
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM F-1/A
Amendment No. 3
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| British Virgin Islands | 3621 | Not applicable | ||
| (State
or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary
Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S.
Employer Identification Number) |
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. Room 104, Building 1-B, No. 3500 Xiupu Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China |
| (Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant’s principal executive offices) |
Mark E. Crone, Esq. The Crone Law Group, PC 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 2446 New York, NY 10170 (646) 861-7891 |
| (Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service) |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after the effective date of this Registration Statement.
If any of the securities being registered on the Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box ☐
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering.☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering.☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act of 1933. ☒
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards† provided pursuant to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☒
COPIES OF COMMUNICATIONS TO:
Mark Crone, Esq. Eric Mendelson, Esq. The Crone Law Group P.C. 420 Lexington Ave, Suite 2446 New York, NY 10170 Phone: (646) 861-7891 |
Lixia Zhang, Esq. Jiangsu Shishan Law Firm Building A, No. 65 Yushan Road High-tech Zone, Suzhou, China Phone: +86 512-68780109 |
THE REGISTRANT HEREBY AMENDS THIS REGISTRATION STATEMENT ON SUCH DATE OR DATES AS MAY BE NECESSARY TO DELAY ITS EFFECTIVE DATE UNTIL THE REGISTRANT SHALL FILE A FURTHER AMENDMENT WHICH SPECIFICALLY STATES THAT THIS REGISTRATION STATEMENT SHALL THEREAFTER BECOME EFFECTIVE IN ACCORDANCE WITH SECTION 8(a) OF THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933 OR UNTIL THE REGISTRATION STATEMENT SHALL BECOME EFFECTIVE ON SUCH DATE AS THE COMMISSION, ACTING PURSUANT TO SECTION 8(a), MAY DETERMINE.
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission is declared effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting any offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted.
Subject to Completion, Dated ____, 2023

TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
5,000,000 Ordinary Shares
___________________
This prospectus relates to the offer and resale of an aggregate 5,000,000 Ordinary Shares, no par value (the “Shares”), of Tian’an Technology Group Ltd., all of which were issued by us in a private placement transaction pursuant to securities purchase agreements (each a “Purchase Agreement”) at a purchase price of $0.10 per share. The holders of the shares are each referred to herein as a “Selling Stockholder” and collectively as the “Selling Stockholders.”
The Selling Stockholders, or their respective transferees, pledgees, donees or other successors-in-interest, will offer and sell their Shares at a fixed price until the Shares are listed on a national securities exchange or quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board, OTCQX, or OTCQB, at which time the Shares may be sold through public or private transactions at prevailing market prices, at prices related to prevailing market prices or at privately negotiated prices. The Selling Stockholders may sell any, all or none of the securities offered by this prospectus, and we do not know when or in what amount the Selling Stockholders may sell their Shares hereunder following the effective date of this registration statement. We provide more information about how a Selling Stockholder may sell its Shares in the section titled “Plan of Distribution” on page 48.
We are registering the Shares on behalf of the Selling Stockholders, to be offered and sold by them from time to time. We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the Shares by the Selling Stockholders in the offering described in this prospectus. We have agreed to bear all of the expenses incurred in connection with the registration of the Shares. The Selling Stockholders will pay or assume discounts, commissions, fees of underwriters, selling brokers or dealer managers and similar expenses, if any, incurred for the sale of the Shares.
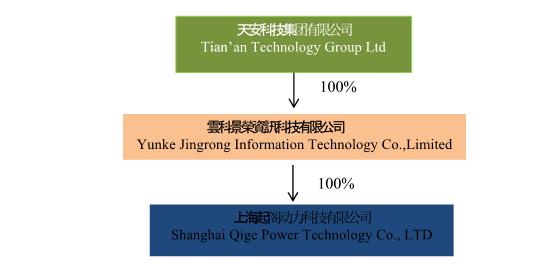
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. (“Tian’an”) is a holding company that was incorporated under the laws of the British Virgin Islands on April 8, 2021. As a holding company with no material operations of our own, we conduct our operations through Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Yunke”), our wholly owned subsidiary. Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Qige”) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke and our operating company in China. Through our subsidiary, Shanghai Qige, we are engaged in the technology driven sales of power control and service systems solutions. The ordinary shares offered by the Selling Stockholders are shares of Tian’an, a British Virgin Islands holding company, and not shares of Yunke or Shanghai Qige. Accordingly, purchasers of Shares in Tian’an will not directly hold equity interests in said operating subsidiaries.
We are a British Virgin Islands holding company that conducts all of its operations through our wholly owned subsidiary. Tian’an and Yunke are holding companies and do not have any actual operations. Shanghai Qige is located in China where all of our assets are held and all of our operations are conducted. Investors in this offering will receive Ordinary Shares in Tian’an Technology Group Ltd., the British Virgin Islands holding company, and will not hold direct investments in our Chinese operating company, Shanghai Qige, a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke. This structure involves unique risks to investors, as further described below. See “You may experience difficulties in effecting service of legal process, enforcing foreign judgments or bringing actions in the British Virgin Islands against us or our management named in the prospectus based on foreign laws”.
The structure of cash flows within our organization, and the applicable regulations, are as follows:
1. Our equity structure is a direct shareholding structure, that is, the overseas entity to be listed in the U.S., Tian’an, directly controls Yunke and Shanghai Qige. See “Corporate History and Structure” for additional details.
2. Within our direct holding structure, the use of funds within our corporate group is legal and compliant with the laws and regulations of the PRC. Because Tian’an and Yunke have no actual operations, there is no funding for these entitles and all the revenue that is generated by Shanghai Qige is used to operate Shanghai Qige. After foreign investors’ funds enter the Company at the close of this offering, the funds can be directly transferred to our PRC subsidiary Shanghai Qige through a WFOE structure.
3. At present the Company has no restrictions on the use of its cash. We have a fund management policy in place which has corresponding internal control rules that are compliant with the laws and regulations of the PRC.
4. At present, we have never distributed any dividends and do not intend to in the future. However, if the Company decides to distribute dividends to its shareholders, the Company will transfer the dividends from the operating subsidiary in accordance with the laws and regulations of the PRC and other countries. Then the subsidiary will transfer the dividends to Tian’an, and the dividends will be distributed from Tian’an to all shareholders respectively in proportion to the shares they hold, regardless of whether the shareholders are U.S. investors or investors in other countries or regions.
As of the date of this registration statement, no transfers, dividends, or distributions have been made between the holding company, its subsidiaries, and consolidated entities, or to investors.
Since our business operations are conducted in China through our operating subsidiary Shanghai Qige, the Chinese government may exercise significant oversight and discretion over the conduct of our business in China and may intervene in or influence our subsidiary’s operations at any time, which could result in a material change in its operations and/or the value of our Ordinary Shares.
China’s economy differs from the economies of most developed countries in many respects, including the amount of government involvement, level of development, growth rate, control of foreign exchange and allocation of resources. Further, the PRC government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. It is possible what we do not receive or maintain appropriate permissions or approvals, inadvertently conclude that such permissions or approvals are not required, or applicable laws, regulations, or interpretations could change and we will be required to obtain such permissions or approvals in the future. Changes in any of these policies, laws and regulations could adversely affect the economy in China and could have a material adverse effect on our business. Any actions by the Chinese government to exert more oversight and control over this offering, or any of our business operations could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors.
The Chinese government may intervene or influence the operation of our PRC operating entity and may exercise significant oversight and discretion over the conduct of our business and may intervene in or influence Shanghai Qige’s operations at any time, which could result in a material change in our operations and/or the value of our Ordinary Shares.
Recent statements by the Chinese government have indicated an intent to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas and/or foreign investments in China-based issuers. Any future action or control by the Chinese government over offerings conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and could cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Recently, the People’s Republic of China (“PRC” or “China”) government initiated a series of regulatory actions and made a number of public statements on the regulation of business operations in China with little advance notice, including cracking down on illegal activities in the securities market, enhancing supervision over China-based companies listed overseas using a variable interest entity structure, adopting new measures to extend the scope of cybersecurity reviews, and expanding efforts in anti-monopoly enforcement. These statements and regulatory actions are new, however, it is highly uncertain how soon legislative or administrative regulation making bodies in China will respond to them, or what existing or new laws or regulations or detailed implementation rules and interpretations will be modified or promulgated, if any, or the potential impact such modified or new laws and regulations will have on our daily business operations or our ability to accept foreign investments and continue to be listed on an U.S. exchange.
| (1) | On December 28, 2021, the Cyberspace Administration of China (“CAC”) adopted and promulgated the Cybersecurity Review Measures (2021), which became effective on February 15, 2022. This regulation provides that any “online platform operators” controlling the personal information of more than one million users which seek to list on a foreign stock exchange should also be subject to cybersecurity review. On November 14, 2021, the CAC published the Network Internet Data Protection Draft Regulations (draft for comments), which reiterates that data handlers that process the personal information of more than one million users listing in a foreign country should apply for a cybersecurity review. It is uncertain that whether Shanghai Qige will be deemed as the “online platform operators” as mentioned above, even though Shanghai Qige does not operate any online platforms. Tian’an and Yunke do not have any operations. We do not believe that Shanghai Qige is directly subject to these regulatory actions or statements, as (a) the Company does not have a variable interest entity structure, and this listing does not refer to the case of an overseas special purpose company directly or indirectly controlled by Chinese companies or individuals controlling the Chinese domestic companies via contractual arrangements; and (b) the business of Shanghai Qige does not involve the collection of user data, implicate cybersecurity, or involve any other type of restricted industry. |
| (2) | The Regulations on Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors (“M&A Rules”) and Anti-Monopoly Law of the People’s Republic of China promulgated by the Standing Committee of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress which became effective in 2008 (“Anti-Monopoly Law”), established additional procedures and requirements that could make merger and acquisition activities by foreign investors more time-consuming and complex. Such regulation requires, among other things, that State Administration for Market Regulation (“SAMR”) be notified in advance of any change-of-control transaction in which a foreign investor acquires control of a PRC domestic enterprise or a foreign company with substantial PRC operations, if certain thresholds under the Provisions of the State Council on the Standard for Declaration of Concentration of Business Operators, issued by the State Council in 2008, are triggered. Moreover, the Anti-Monopoly Law requires that transactions which involve the national security, the examination on the national security shall also be conducted according to the relevant provisions of the State. In addition, PRC Measures for the Security Review of Foreign Investment which became effective in January 2021 require acquisitions by foreign investors of PRC companies engaged in military-related or certain other industries that are crucial to national security be subject to security review before consummation of any such acquisition. China has recently witnessed landscape reform in the antitrust regime at the end of 2021: the draft amendment (“Draft Amendment”) to the Anti-Monopoly Law was published for public comments on October 23 and the national anti-monopoly bureau (“Anti-monopoly Bureau”) was inaugurated in Beijing on November 18. With the law amendment and the institutional reshuffle, some widely held perception of antitrust practice in China should be refreshed. Among other things, all types of monopoly agreements can be exempted if the market share threshold is met, which will be stipulated by the authority in separate regulations. Also, abuse of data, algorithm, technologies, and platform rules that leading to imposition of unfair restrictions on undertakings is expressly listed as abuse of dominant market position. In addition, the Draft Amendment expressly prohibit hub-and-spoke cartel and provide for the same legal liabilities for both the hub and spoke. China is determined to strengthen enforcement against monopolistic practices in all industries. |
| (3) | On December 24, 2021, China Securities Regulatory Commission, or the China Securities Regulatory Commission (the “CSRC”) issued the Administrative Provisions of the State Council Regarding the Overseas Issuance and Listing of Securities by Domestic Enterprises (Draft for Comments) (the “Draft Administrative Provisions”) and the Measures for the Overseas Issuance of Securities and Listing Record-Filings by Domestic Enterprises (Draft for Comments) (the “Draft Filing Measures”, collectively with the Draft Administrative Provisions, the “Draft Rules Regarding Overseas Listing”), which were published for comments only with the comment period expiring on January 23, 2022. The Draft Rules Regarding Overseas Listing lay out the filing regulation arrangement for both direct and indirect overseas listings, and clarify the determination criteria for indirect overseas listing in overseas market. Among other things, if a domestic enterprise intends to indirectly offer and list securities in an overseas market, the record-filing obligation is with a major operating entity incorporated in the PRC and such filing obligation shall be completed within three working days after the overseas listing application is submitted. Up to the issuance of this prospectus, the Draft Rules Regarding Overseas Listing have not yet come into effect, and accordingly the Company and our subsidiaries are currently not affected. |
We are both an “emerging growth company” and a “foreign private issuer” under applicable U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission rules and are subject to reduced public company disclosure requirements. See “Summary-Implications of Being an ‘Emerging Growth Company’ and a ‘Foreign Private Issuer’” on page 9 of this prospectus.
There has been no market for our securities and a public market may not develop, or, if any market does develop, it may not be sustained. We intend to seek quotation of our ordinary shares on The OTC Markets Group, Inc. OTCQX or the OTCQB Venture after effectiveness of the registration statement of this prospectus. Quotation of our Ordinary Shares on the OTC Markets will require a market maker filing an application to quote our ordinary shares and approval of that application. We do not have a market maker willing to file the necessary application for quoting our Ordinary Shares on the OTC Markets as of the date of this prospectus. There is a risk that no public market will develop for our Ordinary Shares.
The audit report included in this prospectus was issued by HHC (“HHC”) a United States based accounting firm that is registered with the PCAOB and can be inspected by the PCAOB. We have no intention of dismissing HHC in the future or of engaging any auditor not subject to regular inspection by the PCAOB. There is no guarantee, however, that any future auditor engaged by the Company would remain subject to full PCAOB inspection during the entire term of our engagement. The PCAOB is currently unable to conduct inspections in China without the approval of Chinese government authorities. If it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate our auditor completely, investors may be deprived of the benefits of such inspection. Any audit reports not issued by auditors that are completely inspected by the PCAOB, or a lack of PCAOB inspections of audit work undertaken in China that prevents the PCAOB from regularly evaluating our auditors’ audits and their quality control procedures, could result in a lack of assurance that our financial statements and disclosures are adequate and accurate. In addition, under the HFCAA, our securities may be prohibited from trading on the Nasdaq or other U.S. stock exchanges if our auditor is not inspected by the PCAOB for three consecutive years, and this ultimately could result in our Ordinary Shares being delisted. Furthermore, on June 22, 2021, the U.S. Senate passed the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act (“AHFCAA”), which, if enacted, would amend the HFCAA and require the SEC to prohibit an issuer’s securities from trading on any U.S. stock exchanges if its auditor is not subject to PCAOB inspections for two consecutive years instead of three.
Pursuant to the HFCAA, the PCOAB issued a Determination Report on December 16, 2021 which found that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely registered public accounting firms headquartered in: (1) mainland China of the People’s Republic of China, because a position taken by one or more authorities in mainland China; and (2) Hong Kong, a Special Administrative Region and dependency of the PRC, because of a position taken by one or more authorities in Hong Kong. In addition the PCOAB’s report identified the specific registered public accounting firms which are subject to these determinations. Our registered public accounting firm HHC is not headquartered in mainland China or Hong Kong and was not identified in this report as a firm subject to the PCAOB’s determination.
Investing in our Ordinary Shares involves a high degree of risk. See section entitled “Risk Factors” starting on page 10. We directly hold equity interests in our operating subsidiaries in China, and we do not currently use a variable interest entity (“VIE”) structure. We are subject to legal and operational risks associated with having our subsidiaries’ operations in China, including risks related to the legal, political and economic policies of the Chinese government, the relations between China and Hong Kong and China and the United States, or Chinese or United States regulations, which risks could result in a material change in our operations and/or cause our Ordinary Shares to significantly decline in value or become worthless and affect our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors. Recently, the PRC government initiated a series of regulatory actions and made a number of public statements on the regulation of business operations in China with little advance notice, including cracking down on illegal activities in the securities market, enhancing supervision over China-based companies listed overseas, adopting new measures to extend the scope of cybersecurity reviews, and expanding efforts in anti-monopoly enforcement. We may be subject to these regulatory actions or statements. Although we have not engaged in any monopolistic behavior, our business does not involve in the collection of user data and may not subject to cybersecurity reviews. We currently expect that these new regulations may not have an impact on our operating subsidiaries or this offering. As of the date of this prospectus, no effective laws or regulations in the PRC explicitly require us to seek approval from the China Securities Regulatory Commission (the “CSRC”) or any other PRC governmental authorities for our overseas listing plan, nor has our Company or any of our subsidiaries received any inquiry, notice, warning or sanctions regarding our planned overseas listing from the CSRC or any other PRC governmental authorities. However, since these statements and regulatory actions by the PRC government are newly published and official guidance and related implementation rules have not been issued, the potential impact that such modified or new laws and regulations will have on our daily business operations, or on our ability to accept foreign investments and be quoted on the OTC Markets, is highly uncertain. The Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (the “SCNPC”) or other PRC regulatory authorities may, in the future, promulgate laws, regulations or implementing rules that require our Company, or any of our subsidiaries, to obtain regulatory approval from Chinese authorities before being quoted in the U.S. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 10 for a discussion of these legal and operational risks and other information that should be considered before making a decision to purchase our Ordinary Shares.
We are an “emerging growth company” under applicable U.S. federal securities laws and are eligible for reduced public company reporting requirements.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed upon the adequacy or accuracy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
Table of Contents
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. Neither we, nor the Selling Stockholders have authorized anyone to provide information different from that contained in this prospectus. We and the Selling Stockholders are offering to sell, and seeking offers to buy, Ordinary Shares only in jurisdictions where offers and sales are permitted. The information contained in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date of this prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or of any sale of our Shares.
| i |
The following summary is qualified in its entirety by, and should be read in conjunction with, the more detailed information and financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. In addition to this summary, we urge you to read the entire prospectus carefully, especially the risks of investing in our Shares discussed under “Risk Factors,” before deciding whether to invest in our Shares.
Conventions that Apply to this Prospectus
Our financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“US GAAP”). We present our consolidated financial statements in U.S. dollars.
Our fiscal year ends on December 31 of each year. References to fiscal 2021 are references to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021 and references to fiscal 2020 are references to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. Some amounts in this prospectus may not total due to rounding. All percentages have been calculated using unrounded amounts.
Throughout this prospectus, we provide a number of key performance indicators used by our management and often used by competitors in our industry. These and other key performance indicators are discussed in more detail in the section entitled “Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations—Key financial and operating metrics.” We define certain terms used in this prospectus as follows:
Unless otherwise indicated or the context otherwise requires, references in this prospectus to:
| ● | “Shares” are to our Ordinary Shares, no par value per share; | |
| ● | “PWM” is to pulse width modulation; | |
| ● | “China” or the “PRC” are to the People’s Republic of China, excluding, for the purposes of this prospectus only, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan; | |
| ● | “DC is to direct current motors; | |
| ● | “Stator” is to the stationary part of the rotary electromagnetic devices, such as the alternator, electric motor or generator; | |
| ● | “BVI” is to the British Virgin Islands; | |
| ● | “AC” is to alternating current motors (or eclectic motors); | |
| ● | “EC” is to electronically commutated series brushless motor controller; | |
| ● | “PWM” is to pulse with modulation control; | |
| ● | “CNC” is to computer numerical control; | |
| ● | “PLC” is to programmable logic controller; | |
| ● | “RMB” or “Renminbi” are to the legal currency of the People’s Republic of China; | |
| ● | “Yuan” or “¥” are to the primary unit of account of the Renminbi (RMB), the legal currency of the People’s Republic of China; | |
| ● | “US$,” “U.S. dollars,” “$,” or “dollars” are to the legal currency of the United States; | |
| ● | Tian’an Technology Group Ltd., is a limited company organized under the laws of the British Virgin Islands and is the holding company of Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd., its wholly owned subsidiary; | |
| ● | Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co, Ltd. is a limited company organized under the laws of China and is the parent company for Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd., its wholly owned subsidiary; | |
| ● | Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd., which is the operating company for Tian’an Technology Group Ltd., is a limited company organized under the laws of China and is the wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd.; and | |
| ● | Unless the context provides otherwise, “we,” “us,” “our company” or “our,” “the Company” and “Tian’an” are to Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. a corporation formed under the laws of the British Virgin Islands, and to our two wholly-owned subsidiaries, Yunke and Shanghai Qige. |
Our reporting currency is the U.S. Dollar. The functional currency of the Company in the PRC is the Renminbi.
| 1 |
This disclosure contains translations of certain Renminbi amounts into U.S. dollar amounts at specified rates solely for the convenience of the reader. The relevant exchange rates are listed below:
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2021 | For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Year ended RMB: USD exchange rate | 0.1573 | 0.1531 | ||||||
| Average yearly RMB: USD exchange rate | 0.1550 | 0.1449 | ||||||
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 | For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 | |||||||
| Year ended RMB: USD exchange rate | 0.1493 | 0.1549 | ||||||
| Average yearly RMB: USD exchange rate | 0.1543 | 0.1545 | ||||||
Market and industry data
Unless otherwise indicated, information in this prospectus concerning economic conditions, our industry, our markets and our competitive position is based on a variety of sources, information from independent industry analysts and publications, as well as our own estimates and research.
Our estimates are derived from publicly available information released by third-party sources, as well as data from our internal research, which we believe to be reasonable. None of the independent industry publications used in this prospectus were prepared on our behalf.
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
The following summary is qualified in its entirety by, and should be read in conjunction with, the more detailed information and financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. In addition to this summary, we urge you to read the entire prospectus carefully, especially the risks of investing in our Shares discussed under “Risk Factors,” before deciding whether to invest in our Shares.
Our Business
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. (“Tian’an”) is a holding company that was incorporated under the laws of the British Virgin Islands on April 8, 2021. Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Yunke”) is our wholly owned subsidiary. Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Qige”) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke and our operating company in China. Through our subsidiary, Shanghai Qige, we are engaged in the technology driven sales of power control and service systems solutions. These products are used in low-speed electric vehicles, such as electric forklifts, golf carts, street sweepers and other types of specialized field vehicles.
Shanghai Qige’s main product is a series of brushless DC motor controllers. Brushless DC motors, for which its controllers are commonly paired with, are common in industrial applications across the world. At the most basic level, there are brushed and brushless motors and there are direct current motors (“DC”) and alternating current motors (“AC”), or eclectic motors. Brushless DC motors do not contain brushes and use a DC current.

| 2 |
In a brushed DC motor, the rotor spins 180-degrees when an electric current is run to the armature, a device through which electric current is passed for generating torque. To go any further, the poles of the electromagnet must flip. The brushes, as the rotor spins, make contact with the stator (the coil of wire housed inside the engine case), flipping the magnetic field and allowing the rotor to spin a full 360-degrees. A brushless DC motor is essentially flipped inside out, eliminating the need for brushes to flip the electromagnetic field. In brushless DC motors, the permanent magnets are on the rotor, and the electromagnets are on the stator. A computer then charges the electromagnets in the stator to rotate the rotor a full 360-degrees.
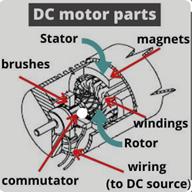
Brushless DC motors typically have an efficiency of 80-85%, while brushed motors are usually only 75-80% efficient. Brushes eventually wear out, sometimes causing dangerous sparking, limiting the lifespan of a brushed motor. Brushless DC motors are quiet, lighter and have much longer lifespans. Because computers control the electrical current, brushless DC motors can achieve much more precise motion control.
Because of all these advantages, brushless DC motors are often used in modern devices where low noise and low heat are required, especially in devices that run continuously.
Our Brushless DC Motor Controller
The majority of Shanghai Qige’s sales during the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, and the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were derived from its Brushless DC Motor Controller. While brushless DC motors are mechanically relatively simple, they do require sophisticated control electronics and regulated power supplies. Brushless motor controllers differ according to the method they use to detect the rotor’s position. Depending on the rotor’s placement, brushless DC motors can be of two types (1) inrunner motor (the rotor is internal, and the stator is on the outside of the motor); or (2) outrunner motor (the rotor is external, so the permanent magnets spin around the stator together with the motor’s case).
Inrunner motors have a more lightweight construction and a better rotational speed because of their smaller rotating diameter. On the other hand, outrunner motors have a higher torque because of the longer arm and greater electromotive force applied to the rotor.
DC motor speed control is perhaps the most common manipulation used in controllers. This speed can be controlled in four different ways: flux variation, armature voltage variation, a change in the supply voltage, and pulse width modulation (“PWM”). PWM is the technique commonly used for achieving speed control in a DC motor. It delivers energy through a series of pulses rather than a continuous signal. By altering the pulse width, the DC motor controller is able to regulate the energy flow to keep it consistent.
While less popular, DC motor torque control is achieved by a DC motor drive regulating the armature current. Since the armature current isn’t regulated, the motor can operate at whatever speed necessary to achieve the desired torque level. The torque level can remain constant achieving a “taper tension effect” for a fixed input reference and torque mode center winders. However, the machine operator can in some circumstances increase the torque set-point as diameter increases.
| 3 |
Shanghai Qige offers an electronically commutated (“EC”) series of brushless DC motor controllers. An EC motor is designed to run on an alternating current (“AC”) power supply, but it in fact bears a closer resemblance to a direct current (“DC”) motor. It is essentially a permanent magnet, brushless DC motor that incorporates on-board electronics. The added electronics allow an EC motor to combine the best features from both AC and DC motors, and then improve on them. Shanghai Qige’s Brushless DC Controller has a fast response, high precision and wide speed regulation system, meeting the trend of high-performance general-purpose driver. By optimizing a pulse with modulation (“PWM”) control technology, and an electromagnetic compatibility design, our motor controller has lower noise and lower electromagnetic interference performance. This allows Shanghai Qige to meet the personalized needs of a variety of customers.
Shanghai Qige’s customers purchase its products mainly via sales agreements, similar to a purchase order (each a “Sales Agreement”). Each Sales Agreement outlines the purchasing terms and conditions to which both Shanghai Qige and the customer must adhere. Shanghai Qige’s customers generally purchase from it in bulk, though Shanghai Qige allows for small or singular purchases. Shanghai Qige’s delivery and payment terms vary depending on the amount of products being purchased. However, in all cases, Shanghai Qige requires payment in full prior to the delivery of its products. Shanghai Qige’s products also have a standard warranty of twelve (12) months, which is customary for the brushless motor industry.
Shanghai Qige manufactures or maintains a limited amount of its products. Shanghai Qige engages third parties to design and produce its products and then delivers directly to its customers. Under certain exceptional situations, Shanghai Qige will provide assistance to its outsourced suppliers for the logistics and transportation management.
As of the date of this prospectus, Shanghai Qige does not have outstanding Sale Agreements due to impact of COVID-19. However, we believe that as the economy continues to recover from the pandemic, Shanghai Qige’s operations will improve.
Shanghai Qige’s Products
DC Brushless Motor Controller
The controller receives the start, stop and braking signals of the motor to control the start, stop and braking of the motor itself. It also receives the position sensor signal and the forward and reverse signals to control the on-off of each power tube of the inverter bridge and generates continuous torque. The controller will receive speed commands and speed feedback signals to control and adjust speed.
Encoder
The encoder is a rotary sensor that converts rotary displacement into a series of digital pulse signals. These pulses can be used to control angular displacement. After the encoder generates electrical signals, it is processed by a computer numerical control (“CNC”) or programmable logic controller (“PLC”) control system.
Cover Assembly
The cover assembly refers to using a transition piece to indirectly connect the cover body to the shell so that the cover body is set at the top opening of the shell without affecting the appearance of the shell. A mounting cavity is formed between the cover body and the transition piece, and a plurality of elements can be installed in the mounting cavity to realize the function of installing elements on the cover body.
Handheld Programmer
The handheld programmer is a tool for programmable integrated circuits to write data. Handheld programming startups are mainly used for chip programming such as single chip microcomputer (including embedded, memory and basic input/output systems). It mainly modifies the program in the read-only memory. The handheld is usually connected with the computer and other equipment and used in conjunction with the programming software.
Shanghai Qige’s products are used in low-speed electric vehicles, such as electric forklifts, golf carts, street sweepers and other types of specialized field vehicles.
| 4 |
Shanghai Qige’s Suppliers
Shanghai Qige uses third-party suppliers to manufacture its products. In late February 2022, Russia launched a large-scale military attack on Ukraine. The invasion significantly amplified already existing geopolitical tensions among Russia, Ukraine, Europe, NATO and the West, including the U.S. In response to the military action by Russia, various countries, including the U.S., the United Kingdom, and the European Union issued broad-ranging economic sanctions against Russia. The Company believes these sanctions will affect companies in other countries (particularly those that have done business with Russia and Ukraine) and in various sectors, industries and markets, such as oil and natural gas.
Shanghai Qige has established, and continues to maintain, long-term cooperative relationships with its third-party suppliers such that the shipping costs of Shanghai Qige have not risen during the COVID-19 pandemic. The third-party suppliers that Shanghai Qige engages are all located in China as is Shanghai Qige’s customer base.
It is possible that the conflict in Ukraine could result in additional repercussions such as the risk of price rise of raw materials, the risk of labor cost increase, and the depression of our industry. However, none of Shanghai Qige’s products rely on materials from Russia, Belarus or the Ukraine.
Shanghai Qige’s Market Opportunity
The Global Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor Drivers Market reported that Brushless DC motor drivers market size was valued at $6.25 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach $11.89 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.3% from 2020 to 2027. With Shanghai Qige’s product lines, Shanghai Qige is well positioned to meet this market demand. Shanghai Qige’s products, specifically its brushless DC motor controllers, are designed to be technologically efficient, have lower energy consumption, higher output, and less weight. The ability of brushless motors to save energy and increase the operational efficiency of equipment in which they are used is expected to drive the growth of the market over the forecast period. These motors offer optimum efficiency and reliability at the same time, which proves to be economical in the majority of their applications. These motors are thermally resistant, require low maintenance, and operate at low temperatures, eliminating any threat of sparks. Shanghai Qige’s brushless DC motor controllers in conjunction with motors are high level performance motors and have shown to be reliable. Shanghai Qige offers customized integrated circuit technology that allows for very promising market prospects. Revenue from sales of our products for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 were 0 and $22,008, respectively, and the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were $37,065 and $26,309, respectively.
Shanghai Qige’s products and operations have been materially impacted by the recent pandemic-related lockdowns in China such that its revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2022 were $0. In order to mitigate the adverse impacts on Shanghai Qige’s business, we intend to actively embrace marketplace changes. We will review our internal structure and policies, areas of business and business model and aim to adjust how Shanghai Qige engages in its current industry and possibly look to enter into differentiated or new business fields. We believe the decrease in Shanghai Qige’s revenue will be temporary.
Strengths
Shanghai Qige is dedicated to the production of high quality products that are tailored to customers’ requirements and commercial needs. Our competitive strengths include:
| ● | Shanghai Qige offers complete product solutions in the form of a multi-segment product system, covering the main markets of the motion control industry. At the same time, Shanghai Qige has core technologies suitable for different application fields that have been tested through independent research and development. | |
| ● | Shanghai Qige focuses on the different and various needs of customers, and has realized, through the organic combination of core technology for different products, how to provide its customers with comprehensive and integrated drive solutions and one-stop services, thereby reducing customers’ procurement costs and enhancing Shanghai Qige’s competitiveness. |
Shanghai Qige has been deeply involved in the low-speed, electric vehicle controller industry for many years and has a solid understanding of the needs of downstream customers. Shanghai Qige has tailored its technology research and development and product design around its customers’ needs.
Shanghai Qige’s marketing strategy is based on this research and the needs of its key customers. Shanghai Qige continues to review its customers’ purchasing trends and power and overall demands. Shanghai Qige maintains communication with its customers and makes offers based on what it believes their current and future need sets are. Shanghai Qige offers preferential pricing when it believes it will be most effective and to maintain long term relationships with its customers.
Shanghai Qige’s products are designed to provide customized settings and functional optimization. Shanghai Qige believes the industrial application of its advanced technological achievements improves the quality of its products, and also contributes to the control of product costs, both of which benefit its customers.
After years of research, Shanghai Qige has developed a marketing strategy targeting the brushless DC motor driver industry where customers looking to lower their carbon footprint while saving energy and increasing the operational efficiency of equipment in which they use. Shanghai Qige’s target customer will likely purchase the controller for motors in items such as: electric forklifts, golf carts, sightseeing vehicles, urban sweepers, simple customers, off-road vehicles, trucks and other special tool vehicles. We believe Shanghai Qige’s motion control products are also well received by its customers.
Continuous Technology Development
Since its inception, Shanghai Qige has focused on providing downstream equipment manufacturers with cost-effective motion control products that suit their individual needs. Subdivision fields, such as motors, have come a long way with their technological advantages.
At the same time, Shanghai Qige is actively researching and developing high-speed and high-precision drive control technology and other research technologies. Shanghai Qige also researches intelligence and integration of the driver system, and constantly aims to enrich its own technical reserves and enhances the level of competition. Shanghai Qige’s research and development management system is focused toward current market needs such that it can meet those needs with technological innovation as a core solution.
Strict Quality Control
Shanghai Qige has established a top-down integrated quality management system to carry out enhanced quality control, quality planning and quality improvement implementations for its product design process which ensure the effectiveness of the entire process. Shanghai Qige aims to be a responsible product supplier; and, in order to ensure the stability and reliability of product quality, in addition to strengthening routine manufacturing process testing, Shanghai Qige also implements a strict testing system to test its products.
| 5 |
Service Network Advantages
Shanghai Qige’s target customers are those who are seeking brushless motors required thermally resistance, low maintenance, low operating temperature, and high efficiency for their equipment. With consideration of the geographical and customer demographic characteristics of its target industry, Shanghai Qige has established a “regional distribution” sales system to satisfy its customers at customized services and rapid responses to their issues.
The application of controller and motor products in market segments not only requires customization of product shape, structure, and interface, but also requires suppliers to provide timely personalized services. Foreign-funded brands generally provide standardized general-purpose products in the domestic market, while their research and development teams may be located overseas. The responsiveness to the individualized needs of domestic customers can be slow, and it can be difficult to meet the emerging needs of customers. In addition, the products provided by foreign brands can have higher prices with multiple functionalities, while domestic downstream customers need products that are suitable for their own specific requirements and have lower comprehensive costs. We believe Shanghai Qige’s products offer more specific individual need-sets at cost-effective rates for domestic downstream industry customers. Shanghai Qige also offers more flexible, personalized, and cost effective service solutions which allow us to build a rapport with its customers.
Growth Strategy
Shanghai Qige will continue to adhere to its business principles of providing high quality and safe products to its consumers and promote social responsibility. We believe that Shanghai Qige’s pursuit of these goals will lead to sustainable growth driven by its capacity expansion based on market demand, solidify its position in the industry, and create long-term value for shareholders, employees and other stakeholders.
| ● | Technological innovation. Shanghai Qige intends to closely track and study the development trend of domestic and international industrial automation control technology, focusing on the breakthrough of synchronous control, high speed range of magnetic weakening control, motion position control, high-speed bus communication technology, high precision torque technology and other technology research so it can maintain its technological standards to meet consumer needs. | |
| ● | Establish a new research and development center in Shanghai. Shanghai Qige intends to uphold its commitment to product quality and to ensure consistently high standards throughout its operations. Shanghai Qige aims to construct a laboratory to further its research and development in Shanghai, China so it can increase its investment in research and development and equipment, accelerate the speed of technology development and talent training, and further improve its current innovation technology research and industrial application capacity. | |
| ● | Market development. Shanghai Qige hopes to expand its sales and distribution network to penetrate new geographic markets, further gaining market share in existing markets and accessing a broader range of customers. Shanghai Qige will continue to expand its sales network, leveraging its local resources to quickly enter new markets, while also minimizing requirements for capital outlay. Shanghai Qige plans to focus on brand customers and concentrate on high-end industry upgrades to its existing marketing system. | |
| ● | Industrial merger and acquisition plan. Shanghai Qige’s goal is to strengthen its market position and accelerate its expansion by expanding its scale and gaining additional market share. Shanghai Qige plans to increase investment in its business and expand its production capacity through horizontal or vertical acquisitions, strategic partnership and joint venture. Shanghai Qige plans to invest additional capital in technology research and development. With more exposure and promotion, Shanghai Qige’s product and brand will be better recognized. Currently Shanghai Qige has no agreements or letters of intent for any acquisitions, partnerships or ventures. | |
| ● | Human resource development. We believe Shanghai Qige’s success greatly depends on its ability to attract, incentivize and retain talented professionals. With a view to maintaining and improving its competitive advantage in the market, Shanghai Qige plans to implement a series of initiatives to attract additional and retain mid- to high-level personnel, including formulating a market-oriented employee compensation structure and implementing a standardized multi-level performance review mechanism. |
| 6 |
Research and Development
Shanghai Qige currently allocates most of its research and development towards advancing the technology and capability of its brushless DC motor controller. According to the CnR.cn, the market size of the electric vehicle controller industry in 2021 was about RMB $32.2 billion, with a year-on-year growth of approximately 6.3%. Shanghai Qige’s current controller is suitable for low-speed electric vehicles (generally the maximum speed is 50km/h). We believe that if Shanghai Qige focuses its efforts on an advanced controller, it will be able to expand its market size and increase its revenue. Shanghai Qige’s current target market is China.
Shanghai Qige believes its advanced controllers will be able to increase the torque and power of brushless DC motors, as well as other brushless motors that have compatibility with its controllers. Shanghai Qige’s advanced brushless DC motor controller are designed to control and maintain the position, speed, or torque of a DC-powered motor and easily reverses, so the DC motor drive current runs in the opposite direction. This will allow the user to enjoy higher starting torque, quick starting and stopping, reversing, variable speeds with voltage input and more. Shanghai Qige intends to have an updated and improved controller within 2-3 years from the date of this prospectus.
Sales and Marketing
Shanghai Qige’s experienced sales and marketing team is equipped with professional technical support personnel familiar with different application fields. We believe Shanghai Qige has sufficient business personnel in the regions it does business and employs a multi-dimensional marketing network system that supports customer service.
At present, Shanghai Qige has two methods by which it markets:
| 1. | Many of Shanghai Qige’s sales are from current customer introductions, references and word-of-mouth promotion. Its marketing model is designed to drive organic growth, leverage positive word-of-mouth, and remove friction from the evaluation and purchasing process. | |
| 2. | Shanghai Qige also employs a sales and marketing team. Its team will actively contact their potential customers, not limited to phone calls. |
Shanghai Qige also has technical support personnel that are experienced and knowledgeable in its industry. They respond quickly and provide customers with comprehensive and in-depth professional services through technical hotlines, door-to-door services, new product seminars and technical training programs.
Challenges
Shanghai Qige’s projects are based on research of current market trends and its judgment of market demand and forecasting. In general, it takes a minimum of 6 months or longer to launch a new product. Although Shanghai Qige conducts detailed market research and technical pre-research before product development and implementation, the ultimate success of its ability to launch a successful product is also affected by the product development cycle, launch timing, customer preferences, competitors’ product strategies, and need of the applicable market. Shanghai Qige’s industry is influenced by many factors, most of which can be difficult to predict. If Shanghai Qige’s research and development is inaccurate, or fails altogether, its projects may not achieve the expected economic benefits, which may lead to a decline in Shanghai Qige’s profitability.
At present, the conflict in Ukraine has not affected Shanghai Qige’s supply chain, material costs or internal staffing. However, in the face of the sudden outbreak of war, the Company has looked to reexamine Shanghai Qige’s business and development plans, such as possibly adjusting its strategy to look for high-quality customers, targeting procurement based on sales, and actively expanding new businesses in order to reduce the threat posed by such risks.
Risk Factor Summary
Shanghai Qige is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties that you should be aware of before making a decision to invest in the Company’s Ordinary Shares. These risks are more fully described in the section titled “Risk Factors” immediately following this prospectus summary. These risks include, among others, the following:
| ● | The industry in which Shanghai Qige operates is a technology-intensive industry, and Shanghai Qige’s core competitiveness depends on its technological research and development capabilities and continuous innovation capabilities; | |
| ● | Because the majority of our operations are in China, our business is subject to the complex and rapidly evolving laws and regulations there, which could have a material adverse on our business. See the risk factors beginning on page 17 in the section entitled “Risks Related to Doing Business in China”; The PRC government exerts substantial influence over the manner in which we must conduct our business activities in China. Please see the risk factors beginning on page 17 in the section entitled “Risks Related to Doing Business in China”; | |
| ● | The Chinese government plays a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies and also exercises significant control over China’s economic growth through allocating resources, controlling payment of foreign currency-denominated obligations, setting monetary policy, and providing preferential treatment to particular industries or companies which could have a material adverse on our business and/or the value of the securities we are registering. See the risk factors beginning on page 17 in the section entitled “Risks Related to Doing Business in China”; | |
| ● | Any actions taken by the Chinese government to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless. See the risk factors beginning on page 17 in the section entitled “Risks Related to Doing Business in China”; | |
| ● | Loss of core technical personnel; | |
| ● | The current COVID-19 pandemic, as well as other epidemics, natural disasters, terrorist activities, political unrest, and other outbreaks could disrupt our delivery and operations, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations; |
| 7 |
| ● | Shanghai Qige faces intense competition in its industry in general. If it fail to compete effectively, it may lose market share and customers, and our business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected; | |
| ● | Failure to maintain the quality and safety of its products could have a material and adverse effect on its reputation, financial condition and results of operations; | |
| ● | If the Company does not obtain substantial additional financing for Shanghai Qige, Shanghai Qige’s ability to execute on its business plan as outlined in this prospectus will be impaired. |
Corporate History and Structure
The following diagram illustrates our corporate structure, including our holding company, as of the date of this prospectus:
Corporate Information
Our address is 3500 1B1 104 Room 104, 1F, Building B, Building 1, No. 3500 Xiupu Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai China. The Company does not have a website. Our agent for service of process in the United States is The Crone Law Group P.C.
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
As a company with less than $1.07 billion in revenue during our last fiscal year, we qualify as an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended, or the JOBS Act. As long as we remain an emerging growth company, we may rely on exemptions from some of the reporting requirements applicable to public companies that are not emerging growth companies. These exemptions include: (1) being permitted to provide only two years of selected financial data (rather than five years) and only two years of audited financial statements (rather than three years), in addition to any required unaudited interim financial statements, with correspondingly reduced “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” disclosure; (2) not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting; and (3) not being required to comply with any new or revised financial accounting standards until such date that a private company is otherwise required to comply with such new or revised accounting standards. We have taken, and may continue to take, advantage of some of these exemptions until we are no longer an emerging growth company. The JOBS Act also provides that an emerging growth company does not need to comply with any new or revised financial accounting standards until such date that a private company is otherwise required to comply with such new or revised accounting standards. However, we have elected to “opt out” of this provision and, as a result, we will comply with new or revised accounting standards as required when they are adopted for public companies. This decision to opt out of the extended transition period under the JOBS Act is irrevocable.
| 8 |
We will remain an emerging growth company until the earliest of: (1) the last day of our fiscal year during which we have total annual gross revenues of at least $1.07 billion; (2) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the completion of our initial public offering; (3) the date on which we have, during the previous three-year period, issued more than $1.00 billion in non-convertible debt; or (4) the date on which we become a “large accelerated filer” under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which would occur if we have been a public company for at least 12 months and the market value of our Ordinary Shares held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter. We will not be entitled to the above exemptions if we cease to be an emerging growth company.
Implications of Our Foreign Private Issuer Status
Because we are a foreign private issuer under the Exchange Act, we are exempt from certain provisions of the securities rules and regulations in the United States that are applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, including: (i) the rules under the Exchange Act requiring the filing of quarterly reports on Form 10-Q or current reports on Form 8-K with the SEC; (ii) the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents, or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; (iii) the sections of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their stock ownership and trading activities and liability for insiders who profit from trades made in a short period of time; and (iv) the selective disclosure rules by issuers of material nonpublic information under Regulation FD.
We will be required to file an annual report on Form 20-F within four months of the end of each fiscal year. In addition, if we are successful at having our shares quoted on the OTCQB, we will publish our results on a quarterly basis through press releases, distributed pursuant to the rules and regulations of the OTCQB. Press releases relating to financial results and material events will also be furnished to the SEC on Form 6-K. However, the information we are required to file with or furnish to the SEC will be less extensive and less timely compared to that required to be filed with the SEC by U.S. domestic issuers. As a result, you may not be afforded the same protections or information, which would be made available to you, were you investing in a U.S. domestic issuer.
The Offering
| Ordinary Shares Offered By Selling Stockholders: | 5,000,000 Ordinary Shares
| |
Ordinary Shares Issued and Outstanding After Completion of this Offering: |
45,000,000
| |
| Ordinary Shares Issued and Outstanding Before Completion of this Offering | 45,000,000 | |
| Use of Proceeds: | The Selling Stockholders will receive all of the net proceeds from the sale of Ordinary Shares. | |
Market for our Ordinary Shares:
|
There is no market for our securities. Our Ordinary Shares are not traded on any exchange or quoted on the OTC Markets. After the effective date of the registration statement relating to this prospectus, we hope to have a market maker file an application for our shares to be eligible for quotation on the OTC Markets. We do not yet have a market maker who has agreed to file such application.
There is no assurance that a trading market will develop, or, if developed, that it will be sustained. Consequently, a purchaser of our Ordinary Shares may find it difficult to resell the securities offered herein should the purchaser desire to do so when eligible for public resale. |
| Risk Factors: | See “Risk Factors” and other information included in this prospectus for a discussion of factors you should carefully consider before deciding to invest in our Ordinary Shares. | |
| Listing: | We intend to apply to quote our Ordinary Shares on the OTCQB. There is no assurance that we will be successful at having our shares quoted. |
| 9 |
Summary Consolidated Financial Data
The following summary consolidated financial data for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 has been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. Our consolidated financial statements are prepared and presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or US GAAP. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of results expected for future periods. You should read this Summary Consolidated Financial Data section together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this prospectus.
Balance Sheet Data | Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 (unaudited) | Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 (unaudited) | ||||||
| Cash | $ | 13,863 | $ | 28,834 | ||||
| Total Assets | $ | 74,235 | $ | 109,568 | ||||
| Liabilities | $ | 250,646 | $ | 625,256 | ||||
| Total Stockholder’s Equity | $ | (176,411 | ) | $ | (515,688 | ) | ||
| Statement of Operations | Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 (unaudited) | Six Months Ended June 30, 2021 (unaudited) | ||||||
| Revenues | $ | - | $ | 22,008 | ||||
| Net Loss for Reporting Periods | $ | (146,468 | ) | $ | (72,004 | ) | ||
| Balance Sheet Data | Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2021 (audited) | Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2020 (audited) | ||||||
| Cash | $ | 456 | $ | 7,998 | ||||
| Total Assets | $ | 78,467 | $ | 62,242 | ||||
| Liabilities | $ | 649,995 | $ | 500,715 | ||||
| Total Stockholder’s Equity | $ | (571,528 | ) | $ | (438,473 | ) | ||
| Statement of Operations | Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2021 (audited) | Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2020 (audited) | ||||||
| Revenues | $ | 37,065 | $ | 26,309 | ||||
| Net Loss for Reporting Periods | $ | (119,255 | ) | $ | (108,158 | ) | ||
An investment in our Shares involves significant risks. You should consider carefully all of the information in this prospectus, including the risks and uncertainties described below, before making an investment in our Shares. Any of the following risks could have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In any such case, the market price of our Shares could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment.
| 10 |
Risks Related To Our Financial Condition and Business Model
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm has expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
As of June 30, 2022 the Company has incurred an accumulated deficit of $680,290 and a negative working capital of $184,075. At December 31, 2021, the Company’s accumulated deficit was $533,822 and the negative working capital is $580,013. The Company will require additional funding to meet its ongoing obligations and to fund anticipated operating losses. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent on raising capital to fund its business plan and ultimately to attain profitable operations. Accordingly, these factors raise substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern from a period of one year from the issuance of these financial statements. The Company intends to continue to fund its business by way of private placements and financing supports from related parties as may be required. As a result, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm included an explanatory paragraph in its report on our financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 with respect to this uncertainty. If the Company is unable to raise capital when needed or on acceptable terms, Shanghai Qige could be forced to delay, reduce, or eliminate its technology development programs, commercialization efforts, general hiring, or to cease operations.
Because the Company is an “emerging growth company,” the Company may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies.”
The Company is an “emerging growth company” as defined under the Jumpstart our Business Startups Act (“JOBS Act”). We will remain an “emerging growth company” for up to five years, or until the earliest of:
| (i) | the last day of the first fiscal year in which our total annual gross revenues exceed $1.07 billion, | |
| (ii) | the date that we become a “large accelerated filer” as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which would occur if the market value of our Ordinary Shares that is held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter, or | |
| (iii) | the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt during the preceding three-year period. |
As an “emerging growth company”, the Company may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies” including, but not limited to:
| ● | not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (“Sarbanes Oxley”) (we also will not be subject to the auditor attestation requirements of section 404(b) as long as we are a “smaller reporting company”, which includes issuers that had a public float of less than $75 million as of the last business day of their most recently completed second fiscal quarter); | |
| ● | reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements; and | |
| ● | exemptions from the requirements of holding a non-binding advisory vote on executive compensation and shareholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. |
In addition, section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Under this provision, an “emerging growth company” can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. However, the Company choosing to “opt out” of such extended transition period and, as a result, the Company will comply with new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for non-emerging growth companies. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that the Company’s decision to opt out of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable.
| 11 |
Defects, errors or any other problems associated with Shanghai Qige’s products and services could diminish demand for its products or services, harm its business and results of operations and subject us to liability.
Shanghai Qige’s customers use its products and services for important aspects of their businesses, and any errors, defects or disruptions to its products and services and any other performance problems with its products and services could damage its customers’ businesses and, in turn, hurt its brand and reputation. Real or perceived errors, failures, bugs or security vulnerabilities in Shanghai Qige’s products could result in negative publicity, loss of or delay in market acceptance, loss of competitive position, lower customer retention or claims by customers for losses sustained by them. In such an event, Shanghai Qige may be required, or may choose, for customer relations or other reasons, to expend additional resources in order to help correct the problem. As a result, its reputation and brand could be harmed, and the business, operating results and financial condition may be adversely affected. Shanghai Qige uses third-party suppliers to manufacture its products. Such finished products may contain defects, errors or other product issues, which may negatively impact the performance of Shanghai Qige’s products and services, and smart devices, damage its reputation, harm its ability to attract new and existing customers, and incur significant support, repair or replacement costs even if Shanghai Qige can be reimbursed from the third-party suppliers.
Shanghai Qige generates a significant portion of its revenues from a limited number of major customers and any loss of business from these customers could have a negative impact on revenues and harm our business.
Shanghai Qige derives a significant portion of its revenues from a limited number of major customers. Its five largest customers in the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 accounted for 0% and approximately 95% of its revenues, respectively. Its five largest customers in the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 accounted for approximately 98.5% and 100% of its revenues, respectively. Shanghai Qige’s ability to maintain close relationships with major customers is essential to the success of its business. The purchase orders placed by specific customers may vary from period to period, and typically does not have long-term purchase commitments from its customers. As a result, most of its customers could reduce or cease their use of Shanghai Qige’s products and services at any time without any penalty or termination charges. A major customer in one year may not provide the same level of revenues in any subsequent year. In addition, reliance on any individual customer for a significant portion of revenues may give that customer a degree of pricing leverage when negotiating contracts and terms of service with Shanghai Qige.
Many factors not within Shanghai Qige’s control could cause the loss of, or reduction in, business or revenues from any customer, and these factors are not predictable. These factors include, among others, pricing pressure from competitors, a change in a customer’s business strategy, or failure of a module supplier to develop competitive products. Customers may choose to pursue alternative technologies and develop alternative products in addition to, or in lieu of, Shanghai Qige’s products, either on their own or in collaboration with others, including competitors. The loss of any major customer, or a significant decrease in the volume of customer demand or the price at which Shanghai Qige sells its products to customers, could materially adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
If the Company is unable to retain key personnel and hire new key personnel, it may not be able to implement our business plan.
The Company’s ability to succeed depends upon the experience and contributions of our key personnel, and in particular, our founder and CEO, Mr. Heng Fei Yang. The loss of the services of these individuals, if they are not adequately replaced, could have a substantial adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. The Company’s future success will also depend on our ability to identify, attract, and retain additional qualified personnel as we expand our operations. There is no guarantee that we will be successful in identifying, attracting, and retaining such personnel. Consequently, the loss of any of those individuals may have a substantial effect on our future success or failure. The Company may have to recruit qualified personnel with competitive compensation packages, equity participation, and other benefits that may affect the working capital available for our operations. Management may have to seek to obtain outside independent professionals to assist them in assessing the merits and risks of any business proposals as well as assisting in the development and operation of company projects. No assurance can be given that the Company will be able to obtain such needed assistance on terms acceptable to us. Our failure to attract additional qualified employees or to retain the services of key personnel could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.
| 12 |
Shanghai Qige’s ability to appropriately respond to changing consumer preferences and demand for new products or product enhancements could significantly harm its customer relationships and product sales and harm our financial condition and operating results.
Shanghai Qige’s industry is subject to changing consumer trends and preferences, especially with respect to technological advancement. Shanghai Qige’s continued success depends in part on its ability to anticipate and respond to these changes, and it may not respond in a timely or commercially appropriate manner to such changes. Its failure to accurately predict these trends could negatively impact consumer opinion of its products and cause the loss of sales. The success of Shanghai Qige’s new product offerings and enhancements depends upon a number of factors, including its ability to:
| ● | accurately anticipate customer needs; | |
| ● | innovate and develop new products or product enhancements that meet these needs; | |
| ● | successfully commercialize new products or product enhancements in a timely manner; | |
| ● | price our products competitively; | |
| ● | manufacture and deliver our products in sufficient volumes and in a timely manner; and | |
| ● | differentiate our product offerings from those of our competitors. |
If Shanghai Qige does not introduce new products or make enhancements to meet the changing needs of its customers in a timely manner, some of its product offerings could be rendered obsolete, which could negatively impact revenues, financial condition and operating results.
If Shanghai Qige is unable to build a sufficient distribution network to meet increasing demand of its products, its ability to execute on its business plan as outlined in this prospectus will be impaired.
Shanghai Qige sells products through its direct sales force and distribution channel. Although Shanghai Qige’s sales and distribution satisfy existing business needs, they might be insufficient to meet demand for its products as they continue to grow the business, which could result in harm to sales and business operations, financial condition and results of operations. To mitigate such risk, the Company intends to invest internally generated cash from operations and capital to be raised to add additional teams to Shanghai Qige’s direct sales force, expand its geographic reach with new distribution channels into other provinces within China and overseas, and establish more sales online. If planned efforts to expand sales and distribution channels are not effective, Shanghai Qige’s ability to execute on business plans and to realize continued growth with be impaired.
Shanghai Qige may lose its competitive advantage and operations may suffer if the Company fails to prevent the loss or misappropriation of, or disputes over, intellectual property or proprietary information.
The Company regards our intellectual property, particularly our patents and trade secrets, to be of considerable value and importance to our business and our success. We rely on a combination of patent, trademark and trade secret laws, as well as confidentiality agreements to protect our intellectual property rights. Failure to protect our intellectual property rights could harm our brands and our reputation, and adversely affect our ability to compete effectively. Further, enforcing or defending our intellectual property rights, including our patents and trade secrets, could result in the expenditure of significant financial and managerial resources.
Production difficulties, quality control problems, inaccurate forecasting and reliance on third-party suppliers could harm Shanghai Qige’s business.
Production difficulties, quality control problems, inaccurate forecasting and Shanghai Qige’s reliance on third party suppliers to manufacture and deliver products that meet its specifications in a timely manner could harm the business. Shanghai Qige could experience production difficulties with respect to its products, including the availability of raw materials, components, packaging and products that do not meet its specifications and quality control standards. These production difficulties and quality problems could result in stock outages or shortages in the markets with respect to such products, harm sales, or create inventory write-downs for unusable products.
| 13 |
Disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic have had a material negative impact on our results of operations, and pose continuing additional risks to our operations.
In December 2019, a novel strain of COVID-19 was reported in Wuhan, China. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization categorized it as a pandemic. To reduce the spread of the COVID-19, the Chinese government has employed measures including city lockdowns, quarantines, travel restrictions, suspension of business activities and school closures. Due to difficulties resulting from the COVID-19 outbreak, including, but not limited to, the temporary closure of the Company’s factory and operations beginning in early February, limited support from the Company’s employees, delayed access to raw material supplies and inability to deliver products to customers on a timely basis, the Company’s business was negatively impacted and is expected to generate lower revenue and net income during the period from February to April 2020. The Company resumed operations on March 2, 2020 and, as such, the extent of the impact of COVID-19 on the Company’s results of operations and financial condition will depend on future developments, including the duration and spread of the outbreak and the impact on the Company’s customers, which are still uncertain and cannot be reasonably estimated at this point of time. The local government of the Company’s PRC subsidiary Shanghai Qige has issued shutdown measures throughout March 2020 to June 2022. The impact of the epidemic and sporadic resumption of work, Shanghai Qige’s operations and our financial results have been adversely materially affected.
Shanghai Qige may face increased competition from new and existing firms with greater capital resources, which could cause market share and profitability to decline if Shanghai Qige does not successfully meet competitive challenges.
Because of the strong prospects and recent growth of Shanghai Qige’s existing business, Shanghai Qige may face new direct competition from some counterparts engaged in other categories of the natural products and ingredients business, such as Shanghai Ningzhong Trading Co., Ltd. in China, which is engaged in the sales of forklifts, construction machinery and equipment as well as electronic system equipment. The size, financial strength, technology foundation and development capabilities of the above-mentioned and similar companies are strong, and potential competition from these firms will be a key competitive challenge in the near future. In addition, Suzhou Yongjian Storage and Logistics Equipment Co., Ltd. and Dezhou Ningjian Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. are companies that may challenge Shanghai Qige given their advanced supply chains and the cost advantages that come with that. Because of the strong capital and brand strength of such companies, they might pose challenges to Shanghai Qige in the future. If Shanghai Qige is unable to continue to expand, innovate, and collaborate to improve its market position in the face of new competition, market share, revenues, and profitability will be adversely affected.
Risks Related To Legal Uncertainty
We may incur material product liability claims, which could increase our costs and harm our financial condition and operating results.
Our industry experiences significant product liability claims. As a supplier of products, we face an inherent business risk of exposure to product liability claims in the event that our products, or the equipment into which our products are incorporated, malfunction and result in personal injury or death. We may be named in product liability claims even if there is no evidence that our systems or components caused the accidents. Product liability claims could result in significant losses as a result of expenses incurred in defending claims or the award of damages. Our products are mainly used in low-speed electric cars such as electric forklifts, golf carts, sightseeing cars and other special tool vehicles. The sale of systems and components for the transportation industry entails a high risk of these claims. In addition, we may be required to participate in recalls involving these systems if any of our systems prove to be defective, or we may voluntarily initiate a recall or make payments related to such claims as a result of various industry or business practices or the need to maintain good customer relationships. Our other products may also be subject to product liability claims or recalls. We cannot assure you that our product liability insurance will be sufficient to cover all product liability claims, that such claims will not exceed our insurance coverage limits or that such insurance will continue to be available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. Any product liability claim brought against us could have a material adverse effect on our reputation and business as the Company currently carries no product liability insurance.
Risks Related to Our Corporate Structure
If the PRC government finds that the agreements that establish the structure for conducting certain of our operations in China do not comply with PRC regulations relating to the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations changes in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our interests in those operations.
Foreign investment in China is extensively regulated and subject to numerous restrictions. Pursuant to the Special Management Measures for the Market Entry of Foreign Investment (Negative List) (2019), or the 2019 Negative List, published by the National Development and Reform Commission, and the Ministry of Commerce, or the MOFCOM, on June 30, 2019, and effective on July 30, 2019, with a few exceptions, foreign investors are not allowed to own more than 50% of the equity interests in a value-added telecommunication services provider and any primary foreign investor must have experience in providing value-added telecommunications services overseas and maintain a good track record.
| 14 |
If the PRC government finds that our contractual arrangements do not comply with its restrictions on foreign investment, or if the PRC government otherwise finds that we or any of its subsidiaries are in violation of PRC laws or regulations or lack the necessary permits or licenses to operate our business, the relevant PRC regulatory authorities, would have broad discretion in dealing with such violations or failures, including, without limitation:
| ● | revoking the business licenses and/or operating licenses of such entities; | |
| ● | discontinuing or placing restrictions or onerous conditions on our operation through any transactions between our PRC subsidiary and consolidated affiliated entities; | |
| ● | imposing fines, confiscating the income from our PRC subsidiary or consolidated affiliated entities, or imposing other requirements with which such entities may not be able to comply; | |
| ● | requiring us to restructure our ownership structure or operations, including terminating the contractual arrangements with our variable interest entity and deregistering the equity pledges of our variable interest entity, which in turn would affect our ability to consolidate, derive economic interests from, or exert effective control over our variable interest entity; or | |
| ● | restricting or prohibiting our use of the proceeds of this offering to finance our business and operations in China. |
Any of these actions could cause significant disruption to our business operations and severely damage our reputation, which would in turn materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. If any of these occurrences result in our inability to direct the activities of our variable interest entity that most significantly impact its economic performance, and/or our failure to receive the economic benefits from our variable interest entity, we may not be able to consolidate the entity in our consolidated financial statements in accordance with US GAAP.
You may experience difficulties in effecting service of legal process, enforcing foreign judgments or bringing actions in the British Virgin Islands against us or our management named in the prospectus based on foreign laws.
Our Company is incorporated under the laws of the British Virgin Islands. We conduct substantially all of our operations in China, and substantially all of our assets are located in China. In addition, all our senior executive officers reside within China for a significant portion of the time and most are PRC nationals. As a result, it may be difficult for our shareholders to effect service of process upon us or those persons inside China. In addition, China does not have treaties providing for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments of courts with the British Virgin Islands and many other countries and regions. Therefore, recognition and enforcement in China of judgments of a court in any of these non-PRC jurisdictions in relation to any matter not subject to a binding arbitration provision may be difficult or impossible.
In addition, BVI companies may not have standing to initiate a shareholder derivative action in a federal court of the United States. The circumstances in which any such action may be brought, and the procedures and defenses that may be available in respect to any such action, may result in the rights of shareholders of a BVI company being more limited than those of shareholders of a company organized in the United States. Accordingly, shareholders may have fewer alternatives available to them if they believe that corporate wrongdoing has occurred. For more information, see “Description of Share Capital—Differences in Corporate Law—Shareholders’ Suits”. The BVI courts are also unlikely to recognize or enforce against us judgments of courts in the United States based on certain liability provisions of U.S. securities law, and to impose liabilities against us, in original actions brought in the BVI, based on certain liability provisions of U.S. securities laws that are penal in nature. There is no statutory enforcement in the BVI of judgments obtained in the United States, although the courts of the BVI will in certain circumstances recognize such a foreign judgment and treat it as a cause of action in itself which may be sued upon as a debt at common law so that no retrial of the issues would be necessary. For more information, see “Enforceability of Civil Liabilities.” This means that even if shareholders were to sue us successfully, they may not be able to recover anything to make up for the losses suffered.
| 15 |
Lastly, under the provisions of the BVI Act, the memorandum and articles of association of a company are binding as between the company and its members and between the members. In general, members are bound by the decision of the majority or special majorities as set out in the articles of association or in the Act. As for voting, the usual rule is that with respect to normal commercial matters members may act from self-interest when exercising the right to vote attached to their shares.
If the majority members have infringed a minority member’s rights, the minority may seek to enforce its rights either by derivative action or by personal action. The BVI Act provides that any member of a company is entitled to payment of the fair value of his shares upon dissenting from certain matters. For more information, see “Description of Share Capital—Differences in Corporate Law—Shareholders’ Suits.”
Generally any other claims against a company by its members must be based on the general laws of contract or tort applicable in the BVI or their individual rights as members as established by the company’s memorandum and articles of association, which are more limited than the rights afforded investors under the laws of many states in the United States.
Governmental control of currency conversion may limit our ability to utilize our revenues effectively and affect the value of your investment.
The PRC government imposes controls on the convertibility of the Renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of currency out of China. We receive substantially all of our revenues in Renminbi. Under our current corporate structure, our British Virgin Islands holding company primarily relies on dividend payments from us to fund any cash and financing requirements it may have. Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, including profit distributions, interest payments and trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval of the SAFE by complying with certain procedural requirements. Specifically, under the existing exchange restrictions, without prior approval of SAFE, cash generated from the operations of our PRC subsidiary in China may be used to pay dividends to our Holding Company. However, approval from or registration with appropriate governmental authorities is required where Renminbi is to be converted into foreign currency and remitted out of China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of loans denominated in foreign currencies. As a result, our Holding Company may need to obtain SAFE approval to use cash generated from our operations to pay off their respective debt in a currency other than Renminbi owed to entities outside China, or to make other capital expenditure payments outside China in a currency other than Renminbi. The PRC government may at its discretion restrict access to foreign currencies for current account transactions in the future. If the foreign exchange control system prevents us from obtaining sufficient foreign currencies to satisfy our foreign currency demands, we may not be able to pay dividends in foreign currencies to our shareholders, including holders of our Shares.
Uncertainties exist with respect to the interpretation and implementation of the newly enacted Foreign Investment Law and its implementing rules, and how they may impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The variable interest entity structure has been adopted by many PRC-based companies, including us, to obtain necessary licenses and permits in the industries that are currently subject to foreign investment restrictions in China. The MOFCOM published a discussion draft of the Proposed Foreign Investment Law in January 2015, or the 2015 Draft FIL, according to which, variable interest entities that are controlled via contractual arrangements would also be deemed as foreign-invested entities, if they are ultimately “controlled” by foreign investors.
In March 2019, the PRC National People’s Congress, or the NPC, promulgated the PRC Foreign Investment Law, or the Foreign Investment Law, and in December 2019, the State Council promulgated the Implementing Regulations of the Foreign Investment Law of PRC, or the FIE Implementing Regulations, to further clarify and elaborate the relevant provisions of the Foreign Investment Law. The Foreign Investment Law and the FIE Implementing Regulations both became effective from January 1, 2020 and replaced the major existing laws and regulations governing foreign investment in the PRC. Pursuant to the Foreign Investment Law, “foreign investments” refer to investment activities conducted by foreign investors (including foreign natural persons, foreign enterprises or other foreign organizations) directly or indirectly in the PRC, which include any of the following circumstances: (i) foreign investors setting up foreign-invested enterprises in the PRC solely or jointly with other investors, (ii) foreign investors obtaining shares, equity interests, property portions or other similar rights and interests of enterprises within the PRC, (iii) foreign investors investing in new projects in the PRC solely or jointly with other investors, and (iv) investment in other methods as specified in laws, administrative regulations, or as stipulated by the State Council.
| 16 |
The Foreign Investment Law and FIE Implementing Regulations do not introduce the concept of “control” in determining whether a company would be considered as a foreign-invested enterprise, nor do they explicitly provide whether the variable interest entity structure would be deemed as a method of foreign investment. However, the Foreign Investment Law has a catch-all provision that includes into the definition of “foreign investments” made by foreign investors in China in other methods as specified in laws, administrative regulations, or as stipulated by the State Council, and as the Foreign Investment Law and FIE Implementing Regulations are newly adopted and relevant government authorities may promulgate more laws, regulations or rules on the interpretation and implementation of the Foreign Investment Law, the possibility cannot be ruled out that the concept of “control” as stated in the 2015 Draft FIL may be embodied in, or the variable interest entity structure adopted by us may be deemed as a method of foreign investment by, any of such future laws, regulations, and rules.
If we are deemed as a foreign-invested enterprise under any of such future laws, regulations, and rules, and any of the businesses that we operate were to be in the “negative list” for foreign investment and therefore be subject to foreign investment restrictions or prohibitions, further actions required to be taken by us under such laws, regulations and rules may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, if future laws, administrative regulations or rules mandate further actions to be taken by companies with respect to existing contractual arrangements, we may face substantial uncertainties as to whether we can complete such actions in a timely manner, or at all. Failure to take timely and appropriate measures to cope with any of these or similar regulatory compliance challenges could materially and adversely affect our current corporate structure, business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Related to Doing Business in China
Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions or government policies could have a material adverse effect on our business and operations.
All of our assets and operations are located in China through our subsidiary Shanghai Qige. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be influenced to a significant degree by political, economic and social conditions in China generally. The Chinese economy differs from the economies of most developed countries in many respects, including the level of government involvement, level of development, growth rate, control of foreign exchange and allocation of resources. Although the Chinese government has implemented measures emphasizing the utilization of market forces for economic reform, the reduction of state ownership of productive assets, and the establishment of improved corporate governance in business enterprises, a substantial portion of productive assets in China is still owned by the government. In addition, the Chinese government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. The Chinese government also exercises significant control over China’s economic growth through allocating resources, controlling payment of foreign currency-denominated obligations, setting monetary policy, and providing preferential treatment to particular industries or companies.
While the Chinese economy has experienced significant growth over the past decades, growth has been uneven, both geographically and among various sectors of the economy, and the rate of growth has been slowing since 2012. Any adverse changes in economic conditions in China, in the policies of the Chinese government or in the laws and regulations in China could have a material adverse effect on the overall economic growth of China. Such developments could adversely affect our business and operating results, lead to reduction in demand for our services and adversely affect our competitive position. The Chinese government has implemented various measures to encourage economic growth and guide the allocation of resources. Some of these measures may benefit the overall Chinese economy, but may have a negative effect on us. For example, our financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected by government control over capital investments or changes in tax regulations. In addition, in the past the Chinese government has implemented certain measures, including interest rate adjustment, to control the pace of economic growth. These measures may cause decreased economic activity in China, which may adversely affect our business and operating results.
| 17 |
Risks related to a future determination that the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (the “PCAOB”) is unable to inspect or investigate our auditor completely.
The audit report included in this prospectus was issued by HHC a United States based accounting firm that is registered with the PCAOB and can be inspected by the PCAOB. We have no intention of dismissing HHC in the future or of engaging any auditor not subject to regular inspection by the PCAOB. There is no guarantee, however, that any future auditor engaged by the Company would remain subject to full PCAOB inspection during the entire term of our engagement. The PCAOB is currently unable to conduct inspections in China without the approval of Chinese government authorities. If it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate our auditor completely, investors may be deprived of the benefits of such inspection. Any audit reports not issued by auditors that are completely inspected by the PCAOB, or a lack of PCAOB inspections of audit work undertaken in China that prevents the PCAOB from regularly evaluating our auditors’ audits and their quality control procedures, could result in a lack of assurance that our financial statements and disclosures are adequate and accurate. In addition, under the HFCAA, our securities may be prohibited from trading on the Nasdaq or other U.S. stock exchanges if our auditor is not inspected by the PCAOB for three consecutive years, and this ultimately could result in our Ordinary Shares being delisted.
Although the audit report included in this prospectus was issued by U.S. auditors who are currently inspected by the PCAOB, if it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate our auditor completely, investors would be deprived of the benefits of such inspection and our Ordinary Shares may be delisted or prohibited from trading.
The audit report included in this prospectus was issued by HHC, a United States based accounting firm that is registered with the PCAOB and can be inspected by the PCAOB. We have no intention of dismissing HHC in the future or of engaging any auditor not subject to regular inspection by the PCAOB. As an auditor of companies that are registered with the SEC and publicly traded in the United States and a firm registered with the PCAOB, our auditor is required under the laws of the United States to undergo regular inspections to assess its compliance with the laws of the United States and professional standards. If we were to engage a different auditor in the future, we would engage an auditor that is United States-based and subject to full PCAOB inspection with all materials related to the audit of our financial statements accessible to the PCAOB. There is no guarantee, however, that any future auditor engaged by the Company would remain subject to full PCAOB inspection during the entire term of our engagement. In such case, we will engage a new qualified and fully inspected auditor, which may result in us delaying or restating our financial statements.
The PCAOB is currently unable to conduct inspections in China without the approval of Chinese government authorities. If it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate our auditor completely, investors may be deprived of the benefits of such inspection. Any audit reports not issued by auditors that are completely inspected by the PCAOB, or a lack of PCAOB inspections of audit work undertaken in China that prevents the PCAOB from regularly evaluating our auditors’ audits and their quality control procedures, could result in a lack of assurance that our financial statements and disclosures are adequate and accurate.
| 18 |
As part of a continued regulatory focus in the United States on access to audit and other information currently protected by national law, in particular mainland China’s, in June 2019, a bipartisan group of lawmakers introduced bills in both houses of the U.S. Congress which, if passed, would require the SEC to maintain a list of issuers for which PCAOB is not able to inspect or investigate the audit work performed by a foreign public accounting firm completely. The proposed Ensuring Quality Information and Transparency for Abroad-Based Listings on our Exchanges (“EQUITABLE”) Act prescribes increased disclosure requirements for these issuers and, beginning in 2025, the delisting from U.S. national securities exchanges such as the Nasdaq of issuers included on the SEC’s list for three consecutive years. It is unclear if this proposed legislation will be enacted. Furthermore, there have been recent deliberations within the U.S. government regarding potentially limiting or restricting China-based companies from accessing U.S. capital markets. On May 20, 2020, the U.S. Senate passed the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act (the “HFCAA”), which includes requirements for the SEC to identify issuers whose audit work is performed by auditors that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely because of a restriction imposed by a non-U.S. authority in the auditor’s local jurisdiction. The U.S. House of Representatives passed the HFCAA on December 2, 2020, and the HFCAA was signed into law on December 18, 2020. Additionally, in July 2020, the U.S. President’s Working Group on Financial Markets issued recommendations for actions that can be taken by the executive branch, the SEC, the PCAOB or other federal agencies and department with respect to Chinese companies listed on U.S. stock exchanges and their audit firms, in an effort to protect investors in the United States. In response, on November 23, 2020, the SEC issued guidance highlighting certain risks (and their implications to U.S. investors) associated with investments in China-based issuers and summarizing enhanced disclosures the SEC recommends China-based issuers make regarding such risks. On December 2, 2021, the SEC adopted final rules relating to the implementation of certain disclosure and documentation requirements of the HFCAA. We will be required to comply with these rules if the SEC identifies us as having a “non-inspection” year (as defined in the interim final rules) under a process to be subsequently established by the SEC. The SEC is assessing how to implement other requirements of the HFCAA, including the listing and trading prohibition requirements described above. Under the HFCAA, our securities may be prohibited from trading on the Nasdaq or other U.S. stock exchanges if our auditor is not inspected by the PCAOB for three consecutive years, and this ultimately could result in our Ordinary Shares being delisted. Furthermore, on June 22, 2021, the U.S. Senate passed the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act (“AHFCAA”), which, if enacted, would amend the HFCAA and require the SEC to prohibit an issuer’s securities from trading on any U.S. stock exchanges if its auditor is not subject to PCAOB inspections for two consecutive years instead of three. On September 22, 2021, the PCAOB adopted a final rule implementing the HFCAA, which provides a framework for the PCAOB to use when determining, as contemplated under the HFCAA, whether the Board is unable to inspect or investigate completely registered public accounting firms located in a foreign jurisdiction because of a position taken by one or more authorities in that jurisdiction. On December 16, 2021, the PCAOB issued a Determination Report which found that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely registered public accounting firms headquartered in: (1) mainland China of the People’s Republic of China, because of a position taken by one or more authorities in mainland China; and (2) Hong Kong, a Special Administrative Region and dependency of the PRC, because of a position taken by one or more authorities in Hong Kong.
Should the PCAOB be unable to fully conduct inspection of our auditor’s work papers, it will make it difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of our auditor’s audit procedures or equity control procedures. Investors may consequently lose confidence in our reported financial information and procedures or quality of the financial statements, which would adversely affect us and our securities.
Because the majority of our operations are in China via our subsidiary Shanghai Qige, our business is subject to the complex and rapidly evolving laws and regulations there. The Chinese government may exercise significant oversight and discretion over the conduct of our business and may intervene in or influence our operations at any time, which could result in a material change in our operations and/or the value of our Ordinary Shares.
We are subject to a variety of laws and regulations that involve matters important to, or may otherwise impact, our business, including, among others, information security and censorship, foreign exchange and taxation. The introduction of new products and services may subject us to additional laws, regulations, or other government scrutiny.
These laws and regulations are continually evolving and may change significantly. As a result, the application, interpretation, and enforcement of these laws and regulations are often uncertain, particularly in the rapidly evolving industry in which we operate. In addition, these laws and regulations may be interpreted and applied inconsistently by different agencies or authorities, and inconsistently with our current policies and practices. These laws and regulations may also be costly to comply with, and such compliance or any associated inquiries or investigations or any other government actions may:
| ● | Delay or impede our development of new services, | |
| ● | Result in negative publicity, increase out operating costs, | |
| ● | Require significant management time and attention, and | |
| ● | Subject us to remedies, administrative penalties and even criminal liabilities that may harm our business, including fines assessed for our current or historical operations, or demands or orders that we modify or even cease our business practice. |
The promulgation of new laws or regulations, or the new interpretation of existing laws and regulations, in each case that restrict or otherwise unfavorably impact the ability or manner in which we conduct our business and could require us to change certain aspects of our business to ensure compliance, which could decrease demand for our products and services, reduce revenues, increase costs, require us to obtain more licenses, permits, approvals or certificates, or subject us to additional liabilities. To the extent any new or more stringent measures are required to be implemented, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected as well as the value of our ordinary shares.
| 19 |
Any actions that may be taken by the Chinese government to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Uncertainties with respect to the PRC legal system could adversely affect us.
The PRC legal system is a civil law system based on written statutes. Unlike the common law system, prior court decisions under the civil law system may be cited for reference but have limited precedential value.
In 1979, the PRC government began to promulgate a comprehensive system of laws and regulations governing economic matters in general. The overall effect of legislation over the past three decades has significantly enhanced the protections afforded to various forms of foreign investments in China. However, China has not developed a fully integrated legal system, and recently enacted laws and regulations may not sufficiently cover all aspects of economic activities in China. In particular, the interpretation and enforcement of these laws and regulations involve uncertainties. Since PRC administrative and court authorities have significant discretion in interpreting and implementing statutory provisions and contractual terms, it may be difficult to evaluate the outcome of administrative and court proceedings and the level of legal protection we enjoy. These uncertainties may affect our judgment on the relevance of legal requirements and our ability to enforce our contractual rights or tort claims. In addition, the regulatory uncertainties may be exploited through unmerited or frivolous legal actions or threats in attempts to extract payments or benefits from us.
Furthermore, the PRC legal system is based in part on government policies and internal rules, some of which are not published on a timely basis or at all and may have retroactive effect. As a result, we may not be aware of our violation of any of these policies and rules until sometime after the violation. In addition, any administrative and court proceedings in China may be protracted, resulting in substantial costs and diversion of resources and management attention.
The PRC government exerts substantial influence over the manner in which we must conduct our business activities through our subsidiary Shanghai Qige.
The PRC government has exercised and continues to exercise substantial control over virtually every sector of the PRC economy through regulation and state ownership. Our ability to operate in China may be harmed by changes in its laws and regulations, including those relating to taxation, import and export tariffs, environmental regulations, land use rights, property, and other matters. We believe that our operations in China are in material compliance with all applicable legal and regulatory requirements. However, the central or local governments of the jurisdictions in which we operate may impose new, stricter regulations or interpretations of existing regulations that would require additional expenditures and efforts on our part to ensure our compliance with such regulations or interpretations.
Accordingly, government actions in the future, including any decision not to continue to support recent economic reforms and to return to a more centrally planned economy and any regional or local variations in the implementation of economic policies, could have a significant effect on economic conditions in China or particular regions thereof and could require us to divest ourselves of any interest we then hold in Chinese properties or joint ventures.
We may rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiary, Shanghai Qige, to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of Shanghai Qige to make payments to us could have a material and adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.
We are a BVI holding company and we rely principally on dividends and other distributions on equity from our PRC subsidiary for our cash requirements, including for services of any debt we may incur. The ability of our PRC subsidiary to pay dividends and other distributions on equity, in turn, depends on the payment they receive from our variable interest entity as service fees pursuant to certain contractual arrangements among our PRC subsidiary, our variable interest entity and its shareholders entered into to comply with certain restrictions under PRC laws on foreign investment.
| 20 |
Additionally, our subsidiary’s ability to distribute dividends is based upon its distributable earnings. Current PRC regulations permit our PRC subsidiary to pay dividends to its shareholder only out of their accumulated profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. In addition, our PRC subsidiary, our variable interest entity and its subsidiaries are required to set aside at least 10% of their after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund a statutory reserve until such reserve reaches 50% of their registered capital. These reserves are not distributable as cash dividends. If our PRC subsidiary incurs debt on its own behalf in the future, the instruments governing the debt may restrict its ability to pay dividends or make other payments to us. Any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiary to distribute dividends or other payments to its shareholders could materially and adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our businesses, pay dividends or otherwise fund and conduct our business.
To address the persistent capital outflow and the RMB’s depreciation against the U.S. dollar in the fourth quarter of 2016, the People’s Bank of China and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange, or SAFE, have implemented a series of capital control measures in the subsequent months, including stricter vetting procedures for China-based companies to remit foreign currency for overseas acquisitions, dividend payments and shareholder loan repayments. For instance, the Circular on Further Improving Reform of Foreign Exchange Administration and Optimizing Genuineness and Compliance Verification, or the SAFE Circular 3, issued on January 26, 2017, provides that the banks shall, when dealing with dividend remittance transactions from domestic enterprise to its offshore shareholders of more than $50,000, review the relevant board resolutions, original tax filing form and audited financial statements of such domestic enterprise based on the principal of genuine transaction. The PRC government may continue to strengthen its capital controls and our PRC subsidiary’s dividends and other distributions may be subject to tightened scrutiny in the future. Any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiary to pay dividends or make other distributions to us could materially and adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our business, pay dividends, or otherwise fund and conduct our business.
In addition, the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law and its implementation rules provide that a withholding tax at a rate of 10% will be applicable to dividends payable by Chinese companies to non-PRC-resident enterprises unless reduced under treaties or arrangements between the PRC central government and governments of other countries or regions where the non-PRC resident enterprises are tax resident. Pursuant to the Arrangement between Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income, the withholding tax rate in respect to the payment of dividends by a PRC enterprise to a Hong Kong enterprise may be reduced to 5% from a standard rate of 10% if the Hong Kong enterprise directly holds at least 25% of the PRC enterprise. Under the Circular of the State Administration of Taxation on the Issues concerning the Application of the Dividend Clauses of Tax Agreements, or SAT Circular 81, promulgated by the State Administration of Taxation, or the SAT, on February 20, 2009, a Hong Kong resident enterprise must meet the following conditions, among others, in order to apply the reduced withholding tax rate: (i) it must be a company; (ii) it must directly own the required percentage of equity interests and voting rights in the PRC resident enterprise; and (iii) it must have directly owned such required percentage in the PRC resident enterprise throughout the 12 months prior to receiving the dividends. Nonresident enterprises are not required to obtain pre-approval from the relevant tax authority in order to enjoy the reduced withholding tax. Instead, nonresident enterprises and their withholding agents may, by self-assessment and on confirmation that the prescribed criteria to enjoy the tax treaty benefits are met, directly apply the reduced withholding tax rate, and file necessary forms and supporting documents when performing tax filings, which will be subject to post-tax filing examinations by the relevant tax authorities. Accordingly, our Hong Kong subsidiary may be able to benefit from the 5% withholding tax rate for the dividends it receives from our PRC subsidiary, if it satisfies the conditions prescribed under the SAT Circular 81, and other relevant tax rules and regulations. However, if the relevant tax authorities consider the transactions or arrangements we have are for the primary purpose of enjoying a favorable tax treatment, the relevant tax authorities may adjust the favorable withholding tax in the future. Accordingly, there is no assurance that the reduced 5% will apply to dividends received by our Hong Kong subsidiary from our PRC subsidiary. This withholding tax will reduce the amount of dividends we may receive from our PRC subsidiary.
| 21 |
Fluctuations in exchange rates could have a material and adverse effect on our results of operations and the value of your investment.
The value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies may fluctuate and is affected by, among other things, changes in political and economic conditions in China and by China’s foreign exchange policies. On July 21, 2005, the PRC government changed its decade-old policy of pegging the value of the Renminbi to the U.S. dollar, and the Renminbi appreciated more than 20% against the U.S. dollar over the following three years. Between July 2008 and June 2010, this appreciation halted and the exchange rate between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar remained within a narrow band. Since June 2010, the Renminbi has fluctuated against the U.S. dollar, at times significantly and unpredictably. It is difficult to predict how market forces or PRC or U.S. government policy may impact the exchange rate between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar in the future.
Significant revaluation of the Renminbi may have a material and adverse effect on your investment. For example, to the extent that we need to convert U.S. dollars we receive from this offering into Renminbi for our operations, appreciation of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar would have an adverse effect on the Renminbi amount we would receive from the conversion. Conversely, if we decide to convert our Renminbi into U.S. dollars for the purpose of making payments for dividends on our Ordinary Shares or for other business purposes, appreciation of the U.S. dollar against the Renminbi would have a negative effect on the U.S. dollar amount available to us.
Very limited hedging options are available in China to reduce our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. To date, we have not entered into any hedging transactions in an effort to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. While we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedges may be limited and we may not be able to adequately hedge our exposure or at all. In addition, our currency exchange losses may be magnified by PRC exchange control regulations that restrict our ability to convert Renminbi into foreign currency.
Governmental control of currency conversion may limit our ability to utilize our revenues effectively and affect the value of your investment.
The PRC government imposes controls on the convertibility of the Renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of currency out of China. We receive substantially all of our revenues in Renminbi. Under our current corporate structure, our Company primarily relies on dividend payments from our PRC subsidiary to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have. Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, including profit distributions, interest payments and trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval of the SAFE by complying with certain procedural requirements. Specifically, under the existing exchange restrictions, without prior approval of SAFE, cash generated from the operations of our PRC subsidiary in China may be used to pay dividends to our company. However, approval from or registration with appropriate governmental authorities is required where Renminbi is to be converted into foreign currency and remitted out of China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of loans denominated in foreign currencies. As a result, we need to obtain SAFE approval to use cash generated from the operations of our PRC subsidiary and variable interest entity to pay off their respective debt in a currency other than Renminbi owed to entities outside China, or to make other capital expenditure payments outside China in a currency other than Renminbi. The PRC government may at its discretion restrict access to foreign currencies for current account transactions in the future. If the foreign exchange control system prevents us from obtaining sufficient foreign currencies to satisfy our foreign currency demands, we may not be able to pay dividends in foreign currencies to our shareholders, including holders of our Ordinary Shares.
Certain PRC regulations may make it more difficult for us to pursue growth through acquisitions.
Among other things, the Rules on Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors, or the M&A Rules, promulgated by six PRC regulatory agencies in 2006 and amended in 2009, established additional procedures and requirements that could make merger and acquisition activities by foreign investors more time-consuming and complex. The M&A Rules require, among other things, that the MOFCOM be notified in advance of any change-of-control transaction in which a foreign investor acquires control of a PRC domestic enterprise, if (i) any important industry is concerned, (ii) such transaction involves factors that have or may have an impact on the national economic security, or (iii) such transaction will lead to a change in control of a domestic enterprise which holds a famous trademark or PRC time-honored brand. Moreover, the Anti-Monopoly Law promulgated by the Standing Committee of the NPC which became effective in 2008 requires that transactions that are deemed concentrations and involve parties with specified turnover thresholds must be cleared by the MOFCOM before they can be completed. In addition, PRC national security review rules which became effective in September 2011 require acquisitions by foreign investors of PRC companies engaged in military-related or certain other industries that are crucial to national security be subject to security review before consummation of any such acquisition. We may pursue potential strategic acquisitions that are complementary to our business and operations. Complying with the requirements of these regulations to complete such transactions could be time-consuming, and any required approval processes, including obtaining approval or clearance from the MOFCOM, may delay or inhibit our ability to complete such transactions, which could affect our ability to expand our business or maintain our market share.
| 22 |
PRC regulations relating to the establishment of offshore special purpose companies by PRC residents may subject our PRC resident beneficial owners or Shanghai Qige’s to liability or penalties, limit our ability to inject capital into Shanghai Qige, limit our Shanghai Qige’s ability to increase its registered capital or distribute profits to us, or may otherwise adversely affect us.
In July 2014, SAFE promulgated the Circular on Relevant Issues Concerning Foreign Exchange Control on Domestic Residents’ Offshore Investment and Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 37, to replace the Circular on Relevant Issues Concerning Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Residents’ Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Offshore Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 75, which ceased to be effective upon the promulgation of SAFE Circular 37. SAFE Circular 37 requires PRC residents (including PRC individuals and PRC corporate entities) to register with local branches of SAFE in connection with their direct or indirect offshore investment activities. SAFE Circular 37 is applicable to our shareholders who are PRC residents and may be applicable to any offshore acquisitions that we make in the future.
Under SAFE Circular 37, PRC residents who control, or have prior to the implementation of SAFE Circular 37 controlled, directly or indirectly of offshore special purpose vehicles, or SPVs, will be required to register such investments with the SAFE or its local branches. The term “control” under SAFE Circular 37 is broadly defined as the operation rights, beneficiary rights or decision-making rights acquired by PRC residents in the SPVs, by means of acquisition, trust, proxy, voting rights, repurchase, convertible bonds or other arrangements. In addition, any PRC resident who is a direct or indirect shareholder of an SPV, is required to update its filed registration with the local branch of SAFE with respect to that SPV, to reflect any material change. Moreover, any subsidiary of such SPV in China is required to urge the PRC resident shareholders to update their registration with the local branch of SAFE. If any PRC shareholder of such SPV fails to make the required registration or to update the previously filed registration, the subsidiary of such SPV in China may be prohibited from distributing its profits or the proceeds from any capital reduction, share transfer or liquidation to the SPV, and the SPV may also be prohibited from making additional capital contribution into its subsidiary in China. On February 13, 2015, the SAFE promulgated a Circular on Further Simplifying and Improving Foreign Exchange Administration Policy on Direct Investment, or SAFE Circular 13, which became effective on June 1, 2015. Under SAFE Circular 13, applications for foreign exchange registration of inbound foreign direct investment and outbound overseas direct investment, including those required under the SAFE Circular 37, will be filed with qualified banks instead of the SAFE. The qualified banks will directly examine the applications and accept registrations under the supervision of the SAFE.
These regulations may have a significant impact on our present and future structuring and investment. We have requested or intend to take all necessary measures to require our shareholders who to our knowledge are PRC residents to make the necessary applications, filings and amendments as required under these regulations. We further intend to structure and execute our future offshore acquisitions in a manner consistent with these regulations and any other relevant legislation. However, because it is presently uncertain how the SAFE regulations and any future legislation concerning offshore or cross-border transactions will be interpreted and implemented by the relevant government authorities in connection with our future offshore financings or acquisitions, we cannot provide any assurances that we will be able to comply with, qualify under, or obtain any approvals required by the regulations or other legislation. Furthermore, we cannot assure you that any PRC shareholders of our company or any PRC company into which we invest will be able to comply with those requirements. Any failure or inability by such individuals or entities to comply with SAFE regulations may subject us to fines or legal sanctions, such as restrictions on our cross-border investment activities or our PRC subsidiary’s ability to distribute dividends to, or obtain foreign exchange-denominated loans from, our company or prevent us from making distributions or paying dividends. As a result, our business operations and our ability to make distributions to you could be materially and adversely affected.
| 23 |
Furthermore, as these foreign exchange regulations are still relatively new and their interpretation and implementation have been constantly evolving, it is unclear how these regulations, and any future regulation concerning offshore or cross-border transactions, will be interpreted, amended and implemented by the relevant governmental authorities. For example, we may be subject to a more stringent review and approval process with respect to our foreign exchange activities, such as remittance of dividends and foreign-currency-denominated borrowings, which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. In addition, if we decide to acquire a PRC domestic company, we cannot assure you that we or the owners of such company, as the case may be, will be able to obtain the necessary approvals or complete the necessary filings and registrations required by the foreign exchange regulations. This may restrict our ability to implement our acquisition strategy and could adversely affect our business and prospects.
If we are classified as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC income tax purposes, such classification could result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders.
Under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law and its implementation rules, an enterprise established outside of the PRC with “de facto management body” within the PRC is considered a “resident enterprise” and will be subject to the enterprise income tax on its global income at the rate of 25%. The implementation rules define the term “de facto management body” as the body that exercises full and substantial control and overall management over the business, productions, personnel, accounts and properties of an enterprise. In 2009, the SAT issued the Circular of the State Administration of Taxation on Issues Concerning the Identification of Chinese-controlled Overseas Registered Enterprises as Resident Enterprises in accordance with the Actual Standards of Organizational Management, or the SAT Circular 82, which provides certain specific criteria for determining whether the “de facto management body” of a PRC-controlled enterprise that is incorporated offshore is located in China. Although this circular only applies to offshore enterprises controlled by PRC enterprises or PRC enterprise groups, not those controlled by PRC individuals or foreigners, the criteria set forth in the circular may reflect the SAT’s general position on how the “de facto management body” text should be applied in determining the tax resident status of all offshore enterprises. According to SAT Circular 82, an offshore incorporated enterprise controlled by a PRC enterprise or a PRC enterprise group will be regarded as a PRC tax resident by virtue of having its “de facto management body” in China and will be subject to PRC enterprise income tax on its global income only if all of the following conditions are met: (i) the places where the senior management and senior management departments responsible for the daily production, operation and management of the enterprise perform their duties are mainly located within the territory of the PRC; (ii) decisions relating to the enterprise’s financial matters (such as money borrowing, lending, financing and financial risk management) and human resource matters (such as appointment, dismissal and salary and wages) are made or are subject to approval by organizations or personnel in the PRC; (iii) the enterprise’s primary assets, accounting books and records, company seals, and board and shareholder resolutions, are located or maintained in the PRC; and (iv) at least 50% of voting board members or senior executives habitually reside in the PRC. In addition, the SAT issued the Bulletin of the State Administration of Taxation on Printing and Distributing the Administrative Measures for Income Tax on Chinese-controlled Resident Enterprises Incorporated Overseas (Trial Implementation) in 2011, providing more guidance on the implementation of SAT Circular 82. This bulletin clarifies matters including resident status determination, post determination administration, and competent tax authorities. In January 2014, the SAT issued the Bulletin of the State Administration of Taxation on Issues concerning the Determination of Resident Enterprises Based on the Standards of Actual Management Institutions, or SAT Bulletin 9. According to SAT Bulletin 9, a Chinese-controlled offshore incorporated enterprise that satisfies the conditions prescribed under the SAT Circular 82 for being recognized as a PRC tax resident must apply for being recognized as a PRC tax resident to the competent tax authority at the place of registration of its main investor within the territory of China.
We believe that Company is not a PRC resident enterprise for PRC tax purposes. However, the tax resident status of an enterprise is subject to determination by the PRC tax authorities and uncertainties remain with respect to the interpretation of the term “de facto management body.” If the PRC tax authorities determine that Company or any of our offshore subsidiaries is a PRC resident enterprise for enterprise income tax purposes, we and our offshore subsidiary will be subject to PRC enterprise income on their worldwide income at the rate of 25%, which would materially reduce our net income. Furthermore, if we are treated as a PRC tax resident enterprise, we may be required to withhold a 10% withholding tax from dividends we pay to our shareholders that are non-resident enterprises. In addition, non-resident enterprise shareholders may be subject to PRC tax on gains realized on the sale or other disposition of Ordinary Shares, if such income is treated as sourced from within the PRC. Furthermore, if we are deemed a PRC resident enterprise, dividends payable to our non-PRC individual shareholders and any gain realized on the transfer of Ordinary Shares by such shareholders may be subject to PRC tax at a rate of 20% unless a reduced rate is available under an applicable tax treaty. It is unclear whether non-PRC shareholders of Company would be able to claim the benefits of any tax treaties between their country of tax residence and the PRC in the event that Company is treated as a PRC resident enterprise.
| 24 |
We face uncertainty with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.
On February 3, 2015, the SAT issued a Bulletin of State Administration of Taxation on Several Issues concerning the Enterprise Income Tax on the Indirect Transfer of Properties by Non-resident Enterprises, or SAT Bulletin 7, which came into effect on February 3, 2015, but will also apply to cases where their PRC tax treatments are not yet concluded. Pursuant to SAT Bulletin 7, an “Indirect Transfer” of PRC assets, including a transfer of equity interests in an unlisted non-PRC holding company of a PRC resident enterprise, by non-PRC resident enterprises may be re-characterized and treated as a direct transfer of the underlying PRC assets, if such arrangement does not have a reasonable commercial purpose and was established for the purpose of avoiding payment of PRC enterprise income tax. As a result, gains derived from such indirect transfer may be subject to PRC enterprise income tax, and the transferee or other person who is obligated to pay for the transfer is obligated to withhold the applicable taxes, currently at a rate of 10% for the transfer of equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise.
On October 17, 2017, the SAT issued the Bulletin of the State Administration of Taxation on Issues Concerning the Withholding of Non-resident Enterprise Income Tax at Source, or SAT Bulletin 37, which came into effect on December 1, 2017. The SAT Bulletin 37 further clarifies the practice and procedure of the withholding of non-resident enterprise income tax.
Where a non-resident enterprise transfers taxable assets in China indirectly by disposing of the equity interests of an overseas holding company, the non-resident enterprise as either transferor or transferee, or the PRC entity whose equity is transferred, may report such Indirect Transfer to the relevant tax authority. Under the “substance over form” principle, the PRC tax authority may disregard the existence of the overseas holding company if it lacks a reasonable commercial purpose and was established for the purpose of reducing, avoiding or deferring PRC tax. As a result, gains derived from such Indirect Transfer may be subject to PRC enterprise income tax, and the transferee or other person who is obligated to pay for the transfer is obligated to withhold the applicable taxes, currently at a rate of 10% for the transfer of equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise. Both the transferor and the transferee may be subject to penalties under PRC tax laws if the transferee fails to withhold the taxes and the transferor fails to pay the taxes.
We face uncertainties as to the reporting and other implications of certain past and future transactions where PRC taxable assets are involved. Our Company may be subject to filing obligations or taxed if our company is transferor in such transactions, and we may be subject to withholding obligations if our company is a transferee in such transactions, under SAT Bulletin 7 and SAT Bulletin 37. For transfer of Ordinary Shares in our company by investors that are non-PRC resident enterprises, our PRC subsidiary may be requested to assist in the filing under SAT Bulletin 7 and SAT Bulletin 37. As a result, we may be required to expend valuable resources to comply with SAT Bulletin 7 and SAT Bulletin 37 or to request the relevant transferors from whom we purchase taxable assets to comply with these circulars, or to establish that our Company should not be taxed under these circulars, which may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations
If the Chinese government chooses to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers, such action could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
On December 28, 2021, the Measures for Cybersecurity Review (2021 version) was promulgated and became effective on February 15, 2022. Pursuant to Article 2 of Measures for Cybersecurity Review (2021 version), the purchase of network products and services by critical information infrastructure operator and the data processing activities carries out online platform operators, which affects or may affect national security, shall be subject to cybersecurity review in accordance with the present Measures. Pursuant to Article 7, an online platform operator who possesses the personal information of more than 1 million users shall declare to the Office of Cybersecurity Review for cybersecurity review.
| 25 |
On November 14, 2021, the CAC published the Network Internet Data Protection Draft Regulations (draft for comments). Article 13 of the Network Internet Data Protection Draft Regulations (draft for comments) reiterates that data handlers that process the personal information of more than one million users listing in a foreign country should apply for a cybersecurity review in compliance with relevant national regulations.
Our business does not involve the collection of user data, implicate cybersecurity, or involve any other type of restricted industry. However, since the Measures for Cybersecurity Review (2021 version) just became effective on February 15, 2022, it is unclear on how it will be interpreted and implemented by the relevant PRC authorities. In addition, since the deadline for feedback of the Network Internet Data Protection Draft Regulations (draft for comments) is December 13, 2021 and the formal Network Internet Data Protection Regulations is not promulgated, it is unclear on how it will be amended by the relevant PRC authorities. As of the date of this prospectus, our PRC subsidiaries have not been involved in any investigations on cybersecurity review initiated by the relevant PRC authorities, and has not received any requirements to obtain permissions from relevant PRC authorities to issue our Ordinary Shares to foreign investors or were denied such permissions by relevant PRC authorities.
However, if there is significant change to current political arrangements between mainland China and Hong Kong, or the applicable laws, regulations, or interpretations change, and our Company or our PRC subsidiaries are required to obtain such approvals in the future, and that our Company does not receive or maintain the approvals or is denied permissions from the PRC authorities, or inadvertently concludes that such approvals are not required, we could incur material costs to ensure compliance, be subject to fines and no longer be permitted to continue our current business operations. We may not be able to list our Ordinary Shares on a U.S. exchange, or continue to offer securities to investors, which would materially affect the interest of the investors and cause significant depreciation of the price of our Ordinary Shares.
Uncertainties with respect to the PRC legal system could limit the legal protections available to you and us.
We conduct all of our business in China through our subsidiary, Shanghai Qige. Our Company is generally subject to laws and regulations applicable to foreign investments in China and, in particular, laws applicable to foreign-invested enterprises. The PRC legal system is based on written statutes, and prior court decisions may be cited for reference but have limited precedential value. Since 1979, a series of new PRC laws and regulations have significantly enhanced the protections afforded to various forms of foreign investments in China. However, since the PRC legal system continues to evolve rapidly, the interpretations of many laws, regulations, and rules are not always uniform, and enforcement of these laws, regulations, and rules involve uncertainties, which may limit legal protections available to you. In addition, any litigation in China may be protracted and result in substantial costs and diversion of resources and management attention.
If our preferential tax treatments and government subsidies are revoked or become unavailable or if the calculation of our tax liability is successfully challenged by the PRC tax authorities, we may be required to pay tax, interest and penalties in excess of our tax provisions.
The Chinese government has provided tax incentives to Chinese private companies, including reduced enterprise income tax rates. For example, under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law and its implementation rules, the statutory enterprise income tax rate is 25%. However, the income tax of an enterprise that has been determined to be a high and new technology enterprise can be reduced to a preferential rate of 15%. According to the Administrative Measures for the Accreditation of High-tech Enterprises promulgated by three PRC regulatory agencies, including SAT, the qualification of high and new enterprise is effective for a renewable three-year permitted. Our Chinese subsidiaries does not meet the qualification of high and new enterprise, our Chinese subsidiaries are subject to the statutory enterprise income tax rate of 25%. Any increase in the enterprise income tax rate applicable to our PRC subsidiary, or any discontinuation, retroactive or future reduction or refund of any of the preferential tax treatments and local government subsidies currently enjoyed by our subsidiaries in China, could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Further, in the ordinary course of our business, we are subject to complex income tax and other tax regulations, and significant judgment is required in the determination of a provision for income taxes. Although we believe our tax provisions are reasonable, if the PRC tax authorities successfully challenge our position and we are required to pay tax, interest, and penalties in excess of our tax provisions, our financial condition and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
| 26 |
Our failure to fully comply with PRC labor-related laws may expose us to potential penalties.
Companies operating in China are required to participate in mandatory employee social security schemes that are organized by municipal and provincial governments, including pension insurance, unemployment insurance, childbirth insurance, work-related injury insurance, medical insurance and housing provident funds. Such schemes have not been implemented consistently by the local governments in China given the different levels of economic development in different locations, but generally require us to make contributions to employee social security plans at specified percentages of the salaries, bonuses and certain allowances of our eligible full-time employees, up to a maximum amount specified by the local government from time to time. We have accrued in financial statements and have made full contributions to the social insurance and housing provident funds in accordance for our eligible full-time employees as required by the relevant PRC laws and regulations. As the date of this prospectus, none of our entities or subsidiaries had received any notice from local authorities or any claim or request from the employees in this regard. Our failure to make full contributions to social insurance and to comply with applicable PRC labor-related laws regarding housing funds may subject us to late payment penalties and other fines or labor disputes, and we could be required to make up the contributions for these plans, which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
According to applicable PRC laws and regulations, employers must open social insurance registration accounts and housing provident fund accounts and pay social insurance and housing provident funds for employees. We may, in the future, become subject to penalties imposed by the local social insurance authorities and the local housing provident fund management centers if we fail to discharge our obligations in relation to payment of social insurance and housing provident funds as an employer.
Failure to comply with PRC regulations relating to the establishment of offshore special purpose companies by PRC residents may subject our PRC resident shareholders to personal liability, limit our ability to acquire PRC companies or to inject capital into our Holding Company, or otherwise materially adversely affect us.
Pursuant to the Circular on Relevant Issues concerning Foreign Exchange Administration of Overseas Investment and Financing and Return Investments Conducted by Domestic Residents through Overseas Special Purpose Vehicle, or Circular 37, which was promulgated by SAFE, and became effective on July 4, 2014, (1) a PRC resident must register with the local SAFE branch before he or she contributes assets or equity interests in an overseas special purpose vehicle, or an Overseas SPV, that is directly established or controlled by the PRC resident for the purpose of conducting investment or financing; and (2) following the initial registration, the PRC resident is also required to register with the local SAFE branch for any major change, in respect of the Overseas SPV, including, among other things, a change in the Overseas SPV’s PRC resident shareholder, name of the Overseas SPV, term of operation, or any increase or reduction of the Overseas SPV’s registered capital, share transfer or swap, and merger or division.
We have requested the beneficial holders of our Ordinary Shares who are PRC residents to register with the relevant branch of SAFE in connection with their equity interests in us and our acquisitions of equity interests in our PRC subsidiaries pursuant to Circular 37 or the predecessor regulation of Circular 37, namely the Notice on Relevant Issues Concerning Foreign Exchange Administration for PRC Residents Engaging in Financing and Roundtrip Investments via Overseas Special Purpose Vehicles, as the case may be. Because of uncertainty over how Circular 37 will be interpreted and implemented, and how or whether SAFE will apply it to us, we cannot predict how it will affect our business operations or future strategies.
In addition, such PRC residents may not always be able to complete the necessary registration procedures required by Circular 37. We also have little control over either our present or prospective direct or indirect shareholders or the outcome of such registration procedures.
We may be exposed to liabilities under the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and Chinese anti-corruption laws, and any determination that we violated these laws could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practice Act, or FCPA, and other U.S. laws that prohibit improper payments or offers of payments to foreign governments and their officials and political parties by U.S. persons and issuers as defined by the relevant statute, for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. We have operations, agreements with third parties, and make most of our sales in China. PRC anti-corruption laws also strictly prohibit bribery of government officials. Our activities in China create the risk of unauthorized payments or offers of payments by the employees, consultants, sales agents, or distributors, even though they may not always be subject to our control. It is our policy to implement safeguards to discourage these practices by our employees. However, our existing safeguards and any future improvements may prove to be less than effective, and the employees, consultants, sales agents, or distributors may engage in conduct for which we might be held responsible. Particularly, most of the hospitals and inoculation centers in China are state-owned entities, whose employees may be recognized as foreign government officials for the purpose of FCPA. Therefore, any payments, expensive gifts or other benefits provided to an employee of the state-owned hospital or inoculation center may be deemed violation of FCPA. Violations of FCPA or PRC anti-corruption laws may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our business, prospects, operating results and financial condition. In addition, the U.S. government may seek to hold us liable for successor liability under FCPA violations committed by companies in which we invest or that we acquire.
| 27 |
Risks Related to Our Shares and This Offering
An active trading market for our Ordinary Shares may never develop and the trading price for our Shares may fluctuate significantly.
We intend to seek quotation of the Ordinary Shares on The OTC Markets Group, Inc. OTCQX or the OTCQB Venture after effectiveness of the registration statement for this prospectus. Quotation of our common stock on the OTC Markets will require a market maker filing an application to quote our common stock and approval of that application. Prior to the completion of this offering, there has been no public market for our Ordinary Shares, and we cannot assure you that a liquid public market for our Shares will develop. If an active public market for our Shares does not develop, the market price and liquidity of our Shares may be materially and adversely affected. The initial public offering price for our Shares was determined based upon several factors, and we can provide no assurance that the trading price of our Shares after this offering will not decline. As a result, investors in our securities may experience a significant decrease in the value of their Shares.
If we are successful at creating a market for our Shares, the trading price of our Shares is likely to be volatile, which could result in substantial losses to investors.
The trading price of our Shares is likely to be volatile and could fluctuate widely due to factors beyond our control. This may happen because of broad market and industry factors, including the performance and fluctuation of the market prices of other companies with business operations located mainly in China that have listed their securities in the United States. In addition to market and industry factors, the price and trading volume for our Shares may be highly volatile for factors specific to our own operations, including the following:
| ● | variations in our revenues, earnings and cash flow; | |
| ● | announcements of new investments, acquisitions, strategic partnerships or joint ventures by us or our competitors; | |
| ● | announcements of new offerings, solutions and expansions by us or our competitors; | |
| ● | changes in financial estimates by securities analysts; | |
| ● | detrimental adverse publicity about us, our services or our industry; | |
| ● | additions or departures of key personnel; and | |
| ● | potential litigation or regulatory investigations. |
Any of these factors may result in large and sudden changes in the volume and price at which our Shares will trade.
In the past, shareholders of public companies have often brought securities class action suits against those companies following periods of instability in the market price of their securities. If we were involved in a class action suit, it could divert a significant amount of our management’s attention and other resources from our business and operations and require us to incur significant expenses to defend the suit, which could harm our results of operations. Any such class action suit, whether or not successful, could harm our reputation and restrict our ability to raise capital in the future. In addition, if a claim is successfully made against us, we may be required to pay significant damages, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
| 28 |
Certain existing shareholders have substantial influence over our Company and their interests may not be aligned with the interests of our other shareholders.
Upon the completion of this offering, our directors and officers will collectively own an aggregate of 92.3% of the total voting power of our outstanding Ordinary Shares immediately after the completion of this offering. As a result, they have substantial influence over our business, including significant corporate actions such as mergers, consolidations, sales of all or substantially all of our assets, election of directors and other significant corporate actions.
They may take actions that are not in the best interest of us or our other shareholders. This concentration of ownership may discourage, delay or prevent a change in control of our company, which could deprive our shareholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their shares as part of a sale of our company and may reduce the price of the Shares. These actions may be taken even if they are opposed by our other shareholders, including those who purchase Shares in this offering. In addition, the significant concentration of share ownership may adversely affect the trading price of the Shares due to investors’ perception that conflicts of interest may exist or arise. For more information regarding our principal shareholders and their affiliated entities, see “Principal Shareholders.”
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they adversely change their recommendations regarding our Ordinary Shares, the market price for our Shares and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our Shares will be influenced by research or reports that industry or securities analysts publish about our business. If one or more analysts who cover us downgrade our Shares, the market price for our Shares would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease to cover us or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause the market price or trading volume for our Shares to decline.
The sale or availability for sale of substantial amounts of our Ordinary Shares could adversely affect their market price.
Sales of substantial amounts of our Ordinary Shares in the public market after the completion of this offering, or the perception that these sales could occur, could adversely affect the market price of our Ordinary Shares and could materially impair our ability to raise capital through equity offerings in the future. The 5,000,000 Ordinary Shares sold in this offering will be freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, and shares held by our existing shareholders may also be sold in the public market in the future subject to the restrictions in Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act. We cannot predict what effect, if any, market sales of securities held by our significant shareholders or any other shareholder or the availability of these securities for future sale will have on the market price of our Shares.
Negative publicity may harm Shanghai Qige’s brand and reputation and have a material adverse effect on business.
Negative publicity about us, including our services, management, business model and practices, compliance with applicable rules, regulations and policies, or our network partners may materially and adversely harm our brand and reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business. We cannot assure you that we will be able to defuse any such negative publicity within a reasonable period of time, or at all. Additionally, allegations, directly or indirectly against us, may be posted on the internet by anyone on a named or anonymous basis, and can be quickly and widely disseminated. Information posted may be inaccurate, misleading and adverse to us, and it may harm our reputation, business or prospects. The harm may be immediate without affording us an opportunity for redress or correction. Our reputation may be negatively affected as a result of the public dissemination of negative and potentially inaccurate or misleading information about our business and operations, which in turn may materially adversely affect our relationships with our customers, employees or business partners, and adversely affect the price of our Shares.
| 29 |
Because we do not expect to pay dividends in the foreseeable future after this offering, you must rely on price appreciation of our Shares for return on your investment.
We currently intend to retain most, if not all, of our available funds and any future earnings after this offering to fund the development and growth of our business. As a result, we do not expect to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Therefore, you should not rely on an investment in our Shares as a source for any future dividend income.
Our board of directors has complete discretion as to whether to distribute dividends. Even if our board of directors decides to declare and pay dividends, the timing, amount and form of future dividends, if any, will depend on our future results of operations and cash flow, our capital requirements and surplus, the amount of distributions, if any, received by us from our subsidiaries, our financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors. Accordingly, the return on your investment in our Shares will likely depend entirely upon any future price appreciation of our Shares. There is no guarantee that our Shares will appreciate in value after this offering or even maintain the price at which you purchased the Shares. You may not realize a return on your investment in our Shares and you may even lose your entire investment in our Shares.
We are exempt from certain corporate governance standards. This may afford less protection to holders of our shares.
We are exempted from certain corporate governance requirements by virtue of being a foreign private issuer. We are required to provide a brief description of the significant differences between our corporate governance practices and the corporate governance practices required to be followed by domestic U.S. companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange. The standards applicable to us are considerably different than the standards applied to domestic U.S. issuers. For instance, we are not required to:
| ● | have a majority of the board be independent (although all of the members of the audit committee must be independent under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act); | |
| ● | have a compensation committee or a nominating or corporate governance committee consisting entirely of independent directors; | |
| ● | have regularly scheduled executive sessions with only independent directors; or | |
| ● | have executive sessions of solely independent directors each year. |
We have relied on and intend to continue to rely on some of these exemptions. As a result, you may not be provided with the benefits of certain corporate governance requirements of the Nasdaq Stock Exchange.
We are an emerging growth company within the meaning of the Securities Act and may take advantage of certain reduced reporting requirements.
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act, and we may take advantage of certain exemptions from requirements applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, most significantly, not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 for so long as we are an emerging growth company until the earliest of (a) the last day of the fiscal year during which we have total annual gross revenues of at least $1.07 billion; (b) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the completion of this offering; (c) the date on which we have, during the preceding three-year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt; or (d) the date on which we are deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” under the Exchange Act, which would occur if the market value of our Shares that are held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
We will incur increased costs as a result of being a public company, particularly after we cease to qualify as an “emerging growth company.”
We will become a public company and expect to incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and the Nasdaq Stock Exchange, impose various requirements on the corporate governance practices of public companies. As a company with less than $1.07 billion in revenues for our last fiscal year, we qualify as an “emerging growth company” pursuant to the JOBS Act. An emerging growth company may take advantage of specified reduced reporting and other requirements that are otherwise applicable generally to public companies. These provisions include exemption from the auditor attestation requirement under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or Section 404, in the assessment of the emerging growth company’s internal control over financial reporting and permission to delay adopting new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. However, we have elected to “opt out” of this provision and, as a result, we will comply with new or revised accounting standards as required when they are adopted for public companies. This decision to opt out of the extended transition period under the JOBS Act is irrevocable.
| 30 |
We expect these rules and regulations to increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some corporate activities more time-consuming and costly. After we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” we expect to incur significant expenses and devote substantial management effort toward ensuring compliance with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the other rules and regulations of the SEC. For example, as a result of becoming a public company, we will need to increase the number of independent directors and adopt policies regarding internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures. We also expect that operating as a public company will make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. In addition, we will incur additional costs associated with our public company reporting requirements. It may also be more difficult for us to find qualified persons to serve on our board of directors or as executive officers. We are currently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to these rules and regulations, and we cannot predict or estimate with any degree of certainty the amount of additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs.
If we fail to establish and maintain proper internal financial reporting controls, our ability to produce accurate financial statements or comply with applicable regulations could be impaired.
We are a private company with limited accounting personnel and other resources with which to address our internal controls and procedures. Our management has not completed an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting, and our independent registered public accounting firm has not conducted an audit of our internal control over financial reporting. In the course of auditing our consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, we identified several material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting and other control deficiencies. A “material weakness” is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
The material weaknesses identified to date relate to (i) a lack of accounting staff and resources with appropriate knowledge of generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“US GAAP”) and SEC reporting and compliance requirements; (ii) a lack of sufficient documented financial closing policies and procedures; (iii) a lack of independent directors and an audit committee; (iv) lack of risk assessment in accordance with the requirement of COSO 2013 framework and (v) a lack of an effective review process by the accounting manager which led to material audit adjustments to the financial statements.
Following the identification of the material weaknesses and control deficiencies, we plan to continue to take remedial measures including (i) hiring more qualified accounting personnel with relevant US GAAP and SEC reporting experience and qualifications to strengthen the financial reporting function and to set up a financial and system control framework; (ii) implementing regular and continuous US GAAP accounting and financial reporting training programs for our accounting and financial reporting personnel; (iii) setting up an internal audit function as well as engaging an external consulting firm to assist us with assessment of Sarbanes-Oxley compliance requirements and improvement of overall internal control; and (iv) appointing independent directors, establishing an audit committee, and strengthening corporate governance.
We plan to take measures to remedy these material weaknesses depending on our resources. The implementation of these measures may not fully address the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, and we cannot conclude that they have been fully remedied. Our failure to correct theses material weaknesses or our failure to discover and address any other material weaknesses could result in inaccuracies in our financial statements and could also impair our ability to comply with applicable financial reporting requirements and related regulatory filings on a timely basis. As a result, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, as well as the trading price of our Ordinary Shares, may be materially and adversely affected. Moreover, ineffective internal control over financial reporting significantly hinders our ability to prevent fraud. Upon the completion of this offering, we will become a public company in the United States subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or Section 404, will require that we include a report from management on our internal control over financial reporting in our annual report on Form 20-F beginning with our annual report for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2022. In addition, once we cease to be an “emerging growth company” as such term is defined in the JOBS Act, our independent registered public accounting firm must attest to and report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Our management may conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is not effective. Moreover, even if our management concludes that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, our independent registered public accounting firm, after conducting its own independent testing, may issue a report that is qualified if it is not satisfied with our internal controls or the level at which our controls are documented, designed, operated or reviewed, or if it interprets the relevant requirements differently from us. In addition, after we become a public company, our reporting obligations may place a significant strain on our management, operational and financial resources and systems for the foreseeable future. We may be unable to timely complete our evaluation testing and any required remediation.
| 31 |
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements about our current expectations and views of future events, which are contained principally in the sections entitled “Prospectus Summary”, “Risk Factors,” “Use of Proceeds,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and “Business.” These forward-looking statements relate to events that involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from those expressed or implied by these statements.
You can identify some of these forward-looking statements by words or phrases such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “aim,” “estimate,” “intend,” “plan,” “believe,” “is/are likely to,” “propose,” “potential,” “continue” or other similar expressions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy and financial needs. The forward-looking statements included in this prospectus relate to, among other things:
| ● | our goals and strategies; | |
| ● | our business and operating strategies and plans for the development of existing and new businesses, ability to implement such strategies and plans and expected time; | |
| ● | our future business development, financial condition and results of operations; | |
| ● | expected changes in our revenues, costs or expenditures; | |
| ● | our dividend policy; | |
| ● | our expectations regarding demand for and market acceptance of our products and services; | |
| ● | our expectations regarding our relationships with customers and business partners; | |
| ● | the trends in, expected growth in and market size of the brushless controller industry; | |
| ● | our ability to maintain and enhance our market position; | |
| ● | our ability to continue to develop new technologies and/or upgrade our existing technologies; | |
| ● | developments in, or changes to, laws, regulations, governmental policies, incentives and taxation affecting our operations; | |
| ● | relevant governmental policies and regulations relating to our businesses and industry; | |
| ● | competitive environment, competitive landscape and potential competitor behavior in our industry and the overall outlook in our industry; | |
| ● | our ability to generate cash flow and profitability and continue as a going concern; | |
| ● | our ability to attract, train and retain executives and other employees; | |
| ● | the development of the global financial and capital markets; | |
| ● | fluctuations in inflation, interest rates and exchange rates; | |
| ● | general business, political, social and economic conditions in China and the overseas markets we have business; | |
| ● | the length and severity of the recent COVID-19 outbreak and its impact on our business and industry; and | |
| ● | assumptions underlying or related to any of the foregoing. |
| 32 |
These forward-looking statements involve various risks and uncertainties. Although we believe that our expectations expressed in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations and our actual results could be materially different from our expectations. Important risks and factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from our expectations are generally set forth in “Prospectus Summary—Our Challenges,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Business,” “Regulation” and other sections in this prospectus. Moreover, we operate in an evolving environment. New risk factors and uncertainties emerge from time to time and it is not possible for our management to predict all risk factors and uncertainties, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. You should read thoroughly this prospectus and the documents that we refer to with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from and worse than what we expect. We qualify all of our forward-looking statements by these cautionary statements.
This prospectus contains information derived from government and private publications. These publications include forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Although we believe the data and information to be reliable, we have not independently verified the accuracy or completeness of the data and information contained in these publications. Statistical data in these publications also include projections based on a number of assumptions. The digital wallet industry may not grow at the rate projected by market data, or at all. Failure of these markets to grow at the projected rate may have a material and adverse effect on our business and the market price of our Ordinary Shares. In addition, the rapidly evolving nature of the industry results in significant uncertainties for any projections or estimates relating to the growth prospects or future condition of our market. Furthermore, if any one or more of the assumptions underlying the market data are later found to be incorrect, actual results may differ from the projections based on these assumptions. See “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Shares and General Risk Factors.” Therefore, you should not place undue reliance on these statements.
You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The forward-looking statements in this prospectus are made based on events and information as of the date of this prospectus. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, after the date on which the statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. You should read this prospectus and the documents that we refer to in this prospectus and have filed as exhibits to the registration statement, of which this prospectus is a part, completely and with the understanding that our actual future results or performance may materially differ from what we expect.
We will not receive any of the proceeds from the sale of the Shares by the Selling Stockholders pursuant to this prospectus. The Selling Stockholders will pay any agent’s commissions and expenses they incur for brokerage, accounting, tax or legal services or any other expenses that they incur in disposing of the Shares. We will bear all other costs, fees and expenses incurred in effecting the registration of the Shares covered by this prospectus and any prospectus supplement.
| 33 |
Penny Stock Regulations
You should note that our stock is a penny stock. The Securities and Exchange Commission has adopted Rule 15g-9 which generally defines “penny stock” to be any equity security that has a market price (as defined) less than $5.00 per share or an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. Our securities are covered by the penny stock rules, which impose additional sales practice requirements on broker-dealers who sell to persons other than established customers and “accredited investors”. The term “accredited investor” refers generally to institutions with assets in excess of $5,000,000 or individuals with a net worth in excess of $1,000,000 or annual income exceeding $200,000 or $300,000 jointly with their spouse. The penny stock rules require a broker-dealer, prior to a transaction in a penny stock not otherwise exempt from the rules, to deliver a standardized risk disclosure document in a form prepared by the SEC which provides information about penny stocks and the nature and level of risks in the penny stock market. The broker-dealer also must provide the customer with current bid and offer quotations for the penny stock, the compensation of the broker-dealer and its salesperson in the transaction and monthly account statements showing the market value of each penny stock held in the customer’s account. The bid and offer quotations, and the broker-dealer and salesperson compensation information, must be given to the customer orally or in writing prior to effecting the transaction and must be given to the customer in writing before or with the customer’s confirmation. In addition, the penny stock rules require that prior to a transaction in a penny stock not otherwise exempt from these rules, the broker-dealer must make a special written determination that the penny stock is a suitable investment for the purchaser and receive the purchaser’s written agreement to the transaction. These disclosure requirements may have the effect of reducing the level of trading activity in the secondary market for the stock that is subject to these penny stock rules. Consequently, these penny stock rules may affect the ability of broker-dealers to trade our securities. We believe that the penny stock rules discourage investor interest in and limit the marketability of our Ordinary Shares.
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our Ordinary Shares. We do not anticipate paying any dividends in the foreseeable future. We currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to finance operations and expand our business. Our board of directors has sole discretion whether to pay dividends. If our board of directors decides to pay dividends, the form, frequency and amount will depend upon our future operations and earnings, capital requirements and surplus, general financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that our directors may deem relevant.
The Companies Law imposes restrictions on our ability to declare and pay dividends. See “Description of share capital and articles of association—Dividend and liquidation rights” for additional information. Payment of dividends may be subject to China withholding taxes. See “Taxation and government programs-China tax considerations and government programs” for additional information.
| 34 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. This discussion contains certain forward-looking statements that involve risk and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ materially from those discussed below. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those identified below and those set forth under the Section entitled “Risk Factors”, and other documents we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of future results.
Overview
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. (“Tian’an”) is a holding company that was incorporated under the laws of the British Virgin Islands on April 8, 2021. Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Yunke”) is our wholly owned subsidiary. Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd., (“Shanghai Qige”) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke and our operating company in China. Through our subsidiary, Shanghai Qige, we are engaged in the technology driven sales of power control and service systems solutions. Our products are used in low-speed electric cars such as electric forklifts, golf carts, sightseeing cars and other special tool vehicles. Our systems can be customized according to the user’s process requirements.
We are living in an era where consumers consistently face energy shortages, environmental pollution, climate change and global warming. Technology has offered solutions to these challenges and has also encouraged the development of engineering industry. Our products are designed to be technologically efficient, have low energy consumption, create high output and be light weight.
Basis of Presentation
Our unaudited consolidated operation data for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 and our audited consolidated operation data for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 have been derived from our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with US GAAP.
Results of Operations
Comparison for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 and 2021
The following table summarizes the results of our operations during the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, respectively during such periods.
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | - | $ | 22,008 | ||||
| Cost of revenue | - | 16,815 | ||||||
| Gross profit | - | 5,193 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 146,239 | 76,159 | ||||||
| Operating loss | (146,239 | ) | (70,966 | ) | ||||
| Total other expense, net | (229 | ) | (1,038 | ) | ||||
| Net loss | $ | (146,468 | ) | $ | (72,004 | ) | ||
Revenue
Revenues were $0 for the six months ended June 30, 2022, a decrease of $22,008 or 100%, compared to $22,008 in the same period for the six months ended June 30, 2021. The decrease was mainly due to the impact from the Chinese zero-COVID policy. The policy enforces temporary lockdowns on millions of people, Chinese cities, and provinces across China. During the six months ended June 30, 2022, our sale and customer service department could execute limited functions to market our products and maintain customer relationships. The adverse effect may further impact the Company’s operations in the remainder of 2022.
Gross Profit
Gross profit was $0 for the six months ended June 30, 2022, a decrease of $5,193 or 100%, compared to $5,193 of gross profit for the six months ended June 30, 2021. The decrease was mainly due to the impact from the Chinese zero-COVID policy. With lockdowns in cities across China, Shangahi Qige lost some of customer base and product demand decreased.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $130,365 for the six months ended June 30, 2022 compared to $46,640 for the six months ended June 30, 2021, representing an increase of $83,725 or 180%. The increase was due to our overseas listing related expenses and fees.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses were $7,578 for the six months ended June 30, 2022 compared to $20,390 for the same period in 2021, representing a decrease of $12,812 or 63%. The decrease was mainly due to the impact of business shutdown implementation during the six month period which forced us to temporarily adjust our research expenditure policy and temporarily cease some research activities.
| 35 |
Operating Loss
Total operating loss was $146,239 for the six months ended June 30, 2022, compared to $70,966 in the same period of 2021, representing an increase of $75,273 or 106%. The increase was mainly due to the increase in general and administrative expenses.
Net Loss
As a result of the above factors, we had a net loss of $146,468 for the six months ended June 30, 2022, compared to a net loss of $72,004 for the six months ended June 30, 2021.
Cash Flows
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2022 totaled $155,975. Cash flow pertaining to operating activities from operations benefited from non-cash expenditures, including depreciation and amortization of $3,667, and a decrease of $10,895 in our VAT credit, which was offset by a decrease in payroll payable of $22,916.
Net cash used in operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2021 totaled $87,459. Cash flow pertaining to operating activities benefited from non-cash expenditures, including depreciation and amortization of $4,962, and an increases of $3,544 in accounts payable, an increase of $6,027 in advances from customers, and an increase of $10,147 in payroll payable. However, those benefits were offset by an increase of $1,516 in other receivables, an increase of $13,234 in inventories, and an increase of $20,743 in advances to suppliers.
Investing Activities
There was no net cash used in investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021.
Financing Activities
For the six months ended June 30, 2022, we reported net cash provided by financing activities of $144,572. This comprises proceeds of $500,000 from subscription receivables and related party loans of $61,184, which were partially offset by repayments of $309,068 to our related parties and repayments of $108,174 to our loan payables.
For the six months ended June 30, 2021, we reported $108,159 net cash provided by financing activities which includes proceeds of $262,708 from our related party loans and repayments of $154,549 to related parties.
Comparison for the Years Ended December 31, 2021 and 2020
The following table summarizes the results of our operations during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, and provides information regarding the dollar and percentage increase or (decrease) during such years.
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 37,065 | $ | 26,309 | ||||
| Cost of revenue | 25,107 | 18,757 | ||||||
| Gross profit | 11,958 | 7,552 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 130,707 | 115,922 | ||||||
| Operating loss | (118,749 | ) | (108,370 | ) | ||||
| Total other income (expense), net | (506 | ) | 212 | |||||
| Net loss | $ | (119,255 | ) | $ | (108,158 | ) | ||
Revenue
Revenues were $37,065 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, an increase of $10,756 or 41%, compared to $26,309 in the same period for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. The increase was mainly due to the addition of two new customers.
Gross Profit
Gross profit was $11,958 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, an increase of $4,406 or 58%, compared to $7,552 of gross profit for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. The increase was mainly due to expansion of Shanghai Qige’s customer base and the increase in the unit prices.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $78,935 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $61,742 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020, representing an increase of $17,193 or 28%. The increase was due to the increased compensation for our personnel.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses were $33,757 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $40,361 for the same period in 2020, representing a decrease of $6,604 or 16%. The decrease was mainly due to the impact of business shutdown implementation during the pandemic which forced us to temporarily adjust our research expenditure policy.
Operating Loss
Total operating loss was $118,749 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, compared to $108,370 in the same period of 2020, representing an increase of $10,379 or 10%. The increase was mainly due to the increase in administrative expenses.
Net Loss
As a result of the above factors, we had a net loss of $119,255 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, compared to a net loss of $108,158 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020.
| 36 |
Cash Flows
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities in the year ended December 31, 2021 totaled $138,375. Cash flow pertaining to operating activities from operations benefited from non-cash expenditures, including depreciation and amortization of $8,654. In addition, we had an increase in inventories of $15,369, an increase in advances to suppliers of $13,733, and a decrease in lease liabilities of $10,907, were partially offset by an increase of $14,426 in payroll payable and collection of $6,200 from due from related parties.
Net cash provided by operating activities in the year ended December 31, 2020 totaled $254. Cash flow pertaining to operating activities benefited from non-cash expenditures, including depreciation and amortization of $25,750. Additionally, we had a decrease in inventory of $19,198, an increase of $11,438 in payroll payable, and collection of $60,680 from due from related parties, were partially offset by our payments at lease liabilities.
Investing Activities
There was no net cash used in investing activities for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Financing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2021, we had net cash of $130,728 inflow from financing activities. This was comprised of repayments of related party loans of $271,265, offset by the proceeds of $293,493 and $108,500 from related party loans and third parties.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, there was no cash provided by (used in) financing activities.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Historically, our primary uses of cash have been to finance working capital needs. As of June 30, 2022, we had current assets of $62,177, we had current liabilities of $246,252, and our working capital deficit was $184,075. We anticipate that our current liquidity is not sufficient to meet the obligations associated with being a company that is fully reporting with the SEC.
To date, we have managed our cash flow requirement through financial supporting from our founder and CEO, Mr. Heng Fei Yang. We may need to raise additional capital to fund our operating expenses, pay our obligations, and grow our Company in the future. Our current resources may be insufficient to satisfy all of our cash requirements and we may seek to sell additional equity or debt securities or obtain a credit facility. Our future operations may be dependent on our ability to secure additional financing. Even if we are able to raise the funds required, it is possible that we could incur unexpected costs and expenses, fail to collect amounts owed to us, or experience unexpected cash requirements that would force us to seek alternative financing. Furthermore, if we issue additional equity or debt securities, stockholders may experience additional dilution or the new equity securities may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of existing holders of our Ordinary Shares.
Our financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP, which contemplates our continuation as a going concern. We have an accumulated deficit of $680,290 as of June 30, 2022. In addition, our current liabilities exceed our current assets by $184,075. These factors raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue operating as a going concern. Our ability to continue our operations as a going concern, realize the carrying value of our assets, and discharge our liabilities in the normal course of business is dependent upon our ability to raise capital sufficient to fund our commitments and ongoing losses, and ultimately generate profitable operations.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources.
Leased Properties
We maintain an office in Room 8, Building 1C, No. 3500, Xiupu Road, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China with space of 72 square meters which we leased from April 17, 2021 to April 16, 2024. The monthly rent for our office space is $520.27 (equivalent to RMB $3,504).
In addition, we also leased a residential space for one of our employees for working from home which is located at No. 3-1904 Xizi Garden, Chengxi Street, Wenling City, Zhejiang Province, China. The lease term is for one year with the expiration date on February 22, 2023.
Intellectual Property
We have legal or beneficial rights over 4 patents (owned by Shanghai Qige) which are related to our current products and services pursuant to a patent authorization agreement by and between our Chief Executive Officer Heng Fei Yang and Shanghai Qige.
Patents in China are principally protected under the Patent Law of the PRC. The duration of a patent right is either 10 years or 20 years from the date of application, depending on the types of patent rights.
| 37 |
The following table illustrates the Company’s current patents:
| Patent | Legal status | Application date | Expiration Date | Publication No. | Inventor / Patentee | |||||
| Brushless DC motor | Authorization | June 1, 2020 | May 31, 2030 | CN212323864U | Heng Fei Yang | |||||
| Forklift driving wheel | Authorization | June 1, 2020 | May 31, 2030 | CN212246107U | Heng Fei Yang | |||||
| Driving wheel(2) | Authorization | August 21, 2020 | August 20, 2030 | CN306579976S | Heng Fei Yang | |||||
| Driving wheel | Authorization | May 21, 2020 | May 20, 2030 | CN306065028S | Heng Fei Yang |
Set forth below are the names of our current directors, officers and significant employees, their ages, all positions and offices that they hold with us, the period during which they have served as such, and their business experience during at least the last five years.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Heng Fei Yang | 42 | Chief Executive Officer and Sole Director | ||
| Cong He | 32 | Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Jianhua Ma | 32 | Technical Director | ||
| Yueming Chen | 68 | Operations Director | ||
| Li Yang | 46 | General Manager |
Heng Fei Yang has served as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and sole director since its inception. He has been involved in the industrial automation equipment manufacturing industry for many years and has unique opinions on the electric drive industry. From November 2015 to February 2018, Mr. Yang served as the technical director of forklift equipment of Wanshaade Environmental Protection Technology (Shanghai) Co., LTD. Between March 2017 and December 2019, Mr. Yang also served as the executive director, legal representative and general manager of Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD. Mr. Yang continues to work with different technologies both domestically and abroad. Given his experience, and his familiarity with market industry technology, he drives our Company’s development and supply-demand relationships. Mr. Yang holds a degree in Business Administration from the Dalian University of Technology. Mr. Yang is well qualified to serve on our board of directors due to his significant experience in the industrial automation equipment manufacturing industry.
Cong He has served as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer since February 2022. Ms. He has helped our Company establish a high-quality financial management system, effectively controlling costs, planning taxes and allocating operating funds as well as participating in the Company’s investment decisions. Ms. He served as the Chief Financial Officer of the Medical Institutions Traditional Medicine Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. from July 2019 to January 2022. Prior to that, Ms. He was employed as Deputy Financial Director of the Beijing Ruihua Vision Investment Management Ltd from March 2014 to July 2019. Ms. He has expertise in strategic planning, finance, budget forecasting, audit and financial reporting. Ms. He holds a degree in Accounting from The Central South University of Forestry and Technology, and is a certified tax agent and intermediate accountant.
Jianhua Ma has served as the Company’s Technical Director since its inception. Mr. Ma has engaged in the research and develop different types of software systems for our Company as well as the multi-dimensional integration of technology to meet our customer’s needs. From May 2011 to March 2016, Mr. Ma served as a test engineer at Lust Transmission System (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. He has more than ten years of experience in machinery, equipment, heavy industry, and industrial automation industries. He is experienced in providing technical solutions to customer while also ensuring technical stability. Mr. Ma is familiar with the market and industry needs and has expertise in low-speed electric vehicle driver and motor and system testing, customized products, and systems under demand, electronic equipment and system quality review and customer maintenance. Mr. Ma holds a degree in Mechanical and Electronic Engineering from the Shanghai Institute of Electrical Engineering.
| 38 |
Yueming Chen has served as the Company’s Operations Director since its inception. He has helped our Company maintain and develop external relations in all aspects and managed and motivated our work performance. Mr. Chen served as the Operations Director for Shanghai SIAI Electronics Co., Ltd. from June 2017 to September 2018. From July 2010 to October 2015, Mr. Chen served as the Operations Manager of Hitachi auto parts (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. He has been involved in the industrial automation industry for approximately thirty years, specializing in the operation of electronic technology and drive control. Mr. Chen has significant experience in electronic equipment design, R & D, testing, customer maintenance, has rich upstream and downstream customer resources, and understands the market demand of the industry. Mr. Chen holds a degree in Mechanical Engineering from Shanghai Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering.
Li Yang has served are our Company’s General Manager since April 2021 where she has overseen the internal and external relationships for the Company. Ms. Yang also oversee our administrative affairs. From December 2017 to December 2020 Ms. Yang served as the administrative manager for United Automotive Electronics Co. Prior to that, Ms. Yang served as the administrative manager of Siyuan Electric Co., Ltd. from March 2013 to September 2017. Ms. Yang holds a degree in Administration from the Liaoning Institute of Science and Technology.
Director Agreements and Indemnification Agreements
None.
Term of Office
Our directors hold office until the next annual meeting of shareholders of the Company and until their successors have been elected and qualified. Our officers are elected by the board of directors and serve at the discretion of the board of directors.
Compensation of Directors and Executive Officers
The compensation paid, and benefits in kind granted, to our principal executive officer and principal financial and accounting officer as of the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021 and up to the date of this report as follows:
| Name and principal position | Year | Salary ($) | Bonus ($) | All other compensation ($) | Total ($) | |||||||||||||||
| Heng Fei Yang, Chief Executive Officer and Sole Director | 2022 | $ | 16,987 | — | $ | 16,987 | ||||||||||||||
| 2021 | $ | 19,533 | — | $ | 19,533 | |||||||||||||||
| Cong He, Chief Financial Officer | 2022 | $ | 29,386 | — | — | 29,386 | ||||||||||||||
| 2021 | $ | — | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
| 39 |
Employment Agreement with Heng Fei Yang
On December 18, 2019, the Company entered into an employment agreement with its Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”), Heng Fei Yang, pursuant to which he receives a monthly base salary of approximately $1,186 (equivalent to RMB $8000). Mr. Yang’s salary may be adjusted based on his work performance, in the sole discretion of the Company. Mr. Yang’s employment is for an initial term of two (2) years, which can be renewed thirty (30) days prior to the expiration of the term if both parties wish to extend. Mr. Yang may be entitled to a bonus, such amount to be determined, at the sole discretion of the Company. The agreement was extended to December 31, 2022.
The Company may terminate Mr. Yang’s employment for cause, at any time, without notice or remuneration, for certain acts, such as serious violation of the Company’s rules and regulations, gross neglect of duty and misconduct resulting in large economic losses, criminal acts and any breach of confidentiality or trade secrets.
Mr. Yang is not permitted to operate on his own or on behalf of other individuals or enterprises any business providing the same or similar competitive products or services. There is a customary confidentiality clause in Mr. Yang’s agreement whereby he has agreed to keep all confidential information confidential. Mr. Yang is not allowed to engage in any activities that may compete with the Company during the term of her employment, and for two years after the termination of her employment.
Employment Agreement with Cong He
On February 1, 2022, the Company entered into an employment agreement with its Chief Financial Officer, Cong He. Pursuant to Ms. He’s employment agreement, she received probationary monthly base salary of approximately $2,216 (equivalent to RMB $15,000) from February 1, 2022 to February 28, 2022. Ms. He currently receives a monthly base salary of approximately $2,393 ((equivalent to RMB $16,200). Ms. He’s salary may be adjusted based on her work performance, in the sole discretion of the Company. Ms. He’s employment is for an initial term of one (1) year, which can be renewed thirty (30) days prior to the expiration of the term if both parties wish to extend. Ms. He may be entitled to a bonus, such amount to be determined, at the sole discretion of the Company.
The Company may terminate Ms. He’s employment for cause, at any time, without notice or remuneration, for certain acts, such as serious violation of the Company’s rules and regulations, gross neglect of duty and misconduct resulting in large economic losses, criminal acts and any breach of confidentiality or trade secrets.
Ms. He is not permitted to operate on his own or on behalf of other individuals or enterprises any business providing the same or similar competitive products or services. There is a customary confidentiality clause in Ms. He’s agreement whereby she has agreed to keep all confidential information confidential. Ms. He is not allowed to engage in any activities that may compete with the Company during the term of her employment, and for two years after the termination of her employment.
Insurance
We do not maintain D&O insurance for our directors and officers.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships among our directors or executive officers. There are no arrangements with any major shareholders, customers or suppliers, pursuant to which any person above was appointed.
Committees of the Board
We currently do not have any committees under the board of directors.
Share Incentive Plan
We currently do not have any stock incentive plans.
| 40 |
The following table sets forth, as of the date of this prospectus, the beneficial ownership of our Ordinary Shares by each executive officer and director, by each person known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our Ordinary Shares and by the executive officers and directors as a group. As used in this table, “beneficial ownership” means the sole or shared power to vote, or to direct the voting of, a security, or the sole or shared investment power with respect to a security (i.e., the power to dispose of, or to direct the disposition of, a security). In addition, for purposes of this table, a person is deemed, as of any date, to have “beneficial ownership” of any security that such person has the right to acquire within 60 days after such date.
The persons named above have full voting and investment power with respect to the shares indicated. Under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission, a person (or group of persons) is deemed to be a “beneficial owner” of a security if he or she, directly or indirectly, has or shares the power to vote or to direct the voting of such security, or the power to dispose of or to direct the disposition of such security. Accordingly, more than one person may be deemed to be a beneficial owner of the same security. A person is also deemed to be a beneficial owner of any security, which that person has the right to acquire within 60 days, such as options or warrants to purchase our Ordinary Shares.
All of our shareholders, including the shareholders listed below, have the same voting rights attached to their Ordinary Shares. See “Description of share capital and articles of association”. None of our principal shareholders or our directors and executive officers have different or special voting rights with respect to their Ordinary Shares. Unless otherwise noted below, each shareholder’s address is, c/o Tian’an Technology Group Ltd., Room 104, Building 1-B, No. 3500, Xiupu Road, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China.
Except as otherwise indicated, all shares are owned directly and the percentage shown is based on 45,000,000 Ordinary Shares issued and outstanding, and 45,000,000 Ordinary Shares outstanding after the close of this offering.
| Title of Class | Name of Beneficial Owner | Amount of Beneficial Ownership | Percent of Class | |||||||
Current Executive Officers And Directors Ordinary Shares | Heng Fei Yang | 40,000,000 | 88.9 | % | ||||||
| Cong He | - | * | ||||||||
| Total of All Current Officers and Directors (2 persons): | 40,000,000 | 88.9 | % | |||||||
* Less than 1%
The following is a description of transactions during our preceding three fiscal years up to the date of this prospectus, to which we were a party or will be party, in which the amount involved exceeded or will exceed the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years, and any of our directors, executive officers or holders of more than 5% of our outstanding capital stock, or any immediate family member of, or person sharing the household with, any of these individuals or entities, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
On July 15, 2019, the Company entered into a loan agreement with one of its related parties, Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd (“Liaoning”), whereby Liaoning loaned the Company $459,315, without interest and with no collateral. The loan is due on demand. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, is the actual controlling owner of Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance of the loan was $196,625 and $459,315, respectively. At June 30, 2022, the outstanding balance was $186,581. The Company repaid the loan amount in August and September 2022 subsequently. As of the date of this report, the loan was paid in full.
On April 15, 2021, the Company entered into loan agreement with the Company’s CEO, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, in the principal amount of $293,493. The loan does not bear interest and has no collateral. The loan is due on demand. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance of the loan was $297,848 and $0, respectively. As of June 30, 2022, the outstanding balance of the loan was $43,809.
On April 8, 2021, the Company issued 100,000,000 ordinary shares, no par value to Heng Fei Yang, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer.
On July 13, 2022, Heng Fei Yang surrendered 60,000,000, no par value, ordinary shares back to the Company. He is currently the beneficial owner of 40,000,000 ordinary shares of the Company.
| 41 |
DESCRIPTION OF SHARE CAPITAL AND ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION
The following is a description of the material terms of our articles of association. The following description may not contain all of the information that is important to you, and we therefore refer you to our articles of association, a copy of which is filed with the SEC as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Share capital
We are a BVI business company limited by shares and our affairs are governed by our memorandum and articles of association, as amended and restated from time to time, and the BVI Business Companies Act (the “BVI Act”).
Pursuant to our memorandum and articles of association (“M&A”) the Company is authorized to issue an unlimited number of ordinary shares of a single class with no par value. There are currently 45,000,000 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. The Company may issue fractional shares. A fractional share shall have the corresponding fractional liabilities, limitations, preferences, privileges, qualifications, restrictions, rights and other attributes of a whole share of the same class and series.
Designations, Powers and Preferences of Shares
Each share in the Company confers upon the shareholder:
| a) | the right to one vote at a meeting of the shareholders of the Company or on any resolution of the shareholders; |
| b) | the right to an equal share in any dividend paid by the Company; and |
| c) | the right to an equal share in the distribution of the surplus assets of the Company on its liquidation. |
The directors may, at their discretion by resolution, redeem, purchase or otherwise acquire all or any of the shares in the Company in accordance with Regulation 3 of the M&A.
Variation of the Rights of Shareholders
As permitted by the BVI Act and our M&A, whenever the capital of our Company is divided into different classes, the rights attached to any such class may only be materially adversely varied with the consent in writing of the shareholders more than fifty percent (50%) of the issued shares of that class.
Rights conferred upon the holders of the shares of any class issued with preferred or other rights shall not, unless otherwise expressly provided by the terms of issue of the shares of that class, be deemed to be varied by the creation or issue of further shares ranking pari passu therewith.
Shareholder meetings
In accordance with, and subject to, our M&A, (a) any director may convene meetings of the members at such time and in such matter and places within our outside the British Virgin Islands as the director considers necessary and desirable; and (b) upon the written request of shareholders entitled to exercise thirty percent (30%) or more of the voting rights in respect of the matter for which the meeting is requested, the directors shall convene a meeting of shareholders within twenty eight (28) days of receiving the written request. Under BVI law, the M&A may be amended to decrease but not increase the required percentage to call a meeting above thirty per cent (30%).
In accordance with, and subject to, our M&A, (a) a meeting of shareholders held in contravention of the requirement to give notice is valid if shareholders holding at least ninety percent (90%) of the total voting rights on all the matters to be considered at the meeting have waived notice of the meeting; (c) a meeting of shareholders is duly constituted if, at the commencement of the meeting, there are present in person or by proxy one or more shareholders holding shares which carry in aggregate not less than a majority of all votes attaching to all shares in issue and entitled to vote at such meeting, and (d) if within half an hour from the time appointed for the meeting a quorum is not present, the meeting shall be dissolved.
Quorum
A quorum for a meeting of the members is duly constituted if, at the commencement of the meeting, there are present in person or by proxy, not less than fifty percent (50%) of the votes of the shares or class or series of shares entitled to vote on the resolutions of members to be considered at the meeting.
| 42 |
Transfer of Shares
Subject to any applicable restrictions or limitations arising pursuant to (i) our M&A; or (ii) the BVI Act, any of our shareholders may transfer all or any of his or her shares by an instrument of transfer in the usual or common form or in any other form which our directors may approve (such instrument of transfer being signed by the transferor and containing the name and address of the transferee). Our directors may decline to register any transfer of shares which is not fully paid up or on which our company has a lien.
Where shares are listed on a recognized exchange, the shares may be transferred without the need for a written instrument of transfer if the transfer is carried out in accordance with the laws, rules, procedures and other requirements applicable to shares registered on the recognized exchange and subject to the Company’s M&A.
Access to Corporate Records
Under the BVI Act, members of the general public, on payment of a nominal fee, can obtain copies of the public records of a company available at the office of the Registrar of Corporate Affairs which will include the company’s certificate of incorporation, its memorandum and articles of association (with any amendments) and records of license fees paid to date and will also disclose any liquidation plan, articles of merger or consolidation and any particulars of charges if either the Company or chargee have elected to file particulars of such charges.
A member of the Company is also entitled, upon giving written notice to us, to inspect (i) our memorandum and articles of association, (ii) the register of members, (iii) the register of directors, and (iv) minutes of meetings and resolutions of members and of those classes of members of which that member is a member, and to make copies and take extracts from the documents and records referred to in (i) to (iv) above.
Indemnification
The Company indemnifies against all expenses, including legal fees, and against all judgments, fine and amounts paid in settlement and reasonably incurred in connection with legal, administrative or investigative proceedings any person who
| a) | in or was a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed proceedings, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative, by reason of the fact that the person is or was a director of the Company; or |
| b) | is or was, at the request of the Company, serving as a director of, or in any other capacity is or was acting for, another body corporate or a partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise. |
Differences in Corporate Law
The BVI Act and the laws of the British Virgin Islands affecting British Virgin Islands companies like us and our shareholders differ from laws applicable to U.S. corporations and their shareholders. Set forth below is a summary of the significant differences between the provisions of the laws of the British Virgin Islands applicable to us and the laws applicable to companies incorporated in the United States and their shareholders.
| 43 |
Mergers and Similar Arrangements
Under the laws of the British Virgin Islands, two or more companies may merge or consolidate in accordance with Section 170 of the BVI Act. A merger means the merging of two or more constituent companies into one of the constituent companies (the “surviving company”) and a consolidation means the uniting of two or more constituent companies into a new company (the “consolidated company”). The procedure for a merger or consolidation between the company and another company (which need not be a BVI company, and which may be the company’s parent or subsidiary, but need not be) is set out in the BVI Act. In order to merge or consolidate, the directors of each constituent company must approve a written plan of merger or consolidation, which with the exception of a merger between a parent company and its subsidiary, must also be approved by a resolution of a majority of the shareholders voting at a quorate meeting of shareholders or by written resolution of the shareholders of the BVI company or BVI companies which are to merge. While a director may vote on the plan of merger or consolidation, or any other matter, even if he has a financial interest in the plan, the interested director must disclose the interest to all other directors of the company promptly upon becoming aware of the fact that he is interested in a transaction entered into or to be entered into by the company. A transaction entered into by our company in respect of which a director is interested (including a merger or consolidation) is voidable by us unless the director’s interest was (a) disclosed to the board prior to the transaction or (b) the transaction is (i) between the director and the company and (ii) the transaction is in the ordinary course of the company’s business and on usual terms and conditions. Notwithstanding the above, a transaction entered into by the company is not voidable if the material facts of the interest are known to the shareholders and they approve or ratify it or the company received fair value for the transaction. In any event, all shareholders must be given a copy of the plan of merger or consolidation irrespective of whether they are entitled to vote at the meeting to approve the plan of merger or consolidation. A foreign company which is able under the laws of its foreign jurisdiction to participate in the merger or consolidation is required by the BVI Act to comply with the laws of that foreign jurisdiction in relation to the merger or consolidation. The shareholders of the constituent companies are not required to receive shares of the surviving or consolidated company but may receive debt obligations or other securities of the surviving or consolidated company, other assets, or a combination thereof. Further, some or all of the shares of a class or series may be converted into a kind of asset while the other shares of the same class or series may receive a different kind of asset. As such, not all the shares of a class or series must receive the same kind of consideration. After the plan of merger or consolidation has been approved by the directors and authorized, if required, by a resolution of the shareholders, articles of merger or consolidation are executed by each company and filed with the Registrar of Corporate Affairs in the British Virgin Islands. The merger or consolidation is effective on the date that the articles of merger or consolidation are registered with the Registrar or on such subsequent date, not exceeding thirty days, as is stated in the articles of merger or consolidation.
As soon as a merger or consolidation becomes effective: (a) the surviving company or consolidated company (so far as is consistent with its memorandum and articles of association, as amended or established by the articles of merger or consolidation) has all rights, privileges, immunities, powers, objects and purposes of each of the constituent companies; (b) in the case of a merger, the memorandum and articles of association of any surviving company are automatically amended to the extent, if any, that changes to its memorandum and articles of association are contained in the articles of merger or, in the case of a consolidation, the memorandum and articles of association filed with the articles of consolidation are the memorandum and articles of the consolidated company; (c) assets of every description, including choses-in-action and the business of each of the constituent companies, immediately vest in the surviving company or consolidated company; (d) the surviving company or consolidated company is liable for all claims, debts, liabilities and obligations of each of the constituent companies; (e) no conviction, judgment, ruling, order, claim, debt, liability or obligation due or to become due, and no cause existing, against a constituent company or against any member, director, officer or agent thereof, is released or impaired by the merger or consolidation; and (f) no proceedings, whether civil or criminal, pending at the time of a merger or consolidation by or against a constituent company, or against any member, director, officer or agent thereof, are abated or discontinued by the merger or consolidation; but: (i) the proceedings may be enforced, prosecuted, settled or compromised by or against the surviving company or consolidated company or against the member, director, officer or agent thereof; as the case may be; or (ii) the surviving company or consolidated company may be substituted in the proceedings for a constituent company. The Registrar of Corporate Affairs shall strike off the register of companies each constituent company that is not the surviving company in the case of a merger and all constituent companies in the case of a consolidation. If the directors determine it to be in the best interests of the company, it is also possible for a merger or consolidation to be approved as a Court approved plan of arrangement or scheme of arrangement in accordance with the BVI Act.
A shareholder may dissent from (a) a merger if the company is a constituent company, unless the company is the surviving company and the member continues to hold the same or similar shares; (b) a consolidation if the company is a constituent company; (c) any sale, transfer, lease, exchange or other disposition of more than fifty percent (50%) in value of the assets or business of the company if not made in the usual or regular course of the business carried on by the company but not including: (i) a disposition pursuant to an order of the court having jurisdiction in the matter, (ii) a disposition for money on terms requiring all or substantially all net proceeds to be distributed to the members in accordance with their respective interest within one year after the date of disposition, or (iii) a transfer pursuant to the power of the directors to transfer assets for the protection thereof; (d) a compulsory redemption of ten percent (10%), or fewer of the issued shares of the company required by the holders of ninety percent (90%), or more of the shares of the company pursuant to the terms of the BVI Act; and (e) a plan of arrangement, if permitted by the British Virgin Islands Court (each, an Action). A shareholder properly exercising his dissent rights is entitled to a cash payment equal to the fair value of his shares.
| 44 |
A shareholder dissenting from an Action must object in writing to the Action before the vote by the shareholders on the merger or consolidation, unless notice of the meeting was not given to the shareholder. If the merger or consolidation is approved by the shareholders, the company must give notice of this fact to each shareholder within twenty (20) days who gave written objection. Such objection shall include a statement that the member proposes to demand payment for his or her shares if the Action is taken. These shareholders then have twenty (20) days to give to the company their written election in the form specified by the BVI Act to dissent from the Action, provided that in the case of a merger, the twenty (20) days starts when the plan of merger is delivered to the shareholder. Upon giving notice of his election to dissent, a shareholder ceases to have any shareholder rights except the right to be paid the fair value of his shares. As such, the merger or consolidation may proceed in the ordinary course notwithstanding his dissent. Within seven (7) days of the later of the delivery of the notice of election to dissent and the effective date of the merger or consolidation, the company shall make a written offer to each dissenting shareholder to purchase his shares at a specified price per share that the company determines to be the fair value of the shares. The company and the shareholder then have thirty (30) days to agree upon the price. If the company and a shareholder fail to agree on the price within the thirty (30) days, then the company and the shareholder shall, within twenty (20) days immediately following the expiration of the 30-day period, each designate an appraiser and these two appraisers shall designate a third appraiser. These three appraisers shall fix the fair value of the shares as of the close of business on the day prior to the shareholders’ approval of the transaction without taking into account any change in value as a result of the transaction.
Shareholders’ Suits
There are both statutory and common law remedies available to our shareholders as a matter of British Virgin Islands law. These are summarized below.
Prejudiced Members
A shareholder who considers that the affairs of the company have been, are being, or are likely to be, conducted in a manner that is, or any act or acts of the company have been, or are, likely to be oppressive, unfairly discriminatory or unfairly prejudicial to him in that capacity, can apply to the court under Section 184I of the BVI Act, inter alia, for an order that his shares be acquired, that he be provided compensation, that the Court regulate the future conduct of the company, or that any decision of the company which contravenes the BVI Act or our memorandum and articles of association be set aside.
Derivative Actions
Section 184C of the BVI Act provides that a shareholder of a company may, with the leave of the Court, bring an action in the name of the company in certain circumstances to redress any wrong done to it. Such actions are known as derivative actions. The BVI Court may only grant permission to bring a derivative action where the following circumstances apply:
| ● | the company does not intend to bring, diligently continue or defend or discontinue proceedings; and | |
| ● | it is in the interests of the company that the conduct of the proceedings not be left to the directors or to the determination of the shareholders as a whole. |
When considering whether to grant leave, the British Virgin Islands Court is also required to have regard to the following matters:
| ● | whether the shareholder is acting in good faith; | |
| ● | whether a derivative action is in the company’s best interests, taking into account the directors’ views on commercial matters; | |
| ● | whether the action is likely to proceed; | |
| ● | the costs of the proceedings; and | |
| ● | whether an alternative remedy is available. |
| 45 |
Restraining or Compliance Order
If a BVI company or a director of a BVI company engages in, proposes to engage in or has engaged in, conduct that contravenes the BVI Act or the memorandum or articles of the company, the Court may, on the application of a shareholder of the company pursuant to Section 184B of the BVI Act, make an order directing the company or director to comply with, or restraining the company or director from engaging in conduct that contravenes, the BVI Act or the company’s memorandum or articles.
Just and Equitable Winding Up
In addition to the statutory remedies outlined above, shareholders can also petition the BVI Court for the winding up of a company under the BVI Insolvency Act, 2003 (as amended), for the appointment of a liquidator to liquidate the company and the court may appoint a liquidator for the company if it is of the opinion that it is just and equitable for the court to so order. Save in exceptional circumstances, this remedy is generally only available where the company has been operated as a quasi-partnership and trust and confidence between the partners has broken down.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
Our transfer agent is Equity Stock Transfer, located at 237 W 37th St., #602, New York, New York, 10018, with a telephone number of (212) 575-5757.
The Shares being offered by the Selling Stockholders are those issued to the Selling Stockholders pursuant to the Purchase Agreements. We are registering the Shares in order to permit the Selling Stockholders to offer such Shares for resale from time to time. Except for the ownership of the Shares, the transactions contemplated pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, and as disclosed in this section under “Material Relationships with Selling Stockholders”, none of the Selling Stockholders have had any material relationship with us within the past three years.
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with Rule 13d-3(d) promulgated by the SEC under the Exchange Act. The percentage of shares beneficially owned prior to the offering is based on 45,000,000 Ordinary Shares outstanding as of September 14, 2022.
None of the Selling Shareholders are a registered broker-dealer or an affiliate of a registered broker-dealer. None of the Selling Shareholders nor any of their respective affiliates have held a position or office, or had any other material relationship, with us or any of our predecessors or affiliates. The Selling Shareholders have acquired their shares solely for investment and not with a view to or for resale or distribution of such securities.
| 46 |
For each Selling Shareholder named below, the number indicated in the column entitled “Beneficial Ownership Before the Offering” includes the Shares owned by each such Selling Shareholder. The number in the column entitled “Beneficial Ownership After the Offering” assumes that all the Shares being registered in this prospectus for said Selling Shareholder are being sold.
| Selling Stockholder | Beneficial Ownership Before the Selling Shareholders Offering | Number of Shares Being Offered | Beneficial Ownership After the Selling Shareholders Offering | Percentage Of Ownership After the Selling Shareholders Offering | ||||||||||||
| Lu Hai-zhi | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wu Hong-hui | 100,000 | 100,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Zheng-zhou | 100,000 | 100,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xiao Wei-juan | 30,000 | 30,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zheng Dong-qing | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Jiang Hai-hua | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wu Cai-chen | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhou Zhi-ying | 600,000 | 600,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Huang Xia-mei | 220,000 | 220,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen He-ping | 80,000 | 80,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Dan-juan | 30,000 | 30,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Li Ai-jun | 40,000 | 40,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Hu Yan-ping | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yu Pei-xin | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Shu-xia | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Pan You-rui | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Shen Ya-ping | 150,000 | 150,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Lin Fei | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Wen-jun | 300,000 | 300,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Ma Fei | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yuan Xue-ya | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xu Ming-hua | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Li Ming-ji | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Shi Cong-zhe | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Jiang Wei | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Meng Qing-hui | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Fu Rao | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Bai Li | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Liu Ying | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Jiang Xiu-yan | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhu Ge-meng | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhang Shu-mei | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Feng jia-wang | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Li Xiao-di | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Li Jing-chun | 30,000 | 30,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen Shan-fen | 40,000 | 40,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| ZhangLian-zhen | 60,000 | 60,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Lai Bi-ying | 30,000 | 30,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xie Yue-qiao | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Chun-lv | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Jiang Ying | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yi Xiu-ying | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen Li-li | 200,000 | 200,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhang Shu-bo | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xian Hong | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhang Peng | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Hu Fang-bin | 50,000 | 50,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wei Bin-hai | 200,000 | 200,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wei Jian-mei | 450,000 | 450,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Shen Wan-ting | 450,000 | 450,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yu Wei-xing | 100,000 | 100,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen Yan | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Liu Ying | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Zhao Yong-wei | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yan Ai-jun | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Li Ping | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Liu Ying | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen Fu-sheng | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Wang Mei-lan | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xie Wei-guang | 20,000 | 20,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Jiang Li-fen | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Chen Ai-qun | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Yang Wen-juan | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Sang Su | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Xiong Mei-jun | 10,000 | 10,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Liu Guang-na | 750,000 | 750,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| TOTAL | 5,000,000 | 5,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
| 47 |
The Selling Stockholders and any of their respective pledgees, assignees and successors-in-interest may, from time to time, sell any or all of their securities covered hereby on any trading market, stock exchange or other trading facility on which the securities are traded or in private transactions. These sales may be at fixed or negotiated prices. The Selling Stockholders may use any one or more of the following methods when selling securities:
| ● | ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers; | |
| ● | block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the securities as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; | |
| ● | purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account; | |
| ● | an exchange distribution in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange; | |
| ● | privately negotiated transactions; | |
| ● | settlement of short sales; | |
| ● | in transactions through broker-dealers that agree with the selling shareholders to sell a specified number of such securities at a stipulated price per security; | |
| ● | through the writing or settlement of options or other hedging transactions, whether through an options exchange or otherwise; | |
| ● | a combination of any such methods of sale; or | |
| ● | any other method permitted pursuant to applicable law. |
The Selling Stockholders may also sell securities under Rule 144 under the Securities Act, if available, rather than under this prospectus.
Broker-dealers engaged by the selling shareholders may arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the selling shareholders (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of securities, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated, but, except as set forth in a supplement to this prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary brokerage commission in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction a markup or markdown in compliance with FINRA IM-2440.
In connection with the sale of the securities covered hereby, the Selling Stockholders may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions, which may in turn engage in short sales of the securities in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The Selling Stockholders may also sell securities short and deliver these securities to close out their short positions, or loan or pledge the securities to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The selling shareholders may also enter into option or other transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or create one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to such broker-dealer or other financial institution of securities offered by this prospectus, which securities such broker-dealer or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
The Selling Stockholders and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the securities may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the securities purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act. We are requesting that each Selling Stockholder inform us that it does not have any written or oral agreement or understanding, directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the securities. We will pay certain fees and expenses incurred by us incident to the registration of the securities.
| 48 |
Because the Selling Stockholders may be deemed to be an “underwriter” within the meaning of the Securities Act, they will be subject to the prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act, including Rule 172 thereunder. In addition, any securities covered by this prospectus which qualify for sale pursuant to Rule 144 under the Securities Act may be sold under Rule 144 rather than under this prospectus. We are requesting that each selling shareholder confirm that there is no underwriter or coordinating broker acting in connection with the proposed sale of the resale securities by the Selling Stockholders.
We intend to keep this prospectus effective until the earlier of (i) the date on which the securities may be resold by the selling shareholders without registration and without regard to any volume or manner-of-sale limitations by reason of Rule 144, without the requirement for us to be in compliance with the current public information requirement under Rule 144 under the Securities Act or any other rule of similar effect or (ii) all of the securities have been sold pursuant to this prospectus or Rule 144 under the Securities Act or any other rule of similar effect. The resale securities will be sold only through registered or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the resale securities covered hereby may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations under the Exchange Act, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale securities may not simultaneously engage in market making activities with respect to the common stock for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M, prior to the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the selling shareholders will be subject to applicable provisions of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing of purchases and sales of the common stock by the Selling Stockholders or any other person. We will make copies of this prospectus available to the Selling Stockholders and are informing the selling shareholders of the need to deliver a copy of this prospectus to each purchaser at or prior to the time of the sale (including by compliance with Rule 172 under the Securities Act).
The validity of the Ordinary Shares offered in this offering and certain legal matters as to British Virgin Island law will be passed upon for us by _____.
Certain legal matters of United States federal securities laws in connection with this offering will be passed upon by The Crone Law Group, P.C.
The consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 included in this prospectus have been audited by HHC, an independent registered public accounting firm. HHC has presented their report with respect to our audited financial statements. The report of HHC, appearing elsewhere herein, is included in reliance upon their authority as experts in accounting and auditing, and which report which report expresses an unqualified opinion on the financial statements and includes an explanatory paragraph referring to substantial doubt that exists regarding the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. The offices of HHC are located at 110-20 71st Ave Suite 633, Forest Hills, NY 11375.
ENFORCEABILITY OF CIVIL LIABILITIES
We are incorporated under the laws of the BVI. Service of process upon us and upon our director and officer who resides outside the United States, may be difficult to obtain within the United States. Furthermore, because all of our assets and our director and officer is located outside the United States, any judgment obtained in the United States against us or our director and officer may not be collectible within the United States.
We have irrevocably appointed The Crone Law Group, P.C. as our agent to receive service of process in any action against us in any U.S. federal or state court arising out of this offering or any purchase or sale of securities in connection with this offering. The address of our agent is 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 2446, New York, NY 10170.
| 49 |
The Company believes that it may be difficult to initiate an action with respect to U.S. securities law in BVI. British Virgin Islands courts may refuse to hear a claim based on an alleged violation of U.S. securities laws reasoning that China is not the most appropriate forum to hear such a claim. In addition, even if a BVI court agrees to hear a claim, it may determine that BVI law and not U.S. law is applicable to the claim. If U.S. law is found to be applicable, the content of applicable U.S. law must be proved as a fact by expert witnesses which can be a time-consuming and costly process. Certain matters of procedure may also be governed by BVI law.
Subject to certain time limitations and legal procedures, BVI courts may enforce a U.S. judgment in a civil matter which, subject to certain exceptions, is non-appealable, including judgments based upon the civil liability provisions of the Securities Act and the Exchange Act and including a monetary or compensatory judgment in a non-civil matter, provided that:
| ● | the judgment was rendered by a court which was, according to the laws of the state of the court, and the rules of private international law currently prevailing in the British Virgin Islands competent to render the judgment; | |
| ● | the obligation imposed by the judgment is enforceable according to the rules relating to the enforceability of judgments in the British Virgin Islands and the substance of the judgment is not contrary to public policy; and | |
| ● | the judgment is executory in the state in which it was given. |
Even if these conditions are met, a BVI court may not declare a foreign civil judgment enforceable if:
| ● | the judgment was given in a state whose laws do not provide for the enforcement of judgments of BVI courts (subject to exceptional cases); | |
| ● | the enforcement of the judgment is likely to prejudice the sovereignty or security of the British Virgin Islands; | |
| ● | the judgment was obtained by fraud; | |
| ● | the opportunity given to the defendant to bring its arguments and evidence before the court was not reasonable in the opinion of the BVI court; | |
| ● | the judgment was rendered by a court not competent to render it according to the laws of private international law as they apply in the British Virgin Islands; | |
| ● | the judgment is contradictory to another judgment that was given in the same matter between the same parties and that is still valid; or | |
| ● | at the time the action was brought in the foreign court, a lawsuit in the same matter and between the same parties was pending before a court or tribunal in the British Virgin Islands. |
WHERE YOU CAN FIND ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
We have filed a registration statement, including relevant exhibits, with the SEC on Form F-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the Ordinary Shares to be sold in this offering. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement on Form F-1, does not contain all of the information contained in the registration statement. You should read our registration statement and its exhibits and schedules for further information with respect to us and our Ordinary Shares.
| 50 |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Table of Contents
| 51 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| As of June 30, | As of December 31, | |||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 13,863 | $ | 456 | ||||
| Other receivables | 2,065 | 2,094 | ||||||
| Inventories | 30,357 | 31,991 | ||||||
| Advances to suppliers | 15,427 | 16,257 | ||||||
| VAT credit | 465 | 11,580 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 62,177 | 62,378 | ||||||
| Noncurrent Assets: | ||||||||
| Equipment, net | 1,607 | 2,277 | ||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | 10,451 | 13,812 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 74,235 | $ | 78,467 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 459 | $ | - | ||||
| Payroll payable | 7,902 | 31,653 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities - current portion | 7,053 | 5,683 | ||||||
| Advance from customers | 448 | 472 | ||||||
| Due to related parties | 230,390 | 494,473 | ||||||
| Loan payables | - | 110,110 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 246,252 | 642,391 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities - noncurrent portion | 4,394 | 7,604 | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 250,646 | 649,995 | ||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | - | - | ||||||
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||||||||
| Common Stock, No par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized; 100,000,000 shares issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021 | - | - | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 500,000 | - | ||||||
| Accumulated deficits | (680,290 | ) | (533,822 | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive loss | 3,879 | (37,706 | ) | |||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | (176,411 | ) | (571,528 | ) | ||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 74,235 | $ | 78,467 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-1 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
(Unaudited)
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | - | $ | 22,008 | ||||
| Cost of revenue | - | 16,815 | ||||||
| Gross profit | - | 5,193 | ||||||
| Operating Expenses: | ||||||||
| Research and development | 7,578 | 20,390 | ||||||
| Selling and marketing | 8,296 | 9,129 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 130,365 | 46,640 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 146,239 | 76,159 | ||||||
| Operating loss | (146,239 | ) | (70,966 | ) | ||||
| Other Income (Expense): | ||||||||
| Interest income, net | 38 | 6 | ||||||
| Other expense, net | (267 | ) | (1,044 | ) | ||||
| Other loss, net | (229 | ) | (1,038 | ) | ||||
| Loss before income taxes | (146,468 | ) | (72,004 | ) | ||||
| Income taxes | - | - | ||||||
| Net loss | (146,468 | ) | (72,004 | ) | ||||
| Other Comprehensive Loss: | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | 41,585 | (5,211 | ) | |||||
| Comprehensive loss | $ | (104,883 | ) | $ | (77,215 | ) | ||
| Loss per common share, basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 100,000,000 | 100,000,000 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-2 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(Unaudited)
| Common Stock | Additional | Accumulated | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Shares | Common Stock | Paid-in Capital | Deficits | Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | 100,000,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (306,409 | ) | $ | 2,331 | $ | (304,078 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | (108,158 | ) | - | (108,158 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | - | (26,237 | ) | (26,237 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | 100,000,000 | - | - | (414,567 | ) | (23,906 | ) | (438,473 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | (119,255 | ) | - | (119,255 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | - | (13,800 | ) | (13,800 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | 100,000,000 | - | - | (533,822 | ) | (37,706 | ) | (571,528 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | (146,468 | ) | - | (146,468 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Collection of subscription receivables | - | - | 500,000 | - | - | 500,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | - | 41,585 | 41,585 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2022 | 100,000,000 | $ | - | $ | 500,000 | $ | (680,290 | ) | $ | 3,879 | $ | (176,411 | ) | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-3 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited)
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||
| Net Loss | $ | (146,468 | ) | $ | (72,004 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to Reconcile Net Loss to Net Cash Used in Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 3,667 | 4,962 | ||||||
| Written off of doubtful accouts | - | (541 | ) | |||||
| Other receivables | (81 | ) | (1,516 | ) | ||||
| Inventories | - | (13,234 | ) | |||||
| Advances to suppliers | - | (20,743 | ) | |||||
| VAT credit | 10,895 | (456 | ) | |||||
| Accounts payable | 475 | 3,544 | ||||||
| Advance from customers | - | 6,027 | ||||||
| Payroll payable | (22,916 | ) | 10,147 | |||||
| Lease liabilities | (1,547 | ) | (9,094 | ) | ||||
| Due from related parties | - | 5,449 | ||||||
| Net Cash Used in Operating Activities | (155,975 | ) | (87,459 | ) | ||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||
| Collection of subscription receivables | 500,000 | - | ||||||
| Loans from related parties | 61,814 | 262,708 | ||||||
| Repayments to related parties | (309,068 | ) | (154,549 | ) | ||||
| Repayments to loan payables | (108,174 | ) | - | |||||
| Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities | 170,096 | 108,159 | ||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY INVESTING ACTIVITIES | - | - | ||||||
| Effect Of Exchange Rate Changes On Cash | 24,810 | 136 | ||||||
| Net Increase in Cash | 13,407 | 20,836 | ||||||
| Cash, beginning of year | 456 | 7,998 | ||||||
| Cash, end of year | $ | 13,863 | $ | 28,834 | ||||
| Supplemental Disclosure Of Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||
| Interest | $ | 38 | $ | 6 | ||||
| Income taxes | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| NON-CASH TRANSACTIONS OF INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||
| Establishment of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for new leases | $ | - | $ | 17,131 | ||||
| Reduction of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for cancelation of old leases | $ | - | $ | 17,909 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-4 |
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. And Subsidiaries
Notes to Unaudited Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTE 1 – NATURE OF OPERATIONS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The consolidated financial statements included data of Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. (“Tian’an”), a holding company incorporated in the British Virgin Islands on April 8, 2021; Yunke Jingrong Information Technology, Co., Ltd. (“Yunke”), a holding company incorporated in Hong Kong on October 27, 2021 and Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Qige”), an operating company incorporated in China (PRC) on August 10, 2016. Shanghai Qige is a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Tian’an. Tian’an, Yunke and Shanghai Qige are collectly referred to as “the Company”. Currently, all of the Company’s operations are conducted through Shanghai Qige. Tian’An and Yunke are holding companies and have no operations. The Company was organized to research, develop, design, sell and service its power drive product systems. The Company’s main products are its Xuan Vector Brushless DC Contoller and its XuanBo Brushless DC Motor. These products are used in low-speed electric vehicles, such as electric forklifts, golf carts, street sweepers and other types of specialized field vehicles.
The Company’s initial marketing efforts are focused on the Eastern China with the intention of developing a nationwide marketing network. Other than providing controllers and motors, Shanghai Qige offers after sale services to its clients.
| Name of Consolidated Companies | Domicile and Date of Incorporation | Paid in Capital | Percentage of Effective Ownership | PercentaPrincipal Activities | ||||
| Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. | April 8, 2021, British Virgin Islands | USD $0 | 100% owned by Mr. Hengfei Yang | Investment holding | ||||
| Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd. | October 27, 2021, PRC | USD $0 | 100% owned by Tian’an | Investment holding | ||||
| Shanghai Quige Power Technology Co., Ltd. | August 10, 2016, PRC | USD $0 | 100% owned by Yunke | Production and distribution of power drive product systems |
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation:
The unaudited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“ US GAAP”) for interim financial information pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”); however, the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been translated and presented in United States Dollars (“USD”). The unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant inter-company transactions and balances have been eliminated. All significant inter-company accounts and transactions have been eliminated. The consolidated financial statements include all adjustments that, in the opinion of management, are necessary to make the financial statements not misleading.
Use of Estimates and Assumptions
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities on the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Management bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions and information that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Estimates and assumptions of future events and their effects cannot be perceived with certainty and, accordingly, these estimates may change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained, and as the Company’s operating environment changes. Significant estimates and assumptions by management include, among others, useful life and impairment analysis of long-lived assets, valuation of inventory and right-of-use assets and liabilities, allowance for credit loss of financial assets, other receivables and prepayments. While management believes that the estimates and assumptions used in the preparation of the financial statements are appropriate, actual results could differ from those estimates. Estimates and assumptions are periodically reviewed and the effects of revisions are reflected in the financial statements in the period they are determined to be necessary.
| F-5 |
Concentrations of Business and Credit Risks
All of the Company’s manufacturing is located in the PRC. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to successfully continue to manufacture its products and failure to do so would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows. Moreover, the success of the Company’s operations is subject to numerous contingencies, some of which are beyond management’s control. These contingencies include general economic conditions, prices of raw materials, competition, governmental and political conditions, and changes in regulations. Since the Company is dependent on trade in the PRC, the Company is subject to various additional political, economic and other uncertainties. Among other risks, the Company’s operations will be subject to the risks of restrictions on transfer of funds, domestic customs, changing taxation policies, foreign exchange restrictions, and political and governmental regulations. The Company operates in China, which may give rise to significant foreign currency risks from fluctuations and the degree of volatility of foreign exchange rates between United States dollars (“USD”) and the Chinese currency Renminbi (“RMB”). The results of operations denominated in foreign currency are translated at the average rate of exchange during the reporting periods.
Risks and Uncertainties
The recent outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19 has spread across the globe and is impacting worldwide economic activity. Conditions surrounding the coronavirus continue to rapidly evolve and government authorities have implemented emergency measures to mitigate the spread of the virus. The outbreak and the related mitigation measures have had and will continue to have a material adverse impact on global economic conditions as well as on the Company’s business activities. The extent to which COVID-19 may impact the Company’s business activities will depend on future developments, such as the ultimate geographic spread of the disease, the duration of the outbreak, travel restrictions, business disruptions, and the effectiveness of actions taken in the United States and other countries to contain and treat the disease. These events are highly uncertain and, as such, the Company cannot determine their financial impact at this time. No adjustments have been made to the amounts reported in these consolidated financial statements as a result of this matter.
Statements of Cash Flows
In accordance with Statement FASB ASC Topic 230, “Statement of Cash Flows”, cash flow from the Company’s operations is calculated based upon the local currencies and translated to the reporting currency using an average foreign exchange rate for the reporting period. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported in the statements of cash flows will not necessarily be the same as the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
Cash
Cash consist primarily of cash on hand and cash in banks which is readily available in checking and saving accounts. The Company maintains cash with various financial institutions in the PRC where its accounts are uninsured. The Company has not experienced any losses from funds held in bank accounts and believes it is not exposed to any risk on its bank accounts.
Advances to Suppliers
The Company periodically makes advances to certain vendors for purchases of raw materials or to service providers for services and records these payments as advances to suppliers. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, advances to suppliers amounted to $15,427 and $16,257, respectively.
| F-6 |
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value. The Company used the weighted average cost method of accounting for inventories. Inventories on hand are evaluated on an on-going basis to determine if any items are obsolete, spoiled, or in excess of future demand. During the on-going evaluation of inventories, if any items of inventories has been determined to be obsolete or spoiled, and the Company will not be able to sell it at a normal profit above its carrying cost, an allowance for impairment of those inventories items will be provided and charged directly to cost of revenue at the period of the impairment determined. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the Company recorded $0 for inventory valuation allowance, respectively.
Equipment
Equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation, and include expenditures that substantially increase the useful lives of existing assets.
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Estimated useful lives are as follows:
| Operating Equipment | 5 years | |
| Office equipment | 5 years |
The cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets sold or otherwise retired are eliminated from the accounts, and any gain or loss is included in the consolidated statements of operations. Maintenance, repairs, and minor renewals are charged directly to expenses as incurred. Significant renewals and betterment to buildings and equipment are capitalized. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the lesser of the useful life or the life of the lease.
Leases
The Company leases space from third parties as its plant sites or office. In accordance with Statement FASB ASC Topic 842, the Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the commencement date of the of the lease contract and recognizes in profit or loss the lease cost or expense during the lease term. As an accounting policy, the Company elect not to recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability requirements to short-term leases, which with a term of 12 months or less, instead, recognizes the lease payments in profit or loss on a straight-line basis over the lease term and variable lease payments in the period in which the obligation for those payments is incurred. The Company generally uses an incremental borrowing rate and discount rate to measure its lease liabilities, as the rate implicit in the lease is typically not readily determinable. Certain lease agreements include renewal options that are under the company’s control. The Company includes optional renewal periods in the lease term only when it is reasonably certain that the Company will exercise its option.
Variable lease payments include payments to lessors for taxes, maintenance, insurance and other operating costs as well as payments that are adjusted based on an index or rate. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any significant residual value guarantees or restrictive covenants.
Revenue Recognition
We adopted Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) Topic 606, Revenues from Contract with Customers (“ASC 606”) for all periods presented. Under ASC 606, revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods and services is transferred to the Company’s customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that we expect to be entitled to in exchange for those goods and services, net of value-added tax. We determine revenue recognition through the following steps:
| ● | Identify the contract with a customer; | |
| ● | Identify the performance obligations in the contract; | |
| ● | Determine the transaction price; | |
| ● | Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and | |
| ● | Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. |
| F-7 |
The transaction price is allocated to each performance obligation on a relative standalone selling price basis. The transaction price allocated to each performance obligation is recognized when that performance obligation is satisfied by the control of the promised goods and services is transferred to the customers, which at a point in time or over time as appropriate.
Our revenues are net of value added tax (“VAT”) collected on behalf of PRC tax authorities in respect to the sales of merchandise. VAT collected from customers, net of VAT paid for purchases, is recorded as a liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets until it is paid to the relevant PRC tax authorities.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company measures its financial and non-financial assets and liabilities, as well as makes related disclosures, in accordance with FASB Accounting Standards Codification No. 820, Fair Value Measurement (“ASC 820”), which provides guidance with respect to valuation techniques to be utilized in the determination of fair value of assets and liabilities. Approaches include, (i) the market approach (comparable market prices), (ii) the income approach (present value of future income or cash flow), and (iii) the cost approach (cost to replace the service capacity of an asset or replacement cost). ASC 820 utilizes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The following is a brief description of those three levels:
Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions, such as valuations derived from valuation techniques in which one more significant inputs or significant value drivers are unobservable.
Loss per Common Share
The basic loss per share is calculated by dividing the Company’s net loss available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares during the year. The diluted loss per share is calculated by dividing the Company’s net loss available to common shareholders by the diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding during the year. The diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding is the basic weighted number of shares adjusted for any potentially dilutive debt or equity. Diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share due to the lack of dilutive instruments in the Company. For the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, the Company had no potential dilutive common stock equivalents outstanding.
Income Taxes
The Company is governed by the Income Tax Law and associated legislations of the PRC. The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC 740 “Income Taxes” (formerly SFAS No. 109 Accounting for Income Taxes), which is an asset and liability approach that requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s financial statements or tax returns. ASC 740 additionally requires the establishment of a valuation allowance to reflect the likelihood of realization of deferred tax assets. Realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon future earnings, if any, of which the timing and amount are uncertain.
According to ASC 740, the evaluation of a tax position is a two-step process. The first step is to determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of any related appeals or litigation based on the technical merits of that position. The second step is to measure a tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not threshold to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in the financial statements. A tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Tax positions that previously failed to meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold should be recognized in the first subsequent period in which the threshold is met. Previously recognized tax positions that no longer meet the more-likely-than-not criteria should be de-recognized in the first subsequent financial reporting period in which the threshold is no longer met. ASC 740 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosures, and transition.
| F-8 |
Translation of Foreign Currencies
For subsidiaries where the functional currency is other than the U.S. dollar, the Company uses the period-end exchange rates to translate assets and liabilities, the average monthly exchange rates to translate revenue and expenses, and historical exchange rates to translate shareholders’ equity, into U.S. dollars. The Company records translation gains and losses in accumulated other comprehensive loss as a component of shareholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheet.
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Year ended RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1573 | 0.1531 | ||||||
| Average yearly RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1550 | 0.1449 | ||||||
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Period ended RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1493 | 0.1549 | ||||||
| Average yearly RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1545 | 0.1545 | ||||||
Comprehensive Loss
The Company’s comprehensive loss includes net loss and unrealized gains and losses on foreign currency translation adjustments. Foreign currency translation adjustment for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, the Company reported $41,585 and $(5,211) as foreign currency translation adjustment.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting, which amends ASC Topic 848, Reference Rate Reform. This ASU provides optional expedients and exceptions for applying GAAP to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions affected by reference rate reform if certain criteria are met. This new guidance is optional and may be elected over time through December 31, 2022 as reference rate reform activities occur. This new guidance is not expected to have a material impact on the Corporation’s consolidated financial statements.
In October 2021, the FASB issued ASU 2021-08, Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers, which amends ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations, The ASU improves the accounting for acquired revenue contracts with customers in a business combination by addressing diversity in practice and inconsistency related to the (1) recognition of an acquired contract liability and (2) payment terms and their direct effect on subsequent revenue recognized by the acquirer. ASU 2021-08 is effective for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2022. Management has not yet evaluated the impact of this ASU on the consolidated financial statements.
The Company does not believe that above recently issued effective pronouncements, or pronouncements issued but not yet effective, if adopted, would have a material effect on the accompanying financial statements.
| F-9 |
NOTE 2 – GOING CONCERN
As of June 30, 2022, the Company has incurred an accumulated deficit of $680,290 and a negative working capital of $184,075. The Company will require additional funding to meet its ongoing obligations and to fund anticipated operating losses. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent on raising capital to fund its business plan and ultimately to attain profitable operations. Accordingly, these factors raise substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern from a period of one year from the issuance of these financial statements. The Company intends to continue to fund its business by way of private placements and financing support from related parties as may be required. These financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts or amounts and classification of liabilities that might result from this uncertainty.
NOTE 3 – INVENTORIES
Inventories consist of the following:
| June 30, 2022 | December 31, 2021 | |||||||
| Finished goods | $ | 30,357 | $ | 31,991 | ||||
| Less: impairment loss | - | - | ||||||
| Inventory, net | $ | 30,357 | $ | 31,991 | ||||
During the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, the Company recognized $0, respectively, as impairment loss from inventory.
NOTE 4 – EQUIPMENT, NET
Equipment consisted of the following:
| June 30, 2022 | December 31, 2021 | |||||||
| Office equipment | $ | 1,045 | $ | 1,101 | ||||
| Operating equipment | 5,821 | 6,135 | ||||||
| 6,866 | 7,236 | |||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (5,259 | ) | (4,959 | ) | ||||
| Equipment, net | $ | 1,607 | $ | 2,277 | ||||
Depreciation expenses for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 were $573 and $573, respectively. Management evaluates if any circumstance change that make aggregate undiscounted future cash flow generated by these equipment will less than its carrying amount at less in annual basis. There are no any impairment situation for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
NOTE 5 – LEASES
The Company’s lease portfolio primarily consists of real estate properties. The following table summarizes the amounts and location of operating and finance leases on the consolidated balance sheets:
| Balance Sheet Caption | June 30, 2022 | December 31, 2021 | ||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||
| Operating | Right-of-use assets | $ | 10,451 | $ | 13,812 | |||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||||
| Total lease assets | $ | 10,451 | $ | 13,812 | ||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||
| Operating | ||||||||||
| Current | Lease liabilities – current portion | $ | 7,053 | $ | 5,683 | |||||
| Noncurrent | Lease liabilities – noncurrent portion | 4,394 | 7,604 | |||||||
| Finance | ||||||||||
| Current | - | - | ||||||||
| Noncurrent | - | - | ||||||||
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 11,447 | $ | 13,287 | ||||||
| F-10 |
The following table summarizes the lease costs recognized in the consolidated statements of earnings:
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Operating lease cost | $ | 3,094 | $ | 4,389 | ||||
| Short-term lease cost | - | - | ||||||
| Variable lease cost | - | - | ||||||
| Total lease cost | $ | 3,094 | $ | 4,389 | ||||
Sublease income for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were insignificant.
The following table presents the weighted-average remaining lease term and weighted-average discount rate for operating and finance leases:
| June 30, 2022 | December 31, 2021 | |||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) | ||||||||
| Operating | 1.83 | 2.33 | ||||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate | ||||||||
| Operating | 6.05 | % | 6.05 | % | ||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||
The following table presents supplementary cash flow information regarding the company’s leases:
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | ||||||||
| Operating cash flows from operating activities | $ | 1,547 | $ | 9,094 | ||||
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liabilities | $ | - | $ | 17,131 | ||||
| Reduction of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for cancelation of old leases | $ | - | $ | 17,909 | ||||
The following table summarizes the future maturities of the Company’s operating lease liabilities as of June 30, 2022:
| Operating Leases | ||||
| 2022 | $ | 5,977 | ||
| 2023 | 5,978 | |||
| 2024 | - | |||
| 2025 | - | |||
| 2026 | - | |||
| Thereafter | - | |||
| Total lease payments | 11,955 | |||
| Less: interest | (508 | ) | ||
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 11,447 | ||
| F-11 |
NOTE 6 – LOAN PAYABLES
On November 20, 2021, the Company entered into a loan agreement of $108,500 with Shenzhen Shihong Education and Culture Ltd. The loan is due on November 22, 2022 without any interest charge if the loan is repaid upon maturity. If the loan is not fully repaid on or before November 22, 2022, the Company will be charged 0.03% interest rate per day. On May 20, 2022, the Company had repaid $108,174 of the loan. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the ending balance of loan payables was $0 and $110,110, respectively.
NOTE 7 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Due to related parties
On July 15, 2019, the Company entered into a loan agreement of $459,315 with one of its related parties, Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd., without interest any charge and no collateral. The loan is due on demand. The Company’s CEO, Mr. Hengfei Yang, is the actual controlling owner of Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd. During the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, the Company repaid $0 and $154,549, respectively. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the outstanding balance of the loan was $186,581 and $196,625, respectively. The loan had been repaid during the third quarter of 2022.
During the first half year of 2022 and 2021, the Company borrowed $61,814 and $262,708 from one of its related parties, Mr. Hengfei Yang, without any interest charge and no collateral. The loan is due on demand. Mr. Hengfei Yang is the Company’s CEO. During the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, the Company repaid $309,068 and $0, respectively. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the outstanding balance of the loan was $43,809 and $297,848, respectively.
NOTE 8 – EQUITY
The Company is authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock without par value. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, it had 100,000,000 shares outstanding, respectively.
On July 13, 2022, the Company’s CEO, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, surrendered 60,000,000, no par value, ordinary shares back to the Company. He is currently the beneficial owner of 40,000,000 ordinary shares of the Company.
On August 22, 2022, the Company issued 500,000 shares of common stock for RMB 3,400,700 or approximately $500,000 which had been collected during the second quarter of 2022.
NOTE 9 – TAXES
Income Taxes
British Virgin Islands (“BVI”)
Tian’an is registered in BVI and are not subject to tax on income or capital gain. In addition, payments of dividends by Tian’an to their shareholders are not subject to withholding tax in the BVI.
Hong Kong
The Company’s subsidiary, Yunke, is incorporated in Hong Kong and has no operating profit or tax liabilities during the period. Yunke is subject to tax at 16.5% on the assessable profits arising in or derived from Hong Kong.
| F-12 |
The PRC
The Company’s subsidiary operating in the PRC is subject to the Corporate Income Tax Law of the PRC at a unified income tax rate of 25%. The reconciliation of income tax rate to the effective income tax rate for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 from our continuing operation is as follows:
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Loss before income taxes from operations in the PRC | $ | (146,468 | ) | $ | (72,004 | ) | ||
| Statutory income tax rate | 25 | % | 25 | % | ||||
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | (36,617 | ) | (18,001 | ) | ||||
| Tax effect of non-deductible items | - | - | ||||||
| Valuation allowance of deferred tax assets | 36,617 | 18,001 | ||||||
| Income tax expense | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
Management believes that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be fully realizable in the future. Accordingly, the Company provided for a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets of $36,617 and $18,001 for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, primarily relating to net operating loss carryforwards from the local tax regime.
Value-Added Tax and Other Withholding and Other Levies
The Company’s products are sold in the PRC and are subject to VAT on the gross sales price. The VAT rates range up to 13%, depending on the type of products sold. The VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company for raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing or acquiring its finished products. The Company records a VAT payable net of payments if the VAT payable on the gross sales is larger than VAT paid by the Company on purchase of materials or finished goods: otherwise, the Company records a VAT deductible in the accompanying financial statements net of any VAT payable at the end of reporting periods. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the Company recorded VAT credit of $465 and $11,580, respectively.
The Company is also subject to other levies such as stamp tax, unban construction tax, additional education tax which are charged by local governments. The rates of such levies are small and vary among the different jurisdictions in which the Company does business. The Company also acts as the personal income tax withholding agent for the salaries paid its employees. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the Company recorded other levies and withholding $0, respectively.
NOTE 10 – NET LOSS PER SHARE
Basic net loss per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year. The dilutive effect of potential common shares outstanding is included in diluted net loss per share. The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021:
| For the Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2022 | 2021 | |||||||
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders | $ | (146,468 | ) | $ | (72,004 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and diluted | 100,000,000 | 100,000,000 | ||||||
| Loss per shares – basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
NOTE 11 – STATUTORY RESERVES
Under the laws of the PRC the Company’s subsidiaries are required to make appropriations to the statutory reserve based on after-tax net earnings and determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles of the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC GAAP”). Appropriation to the statutory reserve should be at least 10% of the after-tax net income until the reserve is equal to 50% of the registered capital. The statutory reserve is established for the purpose of providing employee facilities and other collective benefits to the employees and is non-distributable other than in liquidation.
| F-13 |
NOTE 12 – CONCENTRATIONS OF RISK
The Company is exposed to the following concentrations of risk:
| a. | Credit risk |
Financial instruments that are potentially subject to credit risk consist principally of trade receivables. The Company believes the concentration of credit risk in its trade receivables is substantially mitigated by its ongoing credit evaluation process and relatively short collection terms. The Company does not generally require collateral from customers. The Company evaluates the need for an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon factors surrounding the credit risk of specific customers, historical trends and other information.
| b. | Interest rate risk |
As the Company has no significant interest-bearing assets, the Company’s income and operating cash flows are substantially independent of changes in market interest rates.
| c. | Exchange rate risk |
The reporting currency of the Company is USD, to date the majority of the revenues and costs are denominated in RMB and a significant portion of the assets and liabilities are denominated in RMB. As a result, the Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk as its revenues and results of operations may be affected by fluctuations in the exchange rate between US$ and RMB. If RMB depreciates against US$, the value of RMB revenues and assets as expressed in USD financial statements will decline. The Company does not hold any derivative or other financial instruments that expose to substantial market risk.
| d. | Economic and political risks |
The Company’s operations are conducted in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operation may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environment in the PRC, and by the general state of the PRC economy. The outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic has expanded all over the world since the beginning of 2020, which has greatly slowdown the growth of the global economy, including the PRC, and this effect might be continued until the COVID 2019 was controlled by the human being. The slowdown of the growth of the PRC’s economy might has adversely effect on our current business and future developments if we would not catch the opportunities of the increasing demand of medical from the popular residents.
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to special considerations. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environment and foreign currency exchange. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by changes in the political and social conditions in the PRC, and by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion, remittances abroad, and rates and methods of taxation.
NOTE 13 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On May 16, 2022, the Company entered into the share purchase agreements with 66 individual investors to issue 5 million common shares for RMB 3,400,700 or approximately $500,000. The relevant subscription receivable has been fully collected before June 30, 2022. The 5 million shares of common stock were issued on August 22, 2022.
On July 13, 2022, the Company reverse splited its outstanding shaers from 100 million shares to 40 million shares.
| F-14 |

Report of Independent Registered Public Accountant Firm
To
the shareholders and the Board of Directors of
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. and its subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the related statements of operations and other comprehensive loss, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the two year period ended December 31, 2021, and related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two year period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Substantial Doubt about the Company’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring significant losses and has accumulated deficiency in stockholders’ equity. These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to this matter are also discussed in Note 2. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ HHC
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2022.
Forest
Hills, New York
August 18, 2022
| F-15 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 456 | $ | 7,998 | ||||
| Other receivables | 2,094 | - | ||||||
| Due from related parties | - | 6,124 | ||||||
| Inventories | 31,991 | 11,838 | ||||||
| Advances to suppliers | 16,257 | 2,258 | ||||||
| VAT credit | 11,580 | 9,963 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 62,378 | 38,181 | ||||||
| Noncurrent Assets: | ||||||||
| Equipment, net | 2,277 | 3,351 | ||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | 13,812 | 20,710 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 78,467 | $ | 62,242 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | - | $ | 1,282 | ||||
| Payroll payable | 31,653 | 16,559 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities - current portion | 5,683 | 23,559 | ||||||
| Advance from customers | 472 | - | ||||||
| Due to related parties | 494,473 | 459,315 | ||||||
| Loan payables | 110,110 | - | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 642,391 | 500,715 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities - noncurrent portion | 7,604 | - | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 649,995 | 500,715 | ||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | - | - | ||||||
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||||||||
| Ordinary Shares, no par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized; 100,000,000 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2021 and 2020. | - | - | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | - | - | ||||||
| Accumulated deficits | (533,822 | ) | (414,567 | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive loss | (37,706 | ) | (23,906 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | (571,528 | ) | (438,473 | ) | ||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 78,467 | $ | 62,242 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-16 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 37,065 | $ | 26,309 | ||||
| Cost of revenue | 25,107 | 18,757 | ||||||
| Gross Profit | 11,958 | 7,552 | ||||||
| Operating Expenses: | ||||||||
| Research and development | 33,757 | 40,361 | ||||||
| Selling and marketing | 18,015 | 13,819 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 78,935 | 61,742 | ||||||
| Total Operating Expenses | 130,707 | 115,922 | ||||||
| Operating Loss | (118,749 | ) | (108,370 | ) | ||||
| Other Income (Expense): | ||||||||
| Interest income, net | 30 | 13 | ||||||
| Other income (expense), net | (536 | ) | 199 | |||||
| Net Loss | (119,255 | ) | (108,158 | ) | ||||
| Other Comprehensive Loss: | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | (13,800 | ) | (26,237 | ) | ||||
| Comprehensive Loss | $ | (133,055 | ) | $ | (134,395 | ) | ||
| Loss Per Common Share, Basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
| Weighted Average Number of Shares Outstanding, Basic And Diluted | 100,000,000 | 100,000,000 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-17 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| Ordinary Shares | Additional | Other | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Shares | Ordinary Shares | Paid-in Capital | Accumulated deficits | Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | 100,000,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (306,409 | ) | $ | 2,331 | $ | (304,078 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | (108,158 | ) | - | (108,158 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | (26,237 | ) | (26,237 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | 100,000,000 | - | - | (414,567 | ) | (23,906 | ) | (438,473 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | (119,255 | ) | - | (119,255 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | - | (13,800 | ) | (13,800 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | 100,000,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (533,822 | ) | $ | (37,706 | ) | $ | (571,528 | ) | ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-18 |
TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||
| Net Loss | $ | (119,255 | ) | $ | (108,158 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to Reconcile Net Loss to Net Cash | ||||||||
| Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 8,654 | 25,750 | ||||||
| Expected credit loss expense | - | 507 | ||||||
| Impairment of inventory | (4,170 | ) | 3,898 | |||||
| Written off of doubtful accounts | (543 | ) | - | |||||
| Other receivables | (1,521 | ) | (43 | ) | ||||
| Inventories | (15,369 | ) | 19,198 | |||||
| Advances to suppliers | (13,733 | ) | 2,166 | |||||
| VAT credit | (1,324 | ) | 2,049 | |||||
| Accounts payable | (1,298 | ) | 1,213 | |||||
| Advance from customers | 465 | (1,519 | ) | |||||
| Payroll payable | 14,426 | 11,438 | ||||||
| Lease liabilities | (10,907 | ) | (16,925 | ) | ||||
| Due from related parties | 6,200 | 60,680 | ||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities | (138,375 | ) | 254 | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||
| Loans from related parties | 293,493 | - | ||||||
| Repayments to related parties | (271,265 | ) | - | |||||
| Proceeds from loan payables | 108,500 | - | ||||||
| Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities | 130,728 | - | ||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY INVESTING ACTIVITIES | - | - | ||||||
| Effect Of Exchange Rate Changes On Cash | 105 | 496 | ||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) In Cash | (7,542 | ) | 750 | |||||
| Cash, beginning of year | 7,998 | 7,248 | ||||||
| Cash, end of year | $ | 456 | $ | 7,998 | ||||
| Supplemental Disclosure Of Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||
| Interest | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Income taxes | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| NON-CASH TRANSACTIONS OF INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||
| Establishment of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for new leases | $ | 17,183 | $ | 4,074 | ||||
| Reduction of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for cancelation of old leases | $ | 17,964 | $ | 12,679 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-19 |
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. And Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTE 1 – NATURE OF OPERATIONS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The Consolidated Financial Statements include data of Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. (“Tian’an”), a holding company incorporated in the British Virgin Islands on April 8, 2021; Yunke Jingrong Information Technology, Co., Ltd. (“Yunke”), a holding company incorporated in Hong Kong on October 27, 2021 and Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Qige”), an operating company incorporated in China (PRC) on August 10, 2016. Shanghai Qige is a wholly owned subsidiary of Yunke, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Tian’an. Tian’an, Yunke and Shanghai Qige are collectively referred to as “the Company”. Currently, all of the Company’s operations are conduct through Shanghai Qige. Tian’an and Yunke are holding companies and have no operations. The Company was organized to research, develop, design, sell and service its power drive product systems. The Shanghai Qige’s main products are its Xuan Vector Brushless DC Controller and its XuanBo Brushless DC Motor. These products are used in low-speed electric vehicles, such as electric forklifts, golf carts, street sweepers and other types of specialized field vehicles.
The Company’s initial marketing efforts are in the Eastern China market with the intention of developing a nationwide marketing network. The Company has developed a reputation of excellence in product quality and after sales service.
| Name
of Consolidated Companies |
Domicile
and Date of Incorporation |
Paid
in Capital |
Percentage
of Effective Ownership |
Percent
Principal Activities | ||||
| Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. | April 8, 2021, British Virgin Islands | USD $0 | 100% owned by Mr. Heng Fei Yang | Investment holding | ||||
| Yunke Jingrong Information Technology Co., Ltd. | October 27, 2021, PRC | USD $0 | 100% owned by Tian’an | Investment holding | ||||
| Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. | August 10, 2016, PRC | USD $0 | 100% owned by Yunke | Production and distribution of power drive product systems |
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation:
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) and include the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiary. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”); however, the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been translated and presented in United States Dollars (“USD”). All significant inter-company accounts and transactions have been eliminated. The consolidated financial statements include all adjustments that, in the opinion of management, are necessary to make the financial statements not misleading.
Use of Estimates and Assumptions
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires Management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities on the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
| F-20 |
Management bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other assumptions and information that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Estimates and assumptions of future events and their effects cannot be perceived with certainty and, accordingly, these estimates may change as new events occur, as more experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained, and as the Company’s operating environment changes. Significant estimates and assumptions by management include, among others, useful life and impairment analysis of long-lived assets, valuation of inventory and right-of-use assets and liabilities, allowance for credit loss of financial assets, other receivables and prepayments. While management believes that the estimates and assumptions used in the preparation of the financial statements are appropriate, actual results could differ from those estimates. Estimates and assumptions are periodically reviewed and the effects of revisions are reflected in the financial statements in the period they are determined to be necessary.
Concentrations of Business and Credit Risks
All of the Company’s manufacturing is located in the PRC. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to successfully continue to manufacture its products and failure to do so would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows. Moreover, the success of the Company’s operations is subject to numerous contingencies, some of which are beyond management’s control. These contingencies include general economic conditions, prices of raw materials, competition, governmental and political conditions, and changes in regulations. Since the Company is dependent on trade in the PRC, the Company is subject to various additional political, economic and other uncertainties. Among other risks, the Company’s operations will be subject to the risks of restrictions on transfer of funds, domestic customs, changing taxation policies, foreign exchange restrictions, and political and governmental regulations. The Company operates in China, which may give rise to significant foreign currency risks from fluctuations and the degree of volatility of foreign exchange rates between United States dollars (“USD”) and the Chinese currency Renminbi (“RMB”). The results of operations denominated in foreign currency are translated at the average rate of exchange during the reporting periods.
Risks and Uncertainties
The recent outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19 has spread across the globe and is impacting worldwide economic activity. Conditions surrounding the coronavirus continue to rapidly evolve and government authorities have implemented emergency measures to mitigate the spread of the virus. The outbreak and the related mitigation measures have had and will continue to have a material adverse impact on global economic conditions as well as on the Company’s business activities. The extent to which COVID-19 may impact the Company’s business activities will depend on future developments, such as the ultimate geographic spread of the disease, the duration of the outbreak, travel restrictions, business disruptions, and the effectiveness of actions taken in the United States and other countries to contain and treat the disease. These events are highly uncertain and, as such, the Company cannot determine their financial impact at this time. No adjustments have been made to the amounts reported in these consolidated financial statements as a result of this matter.
Statements of Cash Flows
In accordance with Statement FASB ASC Topic 230, “Statement of Cash Flows”, cash flow from the Company’s operations is calculated based upon the local currencies and translated to the reporting currency using an average foreign exchange rate for the reporting period. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported in the statements of cash flows will not necessarily be the same as the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
Cash
Cash consists primarily of cash on hand and cash in banks which is readily available in checking and saving accounts. The Company maintains cash with various financial institutions in the PRC where its accounts are uninsured. The Company has not experienced any losses from funds held in bank accounts and believes it is not exposed to any risk on its bank accounts.
| F-21 |
Advances to Suppliers
The Company periodically makes advances to certain vendors for purchases of raw materials or to service providers for services and records these payments as advances to suppliers. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, advances to suppliers amounted to $16,257 and $2,258, respectively.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value. The Company used the weighted average cost method of accounting for inventories. The Company regularly evaluates the composition of its inventories to identify slow-moving and obsolete inventories to determine whether valuation allowance is required. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recorded $0 and $3,898 for inventory valuation allowance, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company written off its inventories of $4,170 and $0, respectively.
Equipment
Equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation, and include expenditures that substantially increase the useful lives of existing assets.
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Estimated useful lives are as follows:
| Operating Equipment | 5 years |
| Office equipment | 5 years |
The cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets sold or otherwise retired are eliminated from the accounts, and any gain or loss is included in the consolidated statements of operations. Maintenance, repairs, and minor renewals are charged directly to expenses as incurred. Significant renewals and betterment to buildings and equipment are capitalized. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the lesser of the useful life or the life of the lease.
Leases
The Company leases space from third parties as its plant sites or office. In accordance with Statement FASB ASC Topic 842, the Company recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability at the commencement date of the of the lease contract and recognizes in profit or loss the lease cost or expense during the lease term. As an accounting policy, the Company elects not to recognizes a right-of-use asset and a lease liability requirements to short-term leases, which with a term of 12 months or less, instead, recognizes the lease payments in profit or loss on a straight-line basis over the lease term and variable lease payments in the period in which the obligation for those payments is incurred. The Company generally uses an incremental borrowing rate as discount rate to measure its lease liabilities, as the rate implicit in the lease is typically not readily determinable. Certain lease agreements include renewal options that are under the company’s control. The Company includes optional renewal periods in the lease term only when it is reasonably certain that the Company will exercise its option.
Variable lease payments include payments to lessors for taxes, maintenance, insurance and other operating costs as well as payments that are adjusted based on an index or rate. The company’s lease agreements do not contain any significant residual value guarantees or restrictive covenants.
Revenue Recognition
We adopted Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) Topic 606, Revenues from Contract with Customers (“ASC 606”) for all periods presented. Under ASC 606, revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods and services is transferred to the Company’s customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration that we expect to be entitled to in exchange for those goods and services, net of value-added tax. We determine revenue recognition through the following steps:
| ● | Identify the contract with a customer; | |
| ● | Identify the performance obligations in the contract; | |
| ● | Determine the transaction price; | |
| ● | Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and | |
| ● | Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. |
| F-22 |
The transaction price is allocated to each performance obligation on a relative standalone selling price basis. The transaction price allocated to each performance obligation is recognized when that performance obligation is satisfied by the control of the promised goods and services is transferred to the customers, which at a point in time or over time as appropriate.
Our revenues are net of value added tax (“VAT”) collected on behalf of PRC tax authorities in respect to the sales of merchandise. VAT collected from customers, net of VAT paid for purchases, is recorded as a liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets until it is paid to the relevant PRC tax authorities.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company measures its financial and non-financial assets and liabilities, as well as makes related disclosures, in accordance with FASB Accounting Standards Codification No. 820, Fair Value Measurement (“ASC 820”), which provides guidance with respect to valuation techniques to be utilized in the determination of fair value of assets and liabilities. Approaches include, (i) the market approach (comparable market prices), (ii) the income approach (present value of future income or cash flow), and (iii) the cost approach (cost to replace the service capacity of an asset or replacement cost). ASC 820 utilizes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The following is a brief description of those three levels:
Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions, such as valuations derived from valuation techniques in which one more significant inputs or significant value drivers are unobservable.
Loss per Common Share
The basic loss per share is calculated by dividing the Company’s net loss available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares during the year. The diluted loss per share is calculated by dividing the Company’s net loss available to common shareholders by the diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding during the year. The diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding is the basic weighted number of shares adjusted for any potentially dilutive debt or equity. Diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share due to the lack of dilutive instruments in the Company. For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company had no potential dilutive Ordinary Shares equivalents outstanding.
Income Taxes
The Company is governed by the Income Tax Law and associated legislations of the PRC. The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC 740 “Income Taxes” (formerly SFAS No. 109 Accounting for Income Taxes), which is an asset and liability approach that requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s financial statements or tax returns. ASC 740 additionally requires the establishment of a valuation allowance to reflect the likelihood of realization of deferred tax assets. Realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon future earnings, if any, of which the timing and amount are uncertain.
According to ASC 740, the evaluation of a tax position is a two-step process. The first step is to determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of any related appeals or litigation based on the technical merits of that position. The second step is to measure a tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not threshold to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in the financial statements. A tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Tax positions that previously failed to meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold should be recognized in the first subsequent period in which the threshold is met. Previously recognized tax positions that no longer meet the more-likely-than-not criteria should be de-recognized in the first subsequent financial reporting period in which the threshold is no longer met. ASC 740 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosures, and transition.
| F-23 |
Translation of Foreign Currencies
For subsidiaries where the functional currency is other than the U.S. dollar, the Company uses the period-end exchange rates to translate assets and liabilities, the average monthly exchange rates to translate revenue and expenses, and historical exchange rates to translate shareholders’ equity, into U.S. dollars. The Company records translation gains and losses in accumulated other comprehensive loss as a component of shareholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheet.
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Year ended RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1573 | 0.1531 | ||||||
| Average yearly RMB: USD Exchange rate | 0.1550 | 0.1449 | ||||||
Comprehensive Loss
The Company’s comprehensive loss includes net loss and unrealized gains and losses on foreign currency translation adjustments. Foreign currency translation adjustment losses for the periods ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were $13,800 and $26,237, respectively.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting, which amends ASC Topic 848, Reference Rate Reform. This ASU provides optional expedients and exceptions for applying GAAP to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions affected by reference rate reform if certain criteria are met. This new guidance is optional and may be elected over time through December 31, 2022 as reference rate reform activities occur. This new guidance is not expected to have a material impact on the Corporation’s consolidated financial statements.
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-06, Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity, which amends ASC Subtopic 470-20, Debt with Conversion and Other Options and ASC Subtopic 815-40, Derivatives and Hedging – Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity. The ASU simplifies the accounting for convertible instruments by reducing the number of accounting models for convertible debt instruments and convertible preferred stock. In addition, the ASU enhances information transparency by making targeted improvements to the disclosures for convertible instruments and earnings-per-share guidance and amends the guidance for the derivatives scope exception for contracts in an entity’s own equity to reduce form-over-substance-based accounting conclusions. ASU 2020-06 is effective for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2021. Management has not yet evaluated the impact of this ASU on the consolidated financial statements.
In October 2021, the FASB issued ASU 2021-08, Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers, which amends ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations, The ASU improves the accounting for acquired revenue contracts with customers in a business combination by addressing diversity in practice and inconsistency related to the (1) recognition of an acquired contract liability and (2) payment terms and their direct effect on subsequent revenue recognized by the acquirer. ASU 2021-08 is effective for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2022. Management has not yet evaluated the impact of this ASU on the consolidated financial statements.
The Company does not believe that above recently issued effective pronouncements, or pronouncements issued but not yet effective, if adopted, would have a material effect on the accompanying financial statements.
| F-24 |
NOTE 2 – GOING CONCERN
As of December 31, 2021, the Company has generated revenues from its business operations and has incurred an accumulated deficit of $533,822 and a negative working capital of $580,013. The Company will require additional funding to meet its ongoing obligations and to fund anticipated operating losses. The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern is dependent on raising capital to fund its business plan and ultimately to attain profitable operations. Accordingly, these factors raise substantial doubt as to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern from a period of one year from the issuance of these financial statements. The Company intends to continue to fund its business by way of private placements and financing support from related parties as may be required. These financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts or amounts and classification of liabilities that might result from this uncertainty.
NOTE 3 – INVENTORIES
Inventories consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Finished goods | $ | 31,991 | $ | 15,957 | ||||
| Less: impairment loss | - | (4,119 | ) | |||||
| Inventory, net | $ | 31,991 | $ | 11,838 | ||||
During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company wrote off $4,170 and $0, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recognized $0 and $3,898, respectively, as impairment loss from inventory.
NOTE 4 – EQUIPMENT, NET
Equipment consisted of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Office equipment | $ | 1,101 | $ | 1,072 | ||||
| Operating equipment | 6,135 | 5,970 | ||||||
| 7,236 | 7,042 | |||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (4,959 | ) | (3,691 | ) | ||||
| Equipment, net | $ | 2,277 | $ | 3,351 | ||||
Depreciation expenses for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were $1,149 and $1,074, respectively. Management evaluates if any circumstances change that make aggregate undiscounted future cash flow generate by this equipment will less than its carrying amount at less in annual basis. There are no impairments for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
NOTE 5 – LEASES
The Company’s lease portfolio primarily consists of real estate properties. The following table summarizes the amounts and location of operating and finance leases on the consolidated balance sheets:
| December 31, | ||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Caption | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||
| Operating | Right-of-use assets | $ | 13,812 | $ | 20,710 | |||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||||
| Total lease assets | $ | 13,812 | $ | 20,710 | ||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||
| Operating | ||||||||||
| Current | Lease liabilities – current portion | $ | 5,683 | $ | 23,559 | |||||
| Noncurrent | Lease liabilities – noncurrent portion | 7,604 | - | |||||||
| Finance | ||||||||||
| Current | - | - | ||||||||
| Noncurrent | - | - | ||||||||
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 13,287 | $ | 23,559 | ||||||
| F-25 |
The following table summarizes the lease costs recognized in the consolidated statements of earnings:
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Operating lease cost | $ | 7,505 | $ | 24,676 | ||||
| Short-term lease cost | - | - | ||||||
| Variable lease cost | - | - | ||||||
| Total lease cost | $ | 7,505 | $ | 24,676 | ||||
Sublease income for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 were insignificant.
The following table presents the weighted-average remaining lease term and weighted-average discount rate for operating and finance leases:
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) | ||||||||
| Operating | 2.33 | 0.92 | ||||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate | ||||||||
| Operating | 6.05 | % | 6.05 | % | ||||
| Finance | - | - | ||||||
The following table presents supplementary cash flow information regarding the company’s leases:
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: | ||||||||
| Operating cash flows from operating activities | $ | 10,907 | $ | 16,925 | ||||
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liabilities | $ | 17,183 | $ | 4,074 | ||||
| Reduction of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for cancelation of old leases | $ | 17,964 | $ | 12,679 | ||||
The following table summarizes the future maturities of the Company’s operating lease liabilities as of December 31, 2021:
| Operating Leases | ||||
| 2022 | $ | 6,299 | ||
| 2023 | 7,874 | |||
| 2024 | - | |||
| 2025 | - | |||
| 2026 | - | |||
| Thereafter | - | |||
| Total lease payments | 14,173 | |||
| Less: interest | (886 | ) | ||
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 13,287 | ||
| F-26 |
NOTE 6 – LOAN PAYABLES
On November 20, 2021, the Company entered into a loan agreement with Shenzhen Shihong Education and Culture Ltd in the principal amount of $108,500. The loan is due on November 22, 2022 and will accrue no interest if the loan is repaid upon maturity. If the loan is not fully repaid on or before November 22, 2022, the Company will be charged a rate of 0.03% interest per day. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the ending balance of loan payables was $110,110 and $0, respectively.
NOTE 7 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Due from related parties
For operational purposes, the Company provided certain advances to members of its management team, including its Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”). As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance of the advances to the Company’s management was $0 and $6,124, respectively. The advances were collected as $6,200 and $60,680, respectively, during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Due to related parties
On July 15, 2019, the Company entered into a loan agreement of $459,315 with one of its related parties, Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd., without interest charge and with no collateral. The loan is due on demand. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, is the actual controlling owner of Liaoning Xinjian Linguo Yitang Health Management Ltd. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company repaid $271,265 and $0. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance of the loan was $196,625 and $459,315, respectively. The Company has repaid the loan of $196,625 as of September 2022.
On April 15, 2021, the Company entered into a loan agreement of $293,493 with one of its related parties, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, without interest charge and collateral. The loan is due on demand. Mr. Heng Fei Yang is the Company’s CEO. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance of the loan was $297,848 and $0, respectively.
NOTE 8 – EQUITY
The Company is authorized to issue an unlimited number of Ordinary Shares without par value. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, it had 100,000,000 shares outstanding, respectively.
On July 13, 2022, the Company’s CEO, Mr. Heng Fei Yang, surrendered 60,000,000, no par value, ordinary shares back to the Company. He is currently the beneficial owner of 40,000,000 ordinary shares of the Company.
NOTE 9 – TAXES
Income Taxes
British Virgin Islands (“BVI”)
The Company is a BVI registered corporation and is not subject to tax on income or capital gain. In addition, payments of dividends by Tian’an to their shareholders are not subject to withholding tax in the BVI.
Hong Kong
The Company’s subsidiary, Yunke, is incorporated in Hong Kong and has no operating profit or tax liabilities during the period. Yunke is subject to tax at 16.5% on the assessable profits arising in or derived from Hong Kong.
| F-27 |
The PRC
The Company’s subsidiary operating in the PRC is subject to the Corporate Income Tax Law of the PRC at a unified income tax rate of 25%. The reconciliation of income tax rate to the effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 from our continuing operation is as follows:
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Loss before income taxes from operations in the PRC | $ | (119,255 | ) | $ | (108,158 | ) | ||
| Statutory income tax rate | 25 | % | 25 | % | ||||
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | (29,814 | ) | (27,040 | ) | ||||
| Tax effect of non-deductible items | - | - | ||||||
| Valuation allowance of deferred tax assets | 29,814 | 27,040 | ||||||
| Income tax expense | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
Management believes that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be fully realizable in the future. Accordingly, the Company provided for a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets of $29,814 and $27,040 for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, primarily relating to net operating loss carryforwards from the local tax regime.
Value-Added Tax and Other Withholding and Other Levies
The Company’s products are sold in the PRC and are subject to VAT on the gross sales price. The VAT rates range up to 13%, depending on the type of products sold. The VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company for raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing or acquiring its finished products. The Company records a VAT payable net of payments if the VAT payable on the gross sales is larger than VAT paid by the Company on purchase of materials or finished goods: otherwise, the Company records a VAT deductible in the accompanying financial statements net of any VAT payable at the end of reporting periods. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recorded VAT credit of $11,580 and $9,963, respectively.
The Company is also subject to other levies such as stamp tax, unban construction tax, additional education tax which are charged by local governments. The rates of such levies are small and vary among the different jurisdictions in which the Company does business. The Company also acts as the personal income tax withholding agent for the salaries paid its employees. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recorded other levies and withholding $0, respectively.
NOTE 10 – NET LOSS PER SHARE
Basic net loss per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year. The dilutive effect of potential common shares outstanding is included in diluted net loss per share. The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders | $ | (119,255 | ) | $ | (108,158 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and diluted | 100,000,000 | 100,000,000 | ||||||
| Loss per shares – basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
NOTE 11 – STATUTORY RESERVES
Under the laws of the PRC the Company’s subsidiaries are required to make appropriations to the statutory reserve based on after-tax net earnings and determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles of the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC GAAP”). Appropriation to the statutory reserve should be at least 10% of the after-tax net income until the reserve is equal to 50% of the registered capital. The statutory reserve is established for the purpose of providing employee facilities and other collective benefits to the employees and is non-distributable other than in liquidation.
| F-28 |
NOTE 12 – CONCENTRATIONS OF RISK
The Company is exposed to the following concentrations of risk:
| a. | Credit risk |
Financial instruments that are potentially subject to credit risk consist principally of trade receivables. The Company believes the concentration of credit risk in its trade receivables is substantially mitigated by its ongoing credit evaluation process and relatively short collection terms. The Company does not generally require collateral from customers. The Company evaluates the need for an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon factors surrounding the credit risk of specific customers, historical trends and other information.
| b. | Interest rate risk |
As the Company has no significant interest-bearing assets, the Company’s income and operating cash flows are substantially independent of changes in market interest rates.
| c. | Exchange rate risk |
The reporting currency of the Company is USD, to date the majority of the revenues and costs are denominated in RMB and a significant portion of the assets and liabilities are denominated in RMB. As a result, the Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk as its revenues and results of operations may be affected by fluctuations in the exchange rate between US$ and RMB. If RMB depreciates against US$, the value of RMB revenues and assets as expressed in USD financial statements will decline. The Company does not hold any derivative or other financial instruments that expose to substantial market risk.
| d. | Economic and political risks |
The Company’s operations are conducted in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operation may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environment in the PRC, and by the general state of the PRC economy. The outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic has expanded all over the world since the beginning of 2020, which has greatly slowdown the growth of the global economy, including the PRC, and this effect might be continued until the COVID 2019 was controlled by the human being. The slowdown of the growth of the PRC’s economy might has adversely effect on our current business and future developments if we would not catch the opportunities of the increasing demand of medical from the popular residents.
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to special considerations. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environment and foreign currency exchange. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by changes in the political and social conditions in the PRC, and by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion, remittances abroad, and rates and methods of taxation.
NOTE 13 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In May and June 2022, the Company issued 5 million shares to 66 individuals for RMB $3,400,700 or approximately $500,000. As of the date of this report, the relevant subscription receivables had been collected.
| F-29 |
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following table sets forth the expenses payable by the registrant, in connection with the sale of ordinary shares being registered under this registration statement. All amounts shown are estimates except for the SEC registration fee.
| Selling Commissions | $ | - | ||
| Securities and Exchange Commission registration fee | $ | 46.35 | ||
| Edgar Fees (estimate) | $ | 5,000 | ||
| Translation Fees | $ | - | ||
| Transfer Agent Fees | $ | 750 | ||
| Accounting fees and expenses | $ | 57,500 | ||
| Legal fees and expenses | $ | 125,000 | ||
| Total | $ | 182,546.35 |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
The Company indemnifies against all expenses, including legal fees, and against all judgments, fine and amounts paid in settlement and reasonably incurred in connection with legal, administrative or investigative proceedings any person who
| a) | in or was a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed proceedings, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative, by reason of the fact that the person is or was a director of the Company; or | |
| b) | is or was, at the request of the Company, serving as a director of, or in any other capacity is or was acting for, another body corporate or a partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise. |
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
During the past three years, we have issued the following shares in connection with a private placement without registering the securities under the Securities Act. We believe that each of the following issuances was exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance on Regulation D under the Securities Act or pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act regarding transactions not involving a public offering or in reliance on Regulation S under the Securities Act regarding sales by an issuer in offshore transactions. No underwriters were involved in these issuances of shares.
In May and June 2022, the Company issued 5 million shares to 66 individuals for RMB 3,400,700 or approximately $500,000. The relevant subscription receivable has been collected in May and June 2022. The following table lists each individual’s name and the date of each sale for the shares.
| NAME | NUMBER OF SHARES | DATE | ||
| Lu Hai-zhi | 50,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wu Hong-hui | 100,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wang Zheng-zhou | 100,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Xiao Wei-juan | 30,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Zheng Dong-qing | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Jiang Hai-hua | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wu Cai-chen | 50,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Zhou Zhi-ying | 600,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Huang Xia-mei | 220,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Chen He-ping | 80,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wang Dan-juan | 30,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Li Ai-jun | 40,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Hu Yan-ping | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Yu Pei-xin | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wang Shu-xia | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Pan You-rui | 50,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Shen Ya-ping | 150,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Lin Fei | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Wang Wen-jun | 300,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Ma Fei | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Yuan Xue-ya | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Xu Ming-hua | 50,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Li Ming-ji | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Shi Cong-zhe | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Jiang Wei | 50,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Meng Qing-hui | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Fu Rao | 20,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| BaI Li | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Liu Ying | 10,000 | May 16, 2022 | ||
| Jiang Xiu-yan | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Zhu Ge-meng | 20,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Zhang Shu-mei | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Feng jia-wang | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Li Xiao-di | 10,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Li Jing-chun | 30,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Chen Shan-fen | 40,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| ZhangLian-zhen | 60,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Lai Bi-ying | 30,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Xie Yue-qiao | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Wang Chun-lv | 10,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Jiang Ying | 10,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Yi Xiu-ying | 10,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Chen Li-li | 200,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Zhang Shu-bo | 10,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Xian Hong | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Zhang Peng | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Hu Fang-bin | 50,000 | May 17, 2022 | ||
| Wei Bin-hai | 200,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Wei Jian-mei | 450,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Shen Wan-ting | 450,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Yu Wei-xing | 100,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Chen Yan | 20,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Liu Ying | 10,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Zhao Yong-wei | 10,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Yan Ai-jun | 10,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Li Ping | 10,000 | May 22, 2022 | ||
| Liu Ying | 20,000 | May 24, 2022 | ||
| Chen Fu-sheng | 10,000 | May 25, 2022 | ||
| Wang Mei-lan | 10,000 | May 25, 2022 | ||
| Xie Wei-guang | 20,000 | May 25, 2022 | ||
| Jiang Li-fen | 10,000 | May 25, 2022 | ||
| Chen Ai-qun | 10,000 | May 30, 2022 | ||
| Yang Wen-juan | 10,000 | May 30, 2022 | ||
| Sang Su | 10,000 | June 6, 2022 | ||
| Xiong Mei-jun | 10,000 | June 6, 2022 | ||
| Liu Guang-na | 750,000 | June 6, 2022 |
| II-1 |
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Schedules
| (a) | Exhibits |
| 101.INS | Inline XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |
| * To be filed by amendment |
| II-2 |
Item 17. Undertakings
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the purchasers at the closing specified in the subscription agreements, certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the provisions described in Item 6, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes that:
(1) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(2) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
| II-3 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the registrant certifies that it has reasonable grounds to believe that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form F-1 and has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in Shanghai, China, on February 28, 2023.
| TIAN’AN TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD | ||
| By: | /s/ Heng Fei Yang | |
Heng Fei Yang Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, this registration statement on Form F-1 has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Name | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Heng Fei Yang | Chief Executive Officer, President and Director | February 28, 2023 | ||
| Heng Fei Yang | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Cong He | Chief Financial Officer | February 28, 2023 | ||
| Cong He | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
SIGNATURE OF AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE OF THE REGISTRANT
Pursuant to the Securities Act, the undersigned, the duly authorized representative in the United States of America, has signed this registration statement or amendment thereto in New York, New York, United States of America on February 28, 2023.
| AUTHORIZED U.S. REPRESENTATIVE | ||
| By: | The Crone Law Group, PC | |
| Name: | /s/ Mark E. Crone | |
| Title: | Principal | |
| II-4 |
Exhibit 3.1
















Exhibit 3.3

















Exhibit 3.4





Exhibit 3.5

Exhibit 5.1




Exhibit 10.1

厂房租赁合同
Factory Premises Leasing Contract
(1) 出租方(甲方):
| (1) | Lessor (Party A): |
【上海马力索精密机械有限公司】
【Shanghai MarisoPrecision Machinery Co., Ltd】
法定地址:
Legal Address:
【上海市浦东新区秀浦路3500号】
【Shanghai City, Pudong New District, Xiupu Road, No. 3500】
(2)承租方(乙方):
| (2) | Lessee (Party B): |
【上海起阁动力科技有限公司】
【Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd】
法定地址:
Legal Address:
【上海市浦东新区秀浦路3500号1幢B楼1层104室】
【Shanghai City, Pudong New District, Xiupu Road, No. 3500, Building 1, Block B, Floor 1, Room 104】
签订日期:2021年4月15日
Date of signing: April 15, 2021
签订地: 上海
Place of signing: Shanghai
第一条 租赁合同书
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

Article 1 Leasing contract
1.1甲方:上海马力索精密机械有限公司,是一家根据中华人民共和国(“中国”)法律组建并存续的法人,具有签订本合同书的民事行为能力,其法定地址是上海市浦东新区秀浦路3500号。
1.1 Party A: Shanghai Mariso Precision Machinery Co., Ltd is a legal representative which is set up and survive under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (“China”), in possession of civil capacity to sign this contract, its legal address being Shanghai City, Pudong New District, Xiupu Road, No. 3500.
1.2乙方:上海起阁动力科技有限公司,是一家根据中华人民共和国 (“中国”)法律组建并存续的法人,具有签订本合同书的民事行为能力,其法定地址是上海市浦东新区秀浦路3500号1幢B楼1层104室。
1.2 Party B: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd is a legal is a legal representativewhich is set up and survive under the laws of the Peoples Republic of China (“China”), in possession of civil capacity to sign this contract, its legal address being Shanghai City, Pudong New District, Xiupu Road, No. 3500, Building 1, Block B, Floor 1, Room 104.
1.3甲方与乙方(简称“双方”)于2021年4月15日订立本合同书。
1.3 Party A and Party B (referred to as “both parties”) concluded this contract on April 15, 2021.
1.4双方根据《中华人民共和国合同法》以及其他有关法律、法规,本着本等、自愿、有偿、诚实信用的原则,经友好协商,特此达成如下一致合同书:
1.4 In accordance with the Contract Law of the People’s Republic of China as well as other relevant laws and regulations, in line with the principles of equality, voluntariness, equivalent consideration and good faith, after friendly discussion, after amicable negotiation, hereby reached a consensus on this contract, as follows:
第二条租赁标的物
Article 2 Lease subject
2.1租赁标的物位于上海市浦东新区秀浦路3500号1幢C楼8 号工业厂房(以下简称“工业厂房”,)以及与工业厂房有关的供水、 供电等公用设施。
2.1 The subject matter of the lease is located at Shanghai City, Pudong New District, Xiupu Road, No. 3500,Building 1, Block 8, No. 8Industrial Plant (hereinafter referred to as “Industrial Plant”) and water supply, electricity supply,etc., and other public facilities related to the industrial plant.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

2.2按照本合同书列明的条款及条件,甲方同意将上述工业厂房 出租给乙方。乙方同意承租该工业厂房。
2.2 According the terms and conditions listed in this contract, Party A agrees to lease the above-mentioned industrial plant to Party B. Party B agrees to rent the industrial plant.
2.3工业厂房的租赁建筑面积(租金计价面积)为厂房72平方米,办公室/平方米。租赁期内,任何与面积相关的计算均应以此面积为基础。
2.3 The built-up area (area for rental valuation) of the leased industrial plant is workshop __72__ square meters, office __/__ square meters. During the lease term, any calculation related to area shall be based on this area.
2.4乙方按照本合同书约定,有权自筹资金,按照“中国”法律法规关于装饰装修所规定的要求完成办公室的装修设计及施工工作。双方理解:
2.4 According to the contract, Party B has the right to raise fund on its own, and complete the decoration design and construction work for the office, in light of the requirements as stipulated in China law and regulations on renovation and decoration.Both parties understand:
(1)未经甲方同意,并经原设计单位或者具有相应资质等级的设计单位提出设计方案并经过批准,乙方的装修不得变动建筑主体和承重结构;
(1) Without prior consent from Party A, neither a submission of application for design scheme nor an approval granted from the original designer or any design unit having the similar qualification level, Party B cannot alter the main body of building as well as its weight-bearing structure.
(2)不得损坏工业厂房原有节能设施,降低节能效果;
(2) Should not damage the original energy saving facilities, reduce the energy saving effectiveness;
(3)不得有其他影响建筑结构和使用安全的行为。
(3) There should not any conduct which may affect the building structure or safety for use;
(4)乙方大面积开挖时需向甲方申请,待甲方同意后,方可对工业厂房地面进行施工。
(4) Party B should apply to Party A before large-scale excavation, only afterconsent isobtained from A, construction work on the floor of the industrial plant is carried out.
前述所称建筑主体,是指建筑实体的结构构造,包括屋盖、楼盖、 梁、柱、支撑、墙体、连接接点和基础等。
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

The main body of the building aforementioned refers to thecomposition structure of the building entity, including, roofs, slabs, beams, pillars, braces, walls, connecting points and bases, etc.
前述所称承重结构,是指直接将本身自重与各种外加作用力系统地传递给地基基础的主要结构构件和其连接接点,包括承重墙体、立杆、柱、框架柱、支墩、楼板、梁、屋架、悬索等。
The weight-bearing structure aforementioned refers to the structural parts and their connecting joints which directly transmit the self-weight and various external forces in a systematic manner to the foundation base, including weight-bearing wall, vertical pole, column-shaped pillar, framed column, buttress, floor slab, beam, roof truss, suspension cable and so on.
第三条 租期
Article 3 Lease term
3.1租期
3.1 Lease term
租期自2021年4 月 17日起至 2024 年4月16日止届满,即租期叁年,租期可根据3.3条的规定予以延长。
The lease term starts from April 17th, 2021 to April 16th, 2024 end, for a period of _3_ years, the term can be extended according to the provision under Article 3.3.
3.2免租期
3.2 Rent-free period
无
Nil
3. 3续约
3.3 Renewal
乙方有权在本合同租期届满时各承租意向方同等条件(指承租方的行业、租金、生产经营活动对环境及建筑等方面的影响)下优先续租。每个续约期应从刚刚结束的租期的下一日开始计算。
Party B has the right to renew the contract upon its expiry under the same conditions with other prospective lessees (referred to the industry in which a lessee is involved, rental, impacts of production activity to the environment and building aspect, etc.). Every new period shall commence from the ensuing day of the end of term in existing contract.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]
本合同下的“期限”应包括租期和任何续约期期限。每个续约期内的租金,由双方根据当时的市场价格协商确定。
The “term” spelt out in this contract should include rental period as well as any renewed period. The rent in each renewed period shall be discussed by both parties and determined by reference to the market prices at that time.
3. 4续约的程序
3.4 Procedure for renewal
乙方须在本合同租期或任何续约期届满至少六个月前以书面方式知会是否甲方续约。甲方须在本合同书的租期或任何续约期届满前至少四个月,以书面知会乙方行使续约选择权。如甲方未向乙方发出续约的书面知会,乙方须于本合同书项下期限届满前三个月内向甲方发出第二次续约知会,甲方须于收到该知会后的五(5)工作日内,书面知会乙方其续约的意向。如甲方未就乙方第二次知会发出任何书面知会,本合同书在租期或当时的续约期期限届满时自动终止。
Party B should notify Party A six months at least in advance upon the expiry of the lease or renewal period in writing about its intention whether or not to renew the contract. Party A should notify Party B four months at least in advance upon the expiry of the lease or renewal period in writing about exercising its right to extend the contract. If Party A has not confirmed the renewal in writing, Party B should issue another notification the second time three months before the expiry of the lease term, Party A should notify Party B in writing within (five) working days after receipt of the second notification about its intention to extend the contract. If Party A is unable to issue any notification to Party B in writing on response to Party B’s second notification, this contract shall automatically come to a cessation upon expiry of the lease term or the then renewal period.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

第四条 租赁费用及支付方式
Article 4 Rental fee and Payment mode
4.1租金
4.1 Rent
本合同所指工业厂房的租金只包括房屋使用费、折旧费、与出租工业厂房有关的主体维修维护费、绿化费以及就公共区和公共设备设施的使用的管理费或其它费用,不包括物业费、空调系统使用费、乙方生产经营中支出的水电费(收费标准按国家规定)、非主体的维修费、工商管理费。一个“租约年”指连续十二(12)月(365天)的租赁时间。租期内第一个租约年至第三个租约年的租金标准如下:
The rent for the industrial plant to which this contract refers is comprised of house use fee, depreciation cost, repair and maintenance fee for the main body, afforestation fee, management fee or other expenses for the use of public area as well as public facilities and equipment related to the leased industrial plant; excluding property management fee, usage fee for air conditioning system, water and electricity fees payable for the production activity of Party B (charging standard is in accordance with national provisions), non-subject repair and maintenance fee, trade and industrial administration fee. A lease year is meant for a rental duration of twelve (12) consecutive months (365 days). The rent standard for the first lease year until the third lease year within the lease term is as follows:
厂房租约年的天租金标准为每天每平方米¥ 1.6元;(该价格含税;)
Daily rental standard for the plant’s lease year is CNY1.6Yuan per square meter per day (inclusive of tax)
厂房租约年的月租金标准月含税¥ 3504元(人民币叁仟伍佰零肆元)(365/12天);
Monthly rental standard for plant’s lease year is CNY3,504Yuan (RMBThree Thousand Five Hundred and Four Yuan) including tax (365/12 Days)
租约年的年租金标准为每年含税¥ 42048元(人民币肆万贰仟零肆拾捌元整)(365天);
Yearly rental standard for plant’s lease year is CNY42,048Yuan (RMB Forty Two Thousand and Forty Eight Yuan only) including tax (365 Days)
租金计算周期:3个月。3个月租金为含税¥ 10512元(人 民币壹万零伍佰壹拾贰元整)
Rental calculation cycle: __3__ months. The __3__ month rental is CNY10,512 Yuan (RMB Ten Thousand Five Hundred and Twelve Yuan only) including tax.
月租金的计算方法为:本合同第2.3条约定的租赁建筑面积乘以365天/12乘以相应的天租金标准。
The calculation method for monthly rental is: The leased built-up area agreed under Article 2.3 of this contract multiplied by 365/12 Days times the relevant daily rental standard.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

4.2物业费
4.2 Property management fee
乙方有义务就工业厂房、公共区、公共设备设施的使用向甲方支付管理费或其它费用。
Party B has an obligation to pay Party A property management fees and other expenses for use of the industrial plant, public area, public facilities and equipment.
租期内第一个租约年至第三个租约年的物业管理费标准如下:
The property management fee standard for the first lease year until the third lease year within the lease term is as follows:
物业管理费的月租金标准为每月每平方米¥ 3元;物业管理费的月租金为每月¥ 216元:(人民币贰佰壹拾陆元整)
The standard for monthly property management fee is CNY 3 Yuan. The monthly property management fee is CNY 216 Yuan per month (RMB Two Hundred and Sixteen Yuan only);
物业管理费计算周期:3 个月。3个月物业管理费为¥ 648元:(人民币人民币陆佰肆拾捌元整)
Property management fee calculation cycle: 3 months. The property management fees for three months is CNY 648 Yuan (RMB Six Hundred and Forty Eight Yuan only)
4.1〜4.2所述价格均含税5%/6%,在租赁期内若增值税税率发生变化,乙方承担由税率变动而产生的税金部分。
The prices stated in 4.1 – 4.2 are inclusive of tax 5% / 6 %. Ifa change of the Value Added Tax rate takes place during the lease term, Party B is responsible to bear the tax portion arising from the change in the tax rate.
4.3房租和物业费支付日期及发票
4.3 Date of Payment and Invoice (“fapiao”) for rental and property management fees
租金及物业管理费的支付遵循“先付后用”原则,即:
Payment for rental and property management fees adheres to the principle of “payment first before usage”, namely:
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

第一笔租金(包含:2021 年 4 月 17 日至2021年 7月16日房租及物业费)须在2021 年4 月17日前支付,此后的各期租金及物业管理费以每个季度为一个支付周期,乙方应于每个季度开始之五日前预付该期的应付款项(例如:2021 年7月1日至同年10月31日期间的应付款项,应于2021年6月25 日前预付。)。甲方收到乙方款后叁个工作日内开具租赁发票交予乙方。
The first rental payment (containing: April 17, 2021 to July 16, 2021 plant rental and property management fee)must be paid before April Month 17 Day, 2021 Year. Thereafter, rental and property management fees for every period are paid on quarterly basis as a payment cycle. Party B should settle in advance the payable for each period five days before the beginning of each quarter (for example, the account payable for July 1, 2021 to October 30 of the same year should be settled in advance before June 25, 2021). Party A should issue rental fapiaoto Party B within three working days upon receiving Party B’s payment.
发票:甲方提供租赁发票(增值税专用发票)
Invoice: Party A provides rental invoice (Value Added Tax Special Invoice)
发票抬头:上海起阁动力科技有限公司
Invoice Header: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd
发票内容:租金、物业管理费
Invoice Content: Rental, Property management fee
4.4合同履约保证金
4.4 Security deposit for contract performance
乙方同意,自本合同书签署之日起,乙方应当在签订合同叁个工作日内向甲方支付首期租金及合同履约保证金,合同履约保证金共计为叁个月租金。叁个月租金为含税¥ 10512元(人民币壹万零伍 佰壹拾贰元整),甲方收取合同履约保证金后,应向乙方开具书面收据。本合同届满后,乙方办理完退租手续之日起五(5)个工作日内,除本合同另有约定外甲方将履约保证金返还给乙方(不计利息)。如乙方未在约定期内付清履约保证金,甲方有权单方解除本合同,追究乙方逾期支付履约保证金的违约责任及甲方无需退回已经收到乙方的部分履约保证金,同时甲方有权将标的重新出租给第三方。
Party B agrees that, within three working days from the date of signing this contract, Party B should pay to Party A the first period’srental and the security deposit for contract performance. The security deposit for contract performance is three months of rents totalled CNY 10,512 Yuan (RMB Ten Thousand Five Hundred and Twelve Yuan only) including tax. Upon receiving the security deposit for contract performance, Party A should issue to Party B a receipt in writing. After the expiry of this contract, Party B handles the procedure of returning the lease, unless agreed otherwise in this contract, Party A shall return the deposit to Party B(without interests accrued) within five days after completion of the handover procedure. If Party B is not able to settle the security deposit in full within the agreed period, Party A has the right to terminate the contract unilaterally, going after Party B for liability on breach of contractowing to overdue payment of security deposit, and there is no need for Party A to return any portion of security deposit which has been collected, meanwhile, Party A can lease the subject anew to another third party.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

4.5滞纳金
4.5 Late fee
乙方逾期支付租金及履约保证金,须向甲方支付滞纳金。滞纳金金额为:逾期天数乘以逾期金额的百分之一(1%)。
If Party B delays the payment of rental and security deposit, a late fee must be paid to Party A. The amount of a late fee is: Number of days overdue times amount overdue multiplied with one hundredth (1%).
4.6租金、合同履约保证金及滞纳金的支付方式
4.6 Payment methods for rental, security deposit and late fee
租金及滞纳金的支付由乙方用人民币以银行转账方式支付到甲方指定银行帐户。
Payment of rental and late fee shall be done in RMB via bank transfer to the designated banking account of Party A.
第五条 工业厂房的交付
Article 5 Delivery of industrial plant
5.1工业厂房的交付日期: 2021 年4月17 日。
5.1 The delivery date of the industrial plant: April (Month) 17(Day), 2021 (Year)
5.2甲方须在交付日期(或之前)将工业厂房以完好合法的状态交付。包括但不限于:
5.2 Party A must deliver the industrial plant on the delivery date (or before) in a good and legitimate condition, including but not limited to:
(1)甲方承担完全责任保证该工业厂房满足政府建设及环保法规要求。
(1) Party A shall bear full responsibility to ensure that the industrial plant can satisfy the requirements of governmental provisions on construction and environment protection.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

(2)60KVA电力线路从配电房接入车间。
(2) Power line of 60 kVA is connected from the Power Distribution Room to the Workshop.
(3)消防系统经消防局检验合格。
(3) The fire protection system has passed the inspection of the Fire Safety Bureau.
(4)工业厂房排雨系统采用内置落水管及天沟,漏雨风险较大。甲方须对厂房排雨系统进行细致检查并完善设施,确保交付日后乙方使用时没有漏雨现象。后期如有漏雨现象,甲方免费维修。
(4) The rainwater drainage system of the industrial plant adopts built-in pipes and gutters, the risk of rain leakage is rather high. Party A must conduct a careful inspection on the plant’s rainwater drainage system and improve the facilities, so that there is no rain leakage situation while Party B is using the plant after the delivery date.
5.3资料交付
5.3 Delivery of information materials
本合同签订时,甲方应当提供《房屋所有权证》复印件、消防部门出具的消防系统验收合格文件复印件,甲方提供资料必须是真实有效的文件。
When this contract is signed, Party A should provide a photocopy of the Property Ownership Certificate, a photocopy of the Acceptance Document ofthe Fire Protection System issued by Fire Safety Department. The documents provided by Party A must be authentic and valid.
5.4交接单
5.4 Handover sheet
在交付租赁标的物时,甲方与乙方须签署物业验收交接单,对房屋交付时的情况予以确认
When the subject of the lease is delivered, both Party A and Party B must sign a handover sheet for property acceptance, in order to confirm the situation during delivery of the plant.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

Article 6 Use of the industrial plant
第六条 工业厂房的使用
6.1经营活动
6.1 Operating activities
工业厂房可用于与乙方经批准的经营范围一致的生产及办公的合法用途。
The industrial plant is used for legitimate production activity and office work which are consistent with the scope of operation duly approved by relevant authority.
6.2甲方承诺
6.2 Party A’s promises
甲方承诺对乙方依法享有的经营自主权、收益权不进行干涉。
Party A promises not to interrupt the operation autonomy and the right to earnings enjoyed by Party B according to law.
6.3乙方承诺
6.3 Party B’s promises
乙方确保使用该工业厂房时符合上海市浦东区的消防、环保等方面的要求。厂房中生产作业期间的噪音控制在70分贝以内,无工业废水、废油排放。
Party B assures to comply with the requirements on fire safety and environmental protection in Shanghai City Pudong District while using the industrial plant. The noise during production work in the plant shall be controlled within 70 dB, no discharge of industrial waste water and waste oil.
乙方应在其经营范围内正常使用并爱护工业厂房内部的各项设施,防止非正常损坏。因乙方使用不当或不合理使用工业厂房及其内部的设施而出现损坏或发生故障,乙方自行负责该项维修。
Party B should use the industrial plant under a normal manner within its business scope and take good care of various facilities in the industrial plant, preventing abnormal damage. If Party B uses the industrial plant and its internal facilities improperly or unreasonably until causing damage or breakdown, Party B is responsible for the repair on its own.
乙方承诺不改变公共区域的用途,不破坏公共绿地,并服从甲方 的日常管理。
Party B promises not to alter the use of public area, not to destroy public green space, and obey the daily management by Party A.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

6.4公共区
6.4 Public area
本合同期限内,乙方有权在甲方的管理下使用工业厂房前的公共区(“公共区”)(甲方提供1个车位供乙方停车使用)。超出1个车位以外的车位需求,按照100元/月/个收取费用。
Within the term of this contract, Party B has the right to use the public area (“public area”) in front of the industrial plant under the management of Party A (Party A provides one parking lot for use by Party B). Demand for parking space in excess of one lot shall be charged at CNY 100 Yuan per lot per month.
6.5装修
6.5 Decoration
本合同期限内,经甲方批准,乙方有权随时在工业厂房内进行适当的装修或安装、改装、维修任何装置,包括但不限于设备、器具、设施、线路、悬挂物、标志、招牌及类似的物品(但不得破坏外墙现状)。乙方的装修活动应被视为根据本合同的规定对工业厂房及其内部设施的正常使用,但乙方的装修活动以不损害工业厂房主体结构、 危及工业厂房主体安全及相邻工业厂房安全为限。
Within the term of this contract, after approval by Party A, Party B has right to carry out at any time appropriate decoration or installation, refit and repair any device, including but not limited to equipment, apparatus, facilities, lines, hanging objects, signs, signboards and similar items(however the current exterior status shall not be damaged). The renovation work by Party B should be performed for the normal use of the industrial plant and its internal facilities according to provisions stipulated in the contract, but the renovation work should be carried out to the extent of not damaging the main structure of the industrial plant and not endangering the safety of this plant as well as others in the vicinity.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

6.6工业厂房外招牌
6.6 Signboard outside the plant
乙方如果需要在公司厂房门口安装适当的招牌或有关广告,必须征得甲方的书面许可,并根据有关法律法规办理行政审批许可等手续。甲方的许可仅代表甲方的意见,甲方不对乙方未经办理有关政府部门的审批许可而发生的法律责任承担任何不利后果。乙方将自筹资金安装其全部招牌。所有由乙方自担费用安装的招牌均属于乙方的财产,乙方可随时将其清除。但乙方对招牌在安装或迁离过程中对建筑物的损坏承担维修责任,并对招牌安装后的安全承担全部的责任。
If appropriate signboards or relevant advertisement are to be installed at the company’s factory entrance, Party B must obtain written permission from Party A, and goes through the formalities of administrative examination and approval in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.Party A’s permission represents merely the opinion of Party A, Party A is not going to bear any adverse consequence arising from legal liability due to a default of not having obtained necessary approval fromthe relevant authority. Party B shall raise funds on its own so as to install all its signboards. All signboards which are installed by Party B using its own fund belong to Party B, Party B can dismantle any of them at any time. If damage is caused to the building during the process of installation or dismantling of a signboard, Party B is liable to repair it, besides, Party B is fully responsible for the safety after a signboard is installed.
6.7进出权
6.7 Right of access
在事前知会乙方后,甲方有权在乙方营业时间内,与乙方有关人员一起进入工业厂房检查及对工业厂房作出必要的维修。甲方在进行上述检查和维修时,不得不合理地干扰乙方(正常)的业务,或使乙方由于此种检查或维修而遭受损害或损失。
After notifying Party B in advance, Party A has the right to enter into the industrial plant together with the representatives of Party B during the business hour of Party B, to perform inspection of the building as well as carry out repair and maintenance as needed. During the course of the inspection or repair aforementioned, Party A ought not to disturb the normal business of Party B without proper reasons, or cause Party B to suffer from damage or loss due to that inspection or repair.
6.8 生活垃圾及工业垃圾处理
6.8 Domestic garbage and industrial waste treatment
乙方支付租金及物业费之后,甲方将负责该工业厂房的物业管理及绿化维护工作。厂房及办公室卫生由乙方自行负责打扫,生活垃圾放到甲方指定的位置。
After Party B makes payment of rental and property management fees, Party A shall undertake the day-to-day maintenance of the premises as well as the greening work.Party B is responsible to clean and maintain the hygiene of the industrial plant and office by its own, domestic garbage is placed at special location designated by Party A.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

工业垃圾由乙方自行安排处理。乙方产生的危险废物须按照国家环保法进行备案处理,如由于乙方危险废物处理不当造成厂区环境污染,甲方有权要求乙方恢复到破坏以前的环境或恢复环境产生的一切费用由乙方承担。
Party B shall arrange disposal of the industrial waste by its own too. Dangerous waste produced from Party B’s activity shall be filed for recording according to the National Environment Protection Law. If Party B causes pollution to the plant area due to its failure to properly dispose of the dangerous waste, Party A has the right to demand Party B to recover the environment to its original state or to bear all the cost in restoring the environment.
第七条 水电费
Article 7 Charges for water and electricity
7.1电源、水源
7.1 Power source, water source
本合同约定的租赁期限内,甲方负责为乙方提供“380V”的交流用电电源和公用的水源,按乙方承租面积,为乙方提供每平方米不少于100W的基本用电容量,甲方为乙方配置的基本电容量为 60KVA 。 甲方可协助乙方增加电容量,所需费用由乙方承担。乙方自行承担经营所需水电费用。
Within the lease term agreed in this contract, Party A is responsible to provide to Party B “380V” AC power supply and public water source. Based on Party B’s rented area,Party B is provided with basic power consumption capacity of not less than 100W per square meter, the basic capacitance configured by Party A for Party B is 60kVA. Party A can assist Party B to increase the capacitance, the necessary cost shall be borne by Party B. Party B is responsible to bear on its own the cost of water and electricity arising from its operation.
7.2水电费的计量与收取
7.2 Measurement and collection of water and electricity charges
乙方租赁期间内(含免租期及免费清理期)的水电费按水表、电表读数计量,由甲方代收代缴。不额外承担容量费用。
During the term of lease by Party B (including the rent-free period and free cleaning period), the water and electricity charges are calculated based on the reading of consumption data recorded at respective water meter and electricity meter, to be collected and paid by Party A for Party B. There is no additional charge on capacity.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

厂房用电可以通过安装的电表读数计量,每年按计数收取上年度的电费。
The electricity charge incurred for the plant can be calculated based on reading the consumption data recorded at the electricity meter installed. The electricity charge for the preceding year shall be collected on yearly basis based on the meter reading.
7.3水电费的交纳
7.3 Payment for water and electricity charges
乙方须按照实际使用的电费足额支付给甲方管理人员,如果国家电费有调整,则收费也做相应的调整,开具相应数额的电费发票。
Party B shall settle electricity charge in full amount based on actual usage, payment is made to Party A’s management personnel. If the national electricity rate is adjusted, the electricity charge is revised accordingly, electricity invoice shall be issued with corresponding amount.
第八条工商费、税费
Article 8 Trade and Industrial fee, Tax cost
8.1甲方的责任
8.1 Party A’s obligation
在本合同期限内,甲方承担国家规定应交纳的与工业厂房、公共区有关的房产税、土地使用税、营业税。
Within the lease term of this contract, Party A is responsible to bear the payable for property tax, land use tax and business tax related to the industrial plant and the public area, as prescribed by the national provisions.
8.2乙方的责任
8.2 Party B’s obligation
乙方须负责支付其在工业厂房租赁期间内从事生产经营所引起的一切税项。
Party B must be responsible to pay all taxes relating to the production activity in the industrial plant during the lease term.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

8.3其它税费
8.3 Other taxes
对于任何其它税费,双方须按中国的有关法律,各自承担其应承担的部分。
With regard to other tax fees, both parties must undertake to settle their own respective portions in accordance with the relevant laws and regulations in China.
第九条公用设施
Article 9 Public utilities
甲方交付给乙方的工业厂房应接好所有必要(日常使用)的公用设施,包括供水、污水排放、供电其它等。
The industrial plant delivered by Party A to Party B should be equipped with necessary public utilities (day-to-day usage), including water supply, sewage discharge, power supply and other, etc.
第十条甲方权利和义务
Article 10 Rights and obligation of Party A
10.1甲方应在交付日将符合合同约定的工业厂房交付给乙方使用,并确保交付时及整个租赁期内该工业厂房清洁、可供出租使用,其相关附属设施均处于良好的运行状况。
10.1 Party A should deliver to Party B the industry plant in compliance with the contract on the delivery date for Party B’s use, and ensure that the plant is clean, leasable and usable, the related ancillary facilities are in good working condition, on the delivery day and throughout the lease term.
10.2在租赁期内,甲方应保证工业厂房在整个租赁期内均适用于其预定用途,并符合相关法律、法规和许可。在不限制前述原则的前提下,甲方应负责随时、立即和适当地采取一切必要措施,使该工业厂房完全符合所有适用的,关于工业厂房安全的法律法规。
10.2 During the lease term, Party A should assure that the industrial plant is fit and suitable for its intended use throughout the lease term, and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations as well as in possession of required permits. Without limiting the foregoing principles, Party A should take charge of implementing all necessary measures at any time, immediately and appropriately in order to enable the industrial plant meeting the requirements of applicable laws and regulations on safety.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

10.3甲方应确保工业厂房有良好的物业管理服务,包括但不限于对公共地方及公共设施的保养、维修和清洁服务,可靠的保安服务。
10.3 Party A should ensure the industrial plant offered with good property management services, including but not limited to maintenance of public area and public facilities, repair and maintenance, cleaning services as well as reliable security guarding service.
10.4除了乙方在工业厂房上安装的附着物,设施和消耗品之外,甲方应对工业厂房及其设备设施及时进行维修和保养,包括但不限 于:
10.4 Apart from the fixture, fitting and consumable installed by Party B, Party A should carry out repair and maintenance for the industrial plant and its facilities and equipment, including but not limited to:
(1)维护并保持工业厂房内部结构以及由甲方设置安装的工业厂房内部装置、设施、线路和管道处于良好和可供租赁使用的状况,包括但不限于进行保养和维修或更换,并承担相关费用;但如果最终确定损失或毁坏是由于乙方故意或重大过失所造成的,则由乙方承担费用。其范围包括但不限于:
(1) Maintain the internal structure of the industrial building as well as the fixture and fitting, facilities, lines and pipes installed by Party A in the industrial plant so that they are in good working condition ready for lease and use, including but not limited to maintenance, repair and replacement, and undertake the related expenses; if it is ascertained that the damage or loss is caused by deliberate conduct or significant negligence of Party B, then Party B is held liable for the expenses. The scope includes but not limited to:
工业厂房的内部结构、包括房顶(屋顶和天花板)、地基、外墙、窗户(包括窗玻璃和窗框);
The internal structure of the industrial plant, including rooftop (rooftops and ceilings),foundation, exterior wall, window (including pane and frame);
工业厂房之上或之下的管道和相关设施,包括一切下水道、排水沟、渠道、水槽、雨水管和排污管、下水设备、卫生设施、工业厂房外部或工业厂房之下的有关管道、以及工业厂房管道系统中的各类阀门和管线;
The piping and related facilities above and beneath the industrial plant, including all gully drains, drainage ditch, channel, water tank, rain pipe and cess pipe, launching equipment, sanitary facilities, channel outside and beneath the industrial plant, various valves and pipelines in the piping system of the industrial plant;
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

甲方承建的电气系统、电线、电缆导板、变电站开关、发电机控制中心、照明电路;
The electrical system built by Party A, wire, cable guide, substation switch, generator control centre, lighting circuit;
甲方承建的供应设施和管线,包括电力、供水、取暖/通风和空调系统、燃气设施;
The supply facilities and pipelines built by Party A, including power, water supply, heating, ventilation, air conditioning system and gas facilities;
工厂和办公室等的地面,乙方安装的表面装饰除外。
The ground floors of the workshop and office, excluding the surface decoration installed by Party B.
(2)维护并保持工业厂房外部的设备和设施处于良好和可供租赁使用的状况,包括但不限于维护和保证工业厂房的道路系统和出入通道充足,方便乙方雇员和访客使用,包括车道、停车场、人行道和园林绿化。
(2) Maintain and keep the exterior equipment and facilities of the industrial plant to be in good condition ready for lease and use, including but not limited to maintain and ensure the road system and the vomitorium are sufficient, provide a convenience to employees and visitors of Party B for use, including vehicle lane, parking place, pedestrian lane, and landscaping.
10.5在租赁期内,乙方有权正常地使用工业厂房,而不受甲方或第三方的干扰或妨碍。如果出现第三方的干扰或妨碍,甲方可以帮助乙方进行协调,乙方也可以通过法律途径解决与第三方的争端。
10.5 During the lease term, Party B has the right to use the industrial plant normally, with neither disturbance nor hinderance from Party A or third party. If there is disturbance or hinderance from the third party, Party A can assist Party B for a coordination. Alternatively, Party B can seek legal channel to resolve a dispute with the third party.
10.6如果乙方未根据合同的规定表示续租,甲方有权在租期届满前三(3)个月内,按照与乙方事先约定的时间内,由甲方或甲方的代理陪同可能的租客参观工业厂房。
10.6 If Party B has not expressed an intention to continue a lease upon the expiry of existing lease according to the provision in the contract, within three months before the expiry of the lease, based on prior agreement with Party B on stated timeframe, Party A has the right to arrange a visit to the industrial plant by prospective lessee accompanied by Party A itself or its representative agent.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

第十一条乙方权利和义务
Article 11 Rights and obligation of Party B
11.1乙方应按照本合同的规定向甲方支付履约保证金、租金等 合同明确规定的费用。
11.1 Party B should make good of payments for rental, security deposit and other expenses as clearly stipulated in the contract;
11.2乙方不应将工业厂房用于本合同规定之外的用途,不得在工业厂房内从事任何违反法律、法规、条例或政府规定的行为;也不应违反法律法规或其它有关部门对工业厂房使用的特别规定,但是此种规定必须是签署本合同时已公布的,并且可以从公开途径获得。
11.2 Party B should not use the industrial plant for other purposes not stipulated in the contract, must not engage any activity infringe of laws, regulations, rules and government orders. Party B must not violate the laws, regulations, rules and special orders by relevant authorities on the use of the industrial plant. Nevertheless, those provisions must have been announced when this contract is signed, and are readily available for public.
11.3未经甲方书面同意,乙方不应对工业厂房进行任何结构性的添加或改变,但是甲方不应不合理拒绝乙方的要求。此外,乙方可以不经甲方的同意,进行以装饰为主要目的添加或改变,或不改变工业厂房结构安装乙方认为必要或适当的设备和设施。甲方特此同意,乙方根据经营需要,在通知甲方以后,可在工业厂房内建筑和安装有关结构或其他装置,安装和运行任何机械设备。如果根据法律要求,上述行为应获得有关政府部门的事先批准,甲方应努力协助乙方获得所必需的一切批准和许可。
11.3 Before a written consent is obtained from Party A, Party B should not make any structural addition or alteration to the industrial plant. None-the-less, Party A should not reject unreasonably the request from, Party B. Besides, with a prior consent by Party A, Party B can carry out addition or alteration with primary objective for decoration, or install equipment or facilities which, to Party B, are necessary and appropriate, without changing the structure o the industrial plant. Party A hereby agrees that, according to the need of Party B, after notification to Party A, Party B can construct and install the related structure or other devices inside the industrial plant, install and operate any machinery and equipment. If the activity above-mentioned requires a prior approval from relevant government department as required by law, Party A should assist Party B to secure all necessary approvals and permits.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

11.4乙方应合理使用工业厂房,并保持工业厂房内部非结构部分状态良好、整洁。
11.4 Party B should exercise reasonable care when using the industrial plant, and ensure the non-structural parts in the industrial plant are in good condition, neat and tidy.
11.5乙方应允许甲方或其代理人按事先约定的时间进入该工业厂房,检查内部状况,并进行保养或维修。
11.5 Party B should allow Party A or its representative agents to enter into the industrial plant to conduct inspection of the internal condition, repair and maintenance, according to prior agreement on specific timeframe.
11.6未经甲方事先书面许可,乙方不得在工业厂房之外设置任何其他标志或广告,但是甲方不应不合理拒绝乙方的要求。
11.6 Without prior consent from Party A in writing, Party B should not set up any other signboards or advertisement outside the industrial plant. Nevertheless, Party A should not reject unreasonably the request from Party B.
11.7在租赁期内,乙方需全力配合甲方处理涉及与相关政府沟通备案及政府日常检查事务。
11.7 Party B should actively coordinate with Party A in dealing with and communication with governmental offices about record filing and day-to-day inspection affairs.
第十二条甲方的保证与陈述
Article 12 Party A’s guarantees and representations
12.1甲方在此保证,自本合同签订日起,和/或整个租赁期内:
12.1 Party A hereby guarantees, from the date of signing this contract, throughout the whole of the lease term:
(1)甲方是场地的使用权和工业厂房的唯一与合法的所有人,且根据中国法律法规拥有向乙方出租工业厂房的完全权利;
(1) Party A owns the rights to use the site and is the only legal owner of the industrial plant, and possesses the absolute power to lease the industrial plant to Party B in accordance with China’s laws and regulations;
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

(2)工业厂房通过了竣工验收并取得相关证明;工业厂房完全符合政府部门在建筑、环境保护、卫生、防火和安全方面所制定的标准和要求;
(2) The industrial plant passed the completion acceptance and obtained relevant certification. The industrial plant complies fully with the requirements and standards formulated by relevant governmental authorities on architecture, environment protection, hygiene, fire prevention and safety.
第十三条合同期满和终止
Article 13 Expiry of contract term and Termination of contract
13.1除非双方一致同意续展租赁期,本合同在租赁期满以后自动终止。
13.1 Unless both parties reach a consensus to extend the contract, this contract automatically terminates upon the expiry of the lease term;
13.2 如发生下列情形之一,本合同解除,除了本合同第十二条的规定外,双方互不承担责任:
13.2 This contract is rescinded if one of the circumstances below mentioned occurs, except for the provisions in Article 12 of this contract, both parties are not liable to each other:
(1)工业厂房占用范围内的土地使用权依法提前收回的;
(1) The land use rights covering the area where the industrial plant is located are taken back by law earlier than the original schedule;
(2)工业厂房因社会公共利益或城市建设需要被依法征用的;
(2) The industrial plant is expropriated by law due to public interests of society or the need for urban development;
(3)工业厂房因城市建设需要被依法列入房屋拆迁许可范围的;
(3) The industrial plant is classified in the housing demolition scheme due to the need for urban development;
(4)不可抗力持续或可预见其将持续超过六(6)个月;
(4) Continuation of the force majeure or it is foreseen that the force majeure will last beyond six months;
(5)出现法律、法规禁止出租的其他情况。
(5) Other circumstances under which the industrial plant is prohibited by law and regulation for lease.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

13.3如发生下列情形之一,甲方有权书面通知乙方要求解除本合同,收回工业厂房,并有权要求乙方赔偿损失:
13.3 If one of the circumstances below mentioned occurs, Party A has the right to notify Party B to cancel the contract, take back the industrial plant, and demand Party B to compensate for loss:
(1)乙方未征得甲方事先书面同意改变工业厂房,致使工业厂房损坏的;
(1) Without obtaining a prior consent from, Party A in writing, Party B changes the industrial plant until a cause of damage to the plant;
(2)乙方擅自转租建筑物、转让工业厂房承租权或与他人交换各自承租的房屋的;
(2) Party B sublet the lease of a whole or part of the building, pass on a remaining lease of the building or exchangesits lease with other tenants;
(3)乙方逾期不支付租金超过三十(30)日以上的;
(3) Party B delays due payment for more than 30 days;
(4)乙方不支付租金以外的本合同规定的其它任何应付款项逾期超过三十(30)日以上的;
(4) Party B refuses to settle or delay payments other than rental which are payable as required by the contract for more than 30 days;
(5)乙方将建筑物用于任何非法目的;
(5) Party B uses the building for illegal purpose;
(6)乙方违反本合同的其它约定,且在出租方书面通知后三十 (30)日内乙方未予纠正的;
(6) Party B is in breach of the contract yet has not taken any corrective action within 30 days after Party A issues a written notification;
(7)出现其他归因于乙方,法律法规允许甲方解除合同之情形的。
(7) Other circumstances where the law and regulation allow Party A to terminate the contract due to a default by Party B.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

13.4 如发生下列情形之一,乙方有权书面通知甲方终止本合同,并且要求甲方赔偿损失:
13.4 If one of the circumstances below mentioned occurs, Party B has the right to notify Party A to cancel the contract, and demand Party A to compensate for loss:
(1)甲方延迟交付建筑物三十(30)日以上;
(1) Party A postpones delivery of the building for more than 30 days;
(2)甲方没有对工业厂房或附属设施的损坏或故障及时进行维修,且在收到乙方要求改正的书面通知后三十(30)日内,仍未按照乙方要求采取合理、必要的措施进行改正;
(2) Party A does not perform repair and maintenance for damage or breakdown in the industrial plant or its ancillary facilities on time; within a period of 30 days after a notification is sent from Party B requesting for a repair, Party A has not taken reasonable and necessary measures to rectify the problem based on Party’s B requirement;
(3)租赁期内,工业厂房非因乙方原因或不可抗力原因而遭受损失或毁坏,且因此导致工业厂房整体或部分不适合出租给乙方使用超过三十(30)日;
(3) During the lease term, the industrial plant suffers from damage or loss caused by force majeure event or other factors not due to Party B, until the whole or part of the industrial plant is unsuitable for use by Party B for more than 30 days;
(4)甲方违反本合同规定的任何一项甲方的陈述和保证。
(4) Party A violates one of the guarantees and representations as prescribed in this contract;
(5)甲方违反本合同的其它约定,且在乙方书面通知后三十(30)日内甲方未予纠正的;
(5) Party A violates the other provisions under this contract, and fails to undertake corrective action within 30 days after a written notification is issued by Party B;
(6)出现其他归因于甲方,法律法规允许乙方解除合同之情形的
(6) Other circumstances where the law and regulation allow Party B to terminate the contract due to a default by Party A;
(7)甲方需在合同签订后积极配合乙方提供办理环评,注册等需要的资料。
(7) After signing of the contract, Party A does not actively coordinate with Party B to provide information materials necessary for environmental assessment, registration and so on.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

13.5本合同一方根据上述第13.3条和第13.4条终止本合同的不应减损守约方根据相关法律和本合同所享有的其他权利或救济。
13.5 The termination of this contract by either party according to Clause 13.3 and Clause 13.4 should not derogate the other rights or relief afforded to the observant party based on relevant law and the contract.
13.6本合同终止后,乙方应在租赁期届满或知会解除后的五(5)天内将租赁标的物以良好和清洁的现状(正常的损耗除外)交还甲方。双方将以合同附件二作为验收标准对租赁标的物进行验收。验收过程中,对于最终确认由于乙方故意或过失所造成的甲方提供的工业厂房或设施设备的损失,乙方应承担赔偿责任。但乙方对工业厂房或设施设备的正常磨损以及结构性或内在缺陷不承担责任。
13.6 After the cessation of this contract, Party B should return the subject of the lease to Party A in good and clean condition (except for normal wear and tear), Both parties shall refer to Appendix 2 of the contract as a standard for checking and acceptance to conduct the procedure of checking and acceptance for the lease subject. During the process of checking and acceptance, if it is confirmed that Party causes any damage to the industrial plant due to deliberate improper use or negligence, Party B shall be held liable for a compensation. However, Party B is not liable for damages which are caused by normal wear and tear, structural or inherent defects.
13.7乙方有权搬走乙方在工业厂房上添附的所有设施,但乙方应修复因搬走固定设施而对工业厂房造成的损害。任何设施拆除及修复的问题,可经甲乙双方友好协商解决。
13.7 Party B has the right to move away all those facilities added on the industrial plant. However, Party B should repair the damage caused by dismantling of those facilities. Both Party A and Party B can amicably discuss and resolve any issue pertaining to the dismantling and repair.
第十四条违约责任
14. Liability for breach of contract
14.1如果甲方未能在合同规定的交付日(见5.1)将符合合同规定的工业厂房交付给乙方使用,则乙方有权要求甲方支付延迟交付违约金。延迟交付违约金应按日计算,为月租金的百分之五(5%),自应交付之日起算至实际交付之日止。
14.1 If Party A cannot deliver the industry plant which is in compliance with the contract terms to Party B for use on the delivery date stipulated in the contract (refer Article 5.1), Party B has the right to claim liquidated damages for delayed delivery. The liquidated damages are calculated on daily basis which is five percent of the monthly rental (5%), starting from the agreed delivery date until the end of the actual delivery date.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

14.2如果乙方未能按照合同的约定按时交付或交足租金,则甲方有权要求乙方支付逾期付款违约金。逾期付款违约金应按日计算,为逾期未付金额的百分之一(1%),自应付之日起算至完全付清之日止。
14.2 If Party B cannot pay rental on time or in full, Party A has the right to claim liquidated damages for overdue payment. The liquidated damages are calculated on daily bais which is one percent of the overdue amount (1%), starting from the date of a payable becoming due until the end of the date when it is fully settled.
14.3如果甲方未依照本合同的规定而提前解除合同,则甲方应双倍返还乙方支付的履约保证金作为对乙方的补偿。
14.3 If Party A terminates the contract on early basis without adherence to the provisions of the contract, Party A should compensate Party B in the amount of two times the security deposit.
14.4如果乙方未依照合同的规定提前解除合同,则乙方应将履约保证金作为对甲方的补偿。
14.4 If Party B terminates the contract without adherence to the provisions of the contract, Party B should compensate Party A in the amount of the security deposit to be forfeited.
第十五条 适用法律与争议的解决
Article 15 Applicable Law and Settlement of Disputes
15.1管辖法律
15.1 Governing law
本合同的效力、解释和执行受中国法律管辖。对任何事项若无中国法律适用,则须参照行业习惯、一般商业惯例或国际商业惯例办理。
The effect, explanation and execution of this contract is governed by the China laws. Any matter which is not addressed by the laws in China can be dealt with by reference to the industry practices, general business practices and international business practices.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

15.2争议解决
15.2 Settlement of disputes
如因本合同发生任何争议,双方应首先尝试通过友好协商解决争议。如双方不能通过友好协商解决争议,则任何一方均可将争议提交不动产所在地人民法院诉讼管辖。
In the event a dispute arising in execution of or with relation to this contract, both parties to the dispute shall settle such dispute through friendly negotiation. If negotiation fails, either party can submit a lawsuit to the competent People’s Court where the real estate is located.
第十五条不可抗力
Article 15 Force Majeure
甲方或乙方对于因不可合理控制的事件造成无法在规定时间内履行其本合同项下全部或部分义务则履行义务的期限应根据此不可抗力的影响相应延长。不可合理控制的事件包括但不限于战争(无论是公开宣战或是其它方式的战争)、内乱或军方骚乱、暴动、天灾(洪水、台风、地震、流行病)、禁运、严重火灾、破坏、海上危险、罢工。受影响的一方应当立即将类似事件或延迟以及产生类似事件或延迟的情况书面通知另外一方并在10内提供当地有权政府部门出具的书面证明。但甲方仍有义务采取一切措施及时提供合同服务;如果不可抗力事件持续超过十周的,任何一方在书面通知另外一方的情况下可以终止本合同而不需承担任何责任。
Party A or Party B can correspondingly postpone the date to perform this contract in full or on partial basis based on the impact of the force majeure due to an absence of ability to reasonably control the event. The event which cannot reasonably be control includes but not limited to war (whether it is an open declaration of war or in other forms), civil strife, military riot, rebellion, natural disaster (flood, typhoon, earthquake, epidemic), embargo, serious fire, destruction, maritime danger, strike. The affected party should immediately notify the counter party in writing of the event or the delay and the circumstance causing the event or the delay, and to provide written proof issued by the local competent government within another 10 days. Nevertheless, Party A has still an obligation to make every effort to render contractual services on schedule. If the force majeure event last for more than ten weeks, either party can choose to notify the other in writing to terminate the contract, without bearing any liability.
第十六条其他约定
Article 16 Other provisions
17.1知会
17.1 Notification
与本合同有关的任何知会均用中文书写,并须由专人交付或挂号邮递方式发出。根据本合同的约定发出的知会或通讯的送达,如由专人交付,交付当日视为送达;以邮寄方式发出,信件寄出五(5)天后 (并由专职人员签收)视为送达。
Any notification related to this contract is written in Chinese, and needs to be sent by specially assigned personnel or registered mail. According to the provisions of this contract, if a notification or correspondence is sent by specially assigned personnel, the delivery date is regarded as the service date; if it is sent by registered mail, five days after the notification or correspondence is posted, whereby the receipt is acknowledged by professional personnel, will be regarded as the service date.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

17.2关于乙方的定义
17.2 Regarding the definition for Party B
如乙方在本合同签署时,尚未取得营业执照的,双方约定先由乙方拟定的法定代表人代为签署,待乙方营业执照办理完毕时再加盖乙方公章。加盖公章后,公司成为正式的房屋承租人,原签约的自然人应对承租人的履约情况向出租人承担连带保证责任。保证期间为债务发生后两年。
If a business license of Party B is not yet available when this contract is signed, both parties agree that the legal representative of Party B shall sign this contract on behalf, until the business license of Party B is ready then this contract will be stamped with Party B’s seal. Upon stamping the company’s seal, Party B shall become the official lessee of the building. The original natural person who signs this contract shall bear a joint responsibility to guarantee the performance of the contract by the lessee. The guarantee period is two years after the debt occurrence.
17.3效力
17.3 Effectiveness
本合同在双方法定代表人(或授权代表)签署后生效,并构成对双方具法律约束力的义务。本合同的任何条款或其适用被认定为无效不影响本合同其他部分的效力。
This contract becomes legally effective after it is signed by the legal representatives of two parties (or their appointed representatives), and constitutes legally binding obligations to the two parties.Anyclause in this contract or those clauses which are subsequently amended as non-effective shall not affect the effectiveness of other clauses in the contract.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

17.4修改和补充
17.4 Revision and Supplement
对本合同的任何修改和补充,均须以书面进行,并由双方签字后生效,与本合同具有同等法律效力。
Any revision or supplement to this contract must be performed in writing, and takes effect after being signed by both parties, carrying equal legal effect with this contract.
17.5文字
17.5 Words
本合同以中文书写,本合同书中文文本一式四(4)份;甲方、乙方各执两(2)份。
This contract is written in Chinese. This contract, with Chinese text, is in quadruplicate; Party A and Party B holds two copies each.
17.6完整合同
17.6Completeness
本合同构成双方之间就本合同项下事项所达成的完整协议,并取代双方之间就此达成的一切许诺和协议。
This contract is a complete composition of agreements between two parties on the subject matter and replaces all promises and agreements earlier made between the two parties.
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

附件一工业厂房清单
Appendix 1: Listing of Industrial Plant
附件二物业验收交接单
Appendix 2: Handover Sheet for checking and acceptance
附件三房屋所有权证等
Appendix 3: Property Ownership Certificate, etc
甲方(公章):
Party A (Seal):
授权代表(签章):
Appointed representative (Seal):
联系电话:021-38252000
Contact phone: 021-38252000
开户行:交通银行上海周浦支行 Bank: Bank of Communication Shanghai Branch Zhoupu sub-Branch
银行帐号:310069134018010044556
Account No: 310069134018010044556
传真:021-38252000
Fax: 021-38252000
日期:
Date: |
|
乙方(公章):
Party B (Seal)
授权代表(签章):
Appointed representative (Seal):
Contact phone:
传真:
Fax:
日期:
Date: |
 |
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

附件一:工业厂房清单
Appendix 1: Listing of Industrial Plant
Ⅰ. 场地
Ⅰ. Site
场地坐落位置:该地块位于【康桥秀浦路3500号】,具体以《国有土地使用证》所附的红线图为准。
Location of the site: This Site is located at [KangqiaoXiupu Road, No. 3500], the specific is subject to the Redline Map of the attached “State-owned Land Use Certificate”.
土地使用权人:【上海马力索精密机械有限公司】
Land Use Rights Owner: [Shanghai Mariso Precision Machinery Co., Ltd]
用途:【工业】
Use: [Industrial]
使用权类型:【工业】
Category of Use Rights: [Industrial]
终止日期:【2056年12月30日止】
Expiry of term: [December 30, 2056]
使用权面积:【24101.2】
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

Area if Use Rights: [24101.2]
土地使用权证号:【沪房地浦字2010第216261号】
Land Use Rights Certificate No.: [Hu Fang Di Pu Zi2010 No. 216261]
II.工业厂房
II. Industrial Plant
房地坐落:【康桥秀浦路3500号】
Location of the plant: [KangqiaoXiupu Road, No. 3500]
房地产权利人:【上海马力索精密机械有限公司】
Real estate Owner: [Shanghai Mariso Precision Machinery Co., Ltd]
共有情况:【无】
Joint ownership: [Nil]
登记时间:【2006年12月31日】
Registration date: [December 31, 2006]
总层数:【多层】
Total number of floors: [Many]
房屋结构:【砖混】
Building structure: [Brick and Concrete]
建筑面积:【17122.37】
Built-up area: [17,122.37]
房地产权证编号:【沪房地浦字2010第216261号】
Property Certificate No.: [Hu Fang Di Pu Zi2010 No. 216261]
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

附件二:物业验收交接单
Appendix 2: Handover Sheet for Checking and Acceptance
序号 Serial No. |
设施(设备) 名称 (mm*mm) Facility / Equipment |
数量 Quantity |
性能(状态) Function / Status |
备注 Remark | ||||
| 1. | ||||||||
| 2. | ||||||||
| 3. | ||||||||
| 4. | ||||||||
| 5. | ||||||||
| 6. | ||||||||
| 7. | ||||||||
| 8. | ||||||||
| 9. | ||||||||
| 10. | ||||||||
| 11. | ||||||||
| 12. | ||||||||
| 13. | ||||||||
| 14. | ||||||||
| 15. |
水表底数:0
Water meter: 0
电表底数:)(厂房)电表读数都为
Electricity meter: (Factory building)The electricity meter reads
交付方:XXX (盖章)
Deliverer: XXX (Seal)
经办人(签字):
Handler (Signature):
| 年 月 日 | |
| Date: Year Month Day |
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]

接收方:XXX (盖章)
Recipient: XXX (Seal)
经办人(签字):
Handler (Signature):
| 年 月 日 | |
| Date: Year Month Day |
备注:本物业验收交接单的签署代表甲方己经将租赁房屋及附属设施设备按约交付给了乙 方。
Remark: The signing of the Handover Sheet represents that Party A has handed over the leased buildings and its facilities and equipment to Party B
[English Translation of Attached Chinese Document]
Exhibit 10.2
借款协议
Loan Agreement
借款协议
Loan Agreement
出借人:辽宁鑫健林国医堂健康管理有限公司(下简称甲方)
Lender: Liaoning Xinjianlin Guoyitang Health Management Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Party A)
法人代表:杨恒飞
Legal Representative: Yang Hengfei
统一社会信用代码:91210102MA0P5WA24X
Unified Social Credit Code: 91210102MA0P5WA24X
借款人:上海起阁动力科技有限公司(下简称乙方)
Borrower: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Party B)
法人代表:杨恒飞
Legal Representative: Yang Hengfei
统一社会信用代码:91310115MA1H836T1H
Unified Social Credit Code: 91310115MA1H836T1H
甲乙双方本着公平自愿、诚实守信的原则,经双方协商一致,就借款事项达成如下协议:
On the principle of fairness, willingness and good faith, Party A and Party B reach the following agreement upon consensus through consultation on the matters concerning the loan:
一、借款金额
I. Loan amount
甲方出借给乙方人民币3,000,000.00元(大写:人民币叁佰万元整),作为乙方经营使用。
Party A shall lend to Party B RMB 3,000,000.00 (in words: RMB three million Yuan only)for Party B’s operation.
乙方收款账号信息如下:
Party B’s receiving account information is as follows:
银行户名:上海起阁动力科技有限公司
Account Name: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd.
开户银行:中国银行股份有限公司上海市秀沿路支行
Opening Bank: Bank of China Ltd Shanghai Xiuyan Road Sub-branch
银行账号:436472077315
Account No.: 436472077315
二、借款用途
II. Loan purpose
本借款限于流动资金借款,用于公司经营活动,未经乙方同意,甲方不得挪作他用。
The loan is a working capital loan for the business activities of the Company. Without Party B’s consent, Party A shall not use the loan for other purposes.
借款协议
Loan Agreement
三、借款偿还及还款方式
III. Repayment of loan
1、乙方可根据白身经营情况或根据甲方要求随时还款。如甲方临时需要收回借款,应提前三十天向乙方提出还款申请。
1. Party B may make repayment at any time according to its business situations or Party A’s requirements. Should Party A recover the loan temporarily, it shall apply for repayment to Party B 30 days in advance.
2、还款方式:乙方可以选择分期或一次性偿还借款。
2. Repayment mode: Party B may choose to repay the loan in installments or in a lump sum.
3、借款性质:甲方不收取任何利息,乙方无息使用。
3.Loan nature: Party A shall not charge any interest and Party B shall use the loan without interest.
四、甲方的权利与义务
IV. Party A’s rights and obligations
1、甲方于本协议签订后7个工作日内将约定的资金付至乙方的指定账户。
1. Party A shall pay the agreed loan to the account designated by Party B within 7 working days upon the signature of this Agreement.
2、甲方有权监督乙方借款用途。
2. Party A shall have the right to supervise the use of the loan by Party B.
五、乙方的权利与义务
V. Party B’s rights and obligations
1、按照本合同的约定使用借款,乙方不得将借款挪作他用或用于非法用途。
1. Party B shall use the loan according to the provisions hereof but shall not use the loan for any other or illegal purposes.
2、在本合同项下的借款全部清偿前,未经甲方书面同意,不得以任何理由为他人提供担保借款。
2. Prior to full repayment of the loan hereunder, without Party A’s written consent, Party B shall not provide guarantee loan for others for any reason.
3、乙方应按甲方要求偿还借款。
3. Party B shall repay the loan according to Party A’s requirements
六、违约责任
VI. Liability for breach of contract
1、乙方不按合同规定的用途使用借款,甲方有权收回部分或金部贷款。
1. If Party B fails to use the loan for the purpose specified herein, Party A shall have the right to take back part or all of the loan.
2、如乙方未按甲方要求归还借款的,应向甲方承担违约责任。
2. If Party B fails to repay the loan according to Party A’s requirements, Party B shall bear liability for breach of contract for Party A.
借款协议
Loan Agreement
七、争议的解决方式
VII. Dispute settlement
凡因本协议发生的及与本协议有关的任何争议,甲乙双方应协商解决协商不成的,本协议争议甲方所在地人民法院管辖。
Any and all disputes arising from or in connection with the execution of this Agreement shall be settled by Party A and Party B through consultation. Where consultation fails, disputes hereunder shall be settled under the jurisdiction of the people’s court at the location where Party A is located.
八、合同生效
VIII. Contract effectiveness
本合同经甲、乙双方签字(盖章)后生效。本合同共贰份,双方各执壹份。本合同若有其他未及事宜,双方进一步签定补充条款。
This Contract shall come into force after being signed (sealed) by both parties. The Contract is made out in two originals for Party A and Party B each holding one. In case of any matters not provided herein, both parties shall further sign supplementary provisions.
借款协议
Loan Agreement
(本页为签字页)
(This page is a signature page)
甲方(盖章) Party A (Seal) 授权代表(签字) Authorized Representative (Signature) 日期:2019年7月15日 Date: July 15, 2019 |
乙方(盖章) Party B (Seal) 授权代表(签字) Authorized Representative (Signature) 日期:2019年7月15日 Date: July 15, 2019 |
Exhibit 10.4
市场拓展合作协议
Market expansion cooperation agreement
市场拓展合作协议
Market expansion cooperation agreement
合同编号:SHQG2021110101
Contract No. SHQG2021110101
甲方:上海起阁动力科技有限公司
Party A: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd
统一社会信用代码:91310115MA1H836T1H
Unified social credit Code: 91310115MA1H836T1H
法定代表人:马建华
Legal representative: Ma Jianhua
乙方:何刘
Party B: He Liu
身份证号:342423198910276616
ID no.: 342423198910276616
电话:15216763190
Tel: 15216763190
按照《中华人民共和国民法典》等法律、法规及其他规定,就甲乙双方合作进行拓展业务,经双方协商,达成如下协议:
Both parties have reached the following agreement about the cooperation between Party A and Party B to expand business through negotiation under the civil code of the people’s Republic of China and other laws, regulations, and other provisions:
一、合作内容
I. Cooperation content
甲方聘请乙方担任甲方的市场拓展顾问,为甲方提供市场拓展等方面的帮助,依法维护甲方的合法权益。
Party A employs Party B as Party A’s market development consultant to provide Party A with assistance in market development and safeguard Party A’s legitimate rights and interests according to law.
二、合作产品
II. Cooperative products
产品名称:控制器
Product Name: controller
产品型号:EC-05Z0015N-M-HC
Product model: EC-05Z0015N-M-HC
市场拓展合作协议
Market expansion cooperation agreement
三、甲方责任
III. Obligation of the Party A
1、委托乙方销售甲方指定产品。
1. It shall entrust Party B to sell the products designated by Party A.
2、配合乙方工作,并为乙方提供必要的便利条件。
2. It shall cooperate with Party B and provide necessary convenience for Party B.
3、按本协议的规定,向乙方支付相关费用。
3. It shall pay relevant fees to Party B under the provisions of this agreement.
4、对乙方所提供的业务服务内容负有保密义务,不得泄露给无关第三方。
4. Party B shall be obliged to keep confidential the business services provided by Party B and shall not disclose them to irrelevant third parties.
四、乙方责任
IV. Responsibilities of Party B
1、负责甲方产品的业务拓展工作。
1. It shall be responsible for the business development of Party A’s products.
2、乙方应按照甲方产品定价销售产品,开展的相关拓展工作不得与甲方的业务产生利益冲突。
2. Party B shall sell the products according to the pricing of Party A’s products, and the relevant expansion work shall not conflict with Party A’s business.
3、乙方有责任配合甲方的业务开展工作,且不得以任何形式损害或侵犯甲方的利益。
3. Party B shall be responsible for cooperating with Party A’s business and shall not damage or infringe Party A’s interests in any form.
4、有义务在对知悉的甲方非公开的有关数据及文件资料保密,不得泄露给任何第三方。
4. It is obliged to keep confidential the non-public relevant data and documents of Party A and shall not disclose them to any third party.
5、乙方有责任在每月初将本月拓展计划和上个月拓展情况总结如实与甲方沟通。
5. Party B has the responsibility to truthfully communicate with Party A the development plan for this month and the development summary of last month at the beginning of each month.
五、佣金费用及支付
V. Commission fee and payment
1、佣金费用构成
1. Composition of commission expenses
佣金根据指定产品销售数量计算即30元/台。
The Commission is calculated according to the sales quantity of the specified products, i.e. 30 yuan/set.
2、佣金支付方式
2. Commission payment method
按笔支付,甲方收到合同金额的总价款后支付乙方佣金。
Party A shall pay Party B commission after receiving the total price of the contract amount.
3、乙方账户信息
3. Account information of Party B account name: He Liu
账户名称:何刘
Account name: He Liu
开户银行:中国银行秀沿路支行
Bank of deposit: Bank of China Xiuyan road sub-branch
账号:6217880800005472701
Account No.: 6217880800005472701
市场拓展合作协议
Market expansion cooperation agreement
六、协议解除或终止
VI.Rescission or termination of the agreement
1、甲乙双方当出现违反本协议任何一条时,本协议自动终止。
1. When Party A and Party B violate any article of this agreement, this agreement will be automatically terminated.
2、甲乙双方经过友好协商,可以解除或终止协议。
2. Party A and Party B can cancel or terminate the agreement through friendly negotiation.
七、违约责任
VII. Liability for breach of contract
如任何一方不履行本协议,违约方应当向守约方支付人民币50, 000. 00元作为违约金,并应赔偿对方的经济损失。
The breaching party shall pay RMB 50, 000.00 yuan to the other party as liquidated damages If either party fails to perform this agreement, and shall compensate the other party for its economic losses.
八、其他
8. Other
1、本协议一经双方授权代表签字盖章后即发生效力。
1. This Agreement shall come into force once signed and sealed by the authorized representatives of both parties.
2、本协议书有效期为一年自2021年11月1日起至2022年10月31日止。
2. This agreement is valid for one year and shall be from November 1st, 2021 to October 31st, 2022.
3、本协议一式两份,自双方签字日起生效双方各执壹份,均具同等法律效力。
3. This agreement is made in duplicate, which shall take effect from the date of signature by both parties. Each party holds one copy, and each copy has the same legal effect.
4、本协议未尽事宜,由甲、乙双方另行协商解决。
4. It shall be settled by Party A and Party B through separate negotiation f or matters not covered in this Agreement.
甲方:上海起阁动力科技有限公司
Party A: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd
授权代表
Authorized representative:
日期:2021.11.1
Date: November 1st, 2021
乙方:何刘
Party B: He Liu
日期:2021.11.1
Date: November 1st, 2021
Exhibit 10.5
The contract of sale
Contract Number
Signing date:
Supplier (A) : Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD.
Party (B) :
I. through negotiation, party a and party b enter into the following contract :(the following table is the price of RMB including tax)
| No. | Product Name | Specification Model | Unit | Quantity | Unit price (tax included) | Amount (tax included) | Delivery date | Remarks |
| 1 | The controller | EC-05Z0015N-M-HC | 台 | 10 | 220 | 2200 | Within a week of receipt | |
The amount of (capital) |
Total: | Two thousand two hundred | ||||||
II. Quality Standards: Party A’s quality standards shall be met. All functions are subject to the product installation manual delivered with the package.
III. Product warranty period (within 12 months from the date of spontaneous delivery)
IV. Invoice: Invoice shall be issued if there is no quality problem feedback within five days after receiving and inspecting the goods. If you do not receive the invoice or have any objection to the invoice content within one month after the acceptance of the goods, please confirm with Party A in time.
V. Delivery time: see the delivery date column. Delivery method: Party A shall send the goods to the receiving address designated by Party B by consignment.
The freight shall be borne by Party A and the delivery place shall be designated by Party B. The risk of damage and loss of the goods shall be transferred after Party B signs and receives the goods. If Party B fails to collect the goods in violation of the agreement, the risk of damage and loss of the goods shall be borne by Party B from the date of the breach.
VI. Product acceptance inspection: Party B shall, upon receipt of the goods, timely check and confirm the packaging, appearance, model, quantity and quality of the goods. If Party B fails to raise any objection in writing to Party A within five days, it shall be deemed to have passed the inspection.
Vii. Terms of payment: Delivery upon payment.
Viii. This Contract is made in duplicate, with each party holding one copy. The contract shall come into force only after it is signed and sealed by both parties. The copy of fax shall have the same legal effect.
Ix. Any dispute arising from the contract or the performance of the Contract shall be settled by both parties through negotiation. If negotiation fails, both parties may file a lawsuit to the people’s court in the place where the supplier is located for settlement.
Party A
Company Name: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Address: Room 104, floor 1, Building B, Building 1, No. 3500 xiupu Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Telephone: 021-58070918
Fax: 021-58070918
Bank: Bank of China, Shanghai Xiuyan Road Sub-branch
Account number:
Party B
Company Name:
Company address:
Telephone:
Contact person:
Bank name:
Account number:
Exhibit 10.6
借款协议
Loan Agreement
借款协议
Loan Agreement
协议编号:QGJKXY202104
Agreement number: QGJKXY202104
甲方(出借人):杨恒飞
Party A (Lender): Yang Hengfei
身份证号码:211022198007056571
ID card No.: 211022198007056571
乙方(借款人):上海起阁动力科技有限公司
Party B (Borrower): Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd.
统一社会信用代码:91310115MA1H836T1H
Unified Social Credit Code: 91310115MA1H836T1H
法定代表人:钱华
Legal Representative: Qian Hua
为了明确责任,恪守信用,在双方自愿、协商情况下特签订本合同以资共同信守。
In order to specify responsibilities and abide by credit, Party A and Party B hereby enter into this Contract voluntarily through consultation.
一、借款额度:3, 000, 000. 00元(大写:叁佰万元整)。
I. Loan amount: 3,000,000.00 Yuan (in words: three million Yuan only).
二、借款用途:该笔借款用于公司经营。
II. Loan purpose: the loan shall be used for the operation of the Company.
三、款项支付方式:甲方按乙方需求,在借款额度范围内分批支付款项,具体借款金额以申请书累计金额为准。
III. Payment mode: Party A shall pay the loan in installments within the loan amount according to Party B’s needs. The specific loan amount shall be subject to the accumulative amount of the application.
四、偿还方式:
IV. Repayment mode:
1、乙方可根据自身经营情况或根据甲方要求随时还款。如甲方临时需要收回借款,应提前三十天向乙方提出还款申请。
1. Party B may make repayment at any time according to its business situations or Party A’s requirements. Should Party A recover the loan temporarily, it shall apply for repayment to Party B 30 days in advance.
2、还款方式:乙方可以选择分期或一次性偿还借款。
2. Repayment mode: Party B may choose to repay the loan in installments or in a lump sum.
五、借款性质:该笔款项甲方不收取利息供乙方无息使用。
V. Loan nature: Party A shall not charge any interest but provide the loan for Party B for use free of interest.
六、违约责任
借款协议
Loan Agreement
VI. Liability for breach of contract
1、 如乙方未按甲方要求归还借款的,应向甲方承担违约责任。
1. If Party B fails to repay the loan according to Party A’s requirements, Party B shall bear liability for breach of contract for Party A.
2、 乙方如不按合同规定的用途使用借款,甲方有权随时收回该借款,并要求乙方支付借款总金额百分之三十作为违约金。
2. If Party B does not use the loan for the purpose specified herein, Party A shall have the right to take back the loan at any time and require Party B to pay 30% of the total loan as liquidated damages for breach of contract.
七、合同争议的解决方式:本合同在履行过程中发生的争议,由当事人双方友好协商解决,也可由第三人调节,协商或调节不成的,可以向甲方所在的人民法院起诉。
VII. Dispute settlement: any and all disputes during the execution process of this Contract shall be settled by both parties through friendly consultation, or be mediated by a third party. Where consultation or mediation fails, a lawsuit may be instituted in the people’s court at the location where Party A is located.
八、本合同自双方签字之日起生效。本合同一式两份, 双方各执一份,合同文本具有同等法律效力。
VIII. This Contract shall come into force as of the date of signature of both parties. This Contract is made out in two originals for Party A and Party B each holding one, which shall be equally authentic.
甲方(签字、盖章):杨恒飞 Party A (Signature and Seal): Yang Hengfei
签订日期:2021年4月15日 Date of signing: April 15, 2021 |
乙方(签字、盖章): Party B (Signature and Seal):
签订日期:2021年4月15日 Date of signing: April 15, 2021 |
Exhibit 10.7
Loan Agreement
Party A (lender): Shenzhen Hongyi Education and Culture Co., LTD
Unified Social credit code :91440300MA5ELYWQ26
Legal representative: Wen Nuoyao
Party B (Borrower): Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Unified Social credit Code :91310115MA1H836T1H
Legal representative: Ma Jianhua
Now party A and Party B agree to lend party A the loan according to the relevant provisions of the Civil Code of the People’s Republic of China. In respect of payment to Party B, the following agreements are reached:
Article 1: Amount of loan
For the business operation of the company, Party B needs to borrow RMB 700,000.00 from Party A (in words: Seven hundred thousand Yuan only), both parties agree that Party B shall remit the loan to the account designated by Party A within 3 days after signing the contract.
Article 2: Term of loan
The loan term begins on November 23, 2021 and ends on November 22, 2022.
Article 3: Repayment method
Repay the loan in one lump sum or in installments at the end of the loan term.
Article 4: Loan interest rate
If the borrower pays the loan in lump sum or in installments before the maturity of the loan, the loan is interest-free; In excess of settlement the interest shall be paid according to the total amount of the loan * the daily interest rate 0.03%* the number of days overdue.
Article 5: Liability for breach of contract
1. If Party A fails to make the payment as required by Party B, the loan term shall be extended for each day delayed.
2. If Party B fails to use the loan for the purpose specified in this Contract, Party A shall have the right to recover the loan at any time and request party B to Party B is required to pay 10% of the total amount of the loan as penalty.
Article 6: Effective Date of contract
It shall come into force upon signature and seal by both parties.
Article 7: Settlement of contract disputes
All disputes arising out of this Agreement shall be settled by both parties through negotiation. If no agreement can be reached, both parties agree to proceed from the arbitration committee in the place where Party A is located shall submit the case to the people’s court for arbitration.
Article 8 Miscellaneous
1. Anything not covered herein shall be supplemented by the parties through consultation Such provisions shall have the same effect as this Agreement
2. This Agreement is made in duplicate, with each party holding one copy. Have the same legal effect.
| 1 |
Party A (signature and seal): Shenzhen Hongyi Education culture Co., LTD
Authorized Representative:
Date of Signing: November 20, 2021
Party B (signature and seal): Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Authorized Representative:
Date of Signing: November 20, 2021
| 2 |
Exhibit 10.8
REGULATION S SUBSCRIPTION AGREEMENT
THIS REGULATION S SUBSCRIPTION AGREEMENT (this “Agreement”), dated as of [ ] 2022, is entered into by and between Tian’an Technology Group Limited a corporation organized under the laws of British Virgin Islands (the “Company”), and the Buyer(s) set forth on the signature pages (each, a “Buyer Signature Page”) affixed hereto (individually, a “Buyer” or collectively, the “Buyers”).
WITNESSETH:
WHEREAS, the parties desire that, upon the terms and subject to the conditions contained herein, the Company shall sell to the Buyers, and the Buyers shall purchase from the Company, [ ] shares (the “Shares”) of the Company’s common stock, $[ ] par value per share(“Common Stock”), at a purchase price of [ ] per share (the “Purchae Price”); and
NOW, THEREFORE, in consideration of the mutual covenants and other agreements contained in this Agreement the Company and the Buyer(s) hereby agree as follows:
SECTION 1
1.1 Subscription. Each Buyer, intending to be legally bound, hereby irrevocably subscribes for and agrees to purchase the number of Shares set forth on the Buyer Signature Page affixed hereto, in an offshore transaction negotiated outside the U.S. and to be consummated and closed outside the United States in reliance upon an exemption from securities registration pursuant to Regulation S (“Regulation STM) as promulgated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”).
1.2 Purchase of Shares. Subject to the satisfaction (or waiver) of the terms and conditions of this Agreement, each Buyer agrees, severally and not jointly, to purchase at the Closing (as defined below), and the Company agrees to sell and issue to each Buyer, severally and not jointly, at the Closing, such number of Shares as is set forth on the Buyer Signature Page affixed hereto. Following the Buyer’s execution of this Agreement on the Buyer Signature Page and completion of the Investor Certification affixed hereto as Appendix A and the Anti-Money Laundering Information Form affixed hereto as Appendix B, and prior to the Closing, the Buyer shall wire transfer the aggregate purchase price for the Shares (the “Subscription Amount”) set forth on his or its Buyer Signature Page, in same-day funds in accordance with the instructions set forth immediately below, pursuant to the terms and disbursed in accordance therewith.
Wire Instructions
Bank:
Account Name:
Account #:
1.3 Acceptance or Rejection.
(a) The Buyer understands and agrees that the Company reserves the right to reject this subscription for the Shares if, in its reasonable judgment, it deems such action in the best interest of the Company, at any time prior to the Closing, notwithstanding prior receipt by the Buyer of notice of acceptance of the Buyer’s subscription.
(b) The Buyer understands and agrees that his or its subscription for the Shares is irrevocable.
(c) In the event the sale of the Shares subscribed for by the Buyer is not consummated by the Company for any reason (in which event this Agreement shall be deemed to be rejected), this Agreement and any other agreement entered into between the Buyer and the Company relating to this subscription shall thereafter have no force or effect and the Company shall promptly return or cause to be returned to the Buyer the Subscription Amount remitted to the Company by the Buyer, without interest thereon or deduction therefrom, in exchange for the Shares.
1.4 Offering Period. The Company may offer the Shares at any time through and including June 30, 2022, which date may be extended for an additional thirty (30) days (as such may be extended, the “Offering Period”) at the sole discretion of the Company.
SECTION 2
2.1 Closing. The closing (the “Closing”) of the purchase and sale of the Shares, shall occur on such date as is mutually agreed to by the parties on or before the expiration of the Offering Period.
SECTION 3
3.1 Buyer Representations and Warranties. Each Buyer represents and warrants, severally and not jointly, as to such Buyer, that:
(a) The Buyer is acquiring the Shares for the Buyer’s own account as principal, not as a nominee or agent, for investment purposes only, and not with a view to, or for, resale, distribution, or fractionalization thereof in whole or in part and no other person has a direct or indirect beneficial interest in such Shares or any portion thereof. Further, the Buyer does not have any contract, undertaking, agreement or arrangement with any person to sell, transfer or grant participations to such person or to any third person, with respect to the Shares for which the Buyer is subscribing or any part of the Shares.
(b) The Buyer has full power and authority to enter into this Agreement, the execution and delivery of this Agreement has been duly authorized, if applicable, and this Agreement constitutes a valid and legally binding obligation of the Buyer.
(c) The Buyer is not subscribing for the Shares as a result of or subsequent to any advertisement, article, notice or other communication published in any newspaper, magazine or similar media or broadcast over television or radio, or presented at any seminar or meeting, or any solicitation of a subscription by person previously not known to the Buyer in connection with investment securities generally.
(d) The Buyer understands that the Company is under no obligation to register the Shares under the Securities Act, or to assist the Buyer in complying with the Securities Act or the securities laws of any state of the United States or of any foreign jurisdiction.
(e) The Buyer is (i) experienced in making investments of the kind described in this Agreement and the related documents, (ii) able, by reason of the business and financial experience of its officers (if an entity) and professional advisors (who are not affiliated with or compensated in any way by the Company or any of its affiliates or selling agents), to protect its own interests in connection with the transactions described in this Agreement, and the related documents, and (iii) able to afford the entire loss of its investment in the Shares.
(f) The Buyer acknowledges his or its understanding that the offering and sale of the Shares is intended to be exempt from registration under Regulation S of the Securities Act. In furtherance thereof, in addition to the other representations and warranties of the Buyer made herein, the Buyer further represents and warrants to and agrees with the Company and its affiliates as follows:
(i) The Buyer realizes that the basis for the exemption may not be present if, notwithstanding such representations, the Buyer has in mind merely acquiring the Shares for a fixed or determinable period in the future, or for a market rise, or for sale if the market does not rise. The Buyer does not have any such intention;
(ii) The Buyer has the financial ability to bear the economic risk of his or its investment, has adequate means for providing for his or its current needs and personal contingencies and has no need for liquidity with respect to his or its investment in the Company;
(iii) The Buyer has such knowledge and experience in financial and business matters as to be capable of evaluating the merits and risks of the prospective investment in the Shares. The Buyer also represents it has not been organized for the purpose of acquiring the Shares;
(iv) The Buyer has been provided an opportunity for a reasonable period of time prior to the date hereof to obtain additional information concerning the offering of the Shares, the Company and al other information to the extent the Company possesses such information or can acquire it without unreasonable effort or expense; and
(v) The Buyer has carefully reviewed al of the Company’s filings under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”).
(g) The Buyer is not relying on the Company, or its affiliates or agents with respect to economic considerations involved in this investment. The Buyer has relied solely on his or its own advisors.
(h) No representations or warranties have been made to the Buyer by the Company, or any officer, employee, agent, affiliate or subsidiary of the Company, other than the representations of the Company contained herein, and in subscribing for Shares the Buyer is not relying upon any representations other than those contained herein.
(i) Any resale of the Shares during the “distribution compliance period,” as defined in Rule 902(f) to Regulation S, shall only be made in compliance with exemptions from registration afforded by Regulation S. Further, any such sale of the Shares in any jurisdiction outside of the United States will be made in compliance with the securities laws of such jurisdiction. The Buyer will not offer to sell or sell the Shares in any jurisdiction unless the Buyer obtains all required consents, if any.
(j) The Buyer understands that the Shares are being offered and sold in reliance on an exemption from the registration requirements of United States federal and state securities laws under Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act and that the Company is relying upon the truth and accuracy of the representations, warranties, agreements, acknowledgments and understandings of the Buyer set forth herein in order to determine the applicability of such exemptions and the suitability of the Buyer to acquire the Shares. In this regard, the Buyer represents, warrants and agrees that:
(i) The Buyer is not a U.S. Person (as defined below) and is not an affiliate (as defined in Rule 501(b) under the Securities Act) of the Company and is not acquiring the Shares for the account or benefit of a U.S. Person. A “U.S. Person” means any one of the following:
(A) any natural person resident in the United States of America;
(B) any partnership or corporation organized or incorporated under the laws of the United States of America;
(C) any estate of which any executor or administrator is a U.S. person;
(D) any trust of which any trustee is a U.S. person;
(E) any agency or branch of a foreign entity located in the United States of America;
(F) any non-discretionary account or similar account (other than an estate or trust) held by a dealer or other fiduciary for the benefit or account of a U.S. person;
(G) any discretionary account or similar account (other than an estate or trust) held by a dealer or other fiduciary organized, incorporated or (if an individual) resident in the United States of America; and
(H) any partnership or corporation if:
(1) organized or incorporated under the laws of any foreign jurisdiction; and
(2) formed by a U.S. person principally for the purpose of investing in securities not registered under the Securities Act, unless it is organized or incorporated, and owned, by accredited investors (as defined in Rule 501(a) under the Securities Act) who are not natural persons, estates or trusts.
(ii) At the time of the origination of contact concerning this Agreement and the date of the execution and delivery of this Agreement, the Buyer was outside of the United States.
(iii) The Buyer will not, during the period commencing on the date of issuance of the Shares and ending on the six month anniversary of such date, or such shorter period as may be permitted by Regulation S or other applicable securities law (the “Restricted Period”), offer, sell, pledge or otherwise transfer the Shares in the United States, or to a U.S. Person for the account or for the benefit of a U.S. Person, or otherwise in a manner that is not in compliance with Regulation S.
(iv) The Buyer will, after expiration of the Restricted Period, offer, sell, pledge or otherwise transfer the Shares only pursuant to registration under the Securities Act or an available exemption therefrom and, in accordance with al applicable state and foreign securities laws.
(v) The Buyer was not in the United States, engaged in, and prior to the expiration of the Restricted Period will not engage in, any short selling of or any hedging transaction with respect to the Shares, including without limitation, any put, call or other option transaction, option writing or equity swap, unless in compliance with the Securities Act.
(vi) Neither the Buyer nor or any person acting on his or its behalf has engaged. nor will engage, in any directed selling efforts to a U.S. Person with respect to the Shares and the Buyer and any person acting on his or its behalf have complied and will comply with the “offering restrictions” requirements of Regulation S under the Securities Act.
(vii) The transactions contemplated by this Agreement have not been pre- arranged with a buyer located in the United States or with a U.S. Person and are not part of a plan or scheme to evade the registration requirements of the Securities Act.
(viii) Neither the Buyer nor any person acting on his or its behalf has undertaken or carried out any activity for the purpose of, or that could reasonably be expected to have the effect of, conditioning the market in the United States, its territories or possessions, for any of the Shares. The Buyer agrees not to cause any advertisement of the Shares to be published in any newspaper or periodical or posted in any public place and not to issue any circular relating to the Shares, except such advertisements that include the statements required by Regulation S under the Securities Act, and only offshore and not in the U.S. or its territories, and only in compliance with any local applicable securities laws.
(ix) Each certificate representing the Shares shall be endorsed with the following legends, in addition to any other legend required to be placed thereon by applicable federal or state securities laws:
“THE SECURITIES ARE BEING OFFERED TO INVESTORS WHO ARE NOT U.S. PERSONS (AS DEFINED IN REGULATION S UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933, AS AMENDED (“THE SECURITIES ACT”)) AND WITHOUT REGISTRATION WITH THE UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT IN RELIANCE UPON REGULATION S PROMULGATED UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT.”
“TRANSFER OF THESE SECURITIES IS PROHIBITED, EXCEPT IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE PROVISIONS OF REGULATION S, PURSUANT TO REGISTRATION UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT, OR PURSUANT TO AVAILABLE EXEMPTION FROM REGISTRATION. HEDGING TRANSACTIONS MAY NOT BE CONDUCTED UNLESS IN COMPLIANCE WITH THE SECURITIES ACT.”
(x) The Buyer consents to the Company making a notation on its records or giving instructions to any transfer agent of the Company in order to implement the restrictions on transfer of the Shares set forth in this Section 3.
(k) The Buyer has received al documents, records, books and other information pertaining to the Buyer’s investment in the Company that has been requested by the Buyer. The Buyer has reviewed al reports and other documents filed by the Company with the SEC (the “SEC Documents”).
(l) The Buyer represents and warrants to the Company that all information that the Buyer has provided to the Company, including, without limitation, the information on the Buyer Signature Page affixed hereto, the Investor Certification affixed hereto as Annex A and the Anti- Money Laundering Information Form affixed hereto as Annex B, is correct and complete as of the date hereof.
(m) Other than as set forth herein, the Buyer is not relying upon any other information, representation or warranty by the Company or any officer, director, stockholder, agent or representative of the Company in determining to invest in the Shares. The Buyer has consulted, to the extent deemed appropriate by the Buyer, with the Buyer’s own advisers as to the financial, tax, legal and related matters concerning an investment in the Shares and on that basis believes that his or its investment in the Shares is suitable and appropriate for the Buyer.
(n) The Buyer is aware that no federal or state agency has (i) made any finding or determination as to the fairness of this investment, (i) made any recommendation or endorsement of the Shares or the Company, or (iii) guaranteed or insured any investment in the Shares or any investment made by the Company.
SECTION 4
The Company represents and warrants to each of the Buyers that:
4.1 Organization of the Company. The Company is a corporation duly organized and validly existing and in good standing under the laws of British Virgin Islands, and has al requisite power and authority to own, lease and operate its properties and to carry on its business as now being conducted.
4.2 Authority. (a) The Company has the requisite corporate power and authority to enter into and perform its obligations under this Agreement and to issue the Shares; (b) the execution and delivery of this Agreement by the Company and the consummation by it of the transactions contemplated hereby and thereby have been duly authorized by all necessary corporate action and no further consent or authorization of the Company or its Board of Directors is required; and (c) this Agreement has been duly executed and delivered by the Company and constitutes a valid and binding obligation of the Company enforceable against the Company in accordance with its terms, except as such enforceability may be limited by applicable bankruptcy, insolvency, or similar laws relating to, or affecting generally the enforcement of, creditors’ rights and remedies or by other equitable principles of general application.
4.3 SEC Documents. To the best of Company’s knowledge, the Company has not provided to the Buyer any information that, according to applicable law, rule or regulation, should have been disclosed publicly prior to the date hereof by the Company, but which has not been so disclosed. As of their respective dates, the SEC Documents complied in all material respects with the requirements of the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, as the case may be, and other federal, state and local laws, rules and regulations applicable to such SEC Documents, and none of the SEC Documents contained any untrue statement of a material fact or omitted to state a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary in order to make the statements therein, in light of the circumstances under which they were made, not misleading. The financial statements of the Company included in the SEC Documents comply as to form and substance in al material respects with applicable accounting requirements and the published rules and regulations of the SEC, or other applicable rules and regulations with respect thereto. Such financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles applied on a consistent basis during the periods involved (except (a) as may be otherwise indicated in such financial statements or the notes thereto or (b) in the case of unaudited interim statements, to the extent they may not include footnotes or may be condensed or summary statements) and fairly present in al material respects the financial position of the Company as of the dates thereof and the results of operations and cash flows for the periods then ended (subject, in the case of unaudited statements, to normal year-end audit adjustments).
4.4 Exemption from Registration; Valid Issuances. The sale and issuance of the Shares, in accordance with the terms and on the bases of the representations and warranties of the Buyer set forth herein, may and shall be properly issued by the Company to the Buyer pursuant to Section 4(a)(2), Regulation S and/or any applicable U.S state law. When issued and paid for as herein provided, the Shares shall be duly and validly issued, fully paid, and nonassessable. Neither the sales of the Shares pursuant to, nor the Company’s performance of its obligations under, this Agreement shall (a) result in the creation or imposition of any liens, charges, claims or other encumbrances upon the Shares or any of the assets of the Company, or (b) entitle the other holders of the Common Stock of the Company to preemptive or other rights to subscribe to or acquire the Common Stock or other securities of the Company. The Shares shall not subject the Buyer to personal liability by reason of the ownership thereof.
4.5 No General Solicitation or Advertising in Regard to this Transaction. Neither the Company nor any of its affiliates nor any person acting on its or their behalf (a) has conducted or will conduct any general solicitation (as that term is used in Rule 502(c) of Regulation D) or general advertising with respect to any of the Shares, or (b) made any offers or sales of any security or solicited any offers to buy any security under any circumstances that would require registration of the Common Stock under the Securities Act.
4.6 No Conflicts. The execution, delivery and performance of this Agreement by the Company and the consummation by the Company of the transactions contemplated hereby, including without limitation the issuance of the Shares, do not and will not (a) result in a violation of the Articles of Incorporation or Bylaws of the Company or (b) conflict with, or constitute a material default (or an event that with notice or lapse of time or both would become a material default) under, or give to others any rights of termination, amendment, acceleration or cancellation of, any material agreement, indenture, instrument or any “lock-up” or similar provision ofany underwriting or similar agreement to which the Company is a party, or (¢) result in a violation of any federal, state, local or foreign law, rule, regulation, order, judgment or decree (including federal and state securities laws and regulations )applicable to the Company or by which any property or asset of the Company is bound or affected (except for such conflicts, defaults, terminations, amendments, accelerations, cancellations and violations as would not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on the business, operations, properties, prospects or condition (financial or otherwise) of the Company) nor is the Company otherwise in violation of, conflict with or in default under any of the foregoing. The Company is not required under U.S. federal, state or local law, rule or regulation to obtain any consent, authorization or order of, or make any filing or registration with, any court or governmental agency in order for it to execute, deliver or perform any of its obligations under this Agreement or issue and sell the Common Stock in accordance with the terms hereof (other than any SEC, FINRA, or state securities filings that may be required to be made by the Company subsequent to the Closing); provided that, for purposes of the representation made in this sentence, the Company is assuming and relying upon the accuracy of the relevant representations and agreements of the Buyer herein.
SECTION 5
5.1 Reporting Status. Until the date on which each Buyer shall have sold all of its Shares, the Company shall file in a timely manner (or, with respect to Current Reports on Form 8-K, shall use its reasonable commercial efforts to file in a timely manner) al reports required to be filed with the SEC pursuant to the Exchange Act and the regulations of the SEC thereunder.
5.2 Use of Proceeds. The Company shall use 100% of the net proceeds from the sale of the Shares (after deducting legal and accounting fees and expenses and fees) for working capital and general corporate purposes.
5.3 Listings or Quotation. Until the date on which each Buyer shall have sold all of its Shares the Company shall use its best efforts to maintain the listing or quotation of its Common Stock on the OTC Markets or a national securities exchange.
SECTION 6
6.1 Indemnity. The Buyer agrees to indemnify and hold harmless the Company, its officers and directors, employees and its affiliates and their respective successors and assigns and each other person, if any, who controls any thereof, against any loss, liability, claim, damage and expense whatsoever (including, but not limited to, any and all expenses whatsoever reasonably incurred in investigating, preparing or defending against any litigation commenced or threatened or any claim whatsoever) arising out of or based upon any false representation or warranty or breach or failure by the Buyer to comply with any covenant or agreement made by the Buyer herein or in any other document furnished by the Buyer to any of the foregoing in connection with this transaction.
6.2 Modification. Neither this Agreement nor any provisions hereof shall be modified, discharged or terminated except by an instrument in writing signed by the party against whom any waiver, change, discharge or termination is sought.
6.3 Notices. Any notices, consents, waivers, or other communications required or permitted to be given under the terms of this Agreement must be in writing and will be deemed to have been delivered (i) upon receipt, when delivered personally; (i) upon confirmation of receipt, when sent by facsimile or electronic mail; (i) upon receipt when sent by U.S. certified mail, return receipt requested, or (iv) one (1) day after deposit with a nationally recognized overnight delivery service, in each case properly addressed to the party to receive the same. The addresses and facsimile numbers for such communications shall be:
Tian’an Technology Group Limited
Room 104, Building 1-B, No. 3500
Xiupu Road, Pudong New Area
Shanghai, China
Attention: Yang Hengfei
Telephone: 17127669333
E-Mail: 54382444(@qq.com
With acopy to:
The
Crone Law Group, P.C.
500 Fifth Avenue, Suite 938
New York, NY 10110
Attention: Mason L. Allen
Telephone:
(917) 574-7812
E-Mail: mallen@cronelawgroup.com
If to the Buyer, to his or its address and facsimile number set forth on the Buyer Signature Page affixed hereto. Each party shall provide five (5) days’ prior written notice to the other party of any change in address or email.
6.4 Counterparts. This Agreement may be executed through the use of separate signature pages or in any number of counterparts and by electronic (digital) signature, and each of such counterparts shall, for al purposes, constitute one agreement binding on all parties, notwithstanding that all parties are not signatories to the same counterpart. Signatures may be electronic (digital) transmission.
6.5 Binding Effect. Except as otherwise provided herein, this Agreement shall be binding upon and inure to the benefit of the parties and their heirs, executors, administrators, successors, legal representatives and assigns. If the Buyer is more than one person, the obligation of the Buyer shall be joint and several and the agreements, representations, warranties and acknowledgments herein contained shall be deemed to be made by and be binding upon each such person and his heirs, executors, administrators and successors.
6.6 Entire Agreement. This Agreement and the documents referenced herein contain the entire agreement of the parties and there are no representations, covenants or other agreements except as stated or referred to herein and therein.
6.7 Assignability. This Agreement is not transferable or assignable by the Buyer.
6.8 Applicable Law. This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of New York, without giving effect to conflicts of law principles.
6.9 Pronouns. The use herein of the masculine pronouns “him” or “his” or similar terms shall be deemed to include the feminine and neuter genders as well and the use herein of the singular pronoun shall be deemed to include the plural as well.
[Remainder of page is intentionally left blank. Signature page follows.]
SIGNATURE PAGE
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the parties hereto have executed this Agreement as of the day and year as set forth below.
| Dated: [ ], 2022 | ||
| # of shares: | ||
| SUBSCRIBER (individual) | SUBSCRIBER (entity) | |
| Signature | Signature | |
| Print Name | Print Name | |
| Signature (if joint tenants in common) | ||
| Address Of Principal Residence | Address Of Executive Offices | |
| ID Number(s): | IRS Tax Identification Number | |
| Telephone Number: | Telephone Number: | |
| E-mail Address: | E-mail Address: |
| 1. | If Subscriber is an individual, please submit a copy of non-expired identification for the authorized signatory(ies) on the investment documents, showing name, date of birth, address and signature. The address shown on the identification document MUST match the Investor’s address shown on the Signature Page. | |
| 2. | If the Subscriber is a corporation, limited liability company, trust or other type of entity, please submit the following requisite documents: (i) Articles of Incorporation, By-Laws, Certificate of Formation, Operating Agreement, Trust or other similar documents for the type of entity; and (ii) Corporate Resolution or power of attorney or other similar document granting authority to signatory(ies) and designating that they are permitted to make the proposed investment. |
ACCEPTANCE OF SUBSCRIPTION
| Name of Subscriber | |||
| Accepted for: | [ ], 2022 |
ACCEPTED BY:
| Tian’an Technology Group Limited | ||
| By: | ||
| Name | ||
| Title | ||
| Date: | [ ], 2022 |

Exhibit 10.9
Contract No.:_______________________
Labor Contract
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
Name of Employee: Yang Hengfei
Aug. 24, 2022
Party A (Employer)
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
Director: Yang Hengfei
Party B (Employee)
Name: Yang Hengfei
Gender: Male
ID card No.: 211022198007056571
Address: Room 104, 1/F, Block B, Bldg. 1, No. 3500, Xiupu Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Tel.: 021-58070918
In accordance with the Labor Law of the People’s Republic of China and BVI and other relevant laws and regulations, Party A and Party B make and enter into this Contract on the principle of equality, willingness, good faith and law-abiding upon consensus through consultation. Both parties shall abide by all terms and conditions of this Contract.
1. Term of Contract
1.1 Party A and Party B agree to determine the term of this Contract according to the following 1.1.1:
1.1.1 Fixed Term: from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2022.
1.1.2 Without a fixed term: from this day _______________ to the date when Party A or Party B cancels this Contract according to the stipulations hereof.
1.2 Party A and Party B agree that the probation period of Party B shall be / month(s) and be ended on /___ (the probation period shall be included in the term hereof). If Party A thinks that Party B satisfies Party A’s employment conditions and passes assessment after the expiration of the probation period, Party B shall become a full employee of Party A. Party B shall be automatically regarded as a full employee of Party A if Party B does not receive party A’s formal notice at the end of the probation period.
2. Work contents
2.1 Party A and Party B agree that Party B shall be employed as Party A’s CEO and work at No. 3500, Xiupu Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai.
2.2 During the term hereof, Party B shall be honest, faithful, diligent and dutiful at his corresponding position, fully and properly perform his duties agreed herein and determined by Party A, complete all tasks assigned by Party A and try his best to seek benefits for Party A.
2.3 During the term hereof, Party B shall follow the arrangements and decisions on his daily work made by Party A as required.
3. Working hours
3.1 Party A and Party B agree that Party A shall determine its working hours in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and Party B undertakes to abide by the provisions on working hours formulated and irregularly revised by Party A.
3.2 Party B shall complete all the work tasks agreed herein, specified by Party A and temporarily assigned by Party A within the working hours specified by Party A. Where overtime work is really necessary, Party B shall go through formalities for overtime application and approval according to relevant provisions of Party A.
3.3 Considering that Party A is a manufacturing enterprise, through consultation between Party A and Party B, Party B agrees that Party A may extend Party B’s working hours appropriately according to Party A’s production and operation needs without violating relevant laws and regulations. In other words, Party A may arrange Party B to work overtime on working days, rest days or legal holidays.
3.4 If Party A approves or arranges Party B to work overtime, it shall arrange Party B to take a supplementary leave or pay Party B extra salary thereafter according to Party A’s relevant provisions.
4. Salaries
4.1 The monthly basic salary is 8000 Yuan. The performance salary is / Yuan; other subsidies is / Yuan; and the total monthly salary is / Yuan. Where there is no major defect in work, the performance salary shall be paid together with the basic salary. The monthly salary during the probation period is / Yuan.
4.2 Party B’s salaries may be adjusted according to Party B’s work performance A or the change of Party B’s position and duties, and Party A shall notify Party B of the adjusted salaries in written form.
4.3 Party A shall have the right to determine and implement the payment scope, standard, amount and time of bonus to its employees according to its production and business situations.
4.4 Without violating relevant laws and regulations, Party A shall have the right to adjust the bonus and welfare standards of all employees including Party B according to its production and operation situations.
4.5 Unless as otherwise compulsorily required by laws and regulations, Party A shall not be obliged to pay Party B any extra wages, benefits or subsidies other than those specified in this Contract (including any annexes hereto).
4.6 Party A shall pay the salaries of the previous month on the 10th day of each month. Such payment may be advanced or postponed appropriately if it happens to be a day off or legal holiday.
5. Labor protection and working conditions
5.1 Party A shall, in accordance with the relevant national provisions for labor protection, provide Party B with a workplace and necessary labor protective articles in compliance with the national standards to protect Party B’s safety and health practically during production and work.
5.2 Party B shall be entitled to refuse Party A’s command against rules and adventure homework forced by Party A, and ask Party A to make correction or report to the relevant authorities.
6. Social insurance and benefits
6.1 Party A shall handle social insurance procedures for Party B by law. The expenses for handling social insurance shall be borne according to the relevant provisions of Party A’s registration area.
6.2 Party A shall formulate provisions on legal holidays, annual leave, marriage leave, maternity leave, funeral leave and other leaves in accordance with laws and regulations, and Party B shall be entitled to such leaves according to Party A’s relevant provisions.
6.3 Employees’ year-end bonuses shall be paid according to the Company’s business volume of the current year.
7. Labor discipline
7.1 Party A shall formulate its employee manual, rules and regulations, policies, procedures and other provisions in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and timely and appropriately notify Party B of these provisions.
7.2 Party B shall strictly abide by the laws and regulations of China and the aforesaid provisions of Party A, and fully and appropriately perform various obligations agreed by both Party A and Party B. Party A shall have the right to deal with the offenders of these provisions and both parties’ agreement according to Party A’s relevant provisions and both parties’ agreement.
7.3 Party B warrants that during the term hereof, without party A’s written approval, Party B will not engage in any part-time activities affecting his work or having a stake with Party A, and in particular, Party B shall in no way hold a position in any competitor. In case of any violation, Party A may dismiss Party B immediately.
7.4 Party B warrants that during the term hereof and after the termination or cancellation of this Contract for any reason, Party B shall not take any action damaging Party A’s interests. If it fails to do so, Party B shall be liable for compensation according to law.
8. Confidentiality and non-competition
8.1 During the term hereof, Party B shall keep strictly confidential all the information (either provided in written or oral form, information and materials in connection with Party A or Party A”s business, finance and commerce) that is not known to public and Party A reasonably thinks confidential, including but not limited to, the quotation, data, information and proposals submitted and provided by foreign and domestic research institutions and engineering institutions; the documents and instructions issued by government agencies at all levels; and the research results, analytical data, plans, reports and summaries obtained or generated by Party A in the whole course of work, including intermediate results at each stage (such information is hereinafter collectively referred to as “Confidential Information”), except that such disclosure is (1) required by laws and regulations; or (ii) an order of a competent court or a request of a competent government agency; or (iii) expressly authorized by Party A prior to disclosure. Party B agrees that during the term hereof and after the termination or expiration of this Contract, he shall not engage in any of the following activities:
8.1.1 disclose or transmit any Confidential Information to anyone, Other than Party A’s employees, dispatched personnel or contract employees and/or relevant personnel of Party A’s affiliated companies who should understand such relevant information;
8.1.2 use any Confidential Information for private purposes or unrelated to the performance of his duties in Party A;
8.1.3 disclose any Confidential Information without permission due to failure to fulfill the duty of care and diligence; and violate any laws and regulations of China on the use and disclosure of Party A’s confidential information or trade secrets.
8.2 Party B acknowledges and agrees that, during the term hereof, all relevant original or backup documents, drawings and other materials acquired by Party B for work (including computer files, floppy diskettes, optical disks, and information stored by any other means and other property of any nature) shall be always the property owned by Party A, and shall be returned to Party A according to Party A’s requirements from time to time. In any case, Party B shall return these materials to Party A once the labor relationship between Party A and Party B is terminated.
8.3 Any loss or damage caused to Party A due to Party B’s violation of the aforesaid confidentiality obligation shall be assumed by Party B. Party B warrants that Party A can be fully compensated.
8.4 Party B undertakes not to engage in any activities competing with Party A during the term of the Labor Contract and within two years after the termination of the Labor Contract. If Party A requires Party B to sign a non-competition agreement, Party B undertakes to sign it immediately, provided that the agreement complies with the requirements of relevant national laws and regulations.
9. Inventions
9.1 During the term hereof, the inventions, works, computer software, technical secrets or other information and data completed by Party B for the performance of the work tasks specified in the Contract or assigned by Party A or using Party A’s material and technical conditions, business information, workplace, human resources and other conditions, shall belong to Party A’s technical achievements and Party A shall reserve the intellectual property rights thereof. Party A shall have the right to make free use of the aforesaid technical achievements. However, Party B shall not allow any third party to use or transfer such achievements to any third party at any time. During the process of application, registration and record of job achievements by Party A, Party B agrees to provide information and assistance required by Party A according to Party A’s requirements so as to make Party A to obtain and exercise relevant rights.
9.2 During the term hereof, Party B may use the aforesaid technical achievements when performing the work tasks specified or assigned by Party A. Party B shall not publicize or disclose such technical achievements to any third party, nor allow others to use or disclose such technical achievements.
10. Training
10.1 If Party A invests or arranges Party B to participate in various training, or Party B is in a key position or under other special circumstances, both parties may sign a special agreement separately to define both parties’ relevant rights and obligations.
10.2 If Party B fails to perform the relevant obligations of service life, non-competition and compensation for breach of contract in accordance with the above agreement, that is, Party B violates this Contract and a relevant special agreement, Party B shall be liable for breach of contract in accordance with this Contract and the special agreement. Party A shall have the right to unilaterally cancel or terminate the labor contract relationship with Party B if Party B’s behavior meets the conditions for cancellation or termination of contract as agreed by both parties.
11. Representations and warranties
On the date of signature of this Contract, Party B makes the following representations and warranties to Party A:
11.1 his personal information in writing presented to Party A, including but not limited to his resume, identification certificate, academic certificate and other personal information related to his work and Party A’s employment, and other supporting materials, shall be true, complete and accurate;
11.2 he has no labor relationship with any other entity or individual; the signature of this Contract and the performance of his obligations hereunder shall not violate or conflict with the terms or conditions of other contracts or documents;
11.3 Party B meets all the requirements of laws and regulations related to Party A; including but not limited to, he has obtained the relevant work permits, handled relevant registration and individual income tax payment procedures (except those which should be handled by the employer), and Party B undertakes to maintain the above-mentioned legal status during the term hereof;
11.4 Party B shall truthfully inform Party A whether he has any family relationship with Party A’s existing employees (including regular employees, dispatched employees and contract employees), that is, whether any of his relatives (including parents, spouses, children, brothers, sisters, parents-in-law, brothers-in-law and sisters-in-law, hereinafter collectively referred to as “Party B’s Relative”) work in Party A; Party B shall have no conflict of interest with Party A, that is, none of Party B’s Relative holds any position or has any interest (as owner, partner, shareholder, director or senior management person) in Party A’s suppliers. Party B undertakes to make a written report to his direct manager and the human resources manager within five (5) days if he learns that Party B’s Relative holds position in Party A’s supplier or acquires such interests during his term of office. “Suppliers” refers to all entities or individuals that have business, commerce or economic relations with Party A or provide paid services for Party A.
12. Cancellation of contract
12.1 Party A may immediately terminate this Contract without making any economic compensation to Party B if:
12.1.1 it has been proved that Party B does not satisfy the recruitment requirements during the probation period;
12.1.2 Party B seriously violates labor discipline, Party A’s rules and regulations and both parties’ agreement;
12.1.3 Party B causes any severe damage to Party A’s interests due to dereliction of duty, seeking private benefits or engaging in activities prohibited by Party A;
12.1.4 Party B is subject to criminal liabilities in accordance with law;
12.1.5 Party B violates Party A’s relevant provisions and both parties’ agreement, discloses Party A’s trade secrets and causes severe damage to Party A’s interests; and
12.1.6 other circumstances as prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
12.2 If Party B is under any of the following circumstances, Party A may cancel the Labor Contract by giving a written notice to Party B 30 days in advance, and Party A shall make economic compensation to Party B according to Party A’s provisions as applicable:
12.2.1 Party B falls ill or is injured for a non-work-related reason, who is not able to bear the original post after the expiration of the medical treatment period as prescribed, nor can he assume any other position as arranged by Party A;
12.2.2 Party B is incapable of doing his job and remains so upon training or upon adjustment to his position;
12.2.3 The objective circumstance has altered significantly, on which the conclusion of the Contract is based, which results in that the Contract is unable to be performed, and Party A and Party B fail to reach an agreement on change of the Contract through consultation between both parties; if reduction of its personnel becomes really necessary when Party A comes to the brink of bankruptcy during the period of statutory consolidation or runs deep into difficulties in production and management, Party A shall explain the situations to all employees including Party B, listen to employees’ opinions and report to the local labor administrative department.
12.3 Party B may notify Party A to cancel this Contract immediately under any of the following circumstances:
12.3.1 during the probation period;
12.3.2 Party A forces Party B to work by way of violence, threat or illegal limitation of personal liberty;
12.3.3 12.3.3 Party A fails to pay labor remuneration or provide working conditions as agreed in this Contract or in the employment letter sent to Party B; or other circumstances prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
12.4 Except for these circumstances, Party B shall notify Party A in writing 30 days in advance if he intends to cancel or terminate the Labor Contract during the term hereof, unless as otherwise agreed by the parties.
12.4.1 Upon receipt of the above written notice, Party A shall have the right to decide that Party B shall continue to work for 30 days in accordance with this Contract before leaving the Company, or agree Party B to leave the Company immediately according to Party B’s application;
12.4.2 If Party B fails to give a written notice to Party A 30 days in advance to cancel the Labor Contract and Party A disagrees Party B to leave office immediately, Party B shall pay Party A one month’s average salary of the year prior to the cancellation of the Labor Contract as the payment in lieu of notice;
12.4.3 Upon Party A’s consent, Party B shall handle work handover and separation settlement procedures timely according to the procedures and requirements specified by Party A;
12.4.4 After Party B completes the work handover and separation settlement procedures, Party A shall pay Party B the labor remuneration due to Party B and Party B shall make confirmation and sign for it. If Party B fails to handle the separation and settlement procedures as required by Party A, Party A shall have the right to investigate Party B’s legal liabilities by necessary means.
12.5 Without violating relevant laws and regulations, this Contract may be canceled in advance according to the results agreed by both parties upon consensus through consultation.
12.6 When Party A and Party B discharges this Labor Contract, Party A shall issue a written certification to Party B and go through formalities for cancellation of this Labor Contract timely, except as otherwise provided herein.
13. Termination of contract
13.1 This Contract shall be terminated when the term of this Contract expires or or any condition for termination of the Labor Contract as agreed by both parties occurs. Party A shall issue a written certification to Party B and go through formalities for termination of this Labor Contract timely.
If both Party A and Party B agree to renew this Labor Contract when the contract term expires, both parties shall go through formalities for renewal 30 days prior to the expiration of the contract term.
14. Liability for breach of contract
Both parties shall strictly comply with this Contract after this Contract comes into force. If either party violates its obligations agreed herein and causes losses to the other party, it shall make compensation to the other party for all the losses arising therefrom.
15. Dispute settlement
Any and all labor disputes between Party A and Party B shall be settled firstly through consultation. Where consultation fails, either party may apply for arbitration to the labor dispute arbitration committee at the location China. Where there is no objection to the arbitration award, both parties shall perform the arbitration award. The party which is not satisfied with the arbitration award may bring a lawsuit to the competent people’s court at the location where Party A is registered.
16. Emergency contact person
In case of urgent medical treatment, Party B agrees that Party A may represent Party B to sign on the operation list required by the hospital and Party B warrants that Party A or Party A’s representative may not be held liable therefor. Should Party A contact Party B’s Relative under emergencies, the information of Party B’s emergency contact person is as follows:
Name and emergency contact Tel.: ______________________Address:_______________
17. Contract annexes
17.1 During the performance process of this Contract, other agreements signed by both parties, and the documents and memorandums issued by Party A to Party B, and various regulations formulated by Party A, including but not limited to employee manual, rules and regulations, policies and procedures, etc., are the annexes to this Contract. They are an integral part of this Contract and have the same equal legal force as this Contract.
17.2 If this Contract and an annex hereto are signed at the same time, in case of any discrepancy between this Contract and the annex hereto, this Contract shall prevail. If the time of signature is different, the supplementary agreement signed later shall prevail.
18. Miscellaneous
18.1 This Contract shall be governed and interpreted by the laws of China.
18.2 During the term hereof, any change in Party B’s salaries and benefits as stipulated in sub-clause 4.1 herein shall not affect the validity of any other provisions hereof.
18.3 In the event that any clause of this Contract becomes due to changes in laws and regulations, the validity of other clauses of this Contract shall not be affected.
18.4 The headings of the clauses are provided for reference convenience only but shall not affect the understanding and interpretation of this Contract.
18.5 This Contract is written in Chinese. It is made out in two originals for both parties each holding one, which shall be equally authentic.
18.6 This Contract shall enter into force as of the date of signature of both parties. Upon the expiration of the term hereof, both parties may renew this Contract in the form of signature confirmation.
18.7 The previously signed agreement with Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. shall be void, and this contract shall prevail.
| Party A: (Seal) | Party B: (Signature) Yang Hengfei |
| Authorized Representative: | |
| Aug. 24, 2022 | Aug. 24, 2022 |
Exhibit 10.10
Contract No.:________________
Labor Contract
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
Name of Employee: He Cong
Aug. 24, 2022
Party A (Employer)
Tian’an Technology Group Ltd.
Director: Yang Hengfei
Party B (Employee)
Name: He Cong
Gender: Female
ID card No.: 430122199007170649
Address: Room 601, Building 5, Xiuyi Garden, Lane 1137, Huanqiao Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Tel.: 18640346169
In accordance with the Labor Law of the People’s Republic of China and BVI and other relevant laws and regulations, Party A and Party B make and enter into this Contract on the principle of equality, willingness, good faith and law-abiding upon consensus through consultation. Both parties shall abide by all terms and conditions of this Contract.
1. Term of Contract
1.1 Party A and Party B agree to determine the term of this Contract according to the following 1.1.1:
1.1.1 Fixed Term: from February 1, 2022 to January 31, 2022.
1.1.2 Without a fixed term: from this day___________ to the date when Party A or Party B cancels this Contract according to the stipulations hereof.
1.2 Party A and Party B agree that the probation period of Party B shall be / month(s) and be ended on /___(the probation period shall be included in the term hereof). If Party A thinks that Party B satisfies Party A’s employment conditions and passes assessment after the expiration of the probation period, Party B shall become a full employee of Party A. Party B shall be automatically regarded as a full employee of Party A if Party B does not receive party A’s formal notice at the end of the probation period.
2. Work contents
2.1 Party A and Party B agree that Party B shall be employed as Party A’s CFO. The work location is no fixed location.
2.2 During the term hereof, Party B shall be honest, faithful, diligent and dutiful at his corresponding position, fully and properly perform his duties agreed herein and determined by Party A, complete all tasks assigned by Party A and try his best to seek benefits for Party A.
2.3 During the term hereof, Party B shall follow the arrangements and decisions on his daily work made by Party A as required.
3. Working hours
3.1 Party A and Party B agree that Party A shall determine its working hours in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and Party B undertakes to abide by the provisions on working hours formulated and irregularly revised by Party A.
3.2 Party B shall complete all the work tasks agreed herein, specified by Party A and temporarily assigned by Party A within the working hours specified by Party A. Where overtime work is really necessary, Party B shall go through formalities for overtime application and approval according to relevant provisions of Party A.
3.3 Considering that Party A is a manufacturing enterprise, through consultation between Party A and Party B, Party B agrees that Party A may extend Party B’s working hours appropriately according to Party A’s production and operation needs without violating relevant laws and regulations. In other words, Party A may arrange Party B to work overtime on working days, rest days or legal holidays.
3.4 If Party A approves or arranges Party B to work overtime, it shall arrange Party B to take a supplementary leave or pay Party B extra salary thereafter according to Party A’s relevant provisions.
4. Salaries
4.1 The monthly basic salary is 16000 Yuan. The performance salary is / Yuan; other subsidies is 200 Yuan; and the total monthly salary is 16200 Yuan. Where there is no major defect in work, the performance salary shall be paid together with the basic salary. The monthly salary during the probation period is 15000 Yuan. The probation period is from February 1, 2022 to February 28, 2022.
4.2 Party B’s salaries may be adjusted according to Party B’s work performance A or the change of Party B’s position and duties, and Party A shall notify Party B of the adjusted salaries in written form.
4.3 Party A shall have the right to determine and implement the payment scope, standard, amount and time of bonus to its employees according to its production and business situations.
4.4 Without violating relevant laws and regulations, Party A shall have the right to adjust the bonus and welfare standards of all employees including Party B according to its production and operation situations.
4.5 Unless as otherwise compulsorily required by laws and regulations, Party A shall not be obliged to pay Party B any extra wages, benefits or subsidies other than those specified in this Contract (including any annexes hereto).
4.6 Party A shall pay the salaries of the previous month on the 15th day of each month. Such payment may be advanced or postponed appropriately if it happens to be a day off or legal holiday.
4.7 Seniority salary: 100 yuan/year. Salary adjustments are made on July 1 each year.
5. Labor protection and working conditions
5.1 Party A shall, in accordance with the relevant national provisions for labor protection, provide Party B with a workplace and necessary labor protective articles in compliance with the national standards to protect Party B’s safety and health practically during production and work.
5.2 Party B shall be entitled to refuse Party A’s command against rules and adventure homework forced by Party A, and ask Party A to make correction or report to the relevant authorities.
6. Social insurance and benefits
6.1 Party A shall handle social insurance procedures for Party B by law. The expenses for handling social insurance shall be borne according to the relevant provisions of Party A’s registration area.
6.2 Party A shall formulate provisions on legal holidays, annual leave, marriage leave, maternity leave, funeral leave and other leaves in accordance with laws and regulations, and Party B shall be entitled to such leaves according to Party A’s relevant provisions.
6.3 Employees’ year-end bonuses shall be paid according to the Company’s business volume of the current year.
6.4 Party A provides Party B with a meal subsidy of 15 yuan per day (calculated based on Party B’s actual working days).
7. Labor discipline
7.1 Party A shall formulate its employee manual, rules and regulations, policies, procedures and other provisions in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and timely and appropriately notify Party B of these provisions.
7.2 Party B shall strictly abide by the laws and regulations of China and the aforesaid provisions of Party A, and fully and appropriately perform various obligations agreed by both Party A and Party B. Party A shall have the right to deal with the offenders of these provisions and both parties’ agreement according to Party A’s relevant provisions and both parties’ agreement.
7.3 Party B warrants that during the term hereof, without party A’s written approval, Party B will not engage in any part-time activities affecting his work or having a stake with Party A, and in particular, Party B shall in no way hold a position in any competitor. In case of any violation, Party A may dismiss Party B immediately.
7.4 Party B warrants that during the term hereof and after the termination or cancellation of this Contract for any reason, Party B shall not take any action damaging Party A’s interests. If it fails to do so, Party B shall be liable for compensation according to law.
8. Confidentiality and non-competition
8.1 During the term hereof, Party B shall keep strictly confidential all the information (either provided in written or oral form, information and materials in connection with Party A or Party A”s business, finance and commerce) that is not known to public and Party A reasonably thinks confidential, including but not limited to, the quotation, data, information and proposals submitted and provided by foreign and domestic research institutions and engineering institutions; the documents and instructions issued by government agencies at all levels; and the research results, analytical data, plans, reports and summaries obtained or generated by Party A in the whole course of work, including intermediate results at each stage (such information is hereinafter collectively referred to as “Confidential Information”), except that such disclosure is (1) required by laws and regulations; or (ii) an order of a competent court or a request of a competent government agency; or (iii) expressly authorized by Party A prior to disclosure. Party B agrees that during the term hereof and after the termination or expiration of this Contract, he shall not engage in any of the following activities:
8.1.1 disclose or transmit any Confidential Information to anyone, Other than Party A’s employees, dispatched personnel or contract employees and/or relevant personnel of Party A’s affiliated companies who should understand such relevant information;
8.1.2 use any Confidential Information for private purposes or unrelated to the performance of his duties in Party A;
8.1.3 disclose any Confidential Information without permission due to failure to fulfill the duty of care and diligence; and violate any laws and regulations of China on the use and disclosure of Party A’s confidential information or trade secrets.
8.2 Party B acknowledges and agrees that, during the term hereof, all relevant original or backup documents, drawings and other materials acquired by Party B for work (including computer files, floppy diskettes, optical disks, and information stored by any other means and other property of any nature) shall be always the property owned by Party A, and shall be returned to Party A according to Party A’s requirements from time to time. In any case, Party B shall return these materials to Party A once the labor relationship between Party A and Party B is terminated.
8.3 Any loss or damage caused to Party A due to Party B’s violation of the aforesaid confidentiality obligation shall be assumed by Party B. Party B warrants that Party A can be fully compensated.
8.4 Party B undertakes not to engage in any activities competing with Party A during the term of the Labor Contract and within two years after the termination of the Labor Contract. If Party A requires Party B to sign a non-competition agreement, Party B undertakes to sign it immediately, provided that the agreement complies with the requirements of relevant national laws and regulations.
9. Inventions
9.1 During the term hereof, the inventions, works, computer software, technical secrets or other information and data completed by Party B for the performance of the work tasks specified in the Contract or assigned by Party A or using Party A’s material and technical conditions, business information, workplace, human resources and other conditions, shall belong to Party A’s technical achievements and Party A shall reserve the intellectual property rights thereof. Party A shall have the right to make free use of the aforesaid technical achievements. However, Party B shall not allow any third party to use or transfer such achievements to any third party at any time. During the process of application, registration and record of job achievements by Party A, Party B agrees to provide information and assistance required by Party A according to Party A’s requirements so as to make Party A to obtain and exercise relevant rights.
9.2 During the term hereof, Party B may use the aforesaid technical achievements when performing the work tasks specified or assigned by Party A. Party B shall not publicize or disclose such technical achievements to any third party, nor allow others to use or disclose such technical achievements.
10. Training
10.1 If Party A invests or arranges Party B to participate in various training, or Party B is in a key position or under other special circumstances, both parties may sign a special agreement separately to define both parties’ relevant rights and obligations.
10.2 If Party B fails to perform the relevant obligations of service life, non-competition and compensation for breach of contract in accordance with the above agreement, that is, Party B violates this Contract and a relevant special agreement, Party B shall be liable for breach of contract in accordance with this Contract and the special agreement. Party A shall have the right to unilaterally cancel or terminate the labor contract relationship with Party B if Party B’s behavior meets the conditions for cancellation or termination of contract as agreed by both parties.
11. Representations and warranties
On the date of signature of this Contract, Party B makes the following representations and warranties to Party A:
11.1 his personal information in writing presented to Party A, including but not limited to his resume, identification certificate, academic certificate and other personal information related to his work and Party A’s employment, and other supporting materials, shall be true, complete and accurate;
11.2 he has no labor relationship with any other entity or individual; the signature of this Contract and the performance of his obligations hereunder shall not violate or conflict with the terms or conditions of other contracts or documents;
11.3 Party B meets all the requirements of laws and regulations related to Party A; including but not limited to, he has obtained the relevant work permits, handled relevant registration and individual income tax payment procedures (except those which should be handled by the employer), and Party B undertakes to maintain the above-mentioned legal status during the term hereof;
11.4 Party B shall truthfully inform Party A whether he has any family relationship with Party A’s existing employees (including regular employees, dispatched employees and contract employees), that is, whether any of his relatives (including parents, spouses, children, brothers, sisters, parents-in-law, brothers-in-law and sisters-in-law, hereinafter collectively referred to as “Party B’s Relative”) work in Party A; Party B shall have no conflict of interest with Party A, that is, none of Party B’s Relative holds any position or has any interest (as owner, partner, shareholder, director or senior management person) in Party A’s suppliers. Party B undertakes to make a written report to his direct manager and the human resources manager within five (5) days if he learns that Party B’s Relative holds position in Party A’s supplier or acquires such interests during his term of office. “Suppliers” refers to all entities or individuals that have business, commerce or economic relations with Party A or provide paid services for Party A.
12.Cancellation of contract
12.1 Party A may immediately terminate this Contract without making any economic compensation to Party B if:
12.1.1 it has been proved that Party B does not satisfy the recruitment requirements during the probation period;
12.1.2 Party B seriously violates labor discipline, Party A’s rules and regulations and both parties’ agreement;
12.1.3 Party B causes any severe damage to Party A’s interests due to dereliction of duty, seeking private benefits or engaging in activities prohibited by Party A;
12.1.4 Party B is subject to criminal liabilities in accordance with law;
12.1.5 Party B violates Party A’s relevant provisions and both parties’ agreement, discloses Party A’s trade secrets and causes severe damage to Party A’s interests; and other circumstances as prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
12.2 If Party B is under any of the following circumstances, Party A may cancel the Labor Contract by giving a written notice to Party B 30 days in advance, and Party A shall make economic compensation to Party B according to Party A’s provisions as applicable:
12.2.1 Party B falls ill or is injured for a non-work-related reason, who is not able to bear the original post after the expiration of the medical treatment period as prescribed, nor can he assume any other position as arranged by Party A;
12.2.2 Party B is incapable of doing his job and remains so upon training or upon adjustment to his position;
12.2.3 The objective circumstance has altered significantly, on which the conclusion of the Contract is based, which results in that the Contract is unable to be performed, and Party A and Party B fail to reach an agreement on change of the Contract through consultation between both parties; if reduction of its personnel becomes really necessary when Party A comes to the brink of bankruptcy during the period of statutory consolidation or runs deep into difficulties in production and management, Party A shall explain the situations to all employees including Party B, listen to employees’ opinions and report to the local labor administrative department.
12.3 Party B may notify Party A to cancel this Contract immediately under any of the following circumstances:
during the probation period;
12.3.1 Party A forces Party B to work by way of violence, threat or illegal limitation of personal liberty;
12.3.2 Party A fails to pay labor remuneration or provide working conditions as agreed in this Contract or in the employment letter sent to Party B; or other circumstances prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
12.4 Except for these circumstances, Party B shall notify Party A in writing 30 days in advance if he intends to cancel or terminate the Labor Contract during the term hereof, unless as otherwise agreed by the parties.
12.4.1 Upon receipt of the above written notice, Party A shall have the right to decide that Party B shall continue to work for 30 days in accordance with this Contract before leaving the Company, or agree Party B to leave the Company immediately according to Party B’s application;
12.4.2 If Party B fails to give a written notice to Party A 30 days in advance to cancel the Labor Contract and Party A disagrees Party B to leave office immediately, Party B shall pay Party A one month’s average salary of the year prior to the cancellation of the Labor Contract as the payment in lieu of notice;
12.4.3 Upon Party A’s consent, Party B shall handle work handover and separation settlement procedures timely according to the procedures and requirements specified by Party A;
12.4.4 After Party B completes the work handover and separation settlement procedures, Party A shall pay Party B the labor remuneration due to Party B and Party B shall make confirmation and sign for it. If Party B fails to handle the separation and settlement procedures as required by Party A, Party A shall have the right to investigate Party B’s legal liabilities by necessary means.
12.5 Without violating relevant laws and regulations, this Contract may be canceled in advance according to the results agreed by both parties upon consensus through consultation.
12.6 When Party A and Party B discharges this Labor Contract, Party A shall issue a written certification to Party B and go through formalities for cancellation of this Labor Contract timely, except as otherwise provided herein.
13. Termination of contract
13.1 This Contract shall be terminated when the term of this Contract expires or or any condition for termination of the Labor Contract as agreed by both parties occurs. Party A shall issue a written certification to Party B and go through formalities for termination of this Labor Contract timely.
13.2 If both Party A and Party B agree to renew this Labor Contract when the contract term expires, both parties shall go through formalities for renewal 30 days prior to the expiration of the contract term.
14. Liability for breach of contract
Both parties shall strictly comply with this Contract after this Contract comes into force. If either party violates its obligations agreed herein and causes losses to the other party, it shall make compensation to the other party for all the losses arising therefrom.
15. Dispute settlement
Any and all labor disputes between Party A and Party B shall be settled firstly through consultation. Where consultation fails, either party may apply for arbitration to the labor dispute arbitration committee at the location China. Where there is no objection to the arbitration award, both parties shall perform the arbitration award. The party which is not satisfied with the arbitration award may bring a lawsuit to the competent people’s court at the location where Party A is registered.
16. Emergency contact person
In case of urgent medical treatment, Party B agrees that Party A may represent Party B to sign on the operation list required by the hospital and Party B warrants that Party A or Party A’s representative may not be held liable therefor. Should Party A contact Party B’s Relative under emergencies, the information of Party B’s emergency contact person is as follows:
Name and emergency contact Tel.:Cao Menglong Address: Jazz Guan Di, Yingchang street, Tiexi District, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province
17. Contract annexes
17.1 During the performance process of this Contract, other agreements signed by both parties, and the documents and memorandums issued by Party A to Party B, and various regulations formulated by Party A, including but not limited to employee manual, rules and regulations, policies and procedures, etc., are the annexes to this Contract. They are an integral part of this Contract and have the same equal legal force as this Contract.
17.2 If this Contract and an annex hereto are signed at the same time, in case of any discrepancy between this Contract and the annex hereto, this Contract shall prevail. If the time of signature is different, the supplementary agreement signed later shall prevail.
18. Miscellaneous
18.1 This Contract shall be governed and interpreted by the laws of China.
18.2 During the term hereof, any change in Party B’s salaries and benefits as stipulated in sub-clause 4.1 herein shall not affect the validity of any other provisions hereof.
18.3 In the event that any clause of this Contract becomes due to changes in laws and regulations, the validity of other clauses of this Contract shall not be affected.
18.4 The headings of the clauses are provided for reference convenience only but shall not affect the understanding and interpretation of this Contract.
18.5 This Contract is written in Chinese. It is made out in two originals for both parties each holding one, which shall be equally authentic.
18.6 This Contract shall enter into force as of the date of signature of both parties. Upon the expiration of the term hereof, both parties may renew this Contract in the form of signature confirmation.
18.7 The previously signed agreement with Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. shall be void, and this contract shall prevail.
| Party A: (Seal) | Party B: (Signature) He cong |
| Authorized Representative: | |
| Aug. 24, 2022 | Aug. 24, 2022 |
Exhibit 10.12
Patent Authorization
Patent Authorization
I am Yang Hengfei (ID No.: 211022198007056571) and hereby authorizes the drive wheel (2) (patent No.: ZL2020304814113) to Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. for free use. The use period is the date of termination of the cooperation between the authorized person and the authorized person. The authorized person shall not be used for other profit activities in violation of the law. If the authorized person violates the above provisions, he shall bear the corresponding legal liabilities.
Authorized by: Yang Hengfei
Authorized person: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD.
Authorization date: June 30,2021
Patent Authorization
Patent Authorization
Yang Hengfei (ID No.: 211022198007056571) hereby authorizes the DC brushless motor (patent No: ZL2020209729056) to Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. for free use. The use period is the date of termination of the cooperation between the authorized person and the authorized person. The authorized person shall not be used for other profit activities in violation of the law. If the authorized person violates the above provisions, he shall bear the corresponding legal liabilities.
Authorized by: Yang Hengfei
Authorized person: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Authorization date: January 29,2021
Patent Authorization
Patent Authorization
I am Yang Hengfei (ID No.: 211022198007056571) and hereby authorizes the forklift drive wheel (patent No.: ZL2020209728509) to Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. for free use. The use period is the date of termination of the cooperation between the authorized person and the authorized person.on commission.The person shall not be used for other profit activities in violation of the law. If the authorized person violates the above provisions, he shall bear the corresponding legal liabilities.
Authorized by: Yang Hengfei
Authorized person: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Authorization date: January 13,2021
Patent Authorization
Patent Authorization
I am Yang Hengfei (ID No.: 211022198007056571) and hereby authorizes the drive wheel (patent No.: ZL202030238659.7) to Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., Ltd. for free use. The use period is the date of termination of the cooperation between the authorized person and the authorized person. The authorized person shall not be used for other profit activities in violation of the law. If the authorized person violates the above provisions, he shall bear the corresponding legal liabilities.
Authorized by: Yang Hengfei
Authorized person: Shanghai Qige Power Technology Co., LTD
Authorization date: October 21,2020
Exhibit 23.1

CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS
We consent to the use in the Registration Statement on Form F-1 of Tian’an Technology Group Ltd. of our report dated August 18, 2022 relating to the financial statements and financial statement schedules for the two years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 listed in the accompanying index. We also consent to the reference to our Firm under the heading “Experts” in such Registration Statement.
/s/ HHC
Forest Hills, NY
February 28, 2023
Exhibit 107
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of Each Class of Securities to be Registered | Number of shares of common stock to be registered (1) | Proposed Maximum Offering price Per Share | Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price | Amount of Registration Fee (2) | ||||||||||||
| Ordinary Shares, no par value per share | 5,000,000 | $ | 0.1 | $ | 500,000 | $ | 46.35 | |||||||||
| Total | 5,000,000 | $ | 0.1 | 500,000 | 46.36 | |||||||||||
| (1) | Pursuant to Rule 416(a) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), there are also being registered hereby an additional indeterminate number of ordinary shares of the Registrant’s, no par value (the “Shares”) as may become issuable to the selling stockholder as a result of stock splits, stock dividends and similar transactions, and, in any such event, the number of shares registered hereby shall be automatically increased to cover the additional shares. |
| (2) | Estimated in accordance with Rule 457(c) under the Securities Act solely for the purpose of calculating the registration fee. |