbrl-instance-2003-12-31.xsd",
"http://www.xbrl.org/2003/xbrl-linkbase-2003-12-31.xsd",
"http://www.xbrl.org/2003/xl-2003-12-31.xsd",
"http://www.xbrl.org/2003/xlink-2003-12-31.xsd",
"http://www.xbrl.org/2005/xbrldt-2005.xsd",
"http://www.xbrl.org/lrr/role/negated-2009-12-16.xsd",
"https://www.xbrl.org/dtr/type/2020-01-21/types.xsd",
"https://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021/dei-2021.xsd",
"https://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021/rr-2021.xsd"
]
}
},
"elementCount": 208,
"entityCount": 1,
"hidden": {
"http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021": 8,
"http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021": 10,
"total": 18
},
"keyCustom": 0,
"keyStandard": 71,
"memberCustom": 4,
"memberStandard": 0,
"nsprefix": "valic",
"nsuri": "http://www.valic.com/20230503",
"report": {
"R1": {
"firstAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"td",
"tr",
"table",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "DefaultContext",
"decimals": null,
"first": true,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:ProspectusDate",
"reportCount": 1,
"unique": true,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
},
"groupType": "document",
"isDefault": "false",
"longName": "000000 - Document - Document and Entity Information {Elements}",
"menuCat": "",
"order": "1",
"role": "http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000",
"shortName": "Document and Entity Information",
"subGroupType": "",
"uniqueAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"td",
"tr",
"table",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "DefaultContext",
"decimals": null,
"first": true,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:ProspectusDate",
"reportCount": 1,
"unique": true,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
}
},
"R2": {
"firstAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "S000008005Member",
"decimals": null,
"first": true,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:RiskReturnHeading",
"reportCount": 1,
"unique": true,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
},
"groupType": "disclosure",
"isDefault": "false",
"longName": "000021 - Disclosure - Risk/Return Detail Data {Elements} - Systematic Growth Fund",
"menuCat": "",
"order": "2",
"role": "http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021",
"shortName": "Risk/Return Detail Data- Systematic Growth Fund",
"subGroupType": "",
"uniqueAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "S000008005Member",
"decimals": null,
"first": true,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:RiskReturnHeading",
"reportCount": 1,
"unique": true,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
}
},
"S1": {
"firstAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "S000008005Member",
"decimals": null,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:RiskReturnHeading",
"reportCount": 1,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
},
"groupType": "RR_Summaries",
"isDefault": "true",
"longName": "000000240 - Disclosure - S000008005 [Member]",
"section": 0,
"shortName": "S000008005 [Member]",
"subGroupType": "",
"uniqueAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "S000008005Member",
"decimals": null,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:RiskReturnHeading",
"reportCount": 1,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
}
},
"S2": {
"firstAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"td",
"tr",
"table",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "DefaultContext",
"decimals": null,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:ProspectusDate",
"reportCount": 1,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
},
"groupType": "RR_Summaries",
"isDefault": "false",
"longName": "000006751 - Disclosure - Document and Entity Information",
"section": 1,
"shortName": "Document and Entity Information",
"subGroupType": "",
"uniqueAnchor": {
"ancestors": [
"div",
"td",
"tr",
"table",
"div",
"div",
"body",
"html"
],
"baseRef": "d150800d497.htm",
"contextRef": "DefaultContext",
"decimals": null,
"lang": "en-US",
"name": "rr:ProspectusDate",
"reportCount": 1,
"unitRef": null,
"xsiNil": "false"
}
}
},
"segmentCount": 4,
"tag": {
"dei_AmendmentDescription": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Description of changes contained within amended document.",
"label": "Amendment Description"
}
}
},
"localname": "AmendmentDescription",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"dei_AmendmentFlag": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Boolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.",
"label": "Amendment Flag"
}
}
},
"localname": "AmendmentFlag",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "booleanItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentCreationDate": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The date the document was made available and submitted, in YYYY-MM-DD format. The date of submission, date of acceptance by the recipient, and the document effective date are all potentially different.",
"label": "Document Creation Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentCreationDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentDomain": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Type of the document as assigned by the filer, corresponding to SEC document naming convention standards.",
"label": "Prospectus"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentDomain",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentEffectiveDate": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The date when a document, upon receipt and acceptance, becomes officially effective, in YYYY-MM-DD format. Usually it is a system-assigned date time value, but it may be declared by the submitter in some cases.",
"label": "Document Effective Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentEffectiveDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentInformationDocumentAxis": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The axis of a table defines the relationship between the domain members or categories in the table and the line items or concepts that complete the table.",
"label": "Document [Axis]"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentInformationDocumentAxis",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "For the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.",
"label": "Document Period End Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentPeriodEndDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"dei_DocumentType": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.",
"label": "Document Type"
}
}
},
"localname": "DocumentType",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "submissionTypeItemType"
},
"dei_EntityCentralIndexKey": {
"auth_ref": [
"r78"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK.",
"label": "Entity Central Index Key"
}
}
},
"localname": "EntityCentralIndexKey",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "centralIndexKeyItemType"
},
"dei_EntityDomain": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "All the names of the entities being reported upon in a document. Any legal structure used to conduct activities or to hold assets. Some examples of such structures are corporations, partnerships, limited liability companies, grantor trusts, and other trusts. This item does not include business and geographical segments which are included in the geographical or business segments domains.",
"label": "Series"
}
}
},
"localname": "EntityDomain",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"dei_EntityInvCompanyType": {
"auth_ref": [
"r79"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "One of: N-1A (Mutual Fund), N-1 (Open-End Separate Account with No Variable Annuities), N-2 (Closed-End Investment Company), N-3 (Separate Account Registered as Open-End Management Investment Company), N-4 (Variable Annuity UIT Separate Account), N-5 (Small Business Investment Company), N-6 (Variable Life UIT Separate Account), S-1 or S-3 (Face Amount Certificate Company), S-6 (UIT, Non-Insurance Product).",
"label": "Entity Inv Company Type"
}
}
},
"localname": "EntityInvCompanyType",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "invCompanyType"
},
"dei_EntityRegistrantName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r78"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC.",
"label": "Registrant Name"
}
}
},
"localname": "EntityRegistrantName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "normalizedStringItemType"
},
"dei_LegalEntityAxis": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The set of legal entities associated with a report.",
"label": "Series [Axis]"
}
}
},
"localname": "LegalEntityAxis",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"dei_LegalEntityIdentifier": {
"auth_ref": [
"r0"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A globally unique ISO 17442 value to identify entities, commonly abbreviated as LEI.",
"label": "Legal Entity Identifier"
}
}
},
"localname": "LegalEntityIdentifier",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "legalEntityIdentifierItemType"
},
"dei_TradingSymbol": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Trading symbol of an instrument as listed on an exchange.",
"label": "Trading Symbol"
}
}
},
"localname": "TradingSymbol",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/dei/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "tradingSymbolItemType"
},
"rr_AcquiredFundFeesAndExpensesBasedOnEstimates": {
"auth_ref": [
"r29"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents a statement that \"Acquired Fund\" (as defined) fees and expenses for the current year are based on estimates.",
"label": "Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses, Based on Estimates [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "AcquiredFundFeesAndExpensesBasedOnEstimates",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_AcquiredFundFeesAndExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r38"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 50.0,
"parentTag": "rr_ExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses.",
"label": "Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "AcquiredFundFeesAndExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_AfterTaxesOnDistributionsAndSalesMember": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate the taxes due on any distributions by the Fund by applying the tax rates specified in Instruction 4 to each component of the distributions on the reinvestment date (e.g., ordinary income, short-term capital gain, long-term capital gain). The taxable amount and tax character of each distribution should be as specified by the Fund on the dividend declaration date, but may be adjusted to reflect subsequent recharacterizations of distributions. Distributions should be adjusted to reflect the federal tax impact the distribution would have on an individual taxpayer on the reinvestment date. For example, assume no taxes are due on the portion of any distribution that would not result in federal income tax on an individual, e.g., tax-exempt interest or non-taxable returns of capital. The effect of applicable tax credits, such as the foreign tax credit, should be taken into account in accordance with federal tax law.",
"label": "After Taxes on Distributions and Sales"
}
}
},
"localname": "AfterTaxesOnDistributionsAndSalesMember",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"rr_AfterTaxesOnDistributionsMember": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate the taxes due on any distributions by the Fund by applying the tax rates specified in Instruction 4 to each component of the distributions on the reinvestment date (e.g., ordinary income, short-term capital gain, long-term capital gain). The taxable amount and tax character of each distribution should be as specified by the Fund on the dividend declaration date, but may be adjusted to reflect subsequent recharacterizations of distributions. Distributions should be adjusted to reflect the federal tax impact the distribution would have on an individual taxpayer on the reinvestment date. For example, assume no taxes are due on the portion of any distribution that would not result in federal income tax on an individual, e.g., tax-exempt interest or non-taxable returns of capital. The effect of applicable tax credits, such as the foreign tax credit, should be taken into account in accordance with federal tax law.",
"label": "After Taxes on Distributions"
}
}
},
"localname": "AfterTaxesOnDistributionsMember",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1990": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1990"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1990",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1991": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1991"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1991",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1992": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1992"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1992",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1993": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1993"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1993",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1994": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1994"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1994",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1995": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1995"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1995",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1996": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1996"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1996",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1997": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1997"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1997",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1998": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1998"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1998",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn1999": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 1999"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn1999",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2000": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2000"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2000",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2001": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2001"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2001",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2002": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2002"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2002",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2003": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2003"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2003",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2004": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2004"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2004",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2005": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2005"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2005",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2006": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2006"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2006",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2007": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2007"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2007",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2008": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2008"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2008",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2009": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2009"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2009",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2010": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2010"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2010",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2011": {
"auth_ref": [
"r68"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2011"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2011",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2012": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2012"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2012",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2013": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2013",
"verboseLabel": "2013"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2013",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2014": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2014",
"verboseLabel": "2014"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2014",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2015": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2015",
"verboseLabel": "2015"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2015",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2016": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2016",
"verboseLabel": "2016"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2016",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2017": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2017",
"verboseLabel": "2017"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2017",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2018": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2018",
"verboseLabel": "2018"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2018",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2019": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2019",
"verboseLabel": "2019"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2019",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2020": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2020",
"verboseLabel": "2020"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2020",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2021": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2021",
"verboseLabel": "2021"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2021",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2022": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2022",
"verboseLabel": "2022"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2022",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2023": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2023"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2023",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2024": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2024"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2024",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturn2025": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets).",
"label": "Annual Return 2025"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturn2025",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturnCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r69"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Provide annual total returns beginning with the earliest calendar year. Calculate annual returns using the Instructions to Item 8(a), except that the calculations should be based on calendar years. If a Fund's shares are sold subject to a sales load or account fees, state that sales loads or account fees are not reflected in the bar chart and that, if these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). When a Multiple Class Fund offering one or more Classes offers a new Class in a prospectus that does not offer the shares of any other Class, include the bar chart with annual total returns for any other existing Class for the first year that the Class is offered. Explain in a footnote that the returns are for a Class that is not offered in the prospectus that would have substantially similar annual returns because the shares are invested in the same portfolio of securities and the annual returns would differ only to the extent that the Classes do not have the same expenses. Include return information for the other Class reflected in the bar chart in the performance table.",
"label": "Annual Return Caption [Text]",
"terseLabel": "Caption"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturnCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturnColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r62"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Provide annual total returns beginning with the earliest calendar year. Calculate annual returns using the Instructions to Item 8(a), except that the calculations should be based on calendar years. If a Fund's shares are sold subject to a sales load or account fees, state that sales loads or account fees are not reflected in the bar chart and that, if these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). When a Multiple Class Fund offering one or more Classes offers a new Class in a prospectus that does not offer the shares of any other Class, include the bar chart with annual total returns for any other existing Class for the first year that the Class is offered. Explain in a footnote that the returns are for a Class that is not offered in the prospectus that would have substantially similar annual returns because the shares are invested in the same portfolio of securities and the annual returns would differ only to the extent that the Classes do not have the same expenses. Include return information for the other Class reflected in the bar chart in the performance table.",
"label": "Annual Return, Column [Text]",
"terseLabel": "Column"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturnColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_AnnualReturnInceptionDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart. Provide annual total returns beginning with the earliest calendar year. Calculate annual returns using the Instructions to Item 8(a), except that the calculations should be based on calendar years. If a Fund's shares are sold subject to a sales load or account fees, state that sales loads or account fees are not reflected in the bar chart and that, if these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. When a Multiple Class Fund offers more than one Class in the prospectus, provide annual total returns in the bar chart for only one of those Classes. The Fund can select which Class to include (e.g., the oldest Class, the Class with the greatest net assets). When a Multiple Class Fund offering one or more Classes offers a new Class in a prospectus that does not offer the shares of any other Class, include the bar chart with annual total returns for any other existing Class for the first year that the Class is offered. Explain in a footnote that the returns are for a Class that is not offered in the prospectus that would have substantially similar annual returns because the shares are invested in the same portfolio of securities and the annual returns would differ only to the extent that the Classes do not have the same expenses. Include return information for the other Class reflected in the bar chart in the performance table.",
"label": "Annual Return, Inception Date",
"terseLabel": "Inception Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "AnnualReturnInceptionDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r73"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This item represents Average Annual Total Returns. If a Multiple Class Fund offers a Class in the prospectus that converts into another Class after a stated period, compute average annual total returns in the table by using the returns of the other Class for the period after conversion.",
"label": "Average Annual Return, Caption"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r59"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This item represents Average Annual Total Returns. If a Multiple Class Fund offers a Class in the prospectus that converts into another Class after a stated period, compute average annual total returns in the table by using the returns of the other Class for the period after conversion.",
"label": "Average Annual Return, Column Name"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnInceptionDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r72"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Return Before Taxes.",
"label": "Inception Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnInceptionDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnLabel": {
"auth_ref": [
"r60"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This item represents Average Annual Total Returns. If a Multiple Class Fund offers a Class in the prospectus that converts into another Class after a stated period, compute average annual total returns in the table by using the returns of the other Class for the period after conversion.",
"label": "Label"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnLabel",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnSinceInception": {
"auth_ref": [
"r60"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Return Before Taxes.",
"label": "Since Inception"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnSinceInception",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear01": {
"auth_ref": [
"r60"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Return Before Taxes.",
"label": "1 Year"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnYear01",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear05": {
"auth_ref": [
"r60"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Return Before Taxes.",
"label": "5 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnYear05",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_AverageAnnualReturnYear10": {
"auth_ref": [
"r60"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Return Before Taxes.",
"label": "10 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "AverageAnnualReturnYear10",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartAndPerformanceTableHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r55"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table.",
"label": "Bar Chart and Performance Table [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartAndPerformanceTableHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartClosingTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Bar Chart Closing [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartClosingTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartDoesNotReflectSalesLoads": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the bar chart and table required by Item 4 (b)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section. Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future. Provide annual total returns beginning with the earliest calendar year. Calculate annual returns using the Instructions to Item 8(a), except that the calculations should be based on calendar years. If a Fund's shares are sold subject to a sales load or account fees, state that sales loads or account fees are not reflected in the bar chart and that, if these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown.",
"label": "Bar Chart Does Not Reflect Sales Loads [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartDoesNotReflectSalesLoads",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartFootnotesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r67"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Multiple Class Funds.",
"label": "Bar Chart Footnotes [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartFootnotesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r55"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table.",
"label": "Bar Chart [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturn": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Highest Quarterly Return"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturn",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturnDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Highest Quarterly Return, Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartHighestQuarterlyReturnDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturn": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Lowest Quarterly Return"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturn",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturnDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Lowest Quarterly Return, Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartLowestQuarterlyReturnDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.",
"label": "Bar Chart Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartReasonSelectedClassDifferentFromImmediatelyPrecedingPeriod": {
"auth_ref": [
"r71"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund provides annual total returns in the bar chart for a Class that is different from the Class selected for the most immediately preceding period, explain in a footnote to the bar chart the reasons for the selection of a different Class.",
"label": "Bar Chart, Reason Selected Class Different from Immediately Preceding Period [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartReasonSelectedClassDifferentFromImmediatelyPrecedingPeriod",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartReturnsForClassNotOfferedInProspectus": {
"auth_ref": [
"r69"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "When a Multiple Class Fund offering one or more Classes offers a new Class in a prospectus that does not offer the shares of any other Class, include the bar chart with annual total returns for any other existing Class for the first year that the Class is offered. Explain in a footnote that the returns are for a Class that is not offered in the prospectus that would have substantially similar annual returns because the shares are invested in the same portfolio of securities and the annual returns would differ only to the extent that the Classes do not have the same expenses. Include return information for the other Class reflected in the bar chart in the performance table.",
"label": "Bar Chart, Returns for Class Not Offered in Prospectus [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartReturnsForClassNotOfferedInProspectus",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartYearToDateReturn": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Bar Chart, Year to Date Return"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartYearToDateReturn",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_BarChartYearToDateReturnDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Bar Chart, Year to Date Return, Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "BarChartYearToDateReturnDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_Component1OtherExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r25"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 10.0,
"parentTag": "rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may subdivide this caption into no more than three subcaptions that identify the largest expense or expenses comprising \"Other Expenses,\" but must include a total of all \"Other Expenses.\" Alternatively, the Fund may include the components of \"Other Expenses\" in a parenthetical to the caption.",
"label": "Component1 Other Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "Component1OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_Component2OtherExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r37"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 20.0,
"parentTag": "rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may subdivide this caption into no more than three subcaptions that identify the largest expense or expenses comprising \"Other Expenses,\" but must include a total of all \"Other Expenses.\" Alternatively, the Fund may include the components of \"Other Expenses\" in a parenthetical to the caption.",
"label": "Component2 Other Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "Component2OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_Component3OtherExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r25"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 30.0,
"parentTag": "rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may subdivide this caption into no more than three subcaptions that identify the largest expense or expenses comprising \"Other Expenses,\" but must include a total of all \"Other Expenses.\" Alternatively, the Fund may include the components of \"Other Expenses\" in a parenthetical to the caption.",
"label": "Component3 Other Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "Component3OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_CoregistrantAxis": {
"auth_ref": [
"r2"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Coregistrant Axis may be used to distinguish disclosures that belong to registrants having different Central Index Key (CIK) values that nevertheless all present in the same filing.",
"label": "Coregistrant [Axis]"
}
}
},
"localname": "CoregistrantAxis",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_CoregistrantDomain": {
"auth_ref": [
"r3"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The default member of the Coregistrant axis. It represents any disclosure that applies to the registrant whose Central Index Key (CIK) is that of the default context.",
"label": "Coregistrant [Domain]"
}
}
},
"localname": "CoregistrantDomain",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"rr_DistributionAndService12b1FeesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r44"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 20.0,
"parentTag": "rr_ExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Distribution [and/or Service] (12b-1) Fees\" include all distribution or other expenses incurred during the most recent fiscal year under a plan adopted pursuant to rule 12b-1 [17 CFR 270.12b-1]. Under an appropriate caption or a subcaption of \"Other Expenses,\" disclose the amount of any distribution or similar expenses deducted from the Fund's assets other than pursuant to a rule 12b-1 plan.",
"label": "Distribution and Service (12b-1) Fees"
}
}
},
"localname": "DistributionAndService12b1FeesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_DistributionOrSimilarNon12b1FeesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r22"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 30.0,
"parentTag": "rr_ExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Distribution [and/or Service] (12b-1) Fees\" include all distribution or other expenses incurred during the most recent fiscal year under a plan adopted pursuant to rule 12b-1 [17 CFR 270.12b-1]. Under an appropriate caption or a subcaption of \"Other Expenses,\" disclose the amount of any distribution or similar expenses deducted from the Fund's assets other than pursuant to a rule 12b-1 plan.",
"label": "Distribution or Similar (Non 12b-1) Fees"
}
}
},
"localname": "DistributionOrSimilarNon12b1FeesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_ExchangeFee": {
"auth_ref": [
"r41"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Exchange Fee includes the maximum fee charged for any exchange or transfer of interest from the Fund to another fund. The Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation of the range of exchange fees or a narrative explanation of the fees.",
"label": "Exchange Fee"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExchangeFee",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExchangeFeeOverRedemption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r19"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Exchange Fee includes the maximum fee charged for any exchange or transfer of interest from the Fund to another fund. The Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation of the range of exchange fees or a narrative explanation of the fees.",
"label": "Exchange Fee (as a percentage of Amount Redeemed)"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExchangeFeeOverRedemption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_ExpenseBreakpointDiscounts": {
"auth_ref": [
"r12"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the narrative explanations in the order indicated. A Fund may modify the narrative explanations if the explanation contains comparable information to that shown. The narrative explanation regarding sales charge discounts is only required by a Fund that offers such discounts and should specify the minimum level of investment required to qualify for a discount.",
"label": "Expense Breakpoint Discounts [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseBreakpointDiscounts",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseBreakpointMinimumInvestmentRequiredAmount": {
"auth_ref": [
"r12"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents the minimum level of investment required to qualify for discounted sales charges or fund expenses (SEC Form N-1A 2006-09-14 A.3.instructions.1.b).",
"label": "Expense Breakpoint, Minimum Investment Required [Amount]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseBreakpointMinimumInvestmentRequiredAmount",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "monetaryItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleByYearCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r8"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example by, Year, Caption [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleByYearCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleByYearHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r8"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example by Year [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleByYearHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleClosingTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r31"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example does not reflect sales charges (loads) on reinvested dividends [and other distributions]. If these sales charges (loads) were included, your costs would be higher.",
"label": "Expense Example Closing [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleClosingTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleFootnotesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r10"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example does not reflect sales charges (loads) on reinvested dividends [and other distributions]. If these sales charges (loads) were included, your costs would be higher.",
"label": "Expense Example Footnotes [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleFootnotesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r31"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Heading for Expense Example.",
"label": "Expense Example [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r7"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds.",
"label": "Expense Example Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionByYearCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r9"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption, By Year, Caption [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionByYearCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Contains a command for the SEC Viewer for the role corresponding to ExpenseExampleNoRedemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear01": {
"auth_ref": [
"r9"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption, 1 Year",
"terseLabel": "1 Year"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear01",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear03": {
"auth_ref": [
"r9"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption, 3 Years",
"terseLabel": "3 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear03",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear05": {
"auth_ref": [
"r32"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption, 5 Years",
"terseLabel": "5 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear05",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear10": {
"auth_ref": [
"r32"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares. Include the second 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods and related narrative explanation only if a sales charge (load) or other fee is charged upon redemption.",
"label": "Expense Example, No Redemption, 10 Years",
"terseLabel": "10 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleNoRedemptionYear10",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleYear01": {
"auth_ref": [
"r31"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example, with Redemption, 1 Year",
"terseLabel": "1 Year"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleYear01",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleYear03": {
"auth_ref": [
"r8"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example, with Redemption, 3 Years",
"terseLabel": "3 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleYear03",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleYear05": {
"auth_ref": [
"r8"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example, with Redemption, 5 Years",
"terseLabel": "5 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleYear05",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseExampleYear10": {
"auth_ref": [
"r8"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower.",
"label": "Expense Example, with Redemption, 10 Years",
"terseLabel": "10 Years"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseExampleYear10",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ExpenseFootnotesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r16"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Shareholder Fees.",
"label": "Expense Footnotes [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseFootnotesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r14"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Risk/Return Summary Fee Table Includes the following information, in plain English under rule 421(d) under the Securities Act, after Item 2 Fees and expenses of the Fund This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shared of the Fund. You may qualify for sales charge discounts if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $[_____] in [name of fund family] funds. Shareholder Fees (fees paid directly from your investment) Example This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then you redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return per year and that the Fund's operating expenses remained the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares The Example does not reflect sales charges (loads) on reinvested dividends [and other distributions]. If these sales charges (loads) were included, your costs would be higher. Portfolio Turnover The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or \"turns over\" its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover may indicate higher transaction costs. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the example, affect the Fund's performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund's portfolio turnover rate was __% of the average value of its whole portfolio. Instructions. A.3.instructions.6 New Funds. For purposes of this Item, a \"New Fund\" is a Fund that does not include in Form N-1A financial statements reporting operating results or that includes financial statements for the Fund's initial fiscal year reporting operating results for a period of 6 months or less. The following Instructions apply to New Funds.",
"label": "Expense [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpenseNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r12"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold, and sell shares of the Fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to financial intermediaries, which are not reflected in the tables and examples below. You may qualify for sales charge discounts if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $[ ] in [name of fund family] funds. More information about these and other discounts is available from your financial intermediary and in [identify section heading and page number] of the Fund's prospectus and [identify section heading and page number] of the Fund's statement of additional information",
"label": "Expense Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpenseNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesDeferredChargesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r17"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation showing the amount of deferred sales charges (loads) over time or a narrative explanation of the sales charges (loads) (e.g., __% in the first year after purchase, declining to __% in the __ year and eliminated thereafter).",
"label": "Expenses Deferred Charges [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesDeferredChargesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesExplanationOfNonrecurringAccountFee": {
"auth_ref": [
"r20"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may include an explanation of any non-recurring account fee in a parenthetical to the caption or in a footnote to the table.",
"label": "Expenses Explanation of Nonrecurring Account Fee [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesExplanationOfNonrecurringAccountFee",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesNotCorrelatedToRatioDueToAcquiredFundFees": {
"auth_ref": [
"r30"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may clarify in a footnote to the fee table that the total annual fund operating expenses under Item 3 do not correlate to the ratio of expenses to average net assets given in response to Item 8, which reflects the operating expenses of the Fund and does not include Acquired Fund fees and expenses.",
"label": "Expenses Not Correlated to Ratio Due to Acquired Fund Fees [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesNotCorrelatedToRatioDueToAcquiredFundFees",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesOtherExpensesHadExtraordinaryExpensesBeenIncluded": {
"auth_ref": [
"r24"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "\"Other Expenses\" do not include extraordinary expenses as determined under generally accepted accounting principles (see Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 30). If extraordinary expenses were incurred that materially affected the Fund's \"Other Expenses,\" disclose in a footnote to the table what \"Other Expenses\" would have been had the extraordinary expenses been included.",
"label": "Expenses Other Expenses Had Extraordinary Expenses Been Included [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesOtherExpensesHadExtraordinaryExpensesBeenIncluded",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r26"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 10.0,
"parentTag": "rr_NetExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses. If the Fund is a Feeder Fund, reflect the aggregate expenses of the Feeder Fund and the Master Fund in a single fee table using the captions provided. In a footnote to the fee table, state that the table and Example reflect the expenses of both the Feeder and Master Funds. If the prospectus offers more than one Class of a Multiple Class Fund or more than one Feeder Fund that invests in the same Master Fund, provide a separate response for each Class or Feeder Fund. Base the percentages of \"Annual Fund Operating Expenses\" on amounts incurred during the Fund's most recent fiscal year, but include in expenses amounts that would have been incurred absent expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements. If the Fund has changed its fiscal year and, as a result, the most recent fiscal year is less than three months, use the fiscal year prior to the most recent fiscal year as the basis for determining \"Annual Fund Operating Expenses.\"",
"label": "Expenses (as a percentage of Assets)",
"verboseLabel": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_ExpensesRangeOfExchangeFeesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r19"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation of the range of exchange fees or a narrative explanation of the fees.",
"label": "Expenses Range of Exchange Fees [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesRangeOfExchangeFeesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesRepresentBothMasterAndFeeder": {
"auth_ref": [
"r15"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund is a Feeder Fund, reflect the aggregate expenses of the Feeder Fund and the Master Fund in a single fee table using the captions provided. In a footnote to the fee table, state that the table and Example reflect the expenses of both the Feeder and Master Funds.",
"label": "Expenses Represent Both Master and Feeder [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesRepresentBothMasterAndFeeder",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ExpensesRestatedToReflectCurrent": {
"auth_ref": [
"r27"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "In a footnote to the table, disclose that the expense information in the table has been restated to reflect current fees.",
"label": "Expenses Restated to Reflect Current [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ExpensesRestatedToReflectCurrent",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r38"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 20.0,
"parentTag": "rr_NetExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses. If there were expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements that reduced any Fund operating expenses and will continue to reduce them for no less than one year from the effective date of the Fund's registration statement, a Fund may add two captions to the table one caption showing the amount of the expense reimbursement or fee waiver, and a second caption showing the Fund's net expenses after subtracting the fee reimbursement or expense waiver from the total fund operating expenses. The Fund should place these additional captions directly below the \"Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses\" caption of the table and should use appropriate descriptive captions, such as \"Fee Waiver [and/or Expense Reimbursement]\" and \"Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waiver [and/or Expense Reimbursement],\" respectively. If the Fund provides this disclosure, also disclose the period for which the expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangement is expected to continue, and briefly describe who can terminate the arrangement and under what circumstances.",
"label": "Fee Waiver or Reimbursement",
"negatedTerseLabel": "Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements"
}
}
},
"localname": "FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonPositivePure4Type"
},
"rr_FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssetsDateOfTermination": {
"auth_ref": [
"r28"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents the date of expected termination of any expense reimbursement or fee waiver arrangements that reduce any Fund operating expenses (SEC Form N-1A 2006-09-14 A.3.table.1.11 Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses A.3.instructions.3.e).",
"label": "Fee Waiver or Reimbursement over Assets, Date of Termination"
}
}
},
"localname": "FeeWaiverOrReimbursementOverAssetsDateOfTermination",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_HighestQuarterlyReturnLabel": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Highest Quarterly Return, Label",
"terseLabel": "Label"
}
}
},
"localname": "HighestQuarterlyReturnLabel",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_IndexNoDeductionForFeesExpensesTaxes": {
"auth_ref": [
"r61"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Performance Table includes a parenthetical, indicating that the Index \"(reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes)\". This tag is used when this is reflected in a footnote.",
"label": "Index No Deduction for Fees, Expenses, Taxes [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "IndexNoDeductionForFeesExpensesTaxes",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_LowestQuarterlyReturnLabel": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Lowest Quarterly Return, Label",
"terseLabel": "Label"
}
}
},
"localname": "LowestQuarterlyReturnLabel",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ManagementFeesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r21"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 10.0,
"parentTag": "rr_ExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Management Fees include investment advisory fees (including any fees based on the Fund's performance), any other management fees payable to the investment adviser or its affiliates, and administrative fees payable to the investment adviser or its affiliates that are not included as \"Other Expenses.\"",
"label": "Management Fees (as a percentage of Assets)",
"verboseLabel": "Management Fees"
}
}
},
"localname": "ManagementFeesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumAccountFee": {
"auth_ref": [
"r13"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the caption \"Maximum Account Fees\" only if the Fund charges these fees. A Fund may omit other captions if the Fund does not charge the fees or expenses covered by the captions. Disclose account fees that may be charged to a typical investor in the Fund; fees that apply to only a limited number of shareholders based on their particular circumstances need not be disclosed. Include a caption describing the maximum account fee (e.g., \"Maximum Account Maintenance Fee\" or \"Maximum Cash Management Fee\"). State the maximum annual account fee as either a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of assets. Include in a parenthetical to the caption the basis on which any percentage is calculated. If an account fee is charged only to accounts that do not meet a certain threshold (e.g., accounts under $5)",
"label": "Maximum Account Fee"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumAccountFee",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_MaximumAccountFeeOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r42"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the caption \"Maximum Account Fees\" only if the Fund charges these fees. A Fund may omit other captions if the Fund does not charge the fees or expenses covered by the captions. Disclose account fees that may be charged to a typical investor in the Fund; fees that apply to only a limited number of shareholders based on their particular circumstances need not be disclosed. Include a caption describing the maximum account fee (e.g., \"Maximum Account Maintenance Fee\" or \"Maximum Cash Management Fee\"). State the maximum annual account fee as either a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of assets. Include in a parenthetical to the caption the basis on which any percentage is calculated. If an account fee is charged only to accounts that do not meet a certain threshold (e.g., accounts under $5)",
"label": "Maximum Account Fee (as a percentage of Assets)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumAccountFeeOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumCumulativeSalesChargeOverOfferingPrice": {
"auth_ref": [
"r36"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price). If a sales charge (load) is imposed on shares purchased with reinvested capital gains distributions or returns of capital, include the bracketed words in the third caption.",
"label": "Maximum Cumulative Sales Charge (as a percentage of Offering Price)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumCumulativeSalesChargeOverOfferingPrice",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumCumulativeSalesChargeOverOther": {
"auth_ref": [
"r36"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price). If a sales charge (load) is imposed on shares purchased with reinvested capital gains distributions or returns of capital, include the bracketed words in the third caption.",
"label": "Maximum Cumulative Sales Charge (as a percentage)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumCumulativeSalesChargeOverOther",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumDeferredSalesChargeOverOfferingPrice": {
"auth_ref": [
"r17"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of ____) A.3.instructions.2.a.i \"Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load)\" includes the maximum total deferred sales charge (load) payable upon redemption, in installments, or both, expressed as a percentage of the amount or amounts stated in response to Item 7(a), except that, for a sales charge (load) based on net asset value at the time of purchase, show the sales charge (load) as a percentage of the offering price at the time of purchase. A Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation showing the amount of deferred sales charges (loads) over time or a narrative explanation of the sales charges (loads) (e.g., __% in the first year after purchase, declining to __% in the __ year and eliminated thereafter). A.3.instructions.2.a.ii If more than one type of sales charge (load) is imposed (e.g., a deferred sales charge (load) and a front-end sales charge (load)), the first caption in the table should read \"Maximum Sales Charge (Load)\" and show the maximum cumulative percentage. Show the percentage amounts and the terms of each sales charge (load) comprising that figure on separate lines below.",
"label": "Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (as a percentage of Offering Price)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumDeferredSalesChargeOverOfferingPrice",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumDeferredSalesChargeOverOther": {
"auth_ref": [
"r17"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of ____) \"Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load)\" includes the maximum total deferred sales charge (load) payable upon redemption, in installments, or both, expressed as a percentage of the amount or amounts stated in response to Item 7(a), except that, for a sales charge (load) based on net asset value at the time of purchase, show the sales charge (load) as a percentage of the offering price at the time of purchase. A Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation showing the amount of deferred sales charges (loads) over time or a narrative explanation of the sales charges (loads) (e.g., __% in the first year after purchase, declining to __% in the __ year and eliminated thereafter). If more than one type of sales charge (load) is imposed (e.g., a deferred sales charge (load) and a front-end sales charge (load)), the first caption in the table should read \"Maximum Sales Charge (Load)\" and show the maximum cumulative percentage. Show the percentage amounts and the terms of each sales charge (load) comprising that figure on separate lines below.",
"label": "Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (as a percentage)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumDeferredSalesChargeOverOther",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumSalesChargeImposedOnPurchasesOverOfferingPrice": {
"auth_ref": [
"r36"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of ____) A.3.instructions.2.a.i \"Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load)\" includes the maximum total deferred sales charge (load) payable upon redemption, in installments, or both, expressed as a percentage of the amount or amounts stated in response to Item 7(a), except that, for a sales charge (load) based on net asset value at the time of purchase, show the sales charge (load) as a percentage of the offering price at the time of purchase. A Fund may include in a footnote to the table, if applicable, a tabular presentation showing the amount of deferred sales charges (loads) over time or a narrative explanation of the sales charges (loads) (e.g., __% in the first year after purchase, declining to __% in the __ year and eliminated thereafter). A.3.instructions.2.a.ii If more than one type of sales charge (load) is imposed (e.g., a deferred sales charge (load) and a front-end sales charge (load)), the first caption in the table should read \"Maximum Sales Charge (Load)\" and show the maximum cumulative percentage. Show the percentage amounts and the terms of each sales charge (load) comprising that figure on separate lines below.",
"label": "Maximum Sales Charge Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of Offering Price)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumSalesChargeImposedOnPurchasesOverOfferingPrice",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MaximumSalesChargeOnReinvestedDividendsAndDistributionsOverOther": {
"auth_ref": [
"r39"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Reinvested Dividends[and other Distributions] (as a percentage of ____)",
"label": "Maximum Sales Charge on Reinvested Dividends and Distributions (as a percentage)"
}
}
},
"localname": "MaximumSalesChargeOnReinvestedDividendsAndDistributionsOverOther",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_MoneyMarketSevenDayTaxEquivalentYield": {
"auth_ref": [
"r64"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate a Money Market Fund's 7-day yield under Item 21(a); the Fund's average annual total return under Item 21(b)(1); and the Fund's average annual total return (after taxes on distributions) and average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption) under Items 21(b)(2) and (3), respectively.",
"label": "Money Market Seven Day Tax Equivalent Yield"
}
}
},
"localname": "MoneyMarketSevenDayTaxEquivalentYield",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_MoneyMarketSevenDayYield": {
"auth_ref": [
"r64"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate a Money Market Fund's 7-day yield under Item 21(a); the Fund's average annual total return under Item 21(b)(1); and the Fund's average annual total return (after taxes on distributions) and average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption) under Items 21(b)(2) and (3), respectively.",
"label": "Money Market Seven Day Yield"
}
}
},
"localname": "MoneyMarketSevenDayYield",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r64"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate a Money Market Fund's 7-day yield under Item 21(a); the Fund's average annual total return under Item 21(b)(1); and the Fund's average annual total return (after taxes on distributions) and average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption) under Items 21(b)(2) and (3), respectively.",
"label": "Money Market Seven Day Yield, Caption [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r64"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Calculate a Money Market Fund's 7-day yield under Item 21(a); the Fund's average annual total return under Item 21(b)(1); and the Fund's average annual total return (after taxes on distributions) and average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption) under Items 21(b)(2) and (3), respectively.",
"label": "Money Market Seven Day Yield Column [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldPhone": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Money Market Seven Day Yield Phone"
}
}
},
"localname": "MoneyMarketSevenDayYieldPhone",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_NetExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r38"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": null,
"parentTag": null,
"root": true,
"weight": null
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses.",
"label": "Net Expenses (as a percentage of Assets)",
"verboseLabel": "Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements"
}
}
},
"localname": "NetExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_ObjectiveHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r6"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Investment Objectives/Goals. Disclose the Fund's investment objectives or goals. A Fund also may identify its type or category (e.g., that it is a Money Market Fund or a balanced fund).",
"label": "Objective [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ObjectiveHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ObjectivePrimaryTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r6"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Investment Objectives/Goals. Disclose the Fund's investment objectives or goals. A Fund also may identify its type or category (e.g., that it is a Money Market Fund or a balanced fund).",
"label": "Objective, Primary [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ObjectivePrimaryTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ObjectiveSecondaryTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r6"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Investment Objectives/Goals. Disclose the Fund's investment objectives or goals. A Fund also may identify its type or category (e.g., that it is a Money Market Fund or a balanced fund).",
"label": "Objective, Secondary [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ObjectiveSecondaryTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_OperatingExpensesCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r43"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Annual Fund Operating Expenses (ongoing expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment)",
"label": "Operating Expenses Caption [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "OperatingExpensesCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_OperatingExpensesColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r43"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Annual Fund Operating Expenses (ongoing expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment)",
"label": "Operating Expenses Column [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "OperatingExpensesColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_OtherExpensesNewFundBasedOnEstimates": {
"auth_ref": [
"r34"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents the disclosure for new funds that \"Other Expenses\" are based on estimated amounts for the current fiscal year.",
"label": "Other Expenses, New Fund, Based on Estimates [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "OtherExpensesNewFundBasedOnEstimates",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_OtherExpensesOverAssets": {
"auth_ref": [
"r23"
],
"calculation": {
"http://www.valic.com/role/ScheduleAnnualFundOperatingExpenses000021": {
"order": 40.0,
"parentTag": "rr_ExpensesOverAssets",
"weight": 1.0
}
},
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "\"Other Expenses\" include all expenses not otherwise disclosed in the table that are deducted from the Fund's assets or charged to all shareholder accounts. The amount of expenses deducted from the Fund's assets are the amounts shown as expenses in the Fund's statement of operations (including increases resulting from complying with paragraph 2(g) of rule 6-07 of Regulation S-X [17 CFR 210.6-07]). \"Other Expenses\" do not include extraordinary expenses as determined under generally accepted accounting principles (see Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 30). If extraordinary expenses were incurred that materially affected the Fund's \"Other Expenses,\" disclose in a footnote to the table what \"Other Expenses\" would have been had the extraordinary expenses been included.",
"label": "Other Expenses (as a percentage of Assets):",
"verboseLabel": "Other Expenses"
}
}
},
"localname": "OtherExpensesOverAssets",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativePure4Type"
},
"rr_PerformanceAdditionalMarketIndex": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the bar chart and table required by paragraphs (b)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section. Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.",
"label": "Performance Additional Market Index [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceAdditionalMarketIndex",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceAvailabilityPhone": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If applicable, include a statement explaining that updated performance information is available and providing a Web site address and/or toll-free (or collect) telephone number where the updated information may be obtained.",
"label": "Performance Availability Phone [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceAvailabilityPhone",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceAvailabilityWebSiteAddress": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If applicable, include a statement explaining that updated performance information is available and providing a Website address and/or toll-free (or collect) telephone number where the updated information may be obtained.",
"label": "Performance Availability Website Address [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceAvailabilityWebSiteAddress",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceInformationIllustratesVariabilityOfReturns": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the bar chart and table required by paragraphs (b)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section. Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.",
"label": "Performance Information Illustrates Variability of Returns [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceInformationIllustratesVariabilityOfReturns",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceMeasureAxis": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The Performance Measure Axis has members that distinguish different returns according to whether they are Before Taxes (the default), After Taxes on Distributions, After Taxes on Distributions and Sales, or are a pre-tax measure of returns based on a broadly available market index.",
"label": "Performance Measure [Axis]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceMeasureAxis",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceMeasureDomain": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The default member of the Performance Measure axis. It represents any return that is measured before taxes.",
"label": "Before Taxes"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceMeasureDomain",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r55"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table.",
"label": "Performance Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceOneYearOrLess": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56",
"r63"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "For a Fund that provides annual total returns for only one calendar year or for a Fund that does not include the bar chart because it does not have annual returns for a full calendar year, modify, as appropriate, the narrative explanation required by stating that the information gives some indication of the risks of an investment in the Fund by comparing the Fund's performance with a broad measure of market performance). Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.",
"label": "Performance One Year or Less [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceOneYearOrLess",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformancePastDoesNotIndicateFuture": {
"auth_ref": [
"r56"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the bar chart and table required by paragraphs (b)(2)(ii) and (iii) of this section. Provide a brief explanation of how the information illustrates the variability of the Fund's returns (e.g., by stating that the information provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund's performance from year to year and by showing how the Fund's average annual returns for 1, 5, and 10 years compare with those of a broad measure of market performance). Provide a statement to the effect that the Fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.",
"label": "Performance Past Does Not Indicate Future [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformancePastDoesNotIndicateFuture",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableClosingTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r58"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a table showing the Fund's (A) average annual total return; (B) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions); and (C) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption). A Money Market Fund should show only the returns described in clause (A) of the preceding sentence. All returns should be shown for 1-, 5-, and 10- calendar year periods ending on the date of the most recently completed calendar year (or for the life of the Fund, if shorter), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. The table also should show the returns of an appropriate broad-based securities market index as defined in Instruction 5 to Item 22(b)(7) for the same periods. A Fund that has been in existence for more than 10 years also may include returns for the life of the Fund. A Money Market Fund may provide the Fund's 7-day yield ending on the date of the most recent calendar year or disclose a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain the Fund's current 7-day yield. For a Fund (other than a Money Market Fund or a Fund described in General Instruction C.3.(d)(iii)), provide the information in the following table with the specified captions AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURNS (For the periods ended December 31, _____)",
"label": "Performance Table Closing [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableClosingTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableDoesReflectSalesLoads": {
"auth_ref": [
"r58"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a table showing the Fund's (A) average annual total return; (B) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions); and (C) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption). A Money Market Fund should show only the returns described in clause (A) of the preceding sentence. All returns should be shown for 1-, 5-, and 10- calendar year periods ending on the date of the most recently completed calendar year (or for the life of the Fund, if shorter), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. The table also should show the returns of an appropriate broad-based securities market index as defined in Instruction 5 to Item 22(b)(7) for the same periods. A Fund that has been in existence for more than 10 years also may include returns for the life of the Fund. A Money Market Fund may provide the Fund's 7-day yield ending on the date of the most recent calendar year or disclose a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain the Fund's current 7-day yield. For a Fund (other than a Money Market Fund or a Fund described in General Instruction C.3.(d)(iii)), provide the information in the following table with the specified captions AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURNS (For the periods ended December 31, _____)",
"label": "Performance Table Does Reflect Sales Loads"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableDoesReflectSalesLoads",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableExplanationAfterTaxHigher": {
"auth_ref": [
"r77"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption) is higher than average annual total return, the reason for this result may be explained.",
"label": "Performance Table Explanation after Tax Higher"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableExplanationAfterTaxHigher",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableFootnotesReasonPerformanceInformationForClassDifferentFromImmediatelyPrecedingPeriod": {
"auth_ref": [
"r70"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents disclosure when presented performance information for a class is different from the class selected for the most immediately preceding period (Form N-1A, Item 2., Instr. 3.(c).(ii).(D)).",
"label": "Performance Table Footnotes, Reason Performance Information for Class Different from Immediately Preceding Period [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableFootnotesReasonPerformanceInformationForClassDifferentFromImmediatelyPrecedingPeriod",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableFootnotesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r58"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a table showing the Fund's (A) average annual total return; (B) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions); and (C) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption). A Money Market Fund should show only the returns described in clause (A) of the preceding sentence. All returns should be shown for 1-, 5-, and 10- calendar year periods ending on the date of the most recently completed calendar year (or for the life of the Fund, if shorter), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. The table also should show the returns of an appropriate broad-based securities market index as defined in Instruction 5 to Item 22(b)(7) for the same periods. A Fund that has been in existence for more than 10 years also may include returns for the life of the Fund. A Money Market Fund may provide the Fund's 7-day yield ending on the date of the most recent calendar year or disclose a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain the Fund's current 7-day yield. For a Fund (other than a Money Market Fund or a Fund described in General Instruction C.3.(d)(iii)), provide the information in the following table with the specified captions AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURNS (For the periods ended December 31, _____)",
"label": "Performance Table Footnotes"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableFootnotesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r70"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This item represents Average Annual Total Returns. If a Multiple Class Fund offers a Class in the prospectus that converts into another Class after a stated period, compute average annual total returns in the table by using the returns of the other Class for the period after conversion.",
"label": "Performance Table Heading"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableMarketIndexChanged": {
"auth_ref": [
"r65"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund selects an index that is different from the index used in a table for the immediately preceding period, explain the reason(s) for the selection of a different index and provide information for both the newly selected and the former index.",
"label": "Performance Table Market Index Changed"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableMarketIndexChanged",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r74"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a table showing the Fund's (A) average annual total return; (B) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions); and (C) average annual total return (after taxes on distributions and redemption). A Money Market Fund should show only the returns described in clause (A) of the preceding sentence. All returns should be shown for 1-, 5-, and 10- calendar year periods ending on the date of the most recently completed calendar year (or for the life of the Fund, if shorter), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. The table also should show the returns of an appropriate broad-based securities market index as defined in Instruction 5 to Item 22(b)(7) for the same periods. A Fund that has been in existence for more than 10 years also may include returns for the life of the Fund. A Money Market Fund may provide the Fund's 7-day yield ending on the date of the most recent calendar year or disclose a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain the Fund's current 7-day yield. For a Fund (other than a Money Market Fund or a Fund described in General Instruction C.3.(d)(iii)), provide the information in the following table with the specified captions AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURNS (For the periods ended December 31, _____). For a Fund that provides annual total returns for only one calendar year or for a Fund that does not include the bar chart because it does not have annual returns for a full calendar year, modify, as appropriate, the narrative explanation required by paragraph (c)(2)(i) (e.g., by stating that the information gives some indication of the risks of an investment in the Fund by comparing the Fund's performance with a broad measure of market performance).",
"label": "Performance Table Narrative"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableNotRelevantToTaxDeferred": {
"auth_ref": [
"r75"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Provide a brief explanation that the actual after-tax returns depend on an investor's tax situation and may differ from those shown, and after-tax returns shown are not relevant to investors who hold their Fund shares through tax-deferred arrangements, such as 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts.",
"label": "Performance Table Not Relevant to Tax Deferred"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableNotRelevantToTaxDeferred",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableOneClassOfAfterTaxShown": {
"auth_ref": [
"r58",
"r76"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Provide a brief explanation that if the Fund is a Multiple Class Fund that offers more than one Class in the prospectus, after-tax returns are shown for only one Class and after-tax returns for other Classes will vary.",
"label": "Performance Table One Class of after Tax Shown [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableOneClassOfAfterTaxShown",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PerformanceTableUsesHighestFederalRate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r58"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Provide a brief explanation that after-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual federal marginal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes.",
"label": "Performance Table Uses Highest Federal Rate"
}
}
},
"localname": "PerformanceTableUsesHighestFederalRate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PortfolioTurnoverHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r33"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Disclose the portfolio turnover rate provided in response to Item 14(a) for the most recent fiscal year (or for such shorter period as the Fund has been in operation). Disclose the period for which the information is provided if less than a full fiscal year. A Fund that is a Money Market Fund may omit the portfolio turnover information required by this Item.",
"label": "Portfolio Turnover [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PortfolioTurnoverHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_PortfolioTurnoverRate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r11"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element represents the rate of portfolio turnover presented as a percentage (SEC Form N-1A 2006-09-14 A.3.example.3 Portfolio Turnover A.3.instructions.5 Portfolio Turnover).",
"label": "Portfolio Turnover, Rate"
}
}
},
"localname": "PortfolioTurnoverRate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_PortfolioTurnoverTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r11"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Disclose the portfolio turnover rate provided in response to Item 14(a) for the most recent fiscal year (or for such shorter period as the Fund has been in operation). Disclose the period for which the information is provided if less than a full fiscal year. A Fund that is a Money Market Fund may omit the portfolio turnover information required by this Item.",
"label": "Portfolio Turnover [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "PortfolioTurnoverTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ProspectusDate": {
"auth_ref": [
"r4"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "The date of the prospectus.",
"label": "Prospectus Date"
}
}
},
"localname": "ProspectusDate",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "dateItemType"
},
"rr_ProspectusShareClassAxis": {
"auth_ref": [
"r2"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Prospectus Share Class Axis.",
"label": "Share Class [Axis]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ProspectusShareClassAxis",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ProspectusTable": {
"auth_ref": [
"r2"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Prospectus Table.",
"label": "Prospectus:"
}
}
},
"localname": "ProspectusTable",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RedemptionFee": {
"auth_ref": [
"r40"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "\"Redemption Fee\" (as a percentage of amount redeemed, if applicable) If the Fund is an Exchange-Traded Fund and issues or redeems shares in creation units of not less than 25,000 shares each, exclude any fees charged for the purchase and redemption of the Fund's creation units. \"Redemption Fee\" includes a fee charged for any redemption of the Fund's shares, but does not include a deferred sales charge (load) imposed upon redemption.",
"label": "Redemption Fee",
"negatedLabel": "Redemption Fee"
}
}
},
"localname": "RedemptionFee",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonPositiveMonetaryType"
},
"rr_RedemptionFeeOverRedemption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r18"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "\"Redemption Fee\" (as a percentage of amount redeemed, if applicable) If the Fund is an Exchange-Traded Fund and issues or redeems shares in creation units of not less than 25,000 shares each, exclude any fees charged for the purchase and redemption of the Fund's creation units. \"Redemption Fee\" includes a fee charged for any redemption of the Fund's shares, but does not include a deferred sales charge (load) imposed upon redemption.",
"label": "Redemption Fee (as a percentage of Amount Redeemed)",
"negatedLabel": "Redemption Fee (as a percentage of Amount Redeemed)"
}
}
},
"localname": "RedemptionFeeOverRedemption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonPositivePure4Type"
},
"rr_Risk": {
"auth_ref": [
"r46"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure.",
"label": "Risk [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "Risk",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r46"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure.",
"label": "Risk Caption"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskClosingTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r49"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "(ii) (A) If the Fund is a Money Market Fund that is not a government Money Market Fund, as defined in \u00a7270.2a\u2013 7(a)(16) or a retail Money Market Fund, as defined in \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(a)(25), include the following statement: You could lose money by investing in the Fund. Because the share price of the Fund will fluctuate, when you sell your shares they may be worth more or less than what you originally paid for them. The Fund may impose a fee upon sale of your shares or may temporarily suspend your ability to sell shares if the Fund's liquidity falls below required minimums because of market conditions or other factors. An investment in the Fund is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. The Fund's sponsor has no legal obligation to provide financial support to the Fund, and you should not expect that the sponsor will provide financial support to the Fund at any time. (B) If the Fund is a Money Market Fund that is a government Money Market Fund, as defined in \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(a)(16), or a retail Money Market Fund, as defined in \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(a)(25), and that is subject to the requirements of \u00a7\u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(i) and/or (ii) of this chapter (or is not subject to the requirements of \u00a7\u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(i) and/or (ii) of this chapter pursuant to \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(iii) of this chapter, but has chosen to rely on the ability to impose liquidity fees and suspend redemptions consistent with the requirements of \u00a7\u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(i) and/or (ii)), include the following statement: You could lose money by investing in the Fund. Although the Fund seeks to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, it cannot guarantee it will do so. The Fund may impose a fee upon sale of your shares or may temporarily suspend your ability to sell shares if the Fund's liquidity falls below required minimums because of market conditions or other factors. An investment in the Fund is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. The Fund's sponsor has no legal obligation to provide financial support to the Fund, and you should not expect that the sponsor will provide financial support to the Fund at any time. (C) If the Fund is a Money Market Fund that is a government Money Market Fund, as defined in \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(a)(16), that is not subject to the requirements of \u00a7\u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(i) and/or (ii) of this chapter pursuant to \u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(iii) of this chapter, and that has not chosen to rely on the ability to impose liquidity fees and suspend redemptions consistent with the requirements of \u00a7\u00a7 270.2a\u20137(c)(2)(i) and/or (ii), include the following statement: You could lose money by investing in the Fund. Although the Fund seeks to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, it cannot guarantee it will do so. An investment in the Fund is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. The Fund's sponsor has no legal obligation to provide financial support to the Fund, and you should not expect that the sponsor will provide financial support to the Fund at any time. Instruction. If an affiliated person, promoter, or principal underwriter of the Fund, or an affiliated person of such a person, has contractually committed to provide financial support to the Fund, and the term of the agreement will extend for at least one year following the effective date of the Fund's registration statement, the statement specified in Item 4(b)(1)(ii)(A), Item 4(b)(1)(ii)(B), or Item 4(b)(1)(ii)(C) may omit the last sentence (\"The Fund's sponsor has no legal obligation to provide financial support to the Fund, and you should not expect that the sponsor will provide financial support to the Fund at any time.\"). For purposes of this Instruction, the term \"financial support\" includes any capital contribution, purchase of a security from the Fund in reliance on \u00a7 270.17a\u20139, purchase of any defaulted or devalued security at par, execution of letter of credit or letter of indemnity, capital support agreement (whether or not the Fund ultimately received support), performance guarantee, or any other similar action reasonably intended to increase or stabilize the value or liquidity of the fund's portfolio; however, the term \"financial support\" excludes any routine waiver of fees or reimbursement of fund expenses, routine inter-fund lending, routine inter-fund purchases of fund shares, or any action that would qualify as financial support as defined above, that the board of directors has otherwise determined not to be reasonably intended to increase or stabilize the value or liquidity of the fund's portfolio. (iii) If the Fund is advised by or sold through an insured depository institution, state that: An investment in the Fund is not a deposit of the bank and is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance corporation or any other government agency. Instruction. A Money Market Fund that is advised by or sold through an insured depository institution should combine the disclosure required by Items 4(b)(1)(ii) and (iii) in a single statement.",
"label": "Risk Closing [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskClosingTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_RiskColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r46"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure.",
"label": "Risk Column [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_RiskFootnotesTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r46"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure.",
"label": "Risk Footnotes [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskFootnotesTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_RiskHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r46"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure.",
"label": "Risk [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskLoseMoney": {
"auth_ref": [
"r47",
"r50",
"r51",
"r52"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Summarize the principal risks of investing in the Fund, including the risks to which the Fund's portfolio as a whole is subject and the circumstances reasonably likely to affect adversely the Fund's net asset value, yield, and total return. Unless the Fund is a Money Market Fund, disclose that loss of money is a risk of investing in the Fund. If the Fund is a Money Market Fund, include the following statement: \"You could lose money by investing in the Fund.\"",
"label": "Risk Lose Money [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskLoseMoney",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskMoneyMarketFundMayImposeFeesOrSuspendSales": {
"auth_ref": [
"r50",
"r51"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the statement \"The Fund may impose a fee upon sale of your shares or may temporarily suspend your ability to sell shares if the Fund's liquidity falls below required minimums because of market conditions or other factors.\"",
"label": "Risk Money Market Fund May Impose Fees or Suspend Sales [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskMoneyMarketFundMayImposeFeesOrSuspendSales",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskMoneyMarketFundMayNotPreserveDollar": {
"auth_ref": [
"r51",
"r52"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the statement \"Although the Fund seeks to preserve the value of your investment at $1.00 per share, it cannot guarantee it will do so.\"",
"label": "Risk Money Market Fund May Not Preserve Dollar [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskMoneyMarketFundMayNotPreserveDollar",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskMoneyMarketFundPriceFluctuates": {
"auth_ref": [
"r50"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the statement \"Because the share price of the Fund will fluctuate, when you sell your shares they may be worth more or less than what you originally paid for them.\"",
"label": "Risk Money Market Fund Price Fluctuates [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskMoneyMarketFundPriceFluctuates",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskMoneyMarketFundSponsorMayNotProvideSupport": {
"auth_ref": [
"r50",
"r51",
"r52"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the statement \"The Fund's sponsor has no legal obligation to provide financial support to the Fund, and you should not expect that the sponsor will provide financial support to the Fund at any time.\"",
"label": "Risk Money Market Fund Sponsor May Not Provide Support [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskMoneyMarketFundSponsorMayNotProvideSupport",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r48"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Narrative Risk Disclosure. A Fund may, in responding to this Item, describe the types of investors for whom the Fund is intended or the types of investment goals that may be consistent with an investment in the Fund.",
"label": "Risk Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_RiskNondiversifiedStatus": {
"auth_ref": [
"r54"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If applicable, state that the Fund is non-diversified, describe the effect of non-diversification (e.g., disclose that, compared with other funds, the Fund may invest a greater percentage of its assets in a particular issuer), and summarize the risks of investing in a non-diversified fund.",
"label": "Risk Nondiversified Status [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskNondiversifiedStatus",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskNotInsured": {
"auth_ref": [
"r50",
"r51",
"r52"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Include the statement \"An investment in the Fund is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency.\"",
"label": "RIsk Not Insured [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskNotInsured",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskNotInsuredDepositoryInstitution": {
"auth_ref": [
"r53"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund is advised by or sold through an insured depository institution, state that \"An investment in the Fund is not a deposit of the bank and is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency.\"",
"label": "Risk Not Insured Depository Institution [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskNotInsuredDepositoryInstitution",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskReturnAbstract": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"label": "Risk/Return:"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskReturnAbstract",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021",
"http://www.valic.com/role/DocumentDocumentandEntityInformationElements000000"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_RiskReturnHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r5"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Risk/Return Summary Investment Objectives/Goals Include the following information, in plain English under rule 421(d) under the Securities Act, in the order and subject matter indicated",
"label": "Risk/Return [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "RiskReturnHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ShareClassDomain": {
"auth_ref": [
"r3"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "All members of this domain must be elements with name starting with \"C\" and consisting of a 9-digit Fund share class CIK.",
"label": "Share Classes"
}
}
},
"localname": "ShareClassDomain",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"rr_ShareholderFeeOther": {
"auth_ref": [
"r37"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Other Expenses",
"label": "Shareholder Fee, Other"
}
}
},
"localname": "ShareholderFeeOther",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "NonNegativeMonetaryType"
},
"rr_ShareholderFeesCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r35"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Shareholder Fees (fees paid directly from your investment).",
"label": "Shareholder Fees Caption [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ShareholderFeesCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ShareholderFeesColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r35"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Shareholder Fees (fees paid directly from your investment).",
"label": "Shareholder Fees Column [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ShareholderFeesColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_StrategyHeading": {
"auth_ref": [
"r45"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Principal investment strategies of the Fund. Summarize how the Fund intends to achieve its investment objectives by identifying the Fund's principal investment strategies (including the type or types of securities in which the Fund invests or will invest principally) and any policy to concentrate in securities of issuers in a particular industry or group of industries.",
"label": "Strategy [Heading]"
}
}
},
"localname": "StrategyHeading",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_StrategyNarrativeTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r45"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Principal investment strategies of the Fund. Summarize how the Fund intends to achieve its investment objectives by identifying the Fund's principal investment strategies (including the type or types of securities in which the Fund invests or will invest principally) and any policy to concentrate in securities of issuers in a particular industry or group of industries.",
"label": "Strategy Narrative [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "StrategyNarrativeTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_StrategyPortfolioConcentration": {
"auth_ref": [
"r45"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Principal investment strategies of the Fund. Summarize how the Fund intends to achieve its investment objectives by identifying the Fund's principal investment strategies (including the type or types of securities in which the Fund invests or will invest principally) and any policy to concentrate in securities of issuers in a particular industry or group of industries.",
"label": "Strategy Portfolio Concentration [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "StrategyPortfolioConcentration",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_SupplementToProspectusTextBlock": {
"auth_ref": [
"r1"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "This element contains the text of a prospectus supplement (submission type 497) not already contained in an element containing amended text or other data from a previous submission.",
"label": "Supplement to Prospectus [Text Block]"
}
}
},
"localname": "SupplementToProspectusTextBlock",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ThirtyDayTaxEquivalentYield": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Thirty Day Tax Equivalent Yield"
}
}
},
"localname": "ThirtyDayTaxEquivalentYield",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_ThirtyDayYield": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Thirty Day Yield"
}
}
},
"localname": "ThirtyDayYield",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "pureItemType"
},
"rr_ThirtyDayYieldCaption": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Thirty Day Yield Caption"
}
}
},
"localname": "ThirtyDayYieldCaption",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_ThirtyDayYieldColumnName": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Thirty Day Yield Column [Text]"
}
}
},
"localname": "ThirtyDayYieldColumnName",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "textBlockItemType"
},
"rr_ThirtyDayYieldPhone": {
"auth_ref": [
"r66"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "A Fund (other than a Money Market Fund) may include the Fund's yield calculated under Item 21(b)(2). Any Fund may include its tax-equivalent yield calculated under Item 21. If a Fund's yield is included, provide a toll-free (or collect) telephone number that investors can use to obtain current yield information.",
"label": "Thirty Day Yield Phone"
}
}
},
"localname": "ThirtyDayYieldPhone",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"rr_YearToDateReturnLabel": {
"auth_ref": [
"r57"
],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "If the Fund has annual returns for at least one calendar year, provide a bar chart showing the Fund's annual total returns for each of the last 10 calendar years (or for the life of the Fund if less than 10 years), but only for periods subsequent to the effective date of the Fund's registration statement. Present the corresponding numerical return adjacent to each bar. If the Fund's fiscal year is other than a calendar year, include the year-to-date return information as of the end of the most recent quarter in a footnote to the bar chart. Following the bar chart, disclose the Fund's highest and lowest return for a quarter during the 10 years or other period of the bar chart.",
"label": "Year to Date Return, Label"
}
}
},
"localname": "YearToDateReturnLabel",
"nsuri": "http://xbrl.sec.gov/rr/2021",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "stringItemType"
},
"valic_C000021774Member": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Systematic Growth Fund",
"label": "C000021774 [Member]",
"verboseLabel": "Systematic Growth Fund"
}
}
},
"localname": "C000021774Member",
"nsuri": "http://www.valic.com/20230503",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"valic_Russell1000GrowthIndexMember": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Russell 1000 Growth Index",
"label": "Russell 1000 Growth Index [Member]",
"verboseLabel": "Russell 1000\u00ae Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes)"
}
}
},
"localname": "Russell1000GrowthIndexMember",
"nsuri": "http://www.valic.com/20230503",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"valic_S000008005Member": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Systematic Growth Fund Member",
"label": "S000008005 [Member]",
"verboseLabel": "Systematic Growth Fund"
}
}
},
"localname": "S000008005Member",
"nsuri": "http://www.valic.com/20230503",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
},
"valic_Sandp500IndexMember": {
"auth_ref": [],
"lang": {
"en-us": {
"role": {
"documentation": "Sandp 500 Index",
"label": "Sandp 500 Index [Member]",
"verboseLabel": "S&P 500\u00ae Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes)"
}
}
},
"localname": "Sandp500IndexMember",
"nsuri": "http://www.valic.com/20230503",
"presentation": [
"http://www.valic.com/role/DisclosureRiskReturnDetailDataElementsSystematicGrowthFund000021"
],
"xbrltype": "domainItemType"
}
},
"unitCount": 2
}
},
"std_ref": {
"r0": {
"Publisher": "Global LEI Foundation",
"URI": "www.leiroc.org",
"URIDate": "2013-08-21",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r1": {
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r10": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "6",
"Subsection": "example",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r11": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subsection": "example",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r12": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "b",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r13": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "c",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r14": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "d",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r15": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "i",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "d",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r16": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r17": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "i",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "a",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r18": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "b",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r19": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "c",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r2": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r20": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "d",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r21": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "a",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r22": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "b",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r23": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "i",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "c",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r24": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "ii",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "c",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r25": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "iii",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "c",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r26": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "d",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r27": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "ii",
"Exhibit": "B",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "d",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r28": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "e",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r29": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "vi",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "f",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r3": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "1",
"Subsection": "a",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r30": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "vii",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "f",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r31": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "4",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r32": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "4",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "f",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r33": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "5",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r34": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "6",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "a",
"Subsection": "instructions",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r35": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r36": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "1",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r37": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "10",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r38": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "11",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r39": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "3",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r4": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "3",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "1",
"Subsection": "a",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r40": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "4",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r41": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "5",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r42": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "6",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r43": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "7",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r44": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "9",
"Subsection": "table",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r45": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subsection": "a",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r46": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r47": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "i",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r48": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "instruction",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "i",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r49": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "ii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r5": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "2",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r50": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "ii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r51": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "B",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "ii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r52": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "C",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "ii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r53": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r54": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iv",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r55": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r56": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "i",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r57": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "ii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r58": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r59": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "1",
"Exhibit": "1",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r6": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "2",
"Subsection": "a",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r60": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "1",
"Exhibit": "2",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r61": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "1",
"Exhibit": "5",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iii",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r62": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "1",
"Exhibit": "a",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r63": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "1",
"Exhibit": "b",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r64": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "2",
"Exhibit": "a",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r65": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "2",
"Exhibit": "c",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r66": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "2",
"Exhibit": "d",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r67": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "3",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r68": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "3",
"Exhibit": "a",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r69": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "3",
"Exhibit": "b",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r7": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "1",
"Subsection": "example",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r70": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "3",
"Exhibit": "c",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r71": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "3",
"Example": "ii",
"Exhibit": "c",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Sentence": "D",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r72": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "4",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r73": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "5",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "instructions",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r74": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iv",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r75": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "B",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iv",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r76": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "C",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iv",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r77": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Clause": "D",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "4",
"Subparagraph": "iv",
"Subsection": "b",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r78": {
"Name": "Regulation 12B",
"Number": "240",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "12",
"Subsection": "b-2",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r79": {
"Name": "Regulation S-T",
"Number": "232",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "313",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r8": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "1",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "2",
"Subsection": "example",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
},
"r9": {
"Chapter": "A",
"Name": "Form",
"Number": "N-1A",
"Paragraph": "2",
"Publisher": "SEC",
"Section": "3",
"Subparagraph": "1",
"Subsection": "example",
"role": "http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef"
}
},
"version": "2.2"
}